Содержание
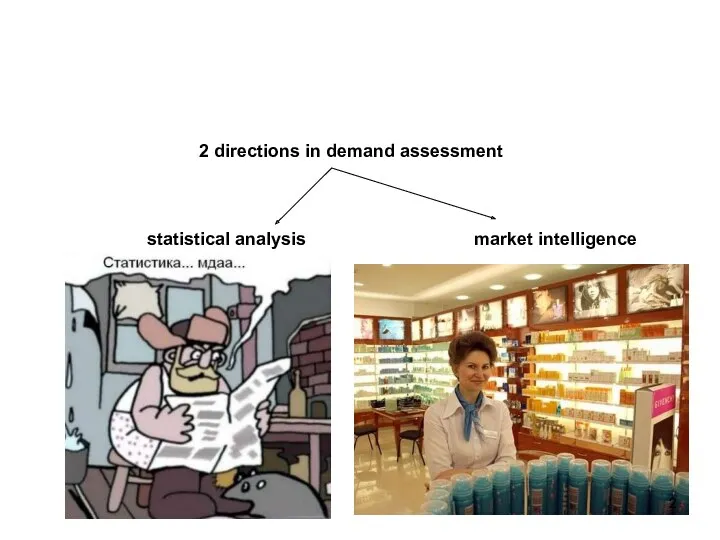
- 2. 2 directions in demand assessment statistical analysis market intelligence Задача статистического анализа: определение параметров функции спроса
- 3. Statistical analysis Steps: 1) Collection, validation and assessment of data 2) The choice of the information
- 4. 1) Collection, validation and assessment of data time series cross-sectional data Statistical analysis
- 5. time series 1) Collection, validation and assessment of data Statistical analysis Examine time changes in the
- 6. Adjustment of necessary information in order to avoid effects such as inflation Deflationary correction: divide all
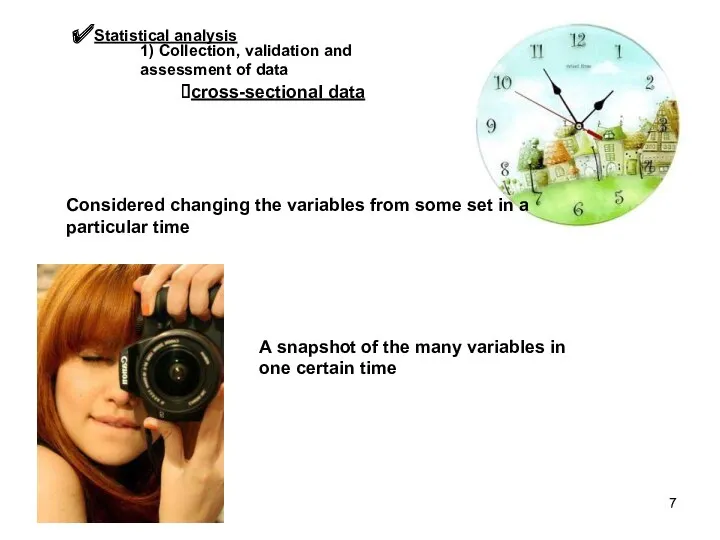
- 7. Statistical analysis 1) Collection, validation and assessment of data cross-sectional data Considered changing the variables from
