Содержание
- 2. Module structure The role of government & market failures The size of government L1 Public goods
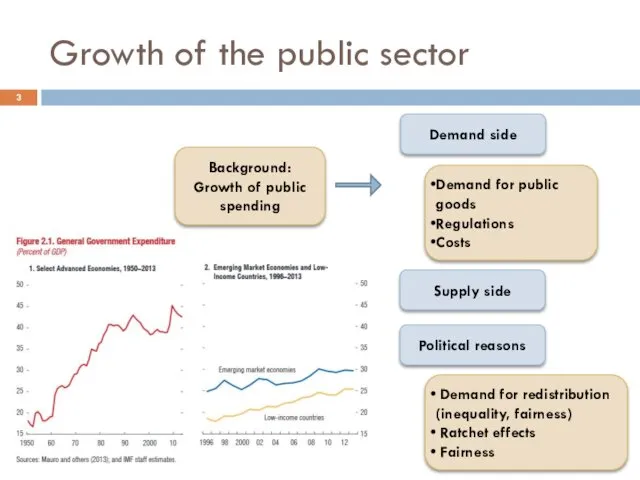
- 3. Growth of the public sector Background: Growth of public spending Demand for public goods Regulations Costs
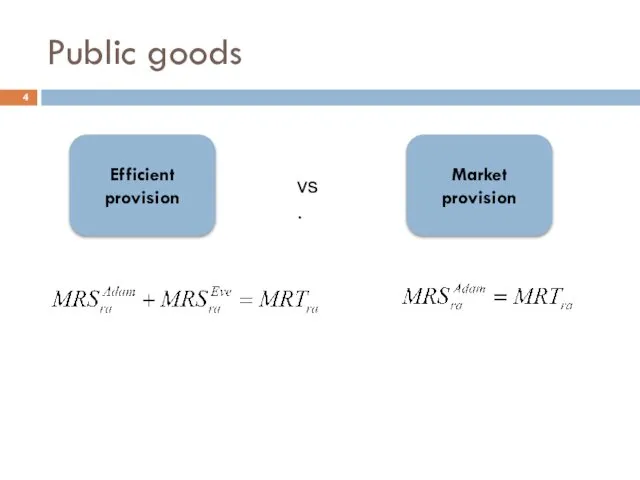
- 4. Public goods Efficient provision Market provision vs.
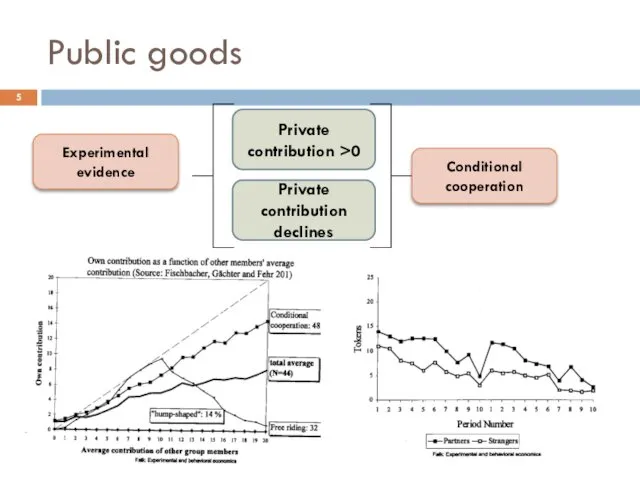
- 5. Public goods Experimental evidence Private contribution >0 Private contribution declines Conditional cooperation
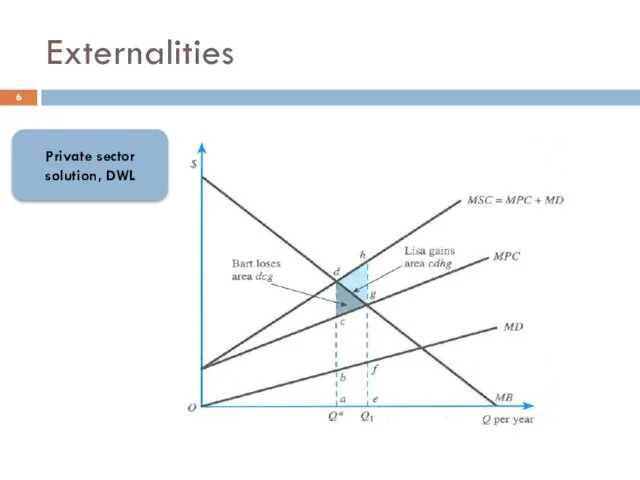
- 6. Externalities Private sector solution, DWL
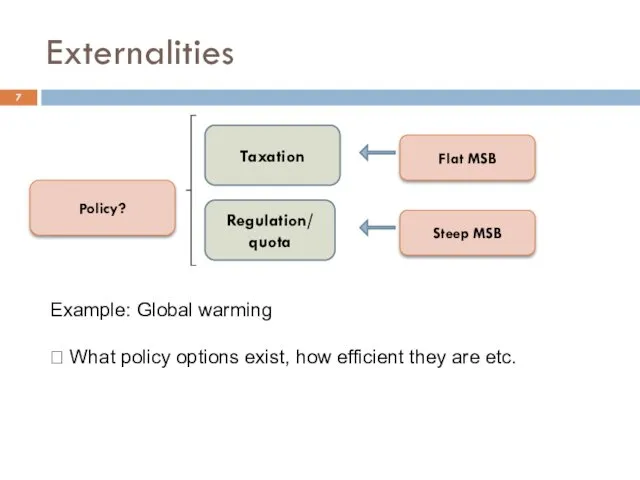
