Содержание
- 2. The Key Achievements of the Housing Policy in 1991 – 2014 Key structural elements of the
- 3. Key Challenges and Threats in the Housing Sector Structure of expenditures for production of housing goods
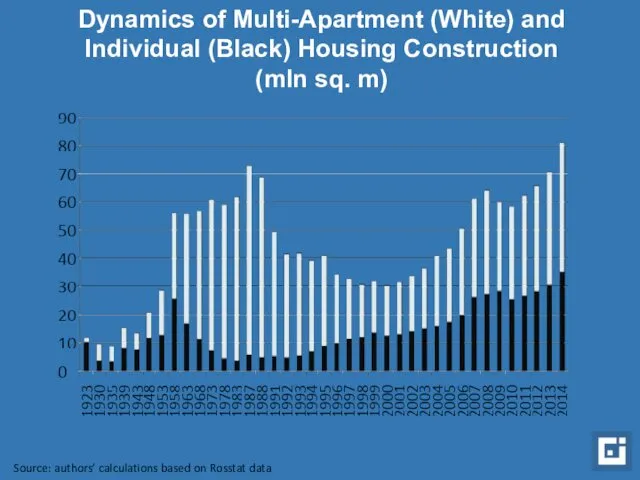
- 4. Dynamics of Multi-Apartment (White) and Individual (Black) Housing Construction (mln sq. m) Source: authors’ calculations based
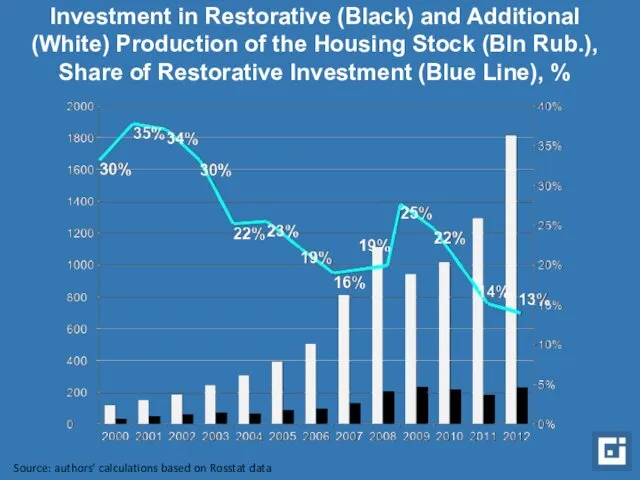
- 5. Investment in Restorative (Black) and Additional (White) Production of the Housing Stock (Bln Rub.), Share of
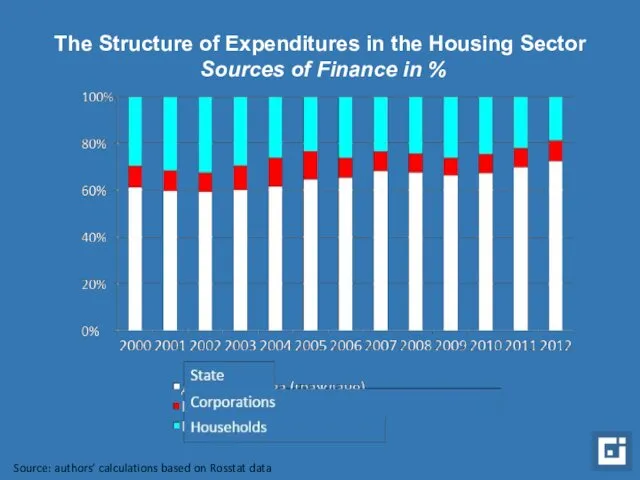
- 6. The Structure of Expenditures in the Housing Sector Sources of Finance in % Source: authors’ calculations
- 7. The New Housing Strategy: Objective and Priorities Main Objective – improvement of quality of housing provision
- 8. Strategic Priorities Fostering developments of housing rental and cooperative sectors Fostering competition in housing construction Redevelopment
- 9. Fostering Developments of Housing Rental and Cooperative sectors, First Home Buyers Support Enhance legislative regulation with
- 10. Fostering competition in housing construction Liquidating excessive administrative barriers in the housing construction market Reducing basic
- 11. Redevelopment and beautification of built-up areas Potential for housing construction under redevelopment of built-up areas projects
- 12. Capital repairs of housing Mass capital repair of multi-apartment buildings built in 1960s-1980s (about 50% of
- 13. Regional differentiation and decentralization of the housing policy Increase financial resources and powers of local government:
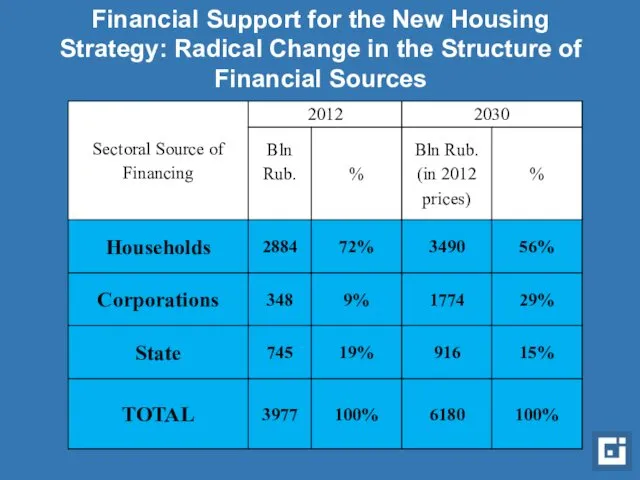
- 14. Financial Support for the New Housing Strategy: Radical Change in the Structure of Financial Sources
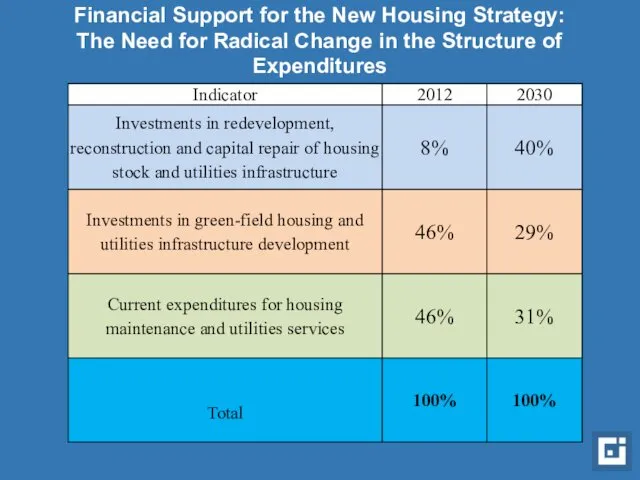
- 15. Financial Support for the New Housing Strategy: The Need for Radical Change in the Structure of
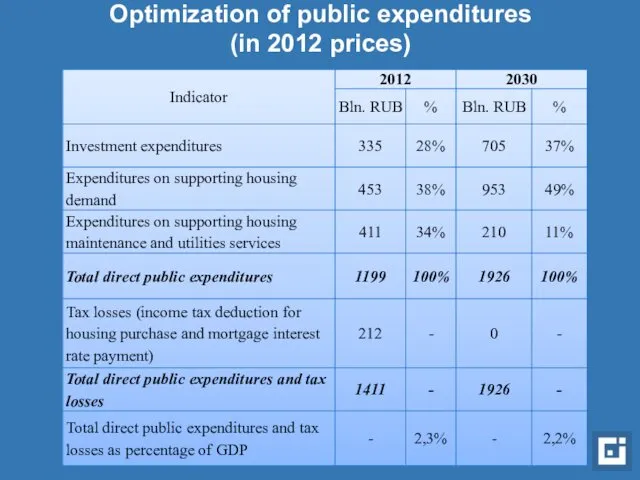
- 16. Optimization of public expenditures (in 2012 prices)
- 18. Скачать презентацию









 Қазақстан Республикасы Президенті Н.Назарбаевтың Қазақстан халқына Нұрлы жол - болашаққа бастар жол. Жолдауы
Қазақстан Республикасы Президенті Н.Назарбаевтың Қазақстан халқына Нұрлы жол - болашаққа бастар жол. Жолдауы Безработица и инфляция как проявления экономической нестабильности
Безработица и инфляция как проявления экономической нестабильности Государственный бюджет
