Содержание
- 2. BRAKES Friction is the resistance to motion between two objects in contact with each other. Dry
- 3. BRAKES Friction between Drums & Shoes or Pads & Rotors slows the car. Friction between TIRES
- 4. BRAKES Air Brakes. (Pneumatic) Hydraulic Brakes use hydraulic fluid pressure to transmit power. (Incompressible) Two pistons
- 5. BRAKES Your browser does not support JavaScript or it is disabled.
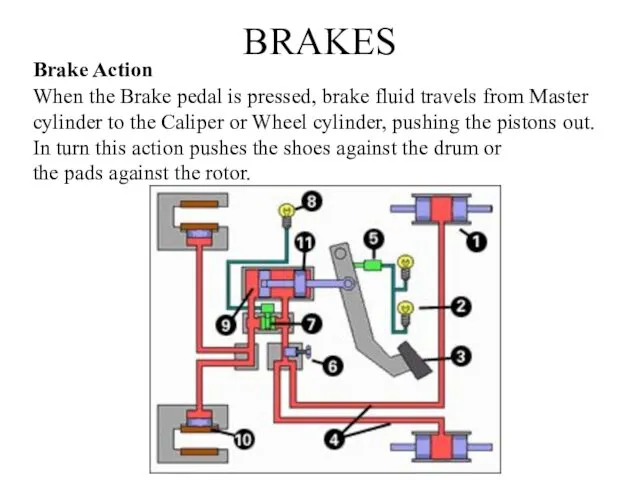
- 6. BRAKES Brake Action Brake Pedal is connected to the Master Cylinder. Each wheel has a brake
- 7. BRAKES Brake Action When the Brake pedal is pressed, brake fluid travels from Master cylinder to
- 8. BRAKES 70% - 80% of the work is done by the front brakes When the vehicle
- 9. BRAKES Brake Lining Brake lining is made of various materials (Asbestos) Some are bonded or glued
- 10. BRAKES Disk brakes found on front of most vehicles as well as at rear of four
- 11. BRAKES Wear Sensors Some pads have wear warning sensors. Squeals without stepping on the brakes. Replace
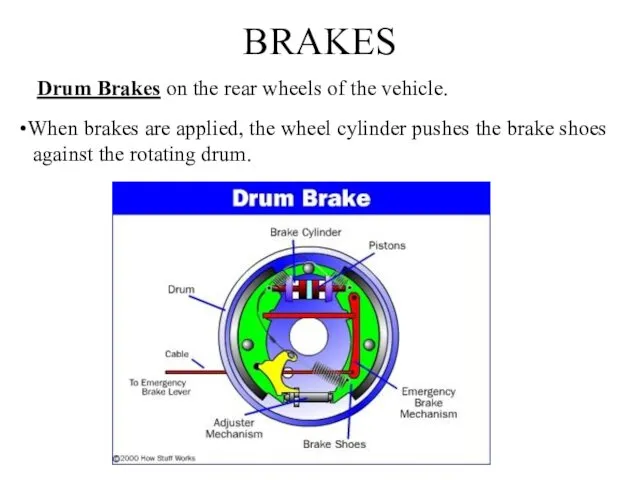
- 12. BRAKES Drum Brakes on the rear wheels of the vehicle. When brakes are applied, the wheel
