Содержание
- 2. CHAPTER 4 Options for Organizing Business CHAPTER 5 Small Business, Entrepreneurship, and Franchising © 2016 by
- 3. Learning Objectives LO 4-1 Define and examine the advantages and disadvantages of the sole proprietorship form
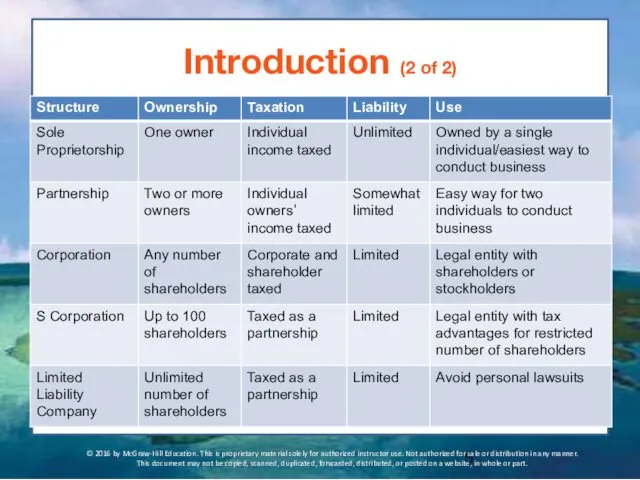
- 4. Introduction (1 of 2) Comparison of Sole Proprietorships, Partnerships and Corporations © 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education.
- 5. Introduction (2 of 2) © 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized
- 6. Sole Proprietorship Sole Proprietorship Businesses owned and operated by one individual; the most common form of
- 7. Advantages of Sole Proprietorship Advantages Ease and cost of formation Allow a high level of secrecy
- 8. Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship Disadvantages Unlimited liability Scarce external funding Owners need diverse skills Success is
- 9. Finding Talented Employees Sole proprietorships have greater difficulty attracting talented employees Large corporations such as McDonald’s
- 10. Entrepreneur This entrepreneur opened his small business as a sole proprietorship As sole proprietor, he keeps
- 11. Partnership Partnership A form of business organization defined by the Uniform Partnership Act as “an association
- 12. Types of Partnerships General Partnership Involves a complete sharing in both the management and the liability
- 13. Advantages of Partnerships Advantages Easy to organize Availability of capital & credit Combined knowledge and skills
- 14. Disadvantages of Partnerships Disadvantages Unlimited liability Responsible for each others’ decisions A new agreement is needed
- 15. Partnerships and Taxes Partnerships are quasi-taxable organizations Partnerships do not pay taxes but do file a
- 16. Keys to Success in Business Partnerships © 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely
- 17. Google In 1996 Stanford students Sergey Brin and Larry Page partnered to form the search engine
- 18. Corporation Corporation A legal entity, created by the state, whose assets and liabilities are separate from
- 19. Stock and Dividends Corporations are typically owned by many individuals and organizations who own shares of
- 20. Creating Corporations Incorporators create the corporation Following state procedure of chartering the corporation Incorporators file legal
- 21. Types of Corporations Domestic Corporation If conducting business in the state in which it is chartered
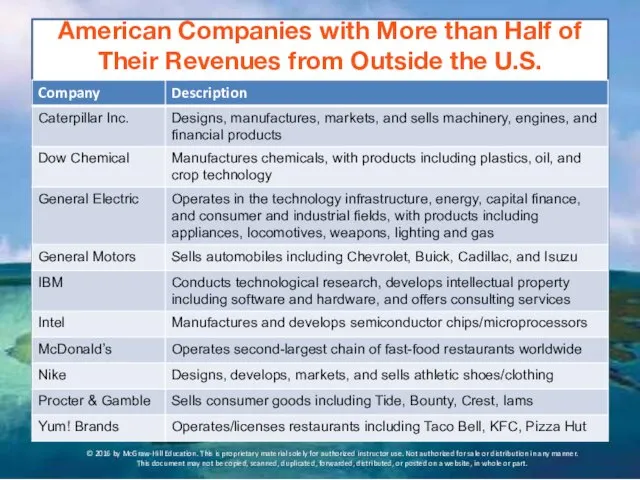
- 22. American Companies with More than Half of Their Revenues from Outside the U.S. © 2016 by
- 23. Private Corporations and Initial Public Offering Private Corporation Owned by just one or a few people
- 24. Mars Corporation © 2016 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use.
