Содержание
- 2. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 1 Business Information Systems in Your Career
- 3. How will a four-step method for business problem solving help you solve information system-related problems? How
- 4. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 1 Business Information Systems in Your Career Shortening the Lines
- 5. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 1 Business Information Systems in Your Career Disney Operational Command
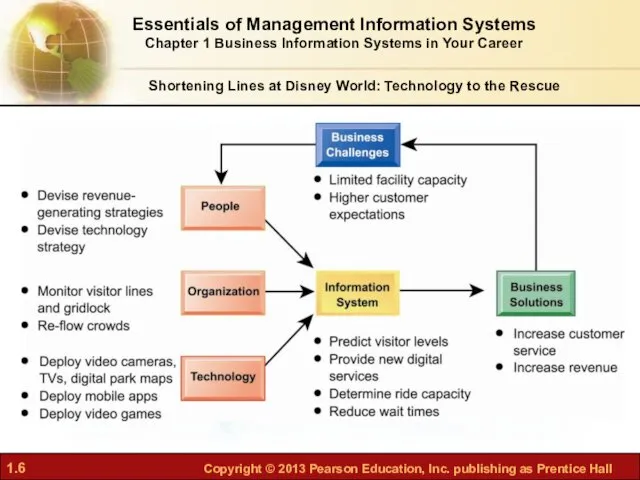
- 6. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 1 Business Information Systems in Your Career Shortening Lines at
- 7. The Role of Information Systems in Business Today In 2011, more than 131 million businesses had
- 8. The Role of Information Systems in Business Today Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 1 Business
- 9. Interactive Session: Organizations Running a Business from the Palm of Your Hand Read the Interactive Session
- 10. The Role of Information Systems in Business Today Globalization Challenges and Opportunities: A Flattened World Internet
- 11. Businesses invest in IT to achieve six important business objectives. Operational excellence New products, services, and
- 12. Operational Excellence: Improved efficiency results in higher profits. Information systems and technologies help improve efficiency and
- 13. Information systems and technologies enable firms to create new products, services, and business models. Business model:
- 14. New Products, Services, and Business Models: The Role of Information Systems in Business Today With multitouch
- 15. Customers who are served well become repeat customers who purchase more. Mandarin Oriental hotel Uses IT
- 16. If managers rely on forecasts, best guesses, and luck, they will misallocate employees, services, and inventory.
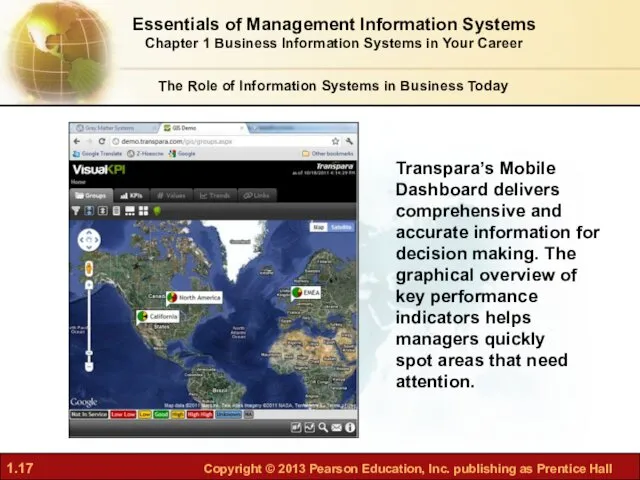
- 17. The Role of Information Systems in Business Today Transpara’s Mobile Dashboard delivers comprehensive and accurate information
- 18. Often results from achieving previous business objectives Advantages over competitors: Charging less for superior products, better
- 19. Businesses may need to invest in information systems out of necessity; simply the cost of doing
- 20. Perspectives on Information Systems and Information Technology Information technology: the hardware and software a business uses
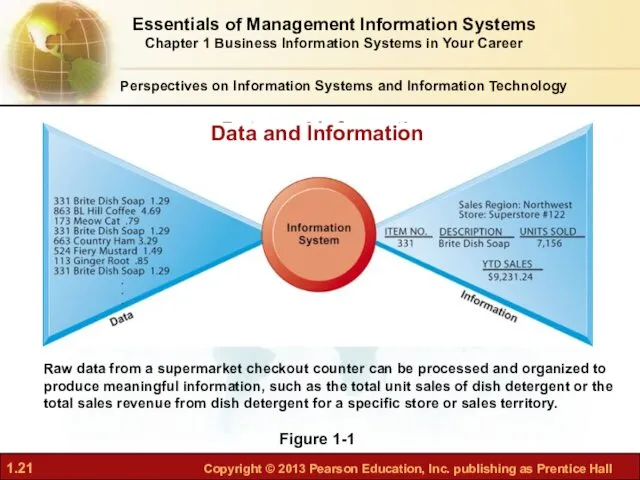
- 21. Perspectives on Information Systems and Information Technology Data and Information Figure 1-1 Raw data from a
- 22. Perspectives on Information Systems and Information Technology Activities in an information system that produce information: Input
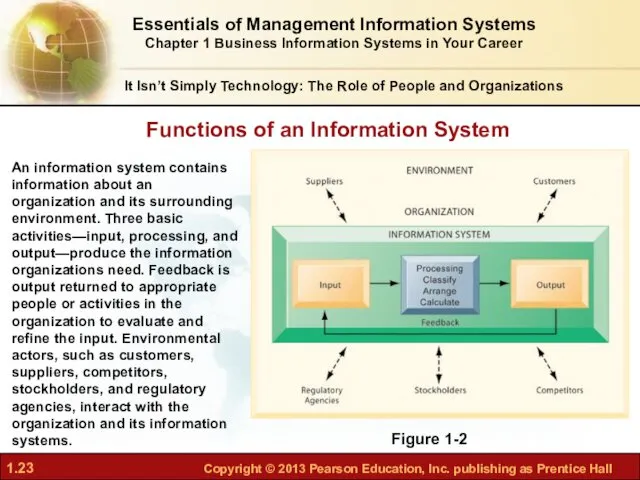
- 23. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations Functions of an Information System Figure
- 24. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations Information systems literacy Includes behavioral and
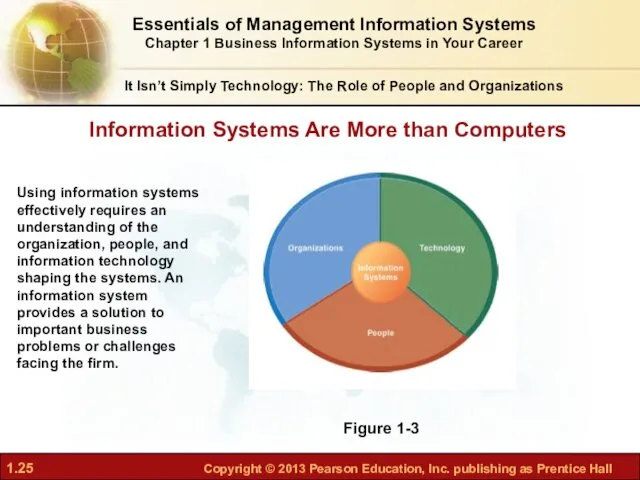
- 25. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations Information Systems Are More than Computers
