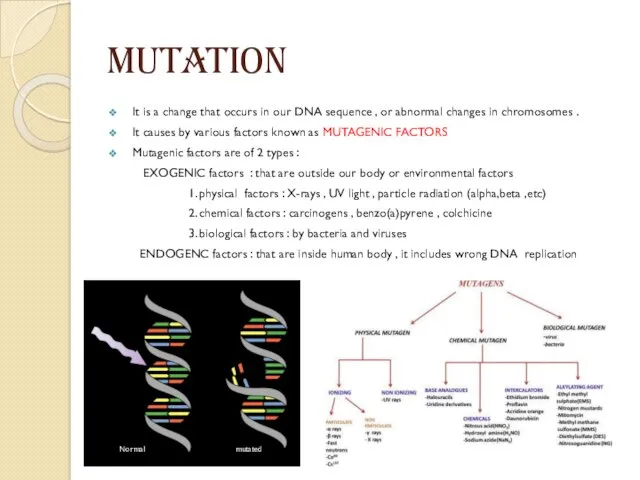
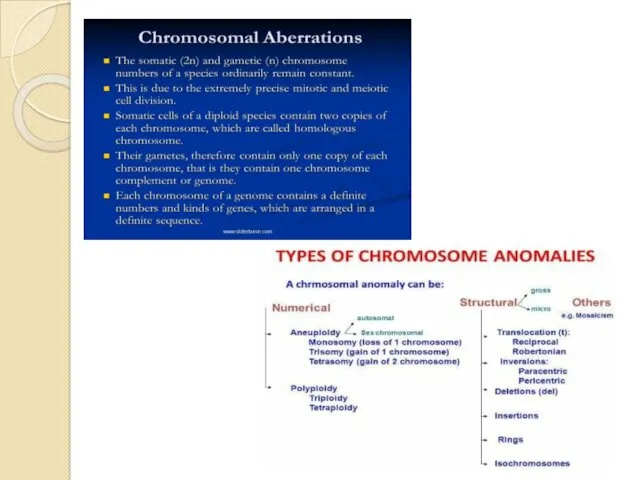
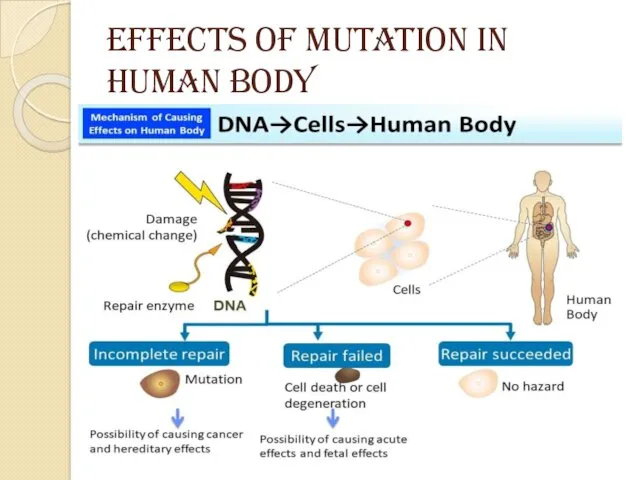
MUTATION
It is a change that occurs in our DNA sequence ,
or abnormal changes in chromosomes .
It causes by various factors known as MUTAGENIC FACTORS
Mutagenic factors are of 2 types :
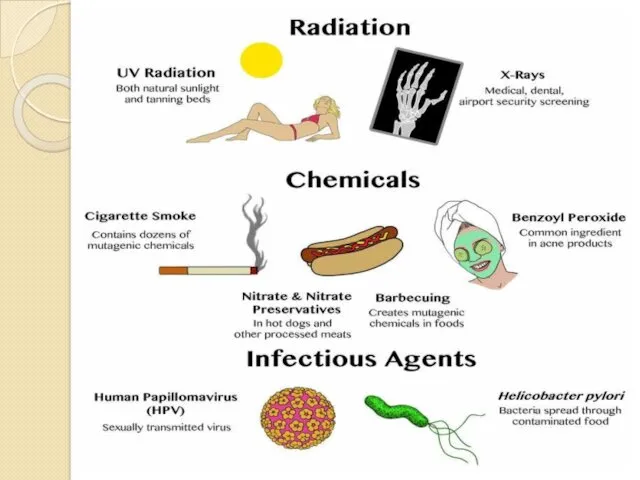
EXOGENIC factors : that are outside our body or environmental factors
1. physical factors : X-rays , UV light , particle radiation (alpha,beta ,etc)
2. chemical factors : carcinogens , benzo(a)pyrene , colchicine
3. biological factors : by bacteria and viruses
ENDOGENC factors : that are inside human body , it includes wrong DNA replication
Normal
mutated



 Загадка человека
Загадка человека Методы типирования
Методы типирования Своя игра. Мир растений
Своя игра. Мир растений Биологические особенности божьей коровки
Биологические особенности божьей коровки Презентация к уроку биологии в 7 классе Развитие насекомых
Презентация к уроку биологии в 7 классе Развитие насекомых Взаимоотношения между организмами
Взаимоотношения между организмами Размножение клеток
Размножение клеток Будова і функції тканин тваринного організму
Будова і функції тканин тваринного організму Анатомия глаза
Анатомия глаза Надотряд типичные птицы или новонёбные
Надотряд типичные птицы или новонёбные Борьба с цистицеркозом
Борьба с цистицеркозом Классификация и морфология микроорганизмов
Классификация и морфология микроорганизмов Продолговатый мозг и варолиев мост. Жизненноважные центры продолговатого мозга
Продолговатый мозг и варолиев мост. Жизненноважные центры продолговатого мозга Семейство бобовые или мотыльковые
Семейство бобовые или мотыльковые Работа мышц
Работа мышц Видоизменения побегов
Видоизменения побегов Особенности новейших технологий производства ферментных препаратов: амилаз, протеаз, липаз, лактаз, глюкоксидаз 2 часть
Особенности новейших технологий производства ферментных препаратов: амилаз, протеаз, липаз, лактаз, глюкоксидаз 2 часть Головной мозг – конечный мозг
Головной мозг – конечный мозг Экология популяций
Экология популяций Факторы устойчивости инфекционных заболеваний пчел
Факторы устойчивости инфекционных заболеваний пчел Ямчатость стебля
Ямчатость стебля Клетка – как орган
Клетка – как орган 20181104_kletochnaya_teoriya_t.shvanna
20181104_kletochnaya_teoriya_t.shvanna Женская половая система. (Часть 3)
Женская половая система. (Часть 3) ГМО (генетически модифицированные организмы)
ГМО (генетически модифицированные организмы) Пищевые добавки
Пищевые добавки Многообразие водных биогеоценозов
Многообразие водных биогеоценозов Опыление цветка
Опыление цветка