Содержание
- 2. Chapter 1 Class objectives 1 Describe the characteristics of the digital economy and e-business. 2 Recognize
- 3. Digital Economy – New Economy E-Business: The use of electronic technologies to transact business. Collaboration: People
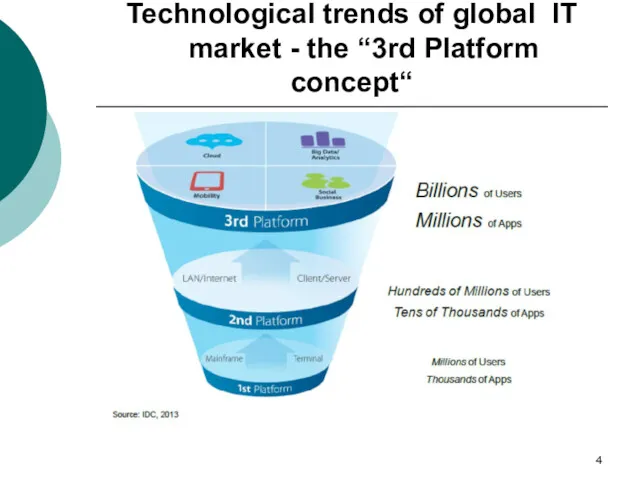
- 4. Technological trends of global IT market - the “3rd Platform concept“
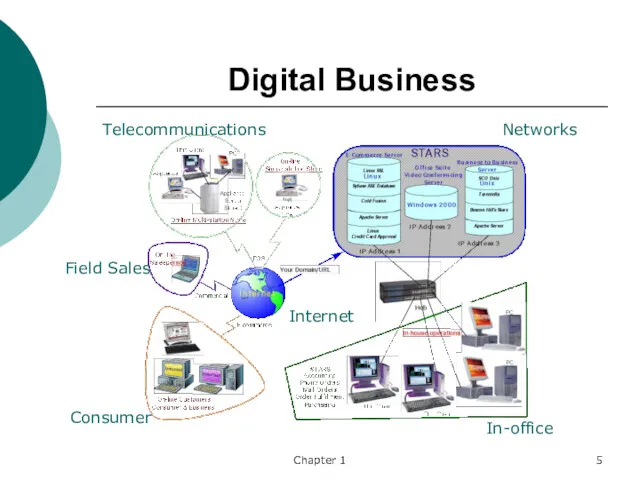
- 5. Chapter 1 Digital Business Networks Internet Telecommunications Consumer In-office Field Sales
- 6. Chapter 1 The Old Economy – Taking Photo’s Buy film in a store Load your camera
- 7. Chapter 1 The New Economy – Taking Photo’s 1st Generation Digital Photography Old economy except 6
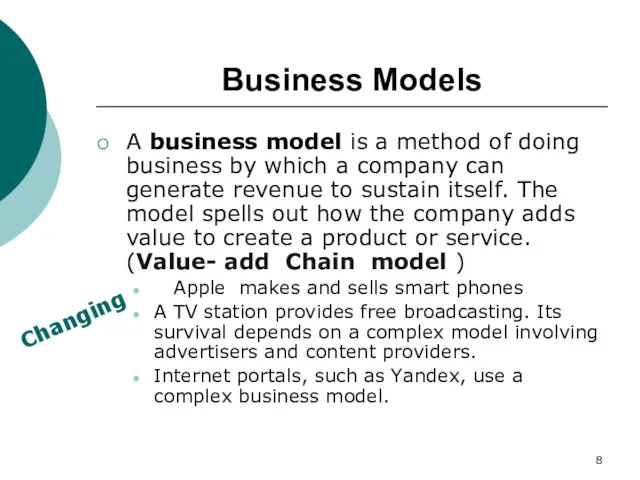
- 8. Business Models A business model is a method of doing business by which a company can
- 9. Chapter 1 Digital Age Business Models Name-Your-Own Price Reverse Auctions Affiliate Marketing E-Marketplaces and Exchanges Electronic
- 10. Chapter 1 Drivers Forcing Changes In Business Models Environmental, organizational, and technological factors are creating a
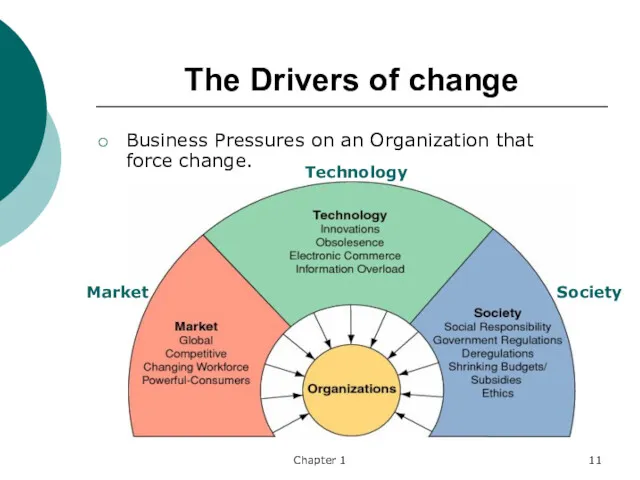
- 11. Chapter 1 The Drivers of change Business Pressures on an Organization that force change. Market Technology
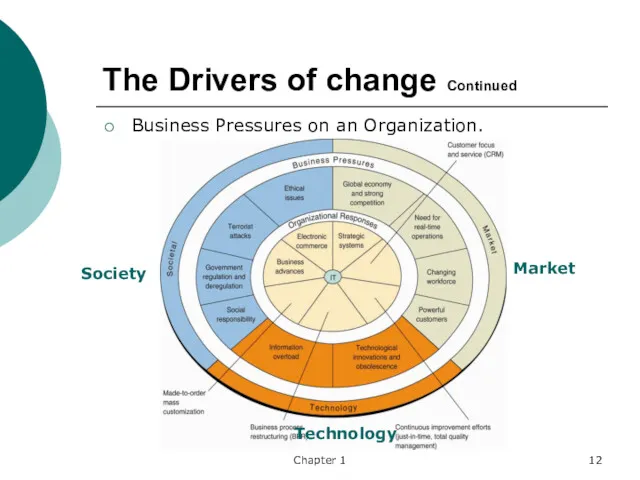
- 12. Chapter 1 The Drivers of change Continued Business Pressures on an Organization. Market Society Technology