Государственный бюджет The national economy as a system
The national economy as a system Внешние эффекты в рыночной экономике и их государственное регулирование
Внешние эффекты в рыночной экономике и их государственное регулирование Демографическая проблема
Демографическая проблема Экономические взгляды Уильяма Петти
Экономические взгляды Уильяма Петти Энергосбережение в быту
Энергосбережение в быту Рынок и рыночный механизм. Спрос и предложение. Издержки
Рынок и рыночный механизм. Спрос и предложение. Издержки Теория спроса и предложения
Теория спроса и предложения Совершенствование управления персоналом предприятия (на примере ОАО Речицкий метизный завод)
Совершенствование управления персоналом предприятия (на примере ОАО Речицкий метизный завод) Абсолютное и сравнительное преимущество в международной торговле. Протекционизм: цели и средства. Импортные тарифы
Абсолютное и сравнительное преимущество в международной торговле. Протекционизм: цели и средства. Импортные тарифы Экономический рост
Экономический рост Евросоюз: начало распада или временные трудности?
Евросоюз: начало распада или временные трудности? Проблема преодоления отсталости развивающихся стран
Проблема преодоления отсталости развивающихся стран Theory of International Relations
Theory of International Relations Бизнес-ангелы и их роль в современной экономике
Бизнес-ангелы и их роль в современной экономике Экономическая среда бизнеса. Конкуренция в экономической среде бизнеса
Экономическая среда бизнеса. Конкуренция в экономической среде бизнеса Антимонопольное законодательство
Антимонопольное законодательство Методы комплексной оценки финансово-хозяйственной деятельности
Методы комплексной оценки финансово-хозяйственной деятельности Диплом алды практикасы бойынша. Есеп
Диплом алды практикасы бойынша. Есеп Планирование ресурсного обеспечения
Планирование ресурсного обеспечения Макроэкономическая нестабильность: инфляция и безработица
Макроэкономическая нестабильность: инфляция и безработица 期末复习
期末复习 Рынки ресурсов. Рынок труда
Рынки ресурсов. Рынок труда Стратегия социально-экономического развития Красноярского края
Стратегия социально-экономического развития Красноярского края Территория опережающего социально-экономического развития ТОСЭР Белорецк
Территория опережающего социально-экономического развития ТОСЭР Белорецк Інноваційно-технологічний ресурс глобального економічного розвитку
Інноваційно-технологічний ресурс глобального економічного розвитку