- 8. Ex: In order to determine the effect of prices on demand, as a variable can be
- 9. Statistical analysis 2) The choice of the information curve The results of the observations are used
- 10. When choosing a curve there are two main questions: What type of equation it is necessary
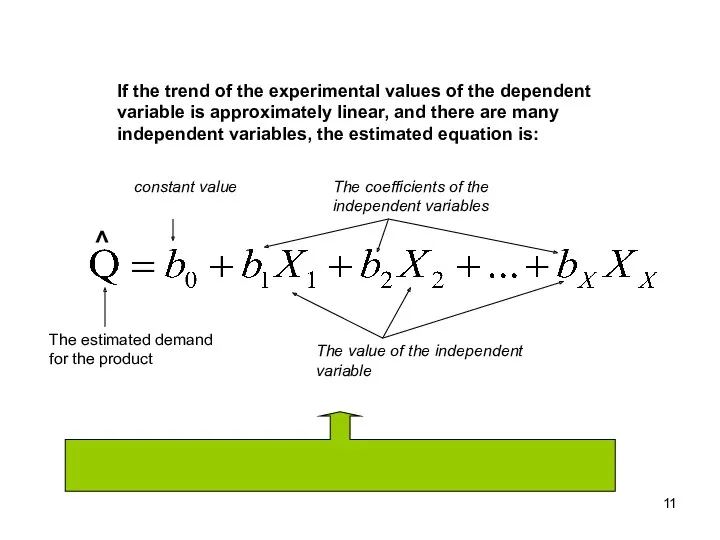
- 11. If the trend of the experimental values of the dependent variable is approximately linear, and there
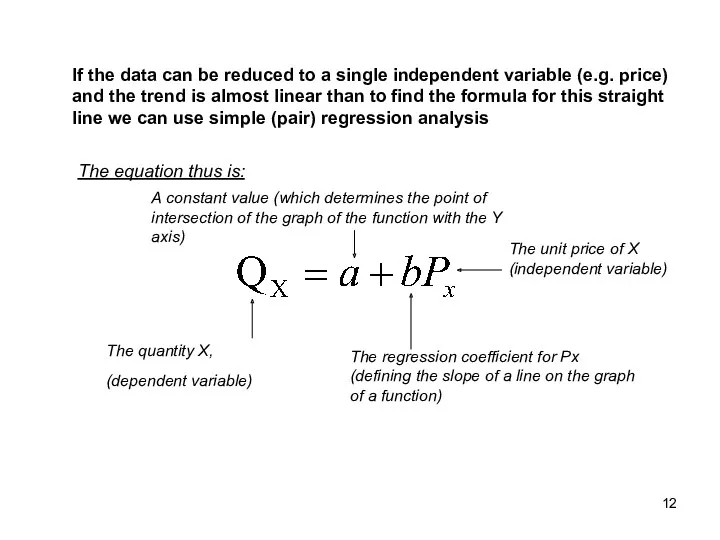
- 12. If the data can be reduced to a single independent variable (e.g. price) and the trend
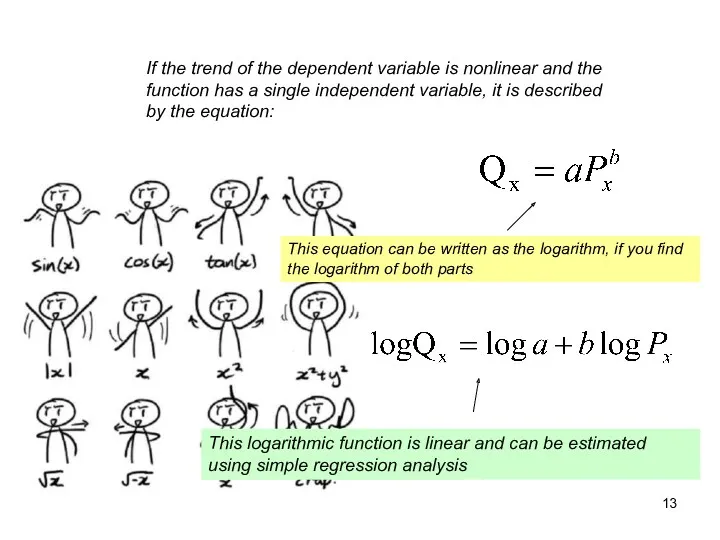
- 13. If the trend of the dependent variable is nonlinear and the function has a single independent
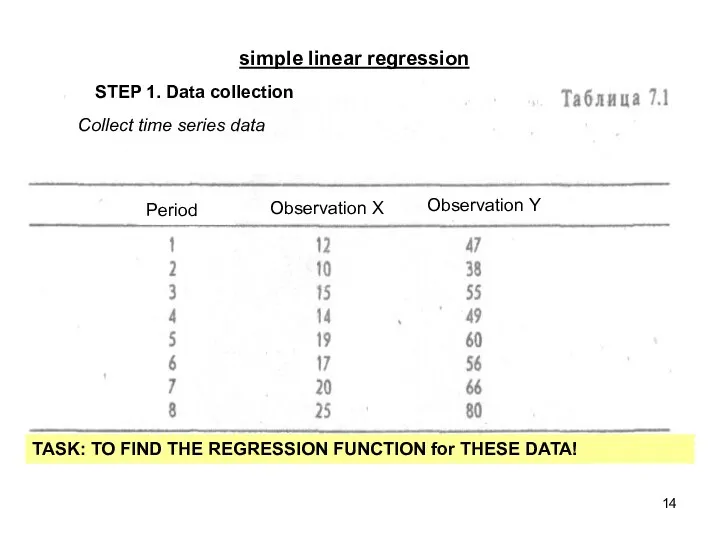
- 14. simple linear regression STEP 1. Data collection TASK: TO FIND THE REGRESSION FUNCTION for THESE DATA!