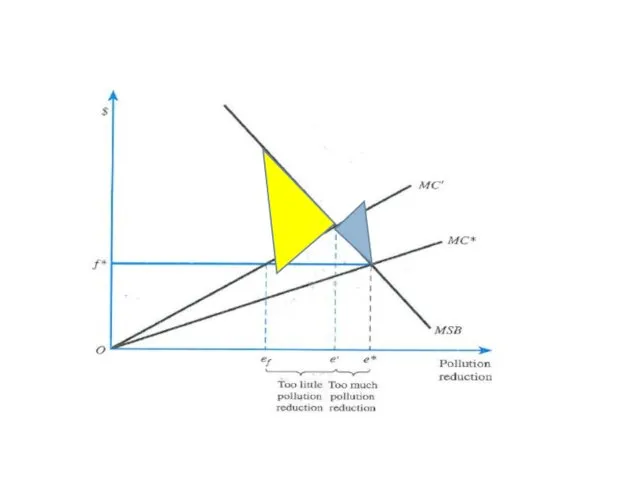
- 7. Externalities Policy? Taxation Regulation/ quota Steep MSB Flat MSB Example: Global warming ? What policy options
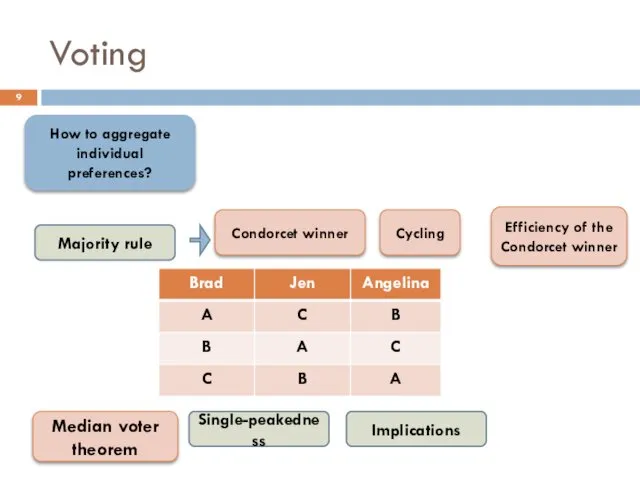
- 9. Voting How to aggregate individual preferences? Majority rule Condorcet winner Cycling Median voter theorem Single-peakedness Implications
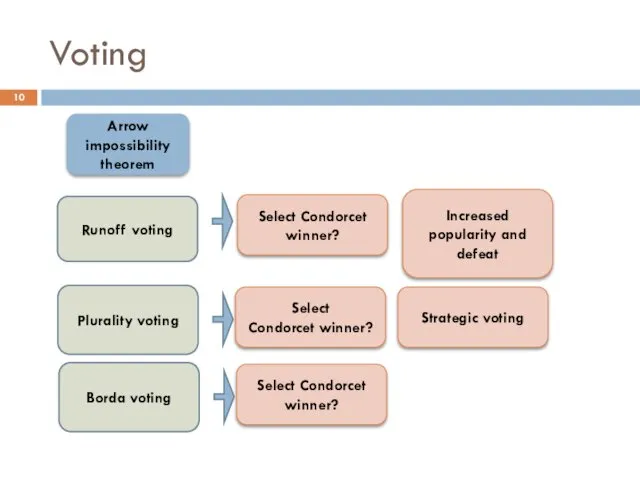
- 10. Voting Plurality voting Runoff voting Select Condorcet winner? Increased popularity and defeat Select Condorcet winner? Strategic
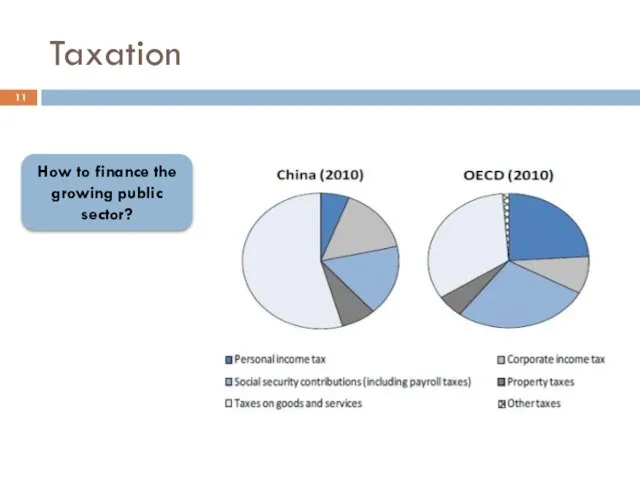
- 11. Taxation How to finance the growing public sector?