- 25. Public Corporations Public Corporations A corporation whose stock anyone may buy, sell, or trade Two types
- 26. Board of Directors A group of individuals, elected by the stockholders to oversee the general operation
- 27. Preferred and Common Stocks Preferred Stock A special type of stock whose owners, though not generally
- 28. Preferred Stock Owners of preferred stock have first claim to profits Dividend payments on preferred stocks
- 29. Advantages of Corporations Advantages Limited liability Ease of transfer of ownership Perpetual life Securing funding is
- 30. Disadvantages of Corporations Disadvantages Double taxation Expensive to form Disclosure of information to the government and
- 31. Volkswagen Volkswagen is the eighth-largest corporation in the world Did You Know? The first corporation with
- 32. Hostile Takeovers Hostile takeovers occur when one individual or company attempts to buy a majority share
- 33. Joint Venture and S Corporation Joint Venture A partnership established for a specific project or for
- 34. Limited Liability Company and Cooperatives Limited Liability Company (LLC) Form of ownership that provides limited liability
- 35. Consumer Cooperative REI REI is organized as a consumer cooperative REI operates a bit differently because
- 36. Employee-Owned Businesses Employee-owned companies have proven to be successful on many fronts whether the company is
- 37. Mergers The combination of two companies (usually corporations) to form a new company Horizontal merger Firms
- 38. Google Acquisitions In 2013, Google paid $3.2 billion for smart home company, Nest Labs Just one
- 39. Trends in Business Ownership (1 of 2) Acquisition The purchase of one company by another, usually
- 40. Trends in Business Ownership (2 of 2) Shark repellant Management requires a large majority of stockholders
- 41. Leveraged Buyout A purchase in which a group of investors borrows money from banks and other
- 42. Build Your Skills Selecting a Form of Business (1 of 2) Ali Bush sees an opportunity
- 43. Build Your Skills Selecting a Form of Business (2 of 2) TASK Using what you’ve learned
- 45. Скачать презентацию








































 Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship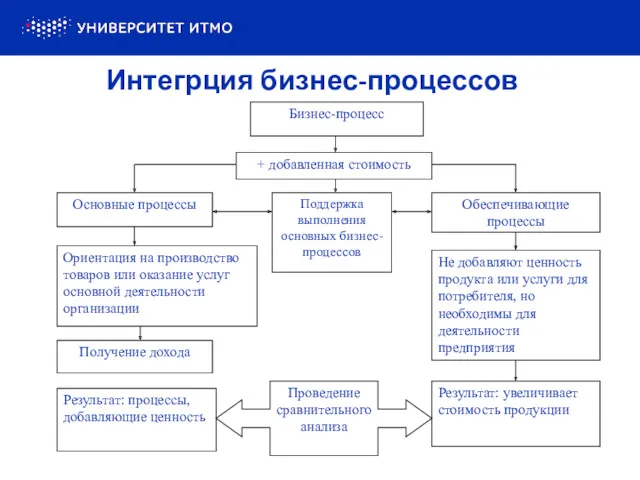 Интеграция бизнес-процессов
Интеграция бизнес-процессов Бизнес перезагрузка
Бизнес перезагрузка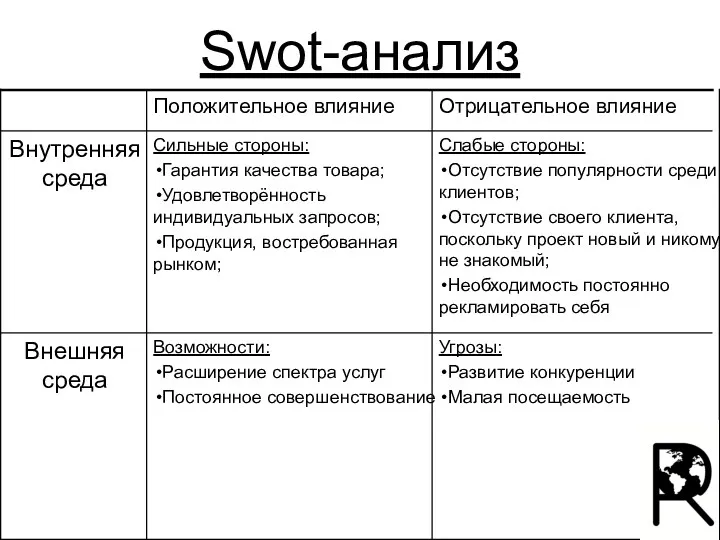 Swot-анализ
Swot-анализ Принцип зависимости (или принцип внешнего воздействия)
Принцип зависимости (или принцип внешнего воздействия) Концепция развития розничной сети
Концепция развития розничной сети Бизнес-планирование
Бизнес-планирование Экологический туризм Челябинской области и перспективы его развития
Экологический туризм Челябинской области и перспективы его развития LG Group (Life is Good, элджи груп) – тұрмыстық электроника
LG Group (Life is Good, элджи груп) – тұрмыстық электроника Southwest airlines
Southwest airlines Cоңғы модель - бағасы бұрынғы. Бизнес мектеп
Cоңғы модель - бағасы бұрынғы. Бизнес мектеп Фонд содействия инновациям. Название проекта. Направление отбора. Шаблон
Фонд содействия инновациям. Название проекта. Направление отбора. Шаблон Бизнес-план 2015 дилерского центра MAN
Бизнес-план 2015 дилерского центра MAN Готовое бизнесрешение
Готовое бизнесрешение Strategies for development of hotel business. Practicum. Theme 1
Strategies for development of hotel business. Practicum. Theme 1 Кәсіпкерлік: мәні, мазмұны мен қалыптасу шарттары. (Тақырып 1)
Кәсіпкерлік: мәні, мазмұны мен қалыптасу шарттары. (Тақырып 1) Бізнес-план кафе White&black
Бізнес-план кафе White&black Авто электроника по оптовым ценам
Авто электроника по оптовым ценам Номерной фонд. Классификация гостиничных номеров
Номерной фонд. Классификация гостиничных номеров Бизнес-план кафе
Бизнес-план кафе Рекламное агентство Аравт
Рекламное агентство Аравт Бизнес-проект Школьная фабрика по изготовлению сувениров 1000 подарков
Бизнес-проект Школьная фабрика по изготовлению сувениров 1000 подарков История компании Coca-Cola
История компании Coca-Cola SWOT-анализ малого и среднего бизнеса Кемеровской области
SWOT-анализ малого и среднего бизнеса Кемеровской области Бизнес-план. Национальный проект по развитию предпринимательства на 2021-2025 годы
Бизнес-план. Национальный проект по развитию предпринимательства на 2021-2025 годы Показатели бизнес-процессов
Показатели бизнес-процессов Комплексная юридическая поддержка бизнеса на расстоянии звонка
Комплексная юридическая поддержка бизнеса на расстоянии звонка Establishment of a Central European Air Cargo Logistics Hub & European Aviation
Establishment of a Central European Air Cargo Logistics Hub & European Aviation