Слайд 2

Vitamins
People need vitamins to stay healthy. They get them from the
food. There are a lot of vitamins in fruit and vegetables.
Слайд 3

Classes of Vitamins
Fat Soluble Vitamins: stored in tissues
Examples
A
D
E
K
Water Soluble Vitamins:
not
stored in tissues, must have constant supply
Examples
B, B1, B2, B6 & B12
Niacin
Folic Acid
C
Слайд 4

Слайд 5

Function, Deficiency Signs & Sources
Vitamin A
Function: development healthy skin and nerve
tissue. Aids in building up resistance to infection. Functions in eyesight and bone formation. ALL ANIMALS require a source of Vitamin A. It is important in the ration of pregnant females.
Deficiency signs: retarded growth in the young, the development of a peculiar condition around the eyes known as Xerophthalmia, night blindness and reproductive disorders.
Sources: whole milk, carotene, animal body oils (cod fish and tuna), legume forages and can be synthetically produced.
Слайд 6

It is in green and yellow vegetables, milk and eggs. Its
necessary for eyesight.
Слайд 7

Vitamin D
Function: is essential for the proper utilization of calcium and
phosphorus to produce normal, healthy bones.
Deficiency signs: retarded growth, misshapen bones (rickets), lameness and osteoporosis.
Sources: Whole milk, sun-cured hays, forage crops, fish liver oils, irradiated yeast.
Слайд 8

Vitamin D
It is in eggs. People can get it from sunlight.
It makes our bones strong.
Слайд 9

Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid)
Function: has an effect on the metabolism of
calcium in the body (Not required in rations of farm animals.).
Deficiency signs: none demonstrated in livestock. Human deficiency: scurvy (swollen and painful joints and bleeding gums) and brittleness of bones.
Sources: citrus fruits, tomatoes, leafy vegetables and potatoes.
Слайд 10

Vitamin C
It is in every fruit and vegetable. You can find
it in black currants, strawberry, oranges, onions, cabbage and green pepper. It is important for building bones and teeth. It helps to prevent colds.
Слайд 11

Vitamin E
Function: normal reproduction.
Deficiency signs: poor growth, "crazy chick" disease,
Muscular Dystrophy, "white muscle" disease in ruminants and swine and "stiff lamb" disease (affects the nerves and muscles).
Sources: synthetic for poultry and swine, cereal grains and wheat germ oil, green forages, protein concentrates, oil seeds (peanut and soybean oil).
Vitamin E rapidly destroyed in rancid or spoiled fats. That is why these may cause white muscle disease. Utilization of Vitamin E is dependent on adequate selenium.
Слайд 12

Vitamin E
It is necessary for skin and body. It is in
the wheat and nuts.
Слайд 13

Vitamin K
Function: necessary for the maintenance of normal blood coagulation.
Deficiency
signs: blood loses its power to clot or the time needed for clotting is longer and serious hemorrhages can result from slight wounds or bruises.
Sources: green leafy forages, fish meal, liver, soybeans, rumen and intestinal synthesis, and the synthetic compounds.
Слайд 14

Vitamin K
It is in cabbage, wheat, fruit – bananas, kiwi and
avocado.
Слайд 15

Vitamin B1 (Thiamin)
Function: required for the normal metabolism of carbohydrates.
Deficiency
signs: loss of appetite, muscular weakness, severe nervous disorders, general weakness and wasting (BeriBeri).
Sources: raw, whole grains and especially their seed coats and embryos; fresh green forage; and yeast, milk and rumen synthesis.
Слайд 16

Vitamin B1
It is in meat, porridge and bread. It is responsible
for the nervous system. Lack of this vitamin leads to serious illnesses and even death.
Слайд 17

Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
Function: necessary for normal embryo development, important in the
metabolism of amino acids and carbohydrates.
Deficiency signs: poor reproduction characterized by small litters and deformed young (cleft palate and club-footedness) curly toe paralysis in chicks, digestive disturbances, general weakness and eye abnormalities.
Sources: milk and dairy by-products, yeast, green forages, well cured hay (especially alfalfa), whole grains, wheat bran and synthetic riboflavin rumen synthesis.
Слайд 18

Слайд 19

Слайд 20

Vitamin B
6
It is in fish, meat, cabbage, tomatoes, potatoes, nuts, pepper
, mushrooms, carrots and greenery.
Слайд 21

Vitamin B
12
It is in eggs, chicken , milk products, wheat, fish
and oysters.
Слайд 22