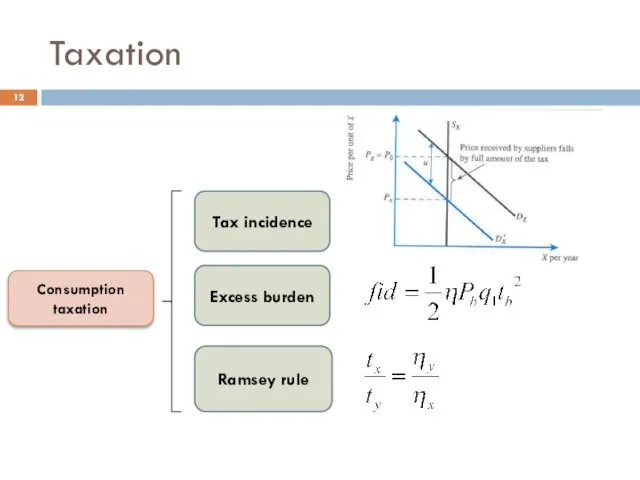
- 12. Taxation Consumption taxation Tax incidence Ramsey rule Excess burden
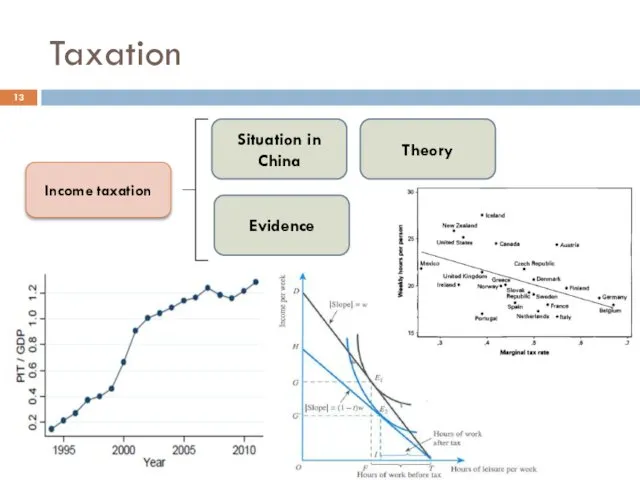
- 13. Taxation Income taxation Situation in China Theory Evidence
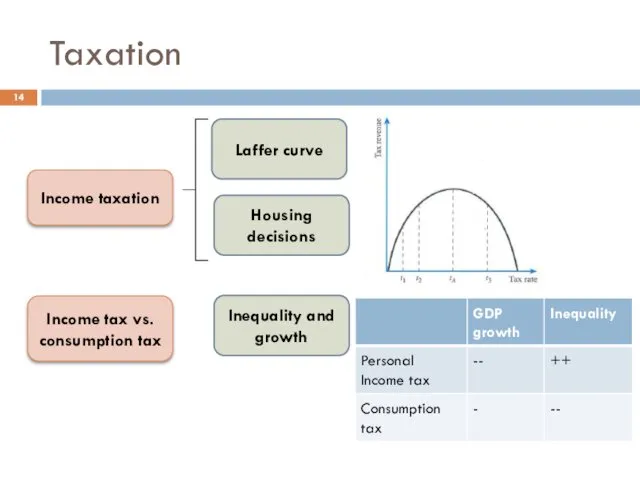
- 14. Taxation Income taxation Laffer curve Housing decisions Income tax vs. consumption tax Inequality and growth
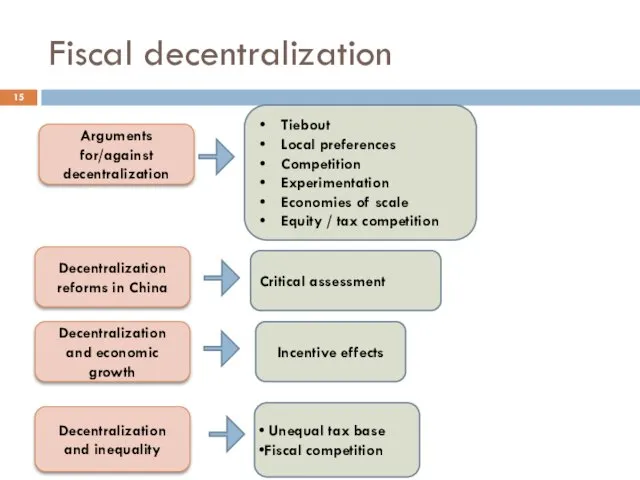
- 15. Fiscal decentralization Decentralization reforms in China Arguments for/against decentralization Tiebout Local preferences Competition Experimentation Economies of
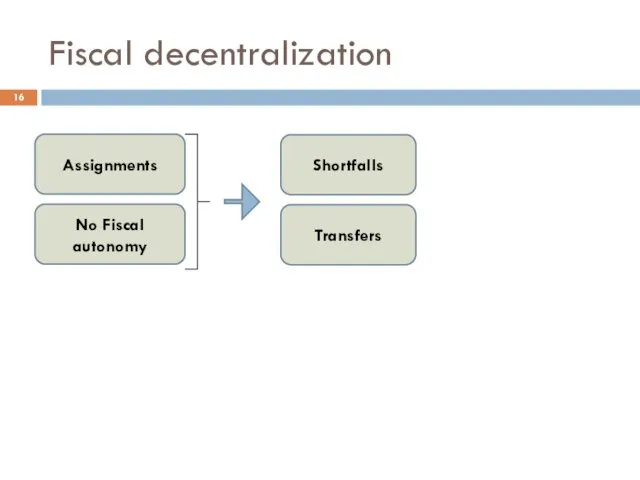
- 16. Fiscal decentralization Assignments No Fiscal autonomy Shortfalls Transfers
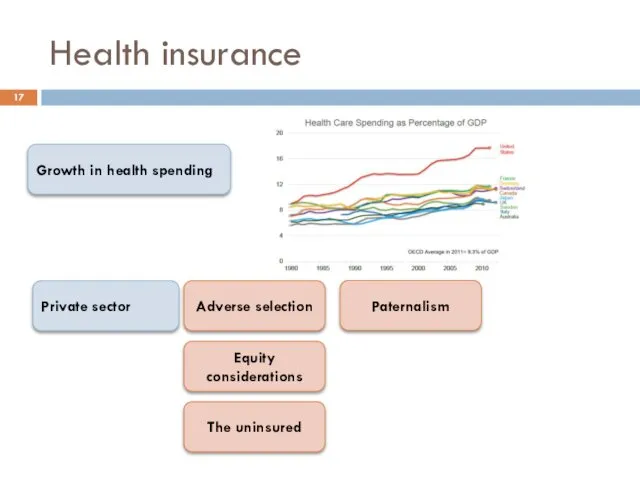
- 17. Health insurance Growth in health spending Private sector Adverse selection Equity considerations The uninsured Paternalism
- 18. Health insurance Design of health insurance Moral hazard Costs Flat-of-the-curve medicine
- 19. Income redistribution & social insurance Social welfare function Inequality measurement and trends Low social mobility Social
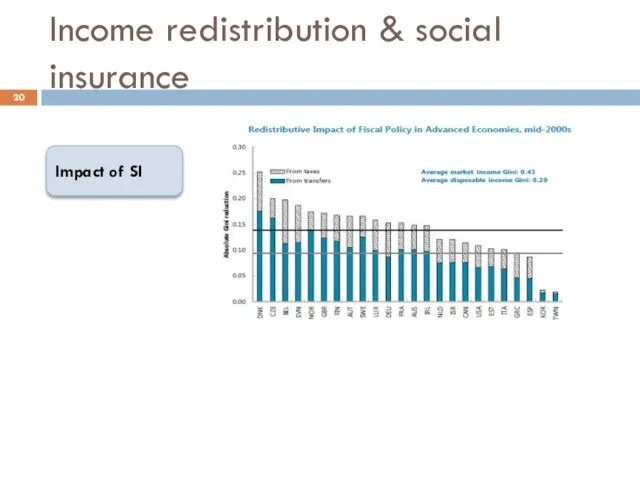
- 20. Income redistribution & social insurance Impact of SI
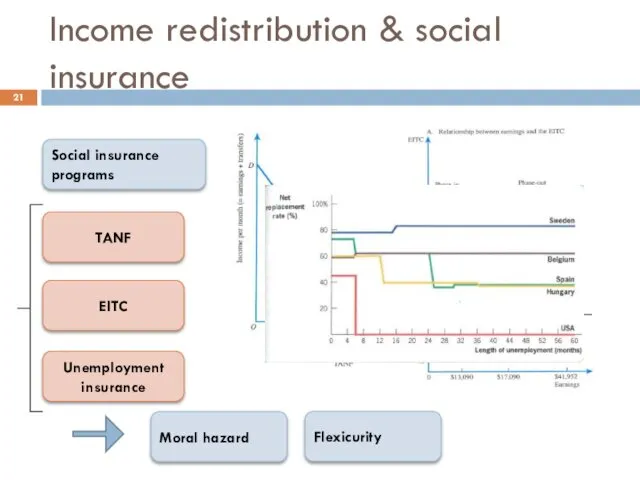
- 21. Income redistribution & social insurance Social insurance programs TANF EITC Unemployment insurance Moral hazard Flexicurity
- 22. What we have learned Theory + empirical evidence (with data) Contradiction between some theories and empirical
- 23. Exam structure 2-hour exam. Answer 2 essay questions from 5. Broad questions 1 hour/Q
