Fill in the Blanks
What are the five main causes of
Genetic Variation?
1. I __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ A __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ of chromosomes, and therefore alleles, during meiosis
2. C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ __ __ between chromatids of H __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ chromosomes during meiosis
3. R __ __ __ __ __ M __ __ __ __ __ between organisms within a species
4. Random fertilization of G __ __ __ __ __ __
M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
Genetic Variation produced P __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ variation (what it looks like)
Numbers 1-4 remix existing alleles in the P __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , where as M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ can produce completely new alleles.
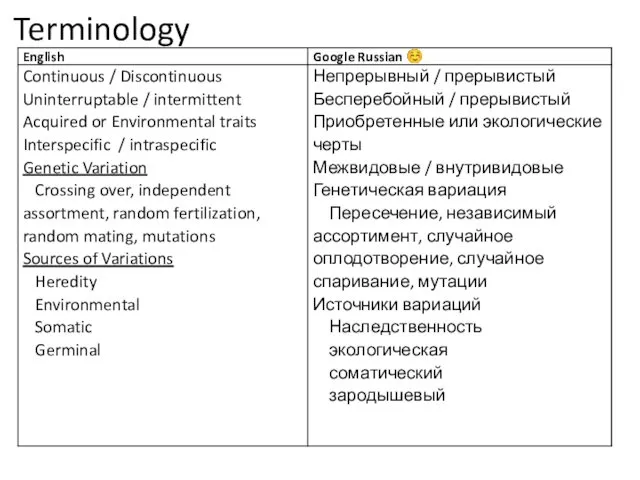
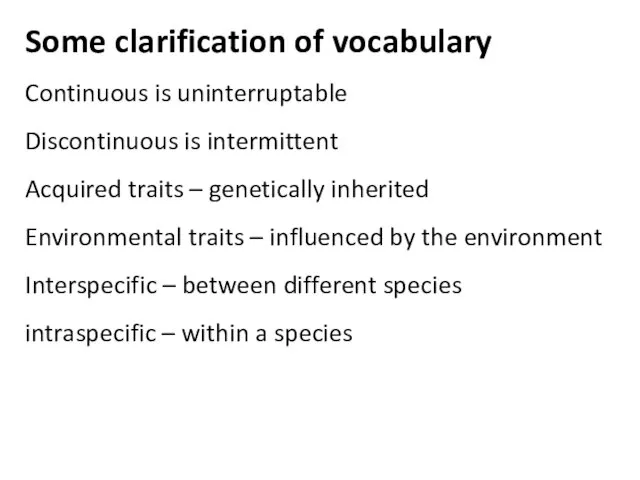

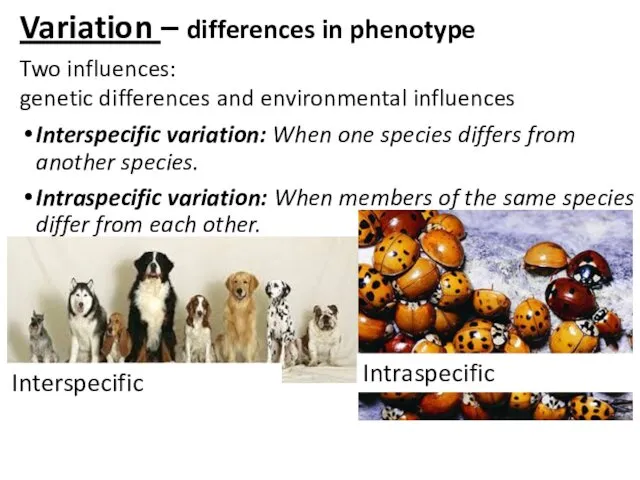

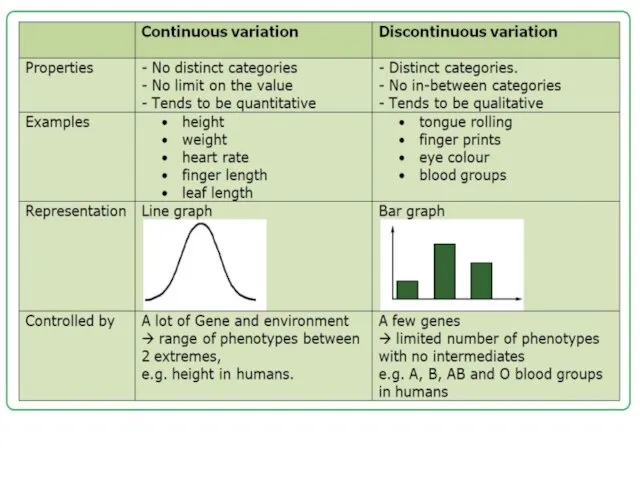

 Основные понятия генетики
Основные понятия генетики Закономерности изменчивости
Закономерности изменчивости Липидтер. Стероидтар. Терпеноидтар. Қорытынды. Пайдаланылған әдебиеттер
Липидтер. Стероидтар. Терпеноидтар. Қорытынды. Пайдаланылған әдебиеттер Органи і системи органів тварин
Органи і системи органів тварин Человек. Быть личностью. Теории происхождения человека
Человек. Быть личностью. Теории происхождения человека Ембріотехнології. Клонування
Ембріотехнології. Клонування Enteric bacterial pathogens
Enteric bacterial pathogens Ядовитые растения Чеченской Республики
Ядовитые растения Чеченской Республики Болезни эмбрионов с/х птицы
Болезни эмбрионов с/х птицы Кейс-метод
Кейс-метод Хвощи, плауны, попоротники
Хвощи, плауны, попоротники Многообразие земноводных
Многообразие земноводных Тяжёлые металлы. Главный источник поступления тяжелых металлов
Тяжёлые металлы. Главный источник поступления тяжелых металлов Интересные факты о змеях
Интересные факты о змеях Жизнь организмов на разных материках
Жизнь организмов на разных материках Репликация ДНК. (Лекция 3)
Репликация ДНК. (Лекция 3) Органы пищеварения у животных
Органы пищеварения у животных Хомячки
Хомячки Общие пути катаболизма
Общие пути катаболизма Структурная организация и функции клеточных мембран. (Лекция 2.1)
Структурная организация и функции клеточных мембран. (Лекция 2.1) Наследование групп крови человека
Наследование групп крови человека Основные фосфолипиды и гликолипиды тканей человека
Основные фосфолипиды и гликолипиды тканей человека Семенные растения. Характеристика отделов голосеменные и покрытосеменные
Семенные растения. Характеристика отделов голосеменные и покрытосеменные Возбудители болезней плодовых и овощных культур
Возбудители болезней плодовых и овощных культур Пути и направления эволюции
Пути и направления эволюции Митохондрии. Пластиды
Митохондрии. Пластиды Микроорганизмдер, антибиотиктер және биологиялық активті заттарды түзушілер
Микроорганизмдер, антибиотиктер және биологиялық активті заттарды түзушілер Биология в искусстве. Интеллектуальный марафон Биологическое соцветие
Биология в искусстве. Интеллектуальный марафон Биологическое соцветие