Vocabulary Review
Nutrients: chemical substances in food that are used by the body
to produce energy and tissues.
Vitamins: essential organic nutrients, required in small amounts, that cannot be synthesized by the body. Required for growth, maintenance, reproduction and lactation.
Vitamin deficiency: decline in health due to the lack of a vitamin in a ration.
Слайд 23

Vocabulary Review
Fat soluble vitamin: a vitamin that can be stored and
accumulated in the liver and other fatty tissues.
Water soluble vitamin: a vitamin that cannot be stored in the tissues. Must be provided regularly as deficiencies can develop in a short time.
Minerals: essential inorganic compounds, required in small amounts. Required for growth, maintenance, reproduction and lactation.
Macrominerals: required in large amounts.
Microminerals required in small amounts.
Слайд 24

Remember: you eat to live,
but don’t live to eat.
Choose healthy
food.
Слайд 25

So, to keep healthy, we should:
First of all to eat useful
food full of vitamins;
To eat more fruits and vegetables, especially apples and kiwi: “An apple a day, keeps the doctor away.”;
To go in for sport: to swim, to play tennis, to play football, to ski and skate;
To go to fitness centres and sports clubs;
Not to eat fat food: hamburgers, chips, crisps and cakes.
























 Размножение организмов
Размножение организмов Видоизмененные корни растений
Видоизмененные корни растений Водоросли -их значение в жизни человека
Водоросли -их значение в жизни человека Углеводы. Функции углеводов
Углеводы. Функции углеводов Исчезающие растения и животные России
Исчезающие растения и животные России презентация к уроку в 9 классе ФОТОСИНТЕЗ
презентация к уроку в 9 классе ФОТОСИНТЕЗ Птахи, які розмножуються взимку
Птахи, які розмножуються взимку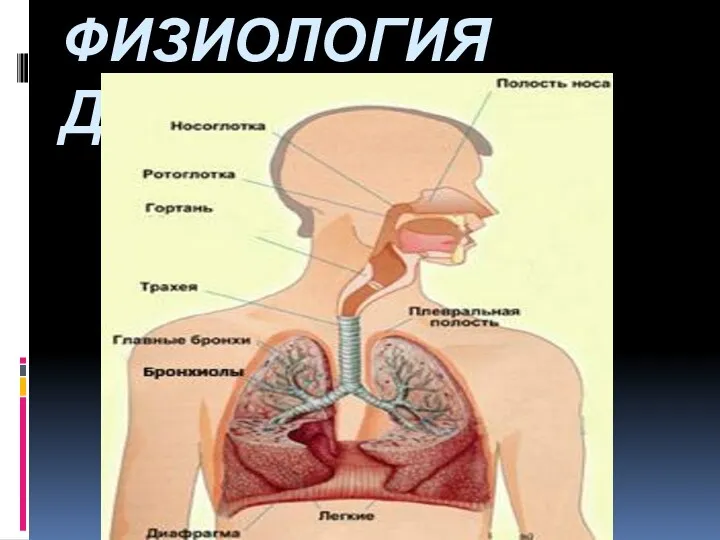 Физиология дыхания
Физиология дыхания Луговые травы
Луговые травы Эволюционное учение Ч. Дарвина
Эволюционное учение Ч. Дарвина Эмбриогенез печени и желчевыводящих путей
Эмбриогенез печени и желчевыводящих путей Синквейн Жизнь
Синквейн Жизнь Витамин C
Витамин C Биология. Метаболизм
Биология. Метаболизм Презентация по теме Доказательства эволюции органического мира
Презентация по теме Доказательства эволюции органического мира охорона первоцвітів. Збереження ранніх квітучих рослин
охорона первоцвітів. Збереження ранніх квітучих рослин Строение тела человека (2 класс)
Строение тела человека (2 класс) Отряд Китообразные
Отряд Китообразные Eukaryotic microorganisms. Fungi
Eukaryotic microorganisms. Fungi Гортань. Функции гортани
Гортань. Функции гортани Буферные системы. Классификация буферных растворов
Буферные системы. Классификация буферных растворов Презентация к уроку биологии в 8 классе по теме Скелет человека. Осевой скелет по программе Д.В. Колесова,Р.Д. Маша,И. Н. Беляева.
Презентация к уроку биологии в 8 классе по теме Скелет человека. Осевой скелет по программе Д.В. Колесова,Р.Д. Маша,И. Н. Беляева. Классификация животных
Классификация животных Обмен веществ и энергии в клетке
Обмен веществ и энергии в клетке Систематика растений. Урок биологии в 7 классе
Систематика растений. Урок биологии в 7 классе Сосуды малого и большого кругов кровообращения
Сосуды малого и большого кругов кровообращения Цветковые растения
Цветковые растения Строение и работа сердца
Строение и работа сердца