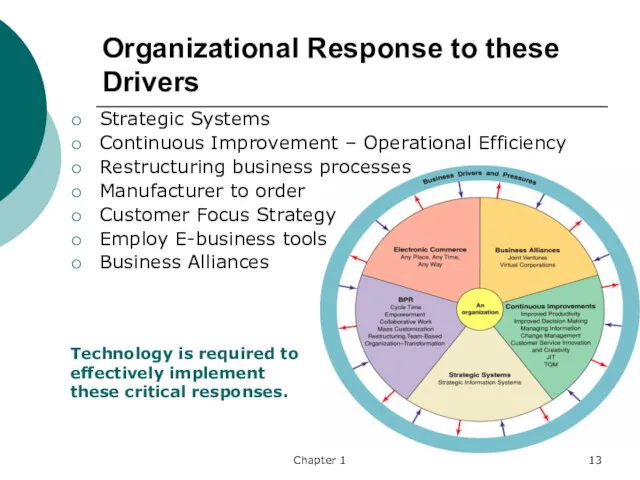
- 13. Chapter 1 Organizational Response to these Drivers Strategic Systems Continuous Improvement – Operational Efficiency Restructuring business
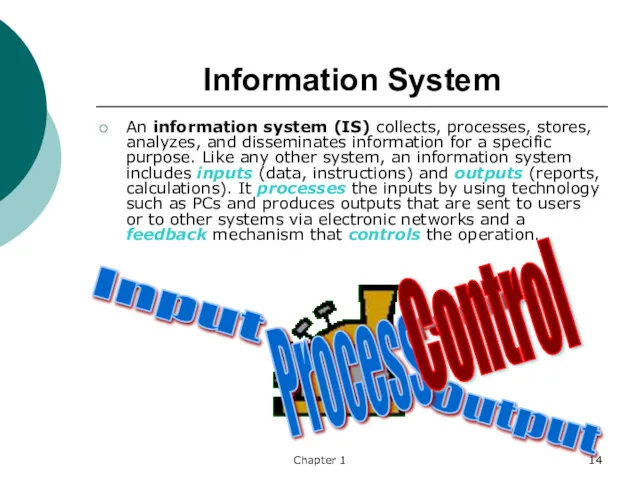
- 14. Chapter 1 Information System An information system (IS) collects, processes, stores, analyzes, and disseminates information for
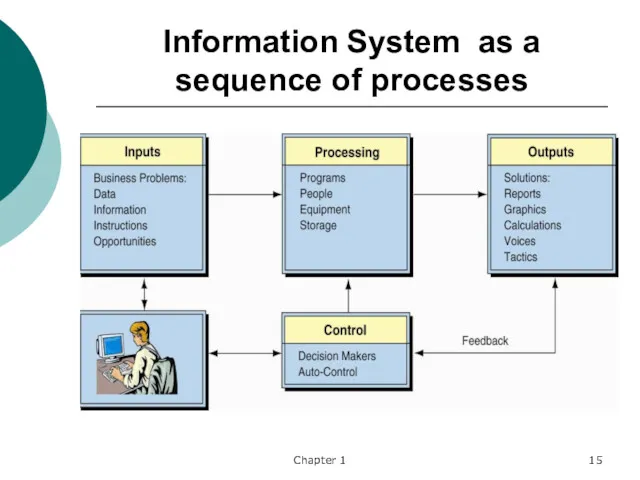
- 15. Chapter 1 Information System as a sequence of processes
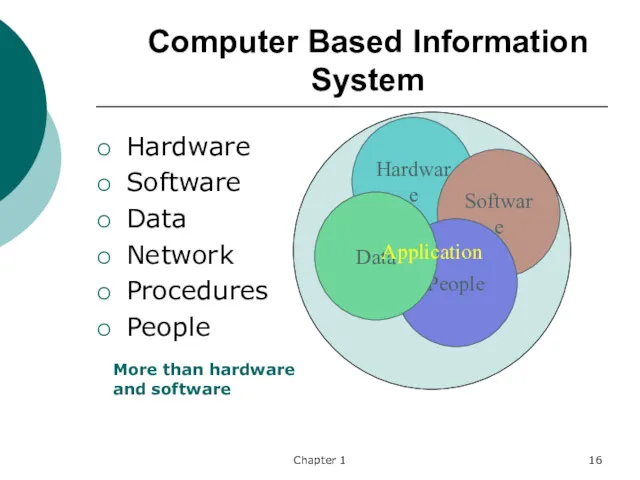
- 16. Chapter 1 Computer Based Information System Hardware Software Data Network Procedures People Hardware Software People Data
- 17. Chapter 1 Applications and Operations Retail operations Wholesale Manufacturing Human Resources Marketing Content management …
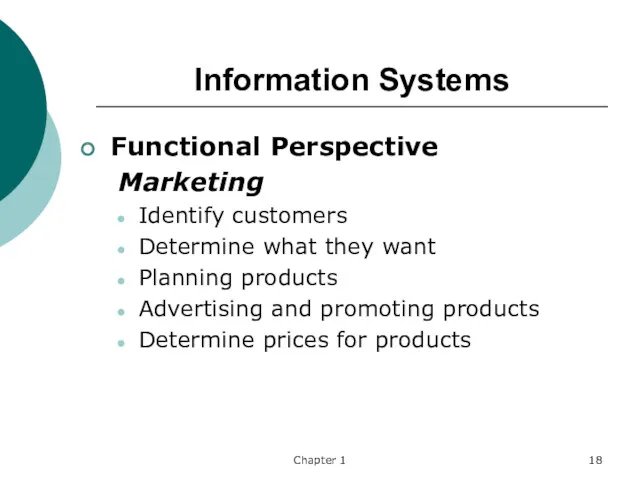
- 18. Chapter 1 Information Systems Functional Perspective Marketing Identify customers Determine what they want Planning products Advertising
- 19. Chapter 1 Information Systems Functional Perspective Sales Contact customers Sell the product Take the order Follow-up
- 20. Chapter 1 Information Systems Functional Perspective Manufacturing Control Equipment and machinery Design new products Quantity of
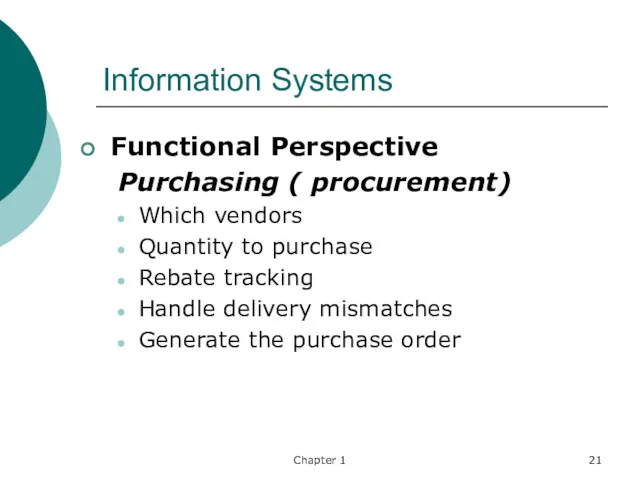
- 21. Chapter 1 Information Systems Functional Perspective Purchasing ( procurement) Which vendors Quantity to purchase Rebate tracking