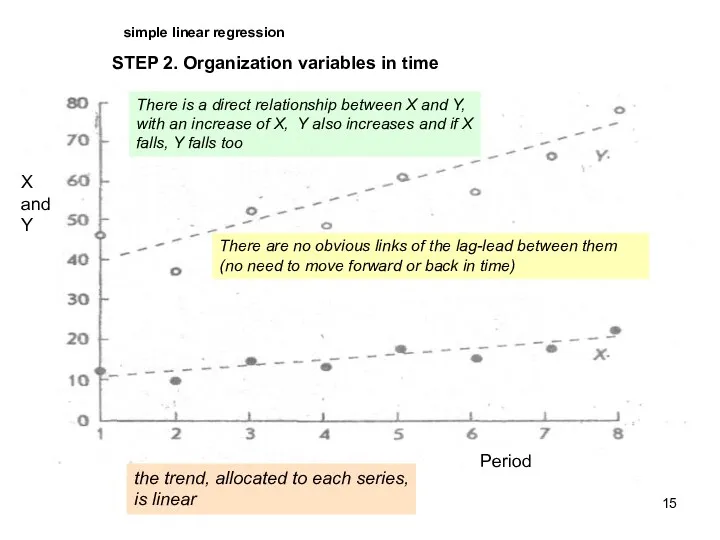
- 15. STEP 2. Organization variables in time simple linear regression Причины: визуализация; определение линейности или нелинейности для
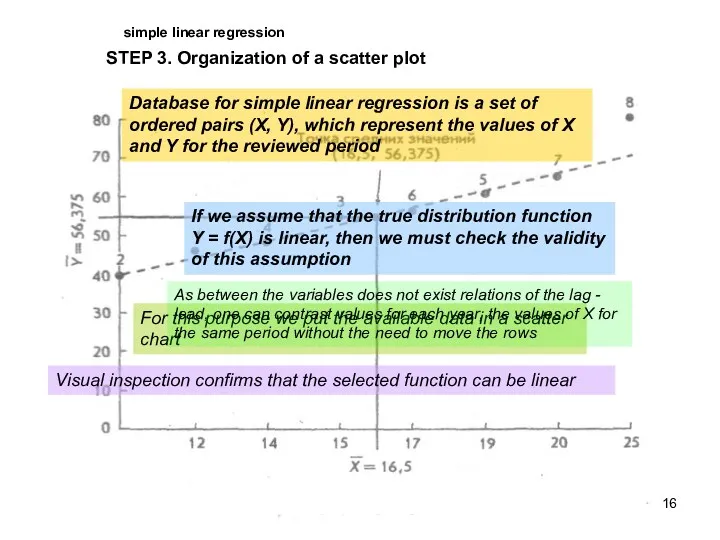
- 16. simple linear regression STEP 3. Organization of a scatter plot Database for simple linear regression is
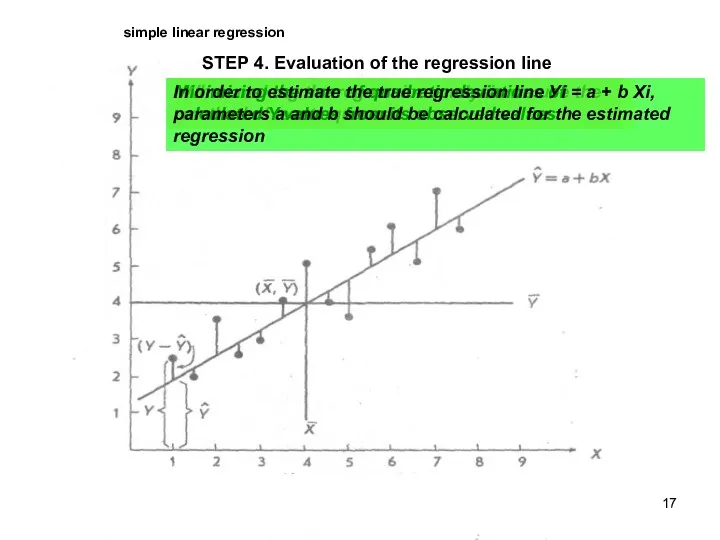
- 17. simple linear regression STEP 4. Evaluation of the regression line When making the regression analysis we
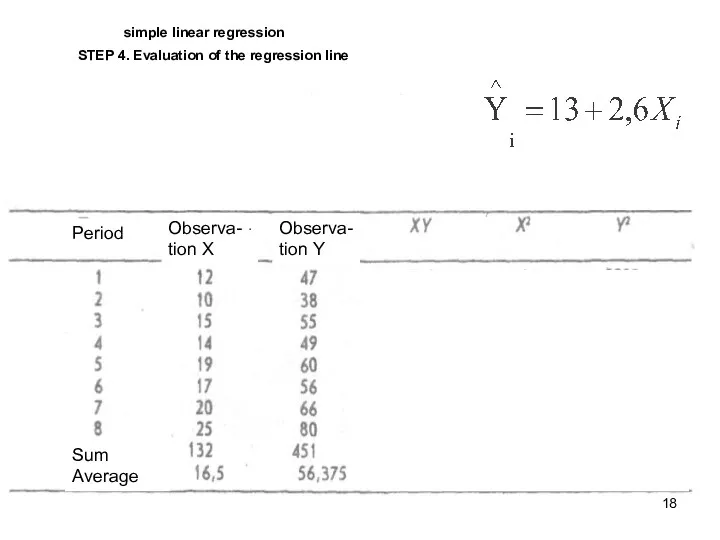
