Содержание
- 2. 1.NATIONAL ECONOMY AS A SYSTEM
- 3. Science section of the economy as a whole, the problems of economic growth and employment, opportunities
- 5. 2. SYSTEM OF NATIONAL ACCOUNTS
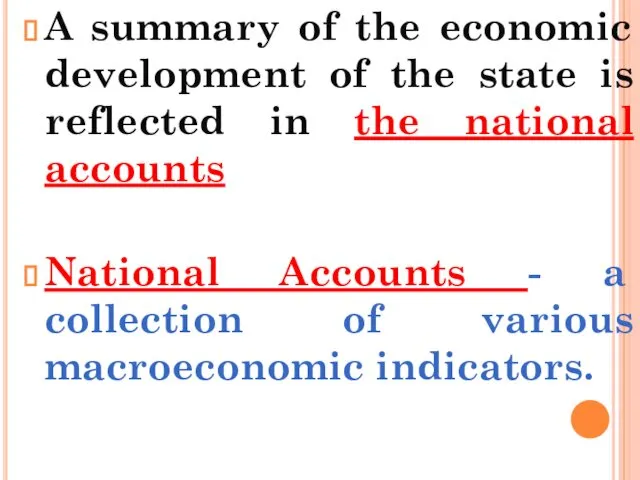
- 6. A summary of the economic development of the state is reflected in the national accounts National
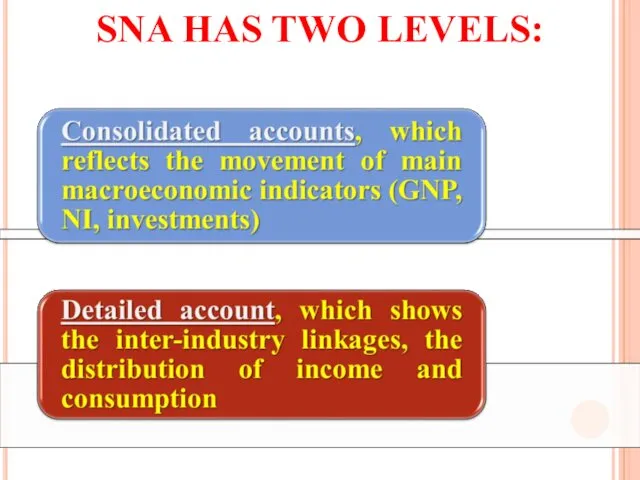
- 7. SNA HAS TWO LEVELS:
- 8. There are many kinds of indicators of economic well-being of society. The primary measure in the
- 9. National Income (NI) - is a newly established annual cost, which has added production in a
- 10. 3. METHODS OF MEASURING GNP
- 12. THE CALCULATION OF GNP EXPENDITURE GNP = C + I + G + Xn , where:
- 13. CALCULATING GNP BY REVENUE IN THIS CASE, GDP IS CONSIDERED AS THE SUM OF REVENUE OF
- 14. THE CALCULATION OF GNP "VALUE ADDED" With this method, the calculation of GNP must sum of
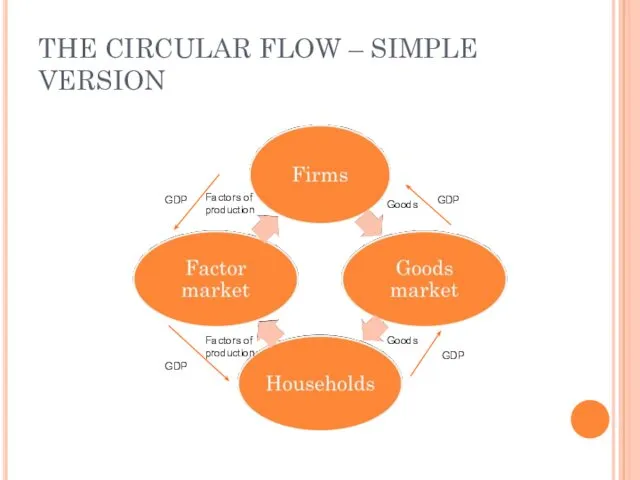
- 15. THE CIRCULAR FLOW – SIMPLE VERSION Factors of production Factors of production Goods Goods GDP GDP
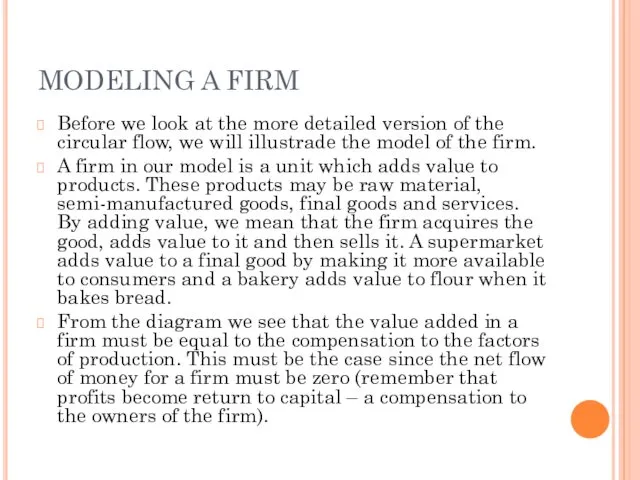
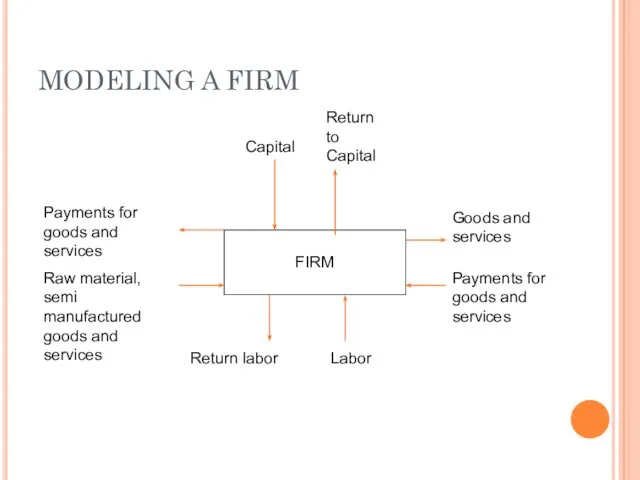
- 16. MODELING A FIRM Before we look at the more detailed version of the circular flow, we
- 17. MODELING A FIRM FIRM Capital Return to Capital Payments for goods and services Raw material, semi
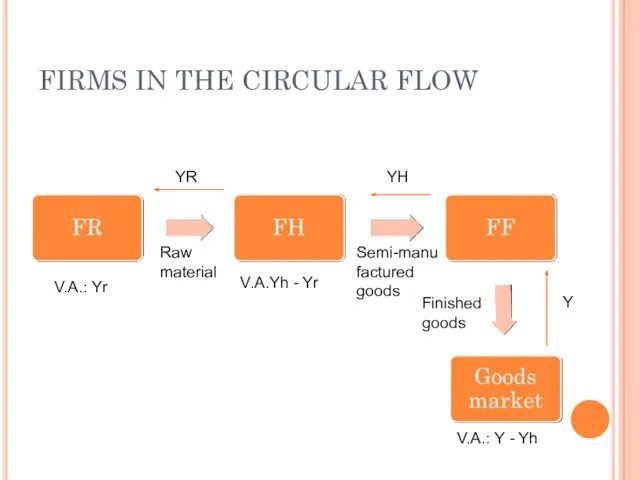