- 24. Exam 2016 Discuss the arguments for and against income redistribution, and explain the reasons for the
- 25. Do not reproduce prepared essays without regard to what the question asks Before you answer… Choose
- 26. Good Practice Use examples whenever possible to support arguments Define technical terms as you introduce them,
- 27. More Good Practice Label graph axes etc. Explain diagrams or figures Equations/figures etc. that are merely
- 28. Bullet Points Answers? Reproducing bullet points does not constitute a good answer, even if the points
- 30. Скачать презентацию







 Памятка Энергодобро – или как экономить элетричество
Памятка Энергодобро – или как экономить элетричество Розрахункові завдання з економіки
Розрахункові завдання з економіки Subject and method of economic theory
Subject and method of economic theory Внешняя торговля Канады
Внешняя торговля Канады Капитал. Кругооборот и оборот капитала. Виды капитала
Капитал. Кругооборот и оборот капитала. Виды капитала Урок национальной технологической инициативы
Урок национальной технологической инициативы Теория производства, издержек и прибыли конкурентной фирмы
Теория производства, издержек и прибыли конкурентной фирмы Экономика и её основные участники
Экономика и её основные участники Индексный метод
Индексный метод Исследовательский проект Разумная экономия энергии
Исследовательский проект Разумная экономия энергии Основы экономики организации. Модель разработки эффективной системы оплаты труда
Основы экономики организации. Модель разработки эффективной системы оплаты труда Движение трудовых ресурсов. Тема 3
Движение трудовых ресурсов. Тема 3 Политическая экономия: потенциал решения проблем, не решаемых неоклассикой
