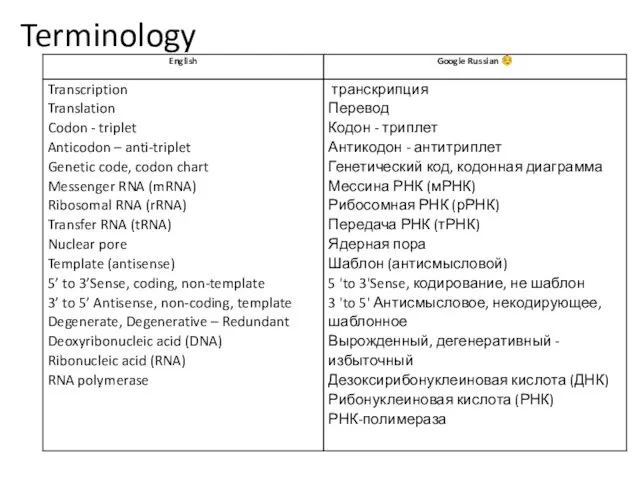
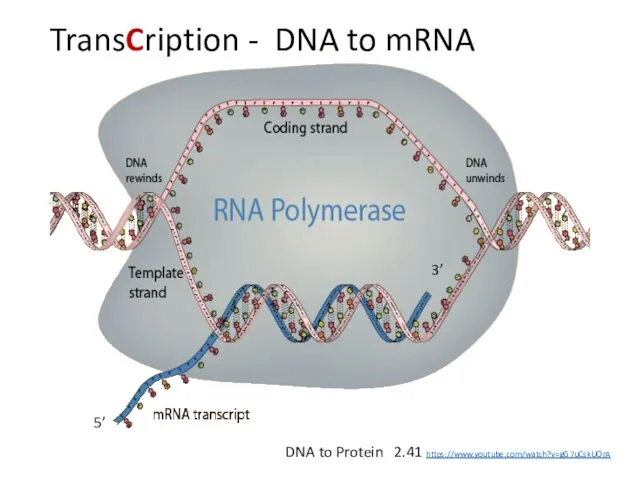
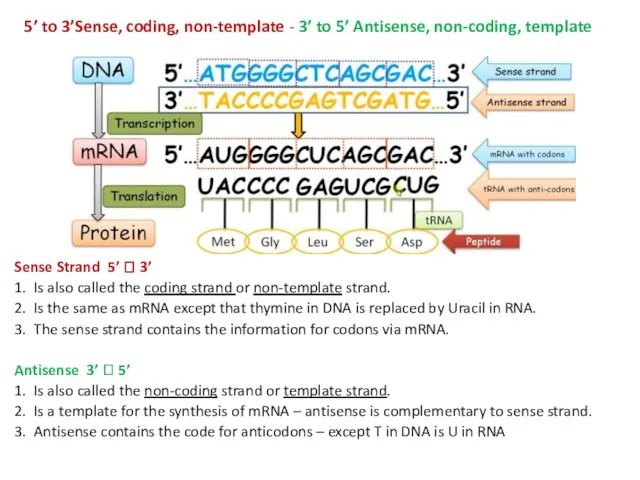
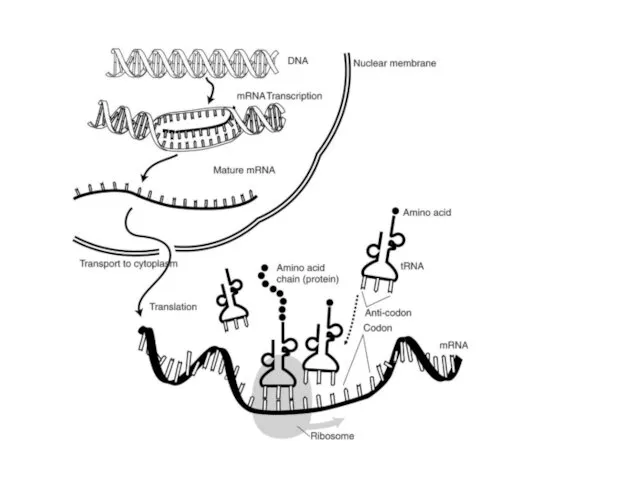
5’ to 3’Sense, coding, non-template - 3’ to 5’ Antisense, non-coding,
template
Sense Strand 5’ ? 3’
1. Is also called the coding strand or non-template strand.
2. Is the same as mRNA except that thymine in DNA is replaced by Uracil in RNA.
3. The sense strand contains the information for codons via mRNA.
Antisense 3’ ? 5’
1. Is also called the non-coding strand or template strand.
2. Is a template for the synthesis of mRNA – antisense is complementary to sense strand.
3. Antisense contains the code for anticodons – except T in DNA is U in RNA

 Социалогический проект Условные рефлексы Павлова в школе
Социалогический проект Условные рефлексы Павлова в школе Науковий дослід: Спостереження за ростом та розвитком рослин
Науковий дослід: Спостереження за ростом та розвитком рослин Строение растительной клетки. Конкурс профессионального мастерства педагогов Мой лучший урок
Строение растительной клетки. Конкурс профессионального мастерства педагогов Мой лучший урок Оценка качества почвы с помощью растения – биоиндикатора
Оценка качества почвы с помощью растения – биоиндикатора Вид. Критерии вида. Популяция
Вид. Критерии вида. Популяция Основы систематики микроорганизмов
Основы систематики микроорганизмов Презентация к статье по использованию растений на уроках биологии.
Презентация к статье по использованию растений на уроках биологии. Тип Моллюски. Общая характеристика
Тип Моллюски. Общая характеристика Исследовательский проект как способ повышения мотивации обучающихся на уроках биологии
Исследовательский проект как способ повышения мотивации обучающихся на уроках биологии Беспозвоночные животные
Беспозвоночные животные Биохимия гормонов
Биохимия гормонов ГМО (генетически модифицированные организмы)
ГМО (генетически модифицированные организмы) Өсімдіктердің радиацияға төзімділігі
Өсімдіктердің радиацияға төзімділігі Мал шаруашылығы
Мал шаруашылығы Четвероногие друзья
Четвероногие друзья Продуктивність екосистем. Ланцюги живлення
Продуктивність екосистем. Ланцюги живлення Желудок
Желудок Влияние факторов внешней среды на микроорганизмы
Влияние факторов внешней среды на микроорганизмы Витамин B1 (Тиамин)
Витамин B1 (Тиамин) Эволюционная теория
Эволюционная теория Гриби
Гриби Животные Красной Книги России - 2
Животные Красной Книги России - 2 Гортензия метельчатая Bombshell
Гортензия метельчатая Bombshell Органы выделения. Строение и работа почек
Органы выделения. Строение и работа почек Млекопитающие. Китообразные. Приспособление к водной среде обитания
Млекопитающие. Китообразные. Приспособление к водной среде обитания Значення рослин для життя на планеті Земля
Значення рослин для життя на планеті Земля Приходько Елена Игнатьевна
Приходько Елена Игнатьевна Стерины и стероиды
Стерины и стероиды