- 26. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations Organizations Coordinate work through structured hierarchy
- 27. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations People Information systems require skilled people
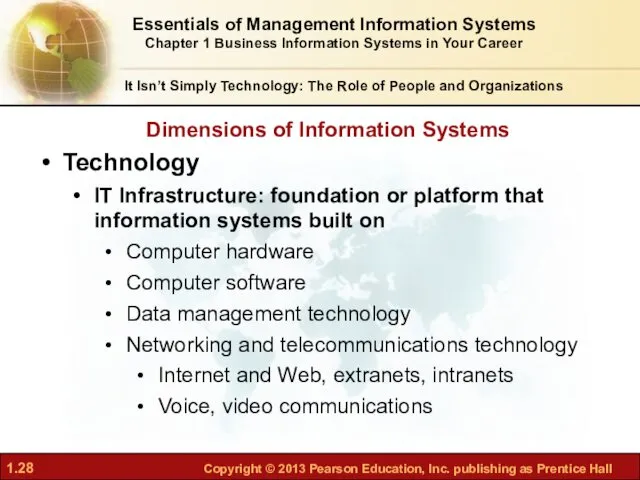
- 28. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations Technology IT Infrastructure: foundation or platform
- 29. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations Interactive Session: Technology UPS Competes Globally
- 30. It Isn’t Simply Technology: The Role of People and Organizations Interactive Session: Technology UPS Competes Globally
- 31. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Few business problems are simple or straightforward. Most business
- 32. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Problem solving: four-step process Problem identification Solution design Choice
- 33. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Problem identification includes: Agreement that problem exists Definition of
- 34. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Typical organizational problems Outdated business processes Unsupportive culture and
- 35. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Typical technology problems Insufficient or aging hardware Outdated software
- 36. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Typical people problems Lack of employee training Difficulties of
- 37. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Solution design Often many possible solutions Consider as many
- 38. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Implementation Building or purchasing solution Testing solution, employee training
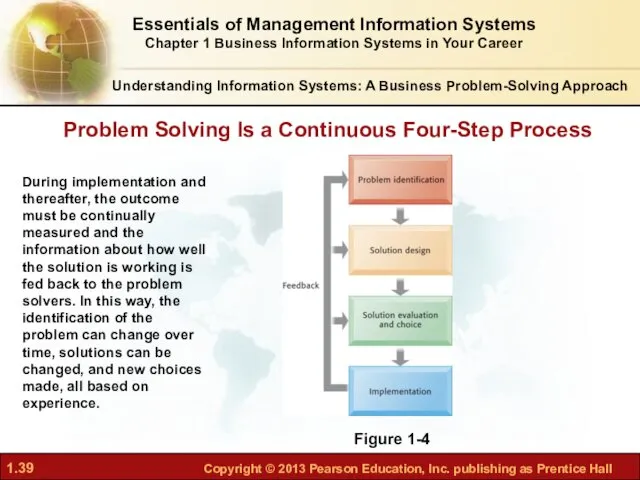
- 39. Problem Solving Is a Continuous Four-Step Process Figure 1-4 During implementation and thereafter, the outcome must
- 40. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Without critical thinking, easy to jump to conclusions, misjudge
- 41. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach Four elements of critical thinking: Maintaining doubt and suspending
- 42. Understanding Information Systems: A Business Problem-Solving Approach When firms cannot achieve business objectives these objectives become
- 43. Success in today’s job market requires a broad set of skills. Job candidates must have problem-solving
- 44. Accounting: Accountants increasingly rely on information systems to summarize transactions, create financial records, organize data, and
- 45. Finance: Relationship between information systems and financial management and services is so strong that many advise
- 46. Marketing: No field has undergone more technology-driven change in the past five years than marketing and
- 47. Operations management in services and manufacturing: Production managers, administrative service managers, and operations analysts Skills: Hardware
- 48. Management: The job of management has been transformed by information systems. Impossible to manage business today
- 49. Information Systems and Your Career The job of management requires extensive use of information systems to
