Содержание
- 2. Our previous lecture : Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 3. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 4. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Our todays lecture : International Exchange of knowledge
- 5. The forms of international economic relations International trade in goods and services; The international movement of
- 6. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
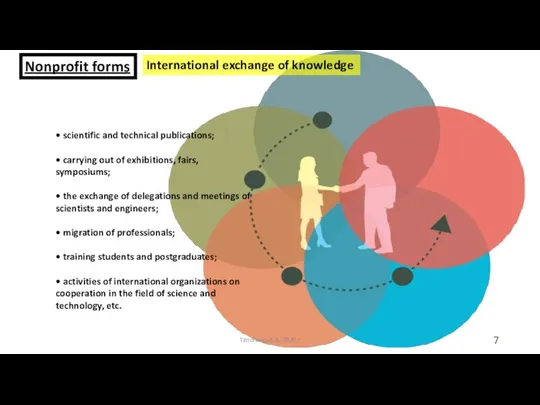
- 7. International exchange of knowledge Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Nonprofit forms • scientific and technical publications; •
- 8. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c International exchange of knowledge On commercial bases • transfer on the terms
- 9. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Licensing gives a licensee certain rights or resources to manufacture and/or market
- 10. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 11. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Examples Suppose Company A, a manufacturer and seller of Baubles, was based
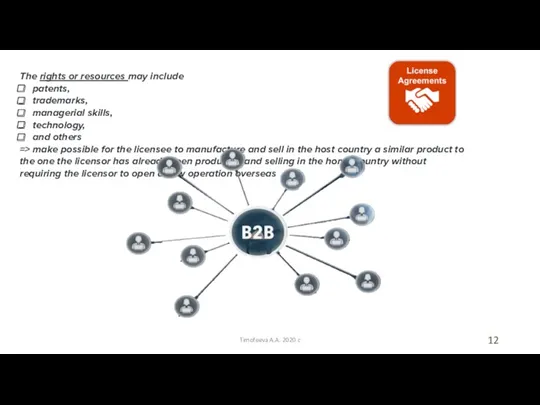
- 12. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c The rights or resources may include patents, trademarks, managerial skills, technology, and
- 13. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c The licensor’s earnings one-time payments royalty payments usually calculated as a percentage
- 14. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Batman The Batman character has been licensed to many companies, such as
- 15. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Licensing: flexible work agreement can be customized to fit the needs and
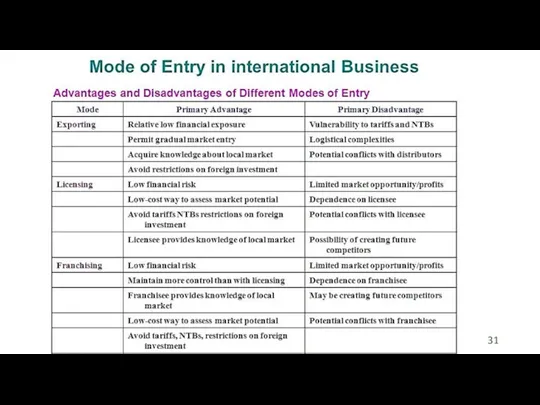
- 16. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Disadvantages and reasons: Lower income than in other entry modes Loss of
- 17. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 18. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
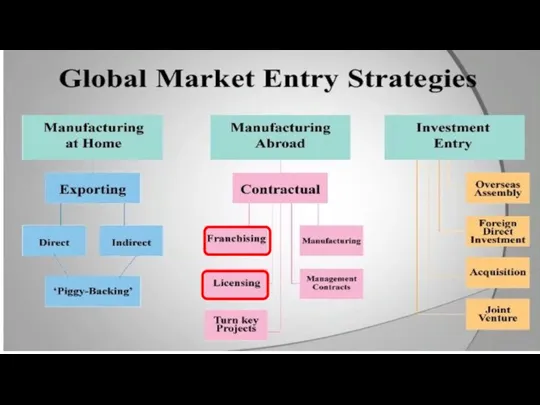
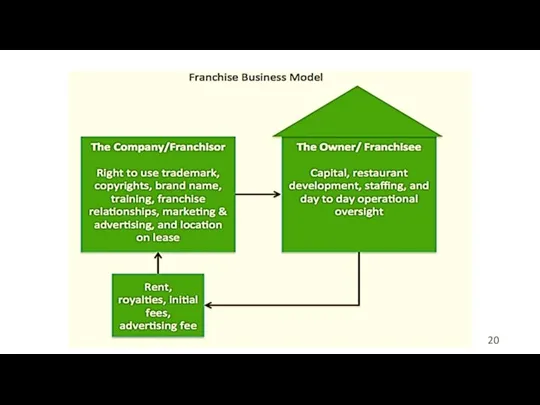
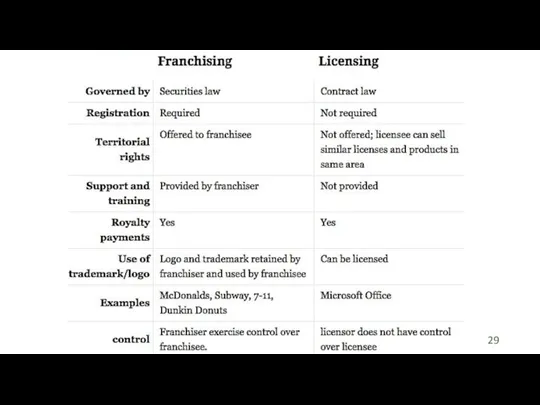
- 19. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Franchising Similar to a licensing agreement multinational firm grants rights on its
