Содержание
- 2. Elasticity . . . … allows us to analyze supply and demand with greater precision. …
- 3. THE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND Price elasticity of demand is a measure of how much the quantity
- 4. The Price Elasticity of Demand and Its Determinants Availability of Close Substitutes Necessities versus Luxuries Definition
- 5. The Price Elasticity of Demand and Its Determinants Demand tends to be more elastic : the
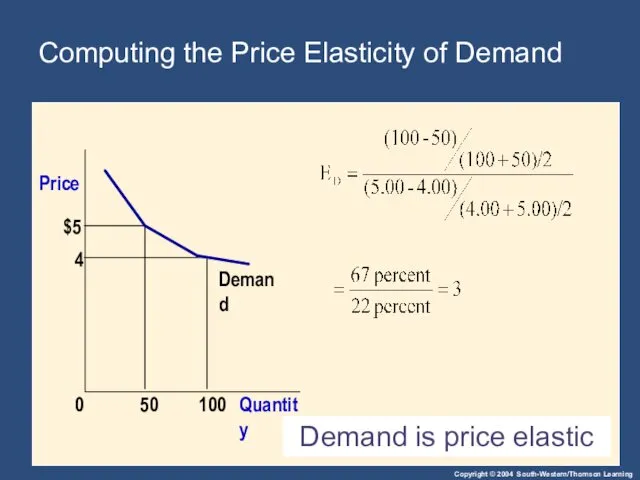
- 6. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand The price elasticity of demand is computed as the percentage
- 7. Example: If the price of an ice cream cone increases from $2.00 to $2.20 and the
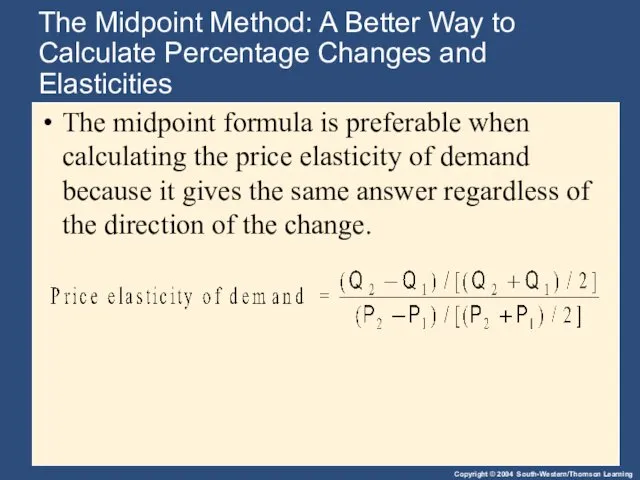
- 8. The Midpoint Method: A Better Way to Calculate Percentage Changes and Elasticities The midpoint formula is
- 9. The Midpoint Method: A Better Way to Calculate Percentage Changes and Elasticities Example: If the price
- 10. The Variety of Demand Curves Inelastic Demand Quantity demanded does not respond strongly to price changes.
- 11. Computing the Price Elasticity of Demand Demand is price elastic $5 4 Demand Quantity 100 0
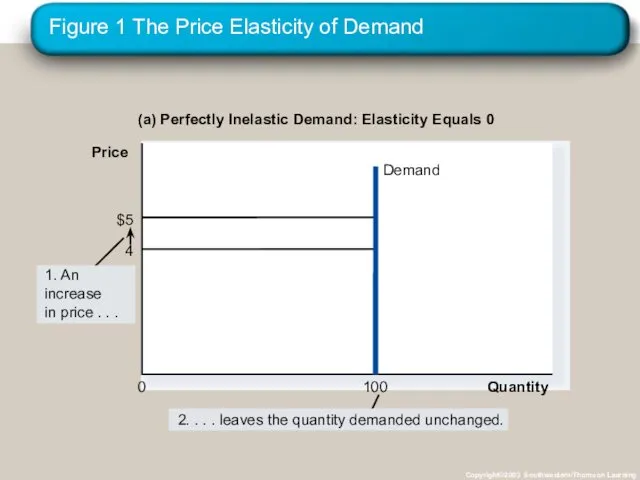
- 12. The Variety of Demand Curves Perfectly Inelastic Quantity demanded does not respond to price changes. Perfectly
- 13. The Variety of Demand Curves Because the price elasticity of demand measures how much quantity demanded