- 22. Chapter 1 Information Systems Functional Perspective Finance Financial Assets Investment management Banking Long term budgets
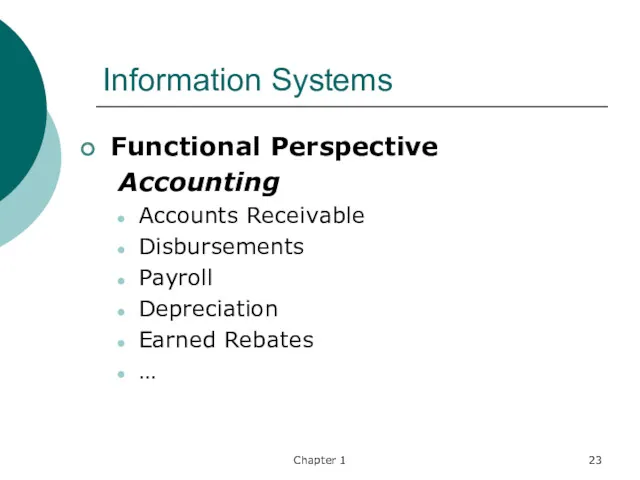
- 23. Chapter 1 Information Systems Functional Perspective Accounting Accounts Receivable Disbursements Payroll Depreciation Earned Rebates …
- 24. Chapter 1 Information Systems Functional Perspective Human Resources Employee wages, salaries & benefits Long term labor
- 25. Chapter 1 Trends in Technology Cost-performance ratio of chips keeps improving. Moore’s Law, his prediction was
- 26. Chapter 1 Trends in Technology Internet Mobile Computing and M-Commerce Wireless networks Ubiquitous Computing Smart Devices
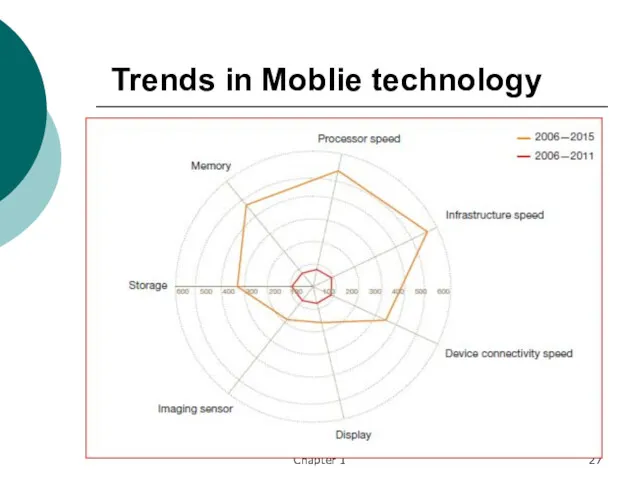
- 27. Trends in Moblie technology Chapter 1
- 28. Chapter 1 Trends in Technology (continued) The Network Computer Optical Networks Storage Area Networks Intranets &
- 29. Chapter 1 Why Study Information Technology ? You will be more effective in your chosen career
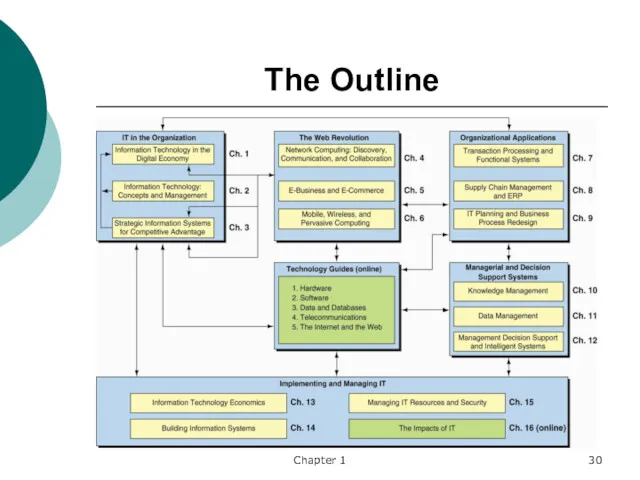
- 30. Chapter 1 The Outline
- 31. Chapter 1 MANAGERIAL ISSUES Recognizing opportunities for using IT and Web-based systems. Who will build, operate,
- 32. Chapter 1 MANAGERIAL ISSUES Continued Ethics and social issues. The implementation of IT involves many ethical
- 34. Скачать презентацию
















 Выпускная работа. Обоснование перспектив развития предприятия Фортуна Крым Трейд