- 50. Information systems: Fast changing and dynamic profession because information technologies are among most important tools for
- 51. Common requirements How IT helps achieve six business objectives Central role of databases Business analytics and
- 53. Скачать презентацию











































 Рибний ресторан
Рибний ресторан Общероссийский конкурс Мой бизнес- моя Россия. Формула успеха
Общероссийский конкурс Мой бизнес- моя Россия. Формула успеха Louis Vuitton
Louis Vuitton Umbro компаниясы
Umbro компаниясы Описание бизнеса. Анализ внешней и внутренней среды. Бизнес-планирование. Тема 05
Описание бизнеса. Анализ внешней и внутренней среды. Бизнес-планирование. Тема 05 Предпринимательская деятельность
Предпринимательская деятельность Как оставить свой след В ІТ-мире
Как оставить свой след В ІТ-мире Способы и критерии оценки эффективности тренинга. Условия переноса результатов тренинга в реальную среду
Способы и критерии оценки эффективности тренинга. Условия переноса результатов тренинга в реальную среду Фонд содействия инновациям. Название проекта. Направление отбора. Шаблон
Фонд содействия инновациям. Название проекта. Направление отбора. Шаблон Создание сети центров по подбору гувернеров пенсионного возраста Бюро бабушкиных услуг
Создание сети центров по подбору гувернеров пенсионного возраста Бюро бабушкиных услуг Бизнес проект. Создание банного комплекса на базе гостиницы Комфорт-отель
Бизнес проект. Создание банного комплекса на базе гостиницы Комфорт-отель Исследование потребительской проточности в Северном районе города Тамбова
Исследование потребительской проточности в Северном районе города Тамбова Коммерциялық тәуекелдерді және сақтандыруларды бақылау Сұрақтар: Тәуекелдердің мазмұны мен классификациясы
Коммерциялық тәуекелдерді және сақтандыруларды бақылау Сұрақтар: Тәуекелдердің мазмұны мен классификациясы Бизнес-план. Құру жолдары және пайдалы кеңестер
Бизнес-план. Құру жолдары және пайдалы кеңестер Особенности формирования внешний и внутренний среды бизнеса
Особенности формирования внешний и внутренний среды бизнеса Как начать бизнес еще в школе. 12-16 лет
Как начать бизнес еще в школе. 12-16 лет Ресторан индийской кухни Слон. Проект
Ресторан индийской кухни Слон. Проект Тренинг. Бизнес с Китаем в сети интернет. (Занятие 1)
Тренинг. Бизнес с Китаем в сети интернет. (Занятие 1) Культура и этика предпринимательства. Лекция 10
Культура и этика предпринимательства. Лекция 10 Использование методологии моделирования бизнес-процессов для совершенствования деятельности гостиничного предприятия
Использование методологии моделирования бизнес-процессов для совершенствования деятельности гостиничного предприятия Гостиничный бизнес
Гостиничный бизнес Coca Cola Presentation
Coca Cola Presentation Будь в команде лучших!
Будь в команде лучших! Організація ресторанного господарства
Організація ресторанного господарства Литературная кофейня Шекспир
Литературная кофейня Шекспир Кафе Paradise
Кафе Paradise Популярные бизнес-модели
Популярные бизнес-модели School of Business. Organisation Structure
School of Business. Organisation Structure