- 14. Figure 1 The Price Elasticity of Demand Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning (a) Perfectly Inelastic Demand: Elasticity Equals
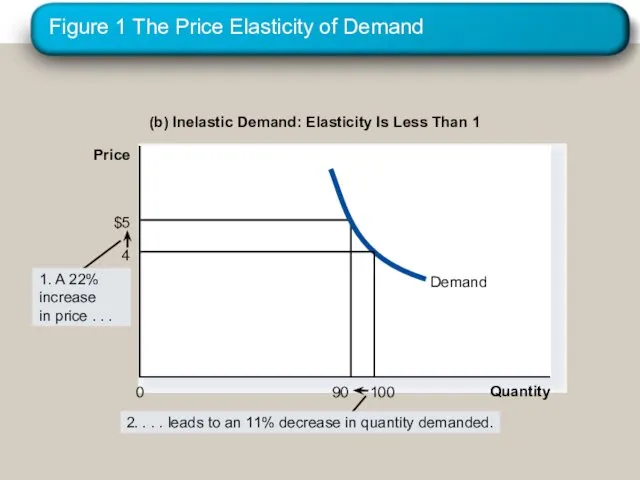
- 15. Figure 1 The Price Elasticity of Demand (b) Inelastic Demand: Elasticity Is Less Than 1 Quantity
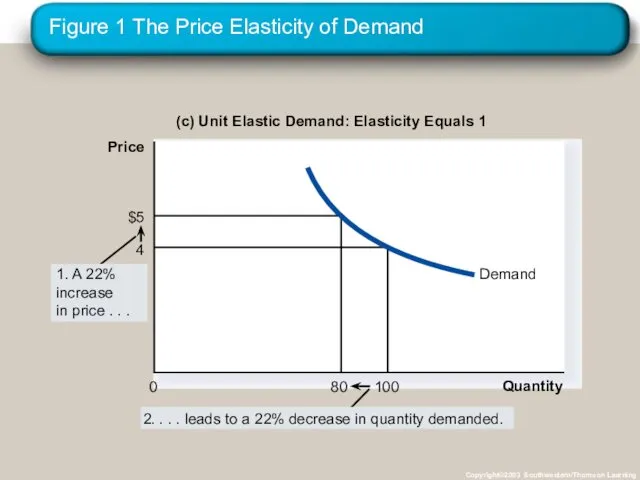
- 16. Figure 1 The Price Elasticity of Demand Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning (c) Unit Elastic Demand: Elasticity Equals
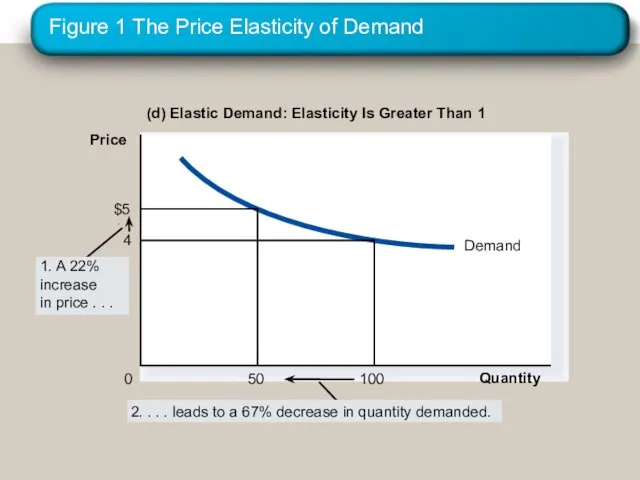
- 17. Figure 1 The Price Elasticity of Demand (d) Elastic Demand: Elasticity Is Greater Than 1 Quantity
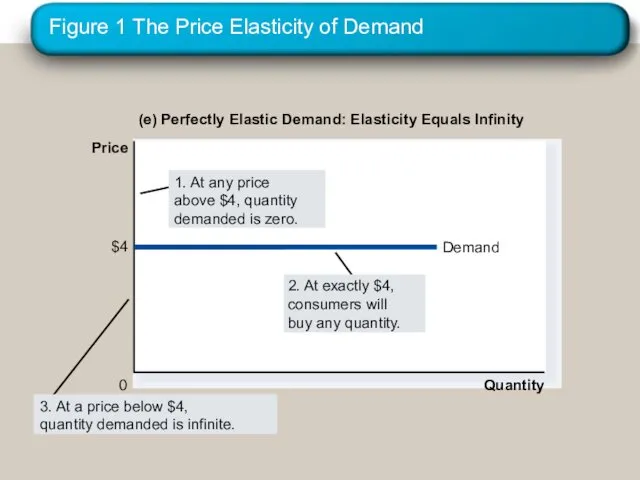
- 18. Figure 1 The Price Elasticity of Demand (e) Perfectly Elastic Demand: Elasticity Equals Infinity Quantity 0
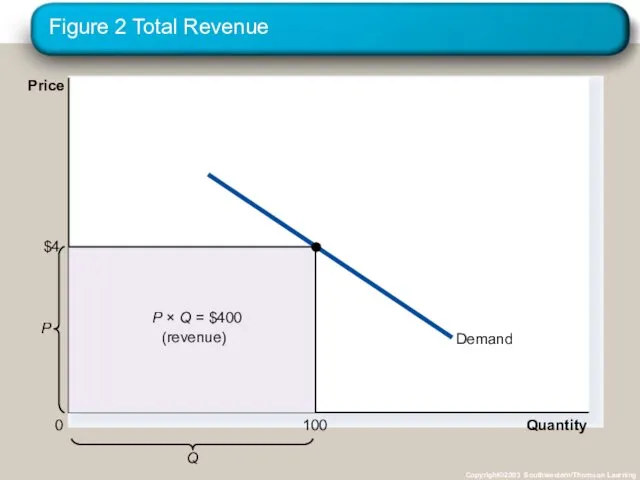
- 19. Total Revenue and the Price Elasticity of Demand Total revenue is the amount paid by buyers
- 20. Figure 2 Total Revenue Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning Quantity 0 Price
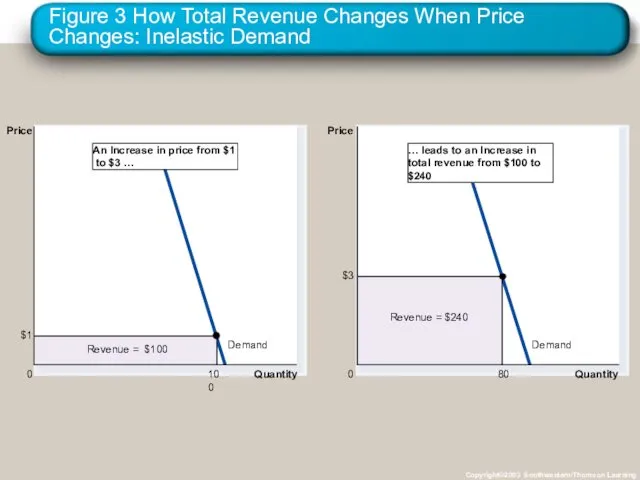
- 21. Elasticity and Total Revenue along a Linear Demand Curve With an inelastic demand curve, an increase
- 22. Figure 3 How Total Revenue Changes When Price Changes: Inelastic Demand Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning Quantity 0
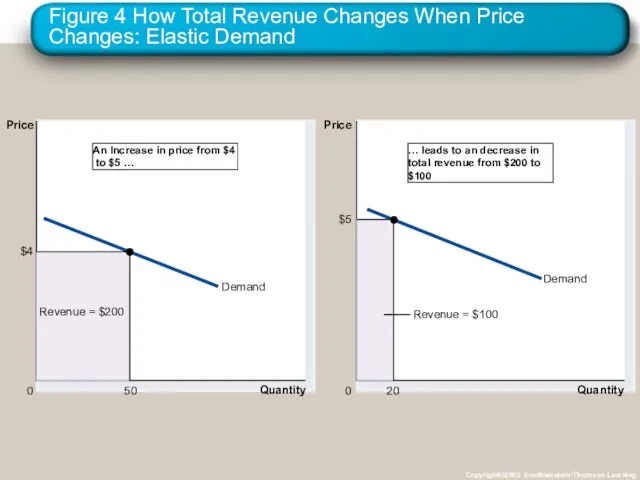