- 18. simple linear regression STEP 4. Evaluation of the regression line Period Observa-tion X Observa-tion X Observa-tion
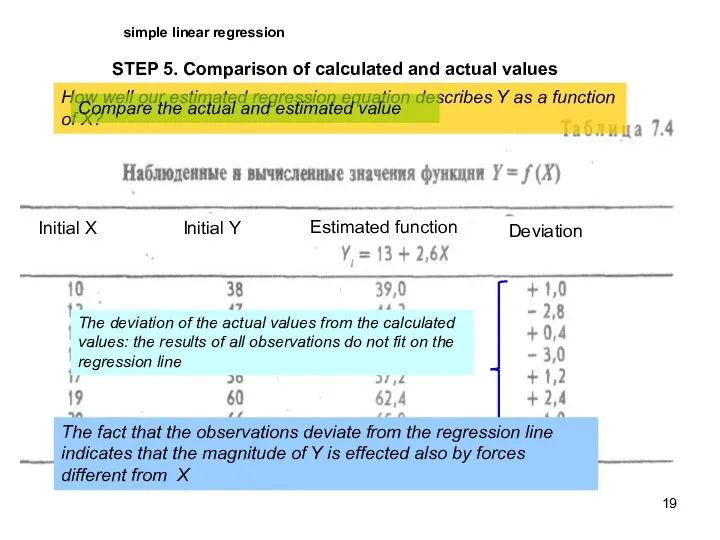
- 19. simple linear regression STEP 5. Comparison of calculated and actual values How well our estimated regression
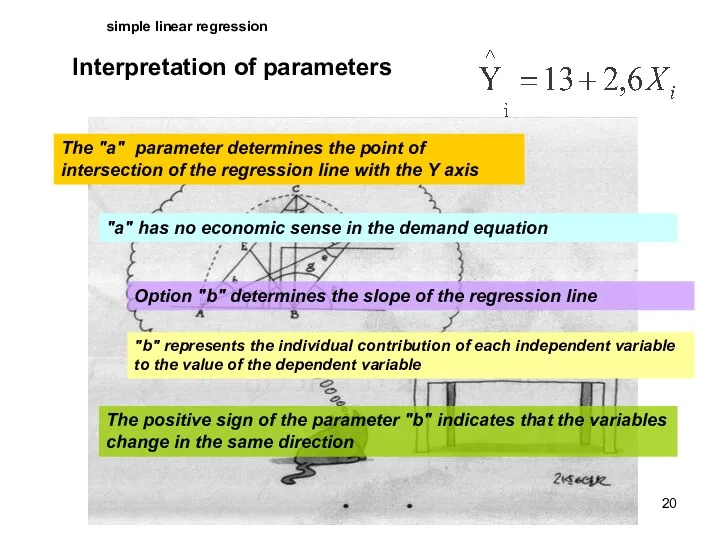
- 20. simple linear regression Interpretation of parameters The "a" parameter determines the point of intersection of the
- 21. simple linear regression Evaluation of the regression equation How informative or accurate the determined Y is?
