Содержание
- 2. Unemployment occurs when a person who is actively searching for employment is unable to find work.
- 3. CYCLICAL UNEMPLOYMENT There is a number of different types of unemployment. One of these is cyclical
- 4. STRUCTURAL UNEMPLOYMENT A second kind of unemployment is structural unemployment. This occurs when changing public tastes
- 5. FRICTIONAL UNEMPLOYMENT This is a natural kind of unemployment that occurs when someone leaves a job
- 6. SEASONAL UNEMPLOYMENT The second kind is seasonal unemployment Some industries have busy periods and periods where
- 7. MEASURING UNEMPLOYMENT In the United States, the government uses surveys, census counts, and the number of
- 9. Скачать презентацию
Слайд 2
Unemployment occurs when a person who is actively searching for employment is unable
Unemployment occurs when a person who is actively searching for employment is unable
to find work. Unemployment is often used as a measure of the health of the economy. The most frequent measure of unemployment is the unemployment rate, which is the number of unemployed people divided by the number of people in the labor force.
Full employment means that everyone who can work and wants to work has got a job
Full employment means that everyone who can work and wants to work has got a job
Слайд 3
CYCLICAL UNEMPLOYMENT
There is a number of different types of unemployment. One
CYCLICAL UNEMPLOYMENT
There is a number of different types of unemployment. One
of these is cyclical unemployment. This type of unemployment varies with the growth and recession cycle of the economy. As the economy grows, demand or labour grows and unemployment falls. As the economy contracts, unemployment grows.
Preventing and alleviating cyclical unemployment during recessions is a major concern behind the study of economics and the purpose of the various policy tools that governments employ on the downside of business cycles to stimulate the economy.
Preventing and alleviating cyclical unemployment during recessions is a major concern behind the study of economics and the purpose of the various policy tools that governments employ on the downside of business cycles to stimulate the economy.
Слайд 4
STRUCTURAL UNEMPLOYMENT
A second kind of unemployment is structural unemployment. This occurs
STRUCTURAL UNEMPLOYMENT
A second kind of unemployment is structural unemployment. This occurs
when changing public tastes or advances in technology cause a fall in demand for some types of work. For example, computer technology has revolutionised the primting industry, and many traditional printers jobs have become obsolete. Sometimes whole regions of a country suffer from high structural unemployment. The north-east of England, for example, was famous for many years for its shipbuilding industry. Competition from abroad forced many shipyards to close. This caused huge unemployment.
How long structural unemployment lasts will depend on two things. Firstly, how easily the workforce can retrain for new jobs. This may be difficult for older workers who find it hard to learn new skills. There is also the question of who pays for the training. The second issue is mobility. to another part of the country will find new jobs more quickly Workers who are able to relocate easily
How long structural unemployment lasts will depend on two things. Firstly, how easily the workforce can retrain for new jobs. This may be difficult for older workers who find it hard to learn new skills. There is also the question of who pays for the training. The second issue is mobility. to another part of the country will find new jobs more quickly Workers who are able to relocate easily
Слайд 5
FRICTIONAL UNEMPLOYMENT
This is a natural kind of unemployment that occurs when
FRICTIONAL UNEMPLOYMENT
This is a natural kind of unemployment that occurs when
someone leaves a job and is looking for another one that suits them. Frictional unemployment often happens because people want to leave their job in order to change careers. Few people walk straight into another job. However, when the economy is in recession, frictional unemployment will be more common because jobs are harder to find.
Frictional unemployment is a natural result of the fact that market processes take time and information can be costly. Searching for a new job, recruiting new workers, and matching the right workers to the right jobs all take time and effort to do, resulting in frictional unemployment.
Frictional unemployment is a natural result of the fact that market processes take time and information can be costly. Searching for a new job, recruiting new workers, and matching the right workers to the right jobs all take time and effort to do, resulting in frictional unemployment.
Слайд 6
SEASONAL UNEMPLOYMENT
The second kind is seasonal unemployment Some industries have busy
SEASONAL UNEMPLOYMENT
The second kind is seasonal unemployment Some industries have busy
periods and periods where there is no work at all. Some freelance farm workers, for example, get most of their work in the spring and summer. Like structural unemployment, seasonal unemployment can affect whole regions of a country. Areas that rely on summer tourism, for example, suffer serious unemployment during the autumn and winter months.