- 23. Elasticity and Total Revenue along a Linear Demand Curve With an elastic demand curve, an increase
- 24. Figure 4 How Total Revenue Changes When Price Changes: Elastic Demand Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning Quantity 0
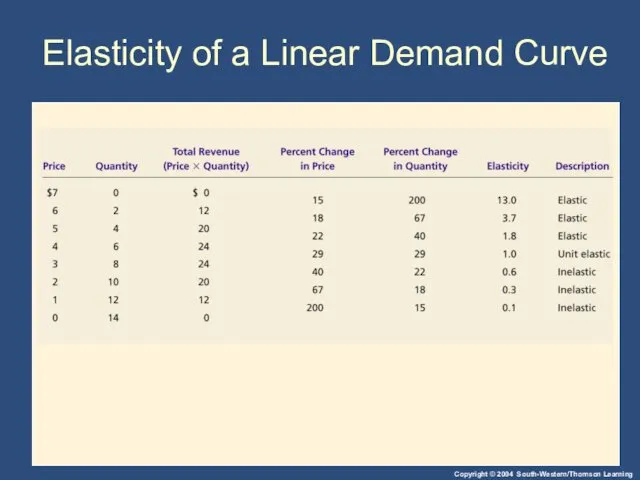
- 25. Elasticity of a Linear Demand Curve
- 26. Income Elasticity of Demand Income elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded of a
- 27. Computing Income Elasticity
- 28. Income Elasticity Types of Goods Normal Goods Inferior Goods Higher income raises the quantity demanded for
- 29. Income Elasticity Goods consumers regard as necessities tend to be income inelastic Examples include food, fuel,
- 30. THE ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY Price elasticity of supply is a measure of how much the quantity
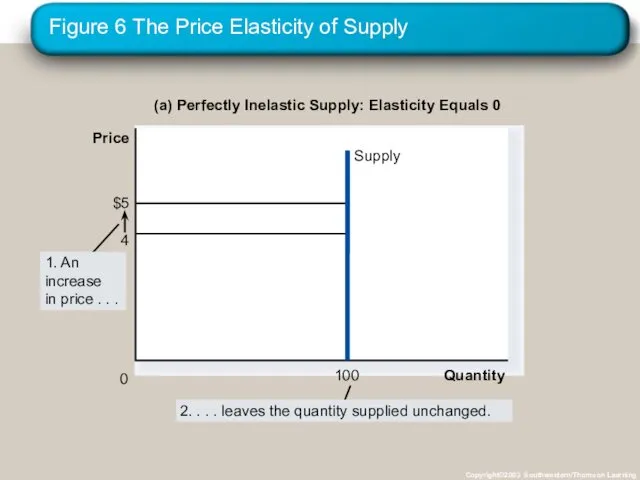
- 31. Figure 6 The Price Elasticity of Supply Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning (a) Perfectly Inelastic Supply: Elasticity Equals
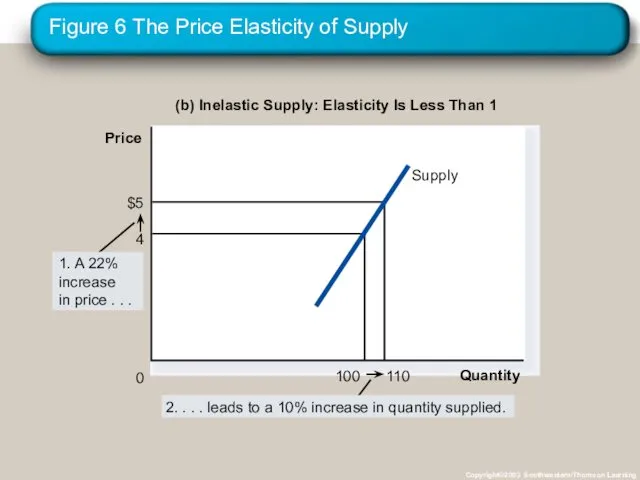
- 32. Figure 6 The Price Elasticity of Supply Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning (b) Inelastic Supply: Elasticity Is Less
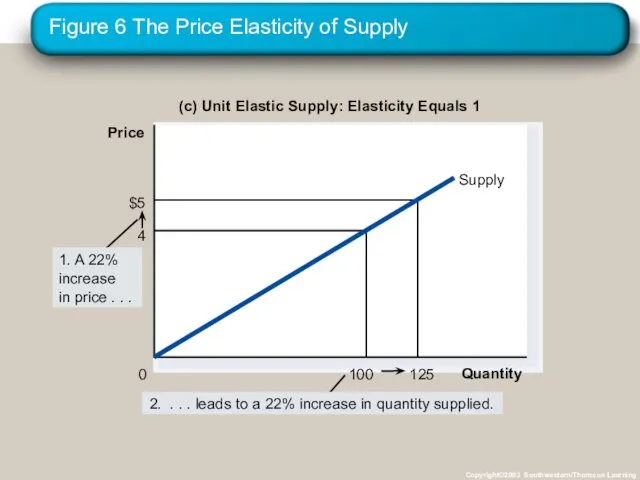
- 33. Figure 6 The Price Elasticity of Supply Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning (c) Unit Elastic Supply: Elasticity Equals
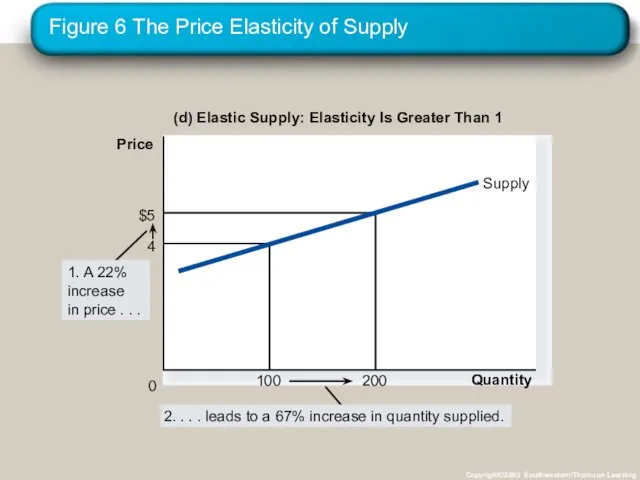