Политическая экономия: потенциал решения проблем, не решаемых неоклассикой Оценка влияний условий финансирования на эффективность проекта
Оценка влияний условий финансирования на эффективность проекта Основные понятия и сущность сервисной деятельности. Тест
Основные понятия и сущность сервисной деятельности. Тест The Business Cycles as a Form of Economic Development
The Business Cycles as a Form of Economic Development Томас Демарк. Можно ли предсказать рынок?
Томас Демарк. Можно ли предсказать рынок? Управление инновационными проектами (лекция 1)
Управление инновационными проектами (лекция 1) Издержки производства и прибыль
Издержки производства и прибыль Размещение предприятий. Метод взвешивания
Размещение предприятий. Метод взвешивания Макроэкономическое равновесие на товарном рынке. Кейнсианская модель доходов и расходов
Макроэкономическое равновесие на товарном рынке. Кейнсианская модель доходов и расходов Инвестиционно-строительная деятельность
Инвестиционно-строительная деятельность Залежність ціни авто від пробігу, об’єму двигуна та віку експлуатації
Залежність ціни авто від пробігу, об’єму двигуна та віку експлуатації Organization The United Nations (UN )
Organization The United Nations (UN ) Геополитическое и экономико-географическое положение России (ЭГП)
Геополитическое и экономико-географическое положение России (ЭГП) Предмет и методы єкономической теории
Предмет и методы єкономической теории О системе грантовой поддержки
О системе грантовой поддержки Формирование Трансатлантического торгового союза
Формирование Трансатлантического торгового союза