- 13. BRAKES Rear brakes are self adjusting. They adjust when the vehicle is reversed and brakes are
- 14. BRAKES
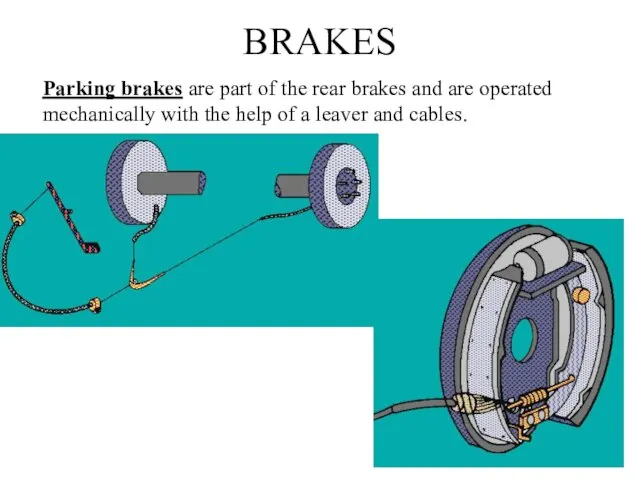
- 15. BRAKES Parking brakes are part of the rear brakes and are operated mechanically with the help
- 16. BRAKES
- 17. BRAKES Master Cylinder Reservoir for brake fluid. Connected to the brake pedal. Pressurizes the system when
- 18. BRAKES Dual Brake system Is a safety feature. If one system fails the other will still
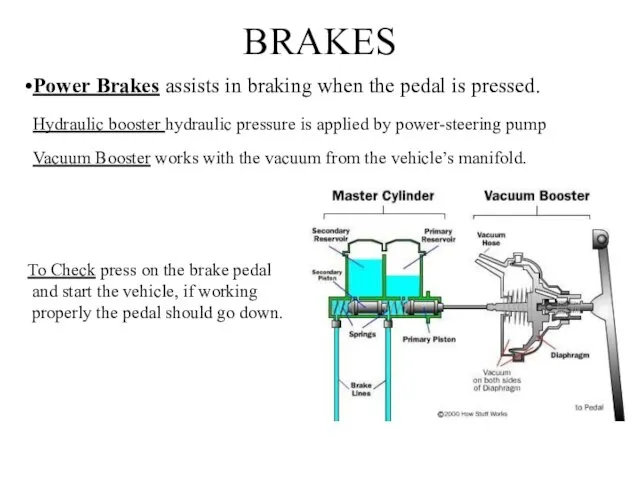
- 19. BRAKES Power Brakes assists in braking when the pedal is pressed. Hydraulic booster hydraulic pressure is
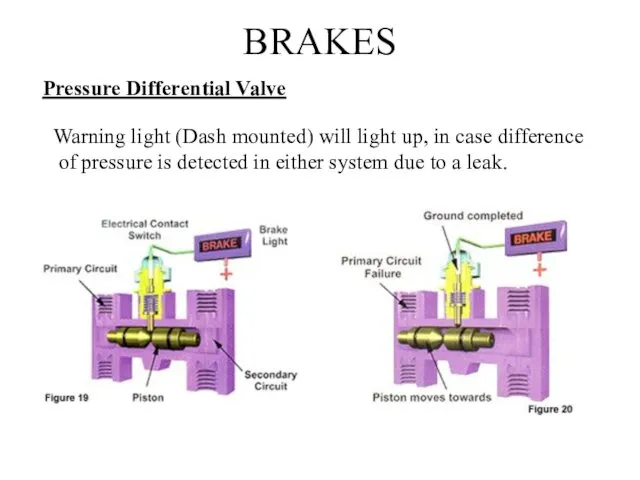
- 20. BRAKES Pressure Differential Valve Warning light (Dash mounted) will light up, in case difference of pressure
- 21. BRAKES Metering Valve On vehicles with front disk and rear drum brakes. In hydraulic line to
- 22. BRAKES Proportioning Valve ON front disk & rear drum system. Installed in hydraulic lines to the
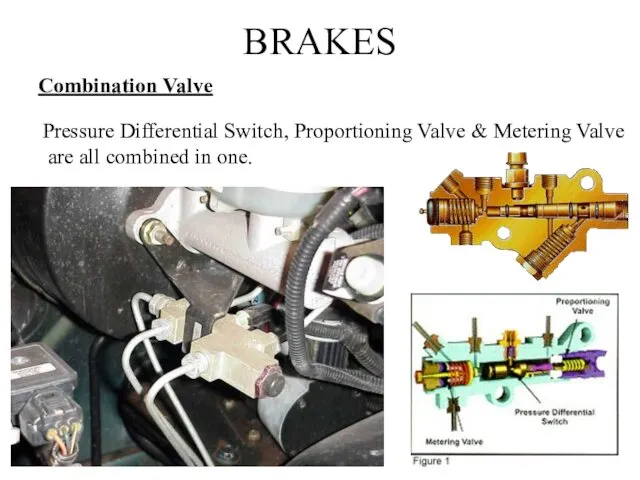
- 23. BRAKES Combination Valve Pressure Differential Switch, Proportioning Valve & Metering Valve are all combined in one.