- 34. Figure 6 The Price Elasticity of Supply Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning (d) Elastic Supply: Elasticity Is Greater
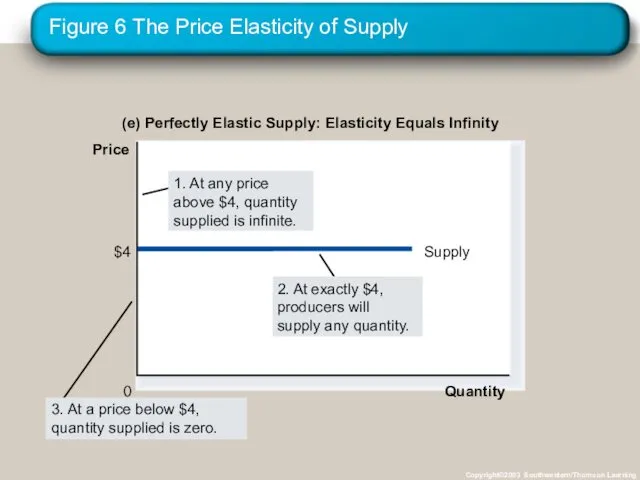
- 35. Figure 6 The Price Elasticity of Supply Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning (e) Perfectly Elastic Supply: Elasticity Equals
- 36. Determinants of Elasticity of Supply Ability of sellers to change the amount of the good they
- 37. Computing the Price Elasticity of Supply The price elasticity of supply is computed as the percentage
- 38. APPLICATION of ELASTICITY Can good news for farming be bad news for farmers? What happens to
- 39. THE APPLICATION OF SUPPLY, DEMAND, AND ELASTICITY Examine whether the supply or demand curve shifts. Determine
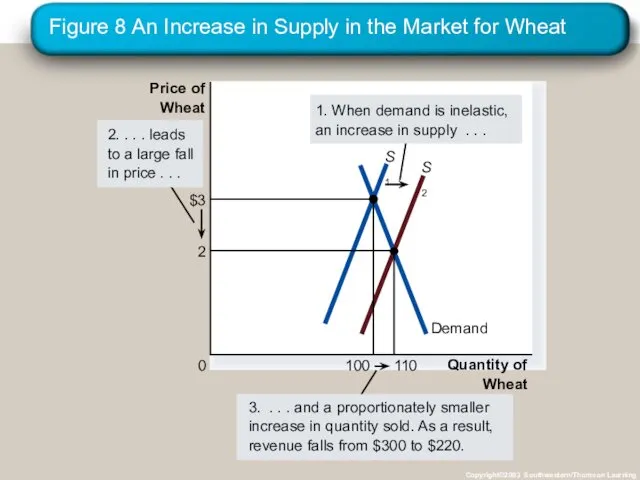
- 40. Figure 8 An Increase in Supply in the Market for Wheat Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning Quantity of
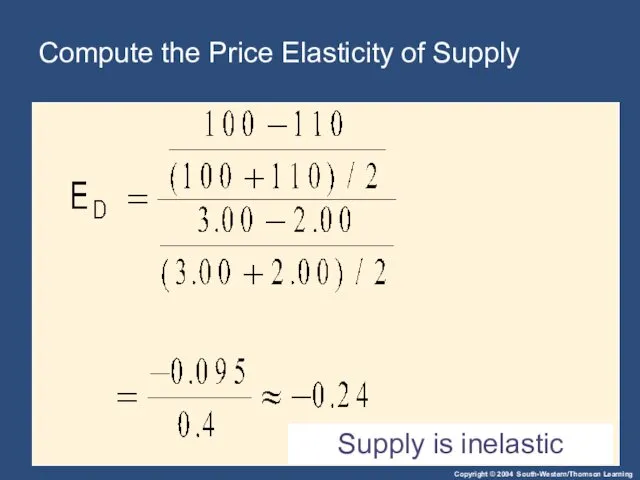
- 41. Compute the Price Elasticity of Supply Supply is inelastic
- 42. Summary Price elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded responds to changes in the
- 43. Summary The income elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded responds to changes in
- 45. Скачать презентацию
























 Основополагающие принципы налогообложения
Основополагающие принципы налогообложения Конкурентоспособность торгового предприятия