- 20. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 21. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 22. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 23. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Multi-Unit Franchises the franchisee owns and runs several outlets in a large
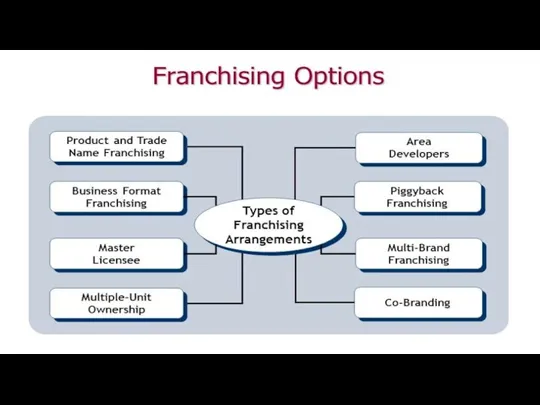
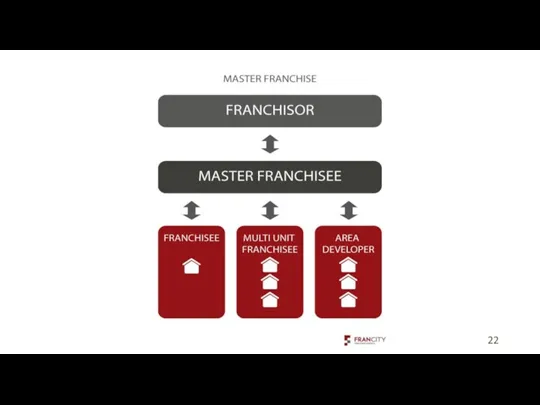
- 24. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Key Terms for Multi-Unit Franchises Area development agreement – With this type
- 25. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c A franchise area developer develop multiple locations in a specific region or
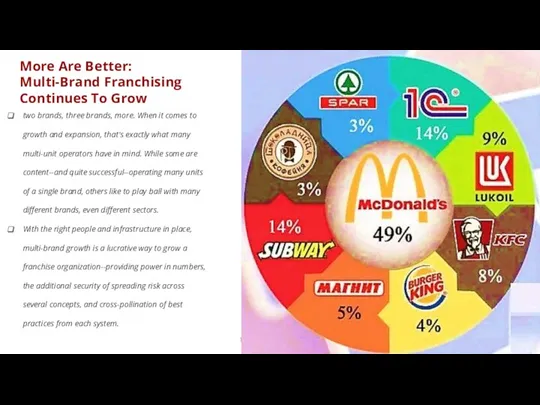
- 26. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c More Are Better: Multi-Brand Franchising Continues To Grow two brands, three brands,
- 27. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 28. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 29. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 30. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 31. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 32. The forms of international economic relations International trade in goods and services; The international movement of
- 33. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c International Currency Relations
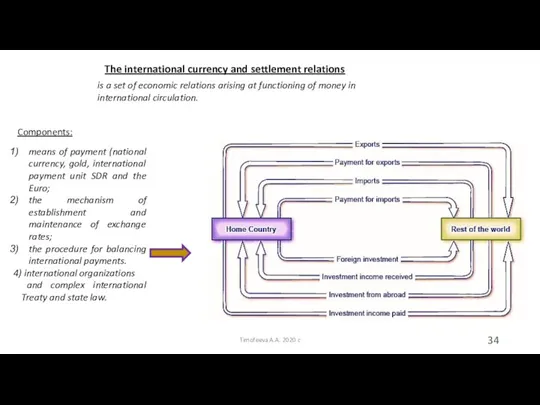
- 34. The international currency and settlement relations Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c means of payment (national currency, gold,
- 35. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c International monetary relations: transactions of two or more countries the main element
- 36. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c What is Forex (FX)? Forex (FX) is the marketplace where various national
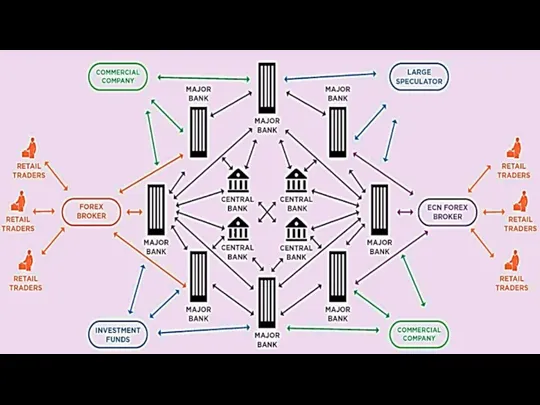
- 37. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c Retail traders can open a forex account and then buy and sell
- 38. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c The largest foreign exchange markets are located in major global financial centers
- 39. Timofeeva A.A. 2020 c
- 41. Скачать презентацию
























 Экономический и политический кризис начала 20-х годов
Экономический и политический кризис начала 20-х годов Metody ustalania wielkości dostaw zapasów
Metody ustalania wielkości dostaw zapasów Потребительское поведение
Потребительское поведение Управление качеством
Управление качеством Рынок труда и безработица