Выпускная работа. Обоснование перспектив развития предприятия Фортуна Крым Трейд Ценообразование на монополизированном рынке
Ценообразование на монополизированном рынке Безработица. Трудоспособное и нетрудоспособное население
Безработица. Трудоспособное и нетрудоспособное население Методы ABC, XYZ. Задача на знание метода ABC
Методы ABC, XYZ. Задача на знание метода ABC Макроэкономика. Сущность макроэкономики, ее основные цели
Макроэкономика. Сущность макроэкономики, ее основные цели Економічна теорія як наука
Економічна теорія як наука Государственные финансы
Государственные финансы Märkte für Produktionsfaktoren
Märkte für Produktionsfaktoren Общая характеристика направления менеджмент и ее профилей. (Раздел 1)
Общая характеристика направления менеджмент и ее профилей. (Раздел 1) Денежно-кредитная политика государства
Денежно-кредитная политика государства Трудовые ресурсы предприятия: основные понятия, структура, показатели
Трудовые ресурсы предприятия: основные понятия, структура, показатели Организация и проведение массовой оценки объектов недвижимости
Организация и проведение массовой оценки объектов недвижимости Interaction of logical and nominal meanings
Interaction of logical and nominal meanings Научно-техническая безопасность и экономический рост
Научно-техническая безопасность и экономический рост Теоретичні засади податків