- 18. FIRMS IN THE CIRCULAR FLOW We aivide all firms into three categories: FR consists of all
- 19. FIRMS IN THE CIRCULAR FLOW YR YH Y Raw material Semi-manufactured goods V.A.: Yr V.A.Yh -
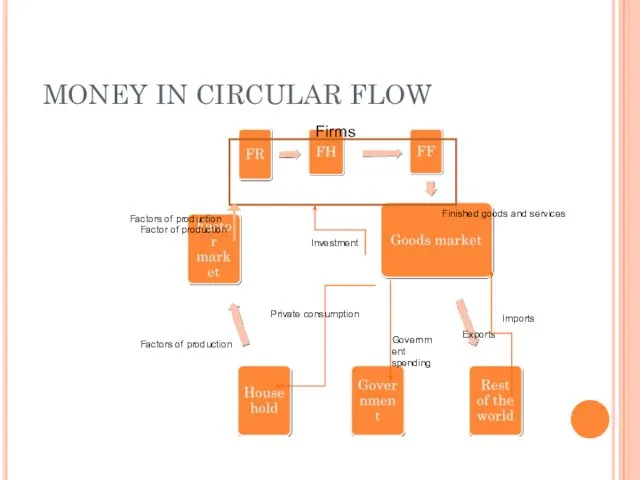
- 20. MONEY IN CIRCULAR FLOW Firms Finished goods and services Exports Imports Government spending Private consumption Investment
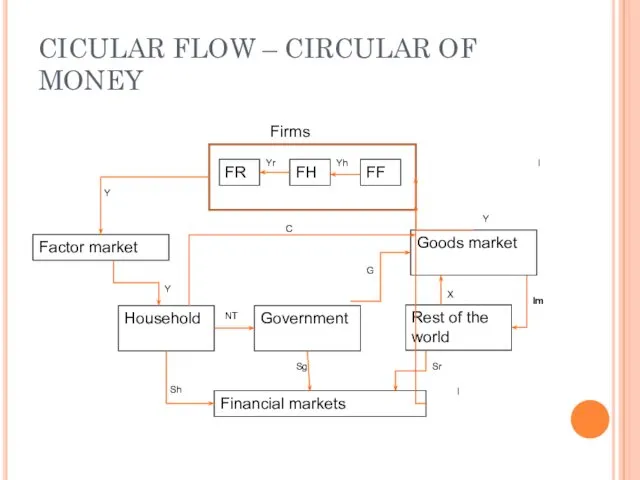
- 21. CICULAR FLOW – CIRCULAR OF MONEY FR FH FF Goods market Rest of the world Government
- 23. Скачать презентацию












 Планування витрат
Планування витрат Экономические реформы 1991-1998
Экономические реформы 1991-1998 Сұраныс пен ұсыныс теориясының негізі
Сұраныс пен ұсыныс теориясының негізі Рынок факторов производства
Рынок факторов производства Күріш өндірісі шығындарының есебін жетілдіру
Күріш өндірісі шығындарының есебін жетілдіру Товар и деньги
Товар и деньги Советский тыл в годы ВОВ
Советский тыл в годы ВОВ Инфляция
Инфляция Издержки производства и прибыль. Лекция 9
Издержки производства и прибыль. Лекция 9 Робототехника в производстве и АПК (10 причин развивать мехатронику и робототехнику)
Робототехника в производстве и АПК (10 причин развивать мехатронику и робототехнику) Економічна таблиця Франсуа Кене та її наукове значення
Економічна таблиця Франсуа Кене та її наукове значення Валютное хеджирование
Валютное хеджирование Определение типа производства. Виды и типы производства