Рынок труда и безработица Инвестиционный паспорт Чагодощенского муниципального округа 2023
Инвестиционный паспорт Чагодощенского муниципального округа 2023 Стратегия экономического развития стран СНГ
Стратегия экономического развития стран СНГ Анализ о включенности в МРТ по первой группе показателей стран Новой Зеландии и ЮАР
Анализ о включенности в МРТ по первой группе показателей стран Новой Зеландии и ЮАР Вимірювання туризму
Вимірювання туризму Сутність РФП, функції та роль в економіці. Суб’єкти та інструменти РФП, їх класифікація та характеристика. Теми 1-2
Сутність РФП, функції та роль в економіці. Суб’єкти та інструменти РФП, їх класифікація та характеристика. Теми 1-2 Человек и экономика. Семейный бюджет (7 класс)
Человек и экономика. Семейный бюджет (7 класс) Внешнеторговый контракт и пакет сопроводительных документов
Внешнеторговый контракт и пакет сопроводительных документов Сущность и классификация затрат. Тема 2
Сущность и классификация затрат. Тема 2 Конкуренция и антимонопольное регулирование
Конкуренция и антимонопольное регулирование Теоретические принципы КСО. Тема №5
Теоретические принципы КСО. Тема №5 Рынок: сущность, механизм, функции
Рынок: сущность, механизм, функции Рынок капитала
Рынок капитала Фармакоэкономический анализ: общие положения. Методы фармакоэкономического анализа
Фармакоэкономический анализ: общие положения. Методы фармакоэкономического анализа Использование методов изучения затрат рабочего времени
Использование методов изучения затрат рабочего времени Современный архитектурный подход и его практическое применение в рамках старых и новых стандартов проектирования
Современный архитектурный подход и его практическое применение в рамках старых и новых стандартов проектирования Аналитический инструментарий региональной экономики
Аналитический инструментарий региональной экономики Аналитическая экономика. Методология и методика научного исследования
Аналитическая экономика. Методология и методика научного исследования Расходы и прибыль фирмы
Расходы и прибыль фирмы Презентация Влияние конкуренции на деятельность фирм
Презентация Влияние конкуренции на деятельность фирм Тема 7. Рынок капитала
Тема 7. Рынок капитала Основные признаки естественной монополии
Основные признаки естественной монополии Открытая экономика и платежный баланс
Открытая экономика и платежный баланс Международные транспортные коридоры
Международные транспортные коридоры