Теоретичні засади податків Собственность. Предпринимательство. Издержки производства. Прибыль
Собственность. Предпринимательство. Издержки производства. Прибыль Контроль за соблюдением норм и правил охраны труда. (Лекция 2)
Контроль за соблюдением норм и правил охраны труда. (Лекция 2) Задачи по экономике
Задачи по экономике Экономическая природа фирмы: основные формы деловых предприятий
Экономическая природа фирмы: основные формы деловых предприятий Нематериальные активы (НМА) организации
Нематериальные активы (НМА) организации Экономика. Главные вопросы экономики
Экономика. Главные вопросы экономики Нобелевские премии по экономике
Нобелевские премии по экономике Введение в логистику
Введение в логистику Основные производственные фонды. Понятие и классификация основных фондов
Основные производственные фонды. Понятие и классификация основных фондов Өндіріс факторларының арақатынасы теориясын эмпирикалық тексеру және олардың шектеулілігі мәселесі
Өндіріс факторларының арақатынасы теориясын эмпирикалық тексеру және олардың шектеулілігі мәселесі Неопределенность и риск в процессе реализации инвестиционных проектов
Неопределенность и риск в процессе реализации инвестиционных проектов Неолиберализм. Сущность и особенности неолиберализма
Неолиберализм. Сущность и особенности неолиберализма Комплексный план развития Куединского муниципального округа Пермского края
Комплексный план развития Куединского муниципального округа Пермского края