Слайд 7
MEASURING UNEMPLOYMENT
In the United States, the government uses surveys, census counts,
MEASURING UNEMPLOYMENT
In the United States, the government uses surveys, census counts,
and the number of unemployment insurance claims to track unemployment.
Many variations of the unemployment rate exist with different definitions concerning who is an "unemployed person" and who is in the "labor force."
Many variations of the unemployment rate exist with different definitions concerning who is an "unemployed person" and who is in the "labor force."
- Предыдущая
Треугольники по видам углов





 Макроекономічне програмування та планування в системі державного регулювання економіки (Тема 3.2)
Макроекономічне програмування та планування в системі державного регулювання економіки (Тема 3.2) Моделирование равновесия фирмы при различных типах рыночных структур. Олигополия
Моделирование равновесия фирмы при различных типах рыночных структур. Олигополия Статистика рынка труда. Основные направления изучения рынка труда
Статистика рынка труда. Основные направления изучения рынка труда Социальная политика и распределение доходов
Социальная политика и распределение доходов Школа физиократов
Школа физиократов Что такое бюджет?
Что такое бюджет? Основы предпринимательства и предпринимательской деятельности
Основы предпринимательства и предпринимательской деятельности Мировая экономика и международное разделение труда
Мировая экономика и международное разделение труда Рынок труда. Заработная плата
Рынок труда. Заработная плата Урок по теме Фирмы и издержки в 11 классе.
Урок по теме Фирмы и издержки в 11 классе.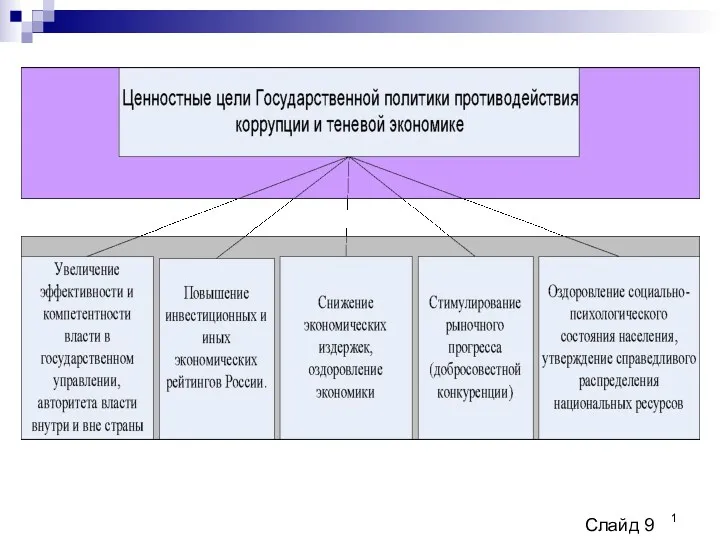 Ценностные цели государственной политики противодействия коррупции и теневой экономике
Ценностные цели государственной политики противодействия коррупции и теневой экономике Новый этап в развитии Российской Федерации
Новый этап в развитии Российской Федерации Эффект безбилетника
Эффект безбилетника Торговля Временем на опционах. Введение в теорию срочных рынков
Торговля Временем на опционах. Введение в теорию срочных рынков Контрольный тест. 7 класс
Контрольный тест. 7 класс Підприємство та підприємництво
Підприємство та підприємництво Расчёт показателей производительности труда, их динамики
Расчёт показателей производительности труда, их динамики Основы теории инноваций
Основы теории инноваций Обеспечение экономической безопасности предприятия
Обеспечение экономической безопасности предприятия Безлицензионный экспорт контролируемых товаров
Безлицензионный экспорт контролируемых товаров Сферы, отрасли, предметы труда и процесс профессиональной деятельности
Сферы, отрасли, предметы труда и процесс профессиональной деятельности Показатели и методы оценки человеческого капитала
Показатели и методы оценки человеческого капитала История кредитной карты
История кредитной карты Человек в системе экономических отношений
Человек в системе экономических отношений Мероприятия по совершенствованию системы организации наставничества в рамках деятельности Университета талантов
Мероприятия по совершенствованию системы организации наставничества в рамках деятельности Университета талантов Ұлттық экономика жүйе ретінде
Ұлттық экономика жүйе ретінде Теория производства фирмы
Теория производства фирмы Организационно-экономическое обоснование выбора средств механизации в растениеводстве
Организационно-экономическое обоснование выбора средств механизации в растениеводстве