Конкурентоспособность торгового предприятия Экономика. Подготовка к ЕГЭ по обществознанию
Экономика. Подготовка к ЕГЭ по обществознанию Капитальное строительство как инвестиционный процесс
Капитальное строительство как инвестиционный процесс World Tourism Market. Introduction to the market and international tourism
World Tourism Market. Introduction to the market and international tourism Генеральный план городского округа Город Сочи
Генеральный план городского округа Город Сочи Основы организации труда на предприятии
Основы организации труда на предприятии Прогноз последствий для роста имиджа Казахстана от проведения выставки Астана ЭКСПО-2017
Прогноз последствий для роста имиджа Казахстана от проведения выставки Астана ЭКСПО-2017 Макроэкономическая наука. Понятия в макроэкономике. (Тема 1)
Макроэкономическая наука. Понятия в макроэкономике. (Тема 1) Введение в макроэкономический анализ. Предмет и метод макроэкономики
Введение в макроэкономический анализ. Предмет и метод макроэкономики Формирование комфортной городской среды
Формирование комфортной городской среды Опыт использования современных технологий в деятельности экономических субъектов
Опыт использования современных технологий в деятельности экономических субъектов На пороге нового века: динамика и противоречия экономического развития
На пороге нового века: динамика и противоречия экономического развития Ұлттық экономикадағы қаржы және ақша-несие жүйесі