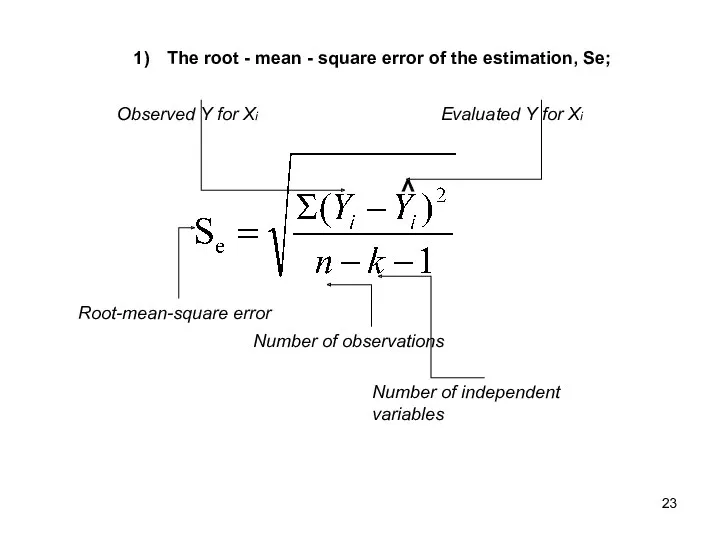
- 22. The root – mean - square error of the estimation, Se; Represents the deviation of experimental
- 23. The root - mean - square error of the estimation, Se; ˄ Root-mean-square error Observed Y
- 24. The more root-mean-square error is, the greater the range of deviations are Root-mean-square error, Se; If
- 25. coefficient of determination, r^2 Shows how well the regression model describes the variation of the dependent
- 26. the correlation coefficient, r, Determines the degree of connection between variables -1 1
- 28. Скачать презентацию










 Життя Вільяма Петті як основоположника класичної політичної економії в Англії в ХVII - ХVІІІ століттях
Життя Вільяма Петті як основоположника класичної політичної економії в Англії в ХVII - ХVІІІ століттях Транспорттағы метеорологиялық болжамдардың экономикалық тиімділігі
Транспорттағы метеорологиялық болжамдардың экономикалық тиімділігі Общая характеристика рыночной экономики. (Тема 4)
Общая характеристика рыночной экономики. (Тема 4) Развитие экономического сотрудничества в Евразии с участием России
Развитие экономического сотрудничества в Евразии с участием России Коммерциализация технологий и разработок
Коммерциализация технологий и разработок Анализ и диагностика финансово-хозяйственной деятельности предприятия. Экономический анализ
Анализ и диагностика финансово-хозяйственной деятельности предприятия. Экономический анализ Микроэкономика. Предмет и методология микроэкономики. Основные понятия
Микроэкономика. Предмет и методология микроэкономики. Основные понятия Экономика и социология труда, как наука
Экономика и социология труда, как наука Определение оптимального объема производства: микроэкономический аспект
Определение оптимального объема производства: микроэкономический аспект Прогнозирование и планирование в условиях рынка
Прогнозирование и планирование в условиях рынка Предмет и методы ЭТ. Базовые экономические категории. Лекция 1
Предмет и методы ЭТ. Базовые экономические категории. Лекция 1 Сущность и задачи (экономическогО) районирования России
Сущность и задачи (экономическогО) районирования России Анализ производства и реализации продукции
Анализ производства и реализации продукции Оснвные средства предприятий
Оснвные средства предприятий Введение в микроэкономику
Введение в микроэкономику Инновационная деятельность и повышение ее инвестиционной привлекательности
Инновационная деятельность и повышение ее инвестиционной привлекательности International Economic. Analysis 1.1
International Economic. Analysis 1.1 Фирменный стиль в рекламе
Фирменный стиль в рекламе Основные макроэкономические показатели
Основные макроэкономические показатели Метод и методика экономического анализа
Метод и методика экономического анализа Роль экономики в жизни общества
Роль экономики в жизни общества Формування поведінки підприємства на ринку промислових товарів. (Тема 1)
Формування поведінки підприємства на ринку промислових товарів. (Тема 1) Экономические основы обеспечения безопасных условий труда. Методы управления охраной труда
Экономические основы обеспечения безопасных условий труда. Методы управления охраной труда ARCH – модель та її практичне застосування в економіці
ARCH – модель та її практичне застосування в економіці Казахстанская модель экономического развития
Казахстанская модель экономического развития Основы антикризисного управления
Основы антикризисного управления Понятие экономика
Понятие экономика Стратегия социально-экономического развития городского округа. Город Уфа Республики Башкортостан до 2030 года
Стратегия социально-экономического развития городского округа. Город Уфа Республики Башкортостан до 2030 года