Определение типа производства. Виды и типы производства Развитие моногородов: итоги и перспективы
Развитие моногородов: итоги и перспективы Синий дизайн
Синий дизайн Теория прав собственности. Альтернативные режимы собственности
Теория прав собственности. Альтернативные режимы собственности Труд. Индустриальное общество
Труд. Индустриальное общество Өнім өндіру мен өткізу шығындары
Өнім өндіру мен өткізу шығындары Сегмент упаковки в экономике замкнутого цикла
Сегмент упаковки в экономике замкнутого цикла Город как система основных отраслей муниципальной экономики
Город как система основных отраслей муниципальной экономики Экономические циклы. Лекция 8
Экономические циклы. Лекция 8 Меркантилизм. Представители меркантилизма
Меркантилизм. Представители меркантилизма Организация коммерческой целесообразности внедрения нового оборудования на примере ЗАО Завод Демидовский
Организация коммерческой целесообразности внедрения нового оборудования на примере ЗАО Завод Демидовский Царство пиццы (бизнес-план)
Царство пиццы (бизнес-план) ГеоШоу. Моргаушский район
ГеоШоу. Моргаушский район Экономика и её основные участники
Экономика и её основные участники Еңбек миграциясы қазақстанда: қазіргі жағдайы мен болашағы
Еңбек миграциясы қазақстанда: қазіргі жағдайы мен болашағы Экономическая сущность инвестиций и виды инвестиций. (Тема 1)
Экономическая сущность инвестиций и виды инвестиций. (Тема 1)