Ұлттық экономикадағы қаржы және ақша-несие жүйесі Экономические системы
Экономические системы Познавательные ограничения и поведение потребителя
Познавательные ограничения и поведение потребителя Обгрунтування вибору постачальників товарів торговельного підприємства
Обгрунтування вибору постачальників товарів торговельного підприємства Политика распределения. Практика 5
Политика распределения. Практика 5 Мировое хозяйство
Мировое хозяйство “Роль економіки Іспанії у Європейському Союзі
“Роль економіки Іспанії у Європейському Союзі Сертификация. Принципы, цели, задачи
Сертификация. Принципы, цели, задачи Chartered Financial Analyst® exam (level 1). Study Session 5. Economics
Chartered Financial Analyst® exam (level 1). Study Session 5. Economics Понятие, содержание и субъекты экономической деятельности и экономических отношений
Понятие, содержание и субъекты экономической деятельности и экономических отношений Economia de piață. (Curs 2)
Economia de piață. (Curs 2) Экономикалық саясаттың негізгі бағыттары. Тақырып 14
Экономикалық саясаттың негізгі бағыттары. Тақырып 14 Модели эндогенного роста. Часть 2
Модели эндогенного роста. Часть 2 Актуальные вопросы автоматизации в управлении экономикой. Тема 1
Актуальные вопросы автоматизации в управлении экономикой. Тема 1 Экономика фирм и роль транснациональных корпораций (ТНК)
Экономика фирм и роль транснациональных корпораций (ТНК)