- 24. BRAKES Brake Fluid Use the one recommended by the manufacturer. DOT3 DOT4 DOT5 Properties High Boiling
- 25. BRAKES Problems Spongy brakes are caused if air gets in the system, hence brake bleeding is
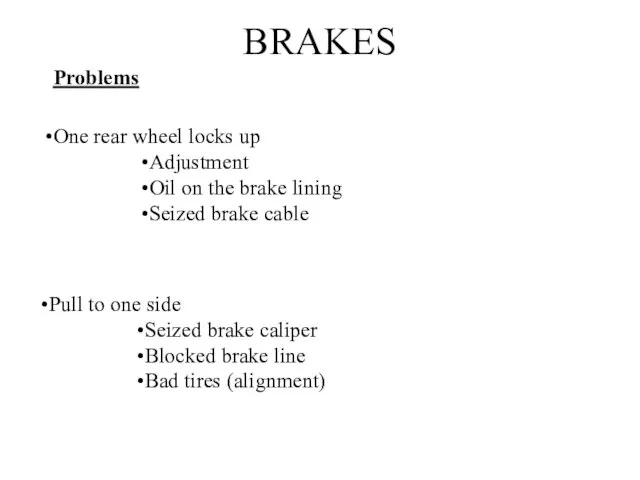
- 26. BRAKES Problems One rear wheel locks up Adjustment Oil on the brake lining Seized brake cable
- 27. BRAKES Credits Google search engine “How stuff works”
- 28. BRAKES
- 30. Скачать презентацию




















 Динамика КШМ, часть 1. Лекция №2
Динамика КШМ, часть 1. Лекция №2 Механика грунтов и подземных сооружений. Лекция 1
Механика грунтов и подземных сооружений. Лекция 1 Дисперсия. Интерференция и дифракция света
Дисперсия. Интерференция и дифракция света Атмосферное давление. Интегрированный урок
Атмосферное давление. Интегрированный урок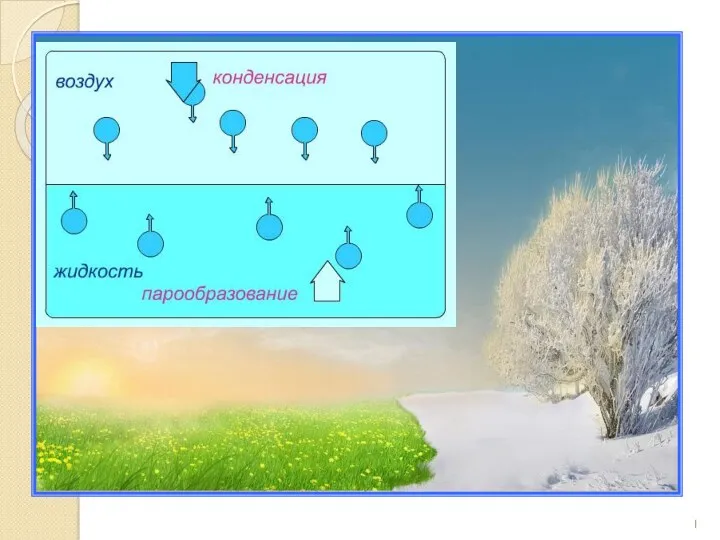 Влажность воздуха
Влажность воздуха игра Всё в нашем мире не случайно
игра Всё в нашем мире не случайно Сверхпроводимость II рода. Криогенные и сверхпроводящие электроэнергетические устройства. Лекция 3
Сверхпроводимость II рода. Криогенные и сверхпроводящие электроэнергетические устройства. Лекция 3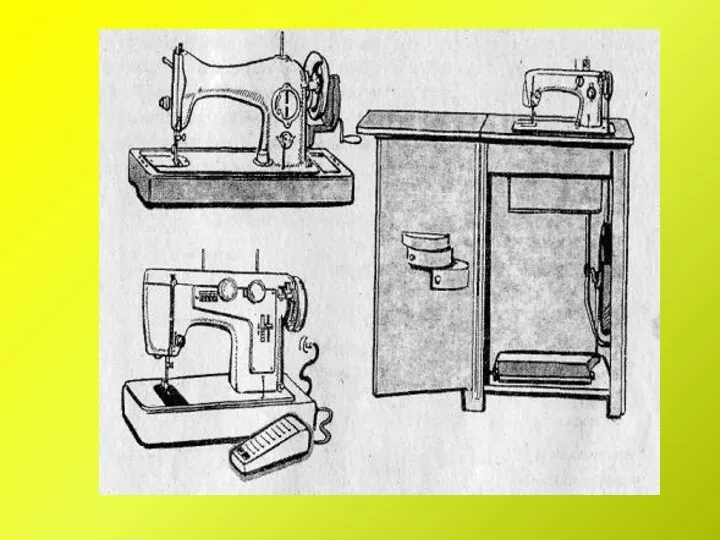 Бытовая швейная машина
Бытовая швейная машина Свойства жидкостей. Поверхностное натяжение
Свойства жидкостей. Поверхностное натяжение Возможности ЛТЛС
Возможности ЛТЛС Импульс тела. Закон сохранения импульса
Импульс тела. Закон сохранения импульса Почему радуга разноцветная
Почему радуга разноцветная Задачи. 11 класс
Задачи. 11 класс Основы проектирования. Детали машин и основы конструирования. Основные понятия деталей машин
Основы проектирования. Детали машин и основы конструирования. Основные понятия деталей машин Электрохимические процессы
Электрохимические процессы Источники света. Прямолинейное распространение света
Источники света. Прямолинейное распространение света Установка сайлентблоков с наружной металлической обоймой
Установка сайлентблоков с наружной металлической обоймой Кран машиниста поезда № 394 (395)
Кран машиниста поезда № 394 (395) Электр тізбектерінің пассивтік бөліктерін эквивалентті түрлендіру. Тұрақты токтың қарапайым тізбектерін есептеу әдістері
Электр тізбектерінің пассивтік бөліктерін эквивалентті түрлендіру. Тұрақты токтың қарапайым тізбектерін есептеу әдістері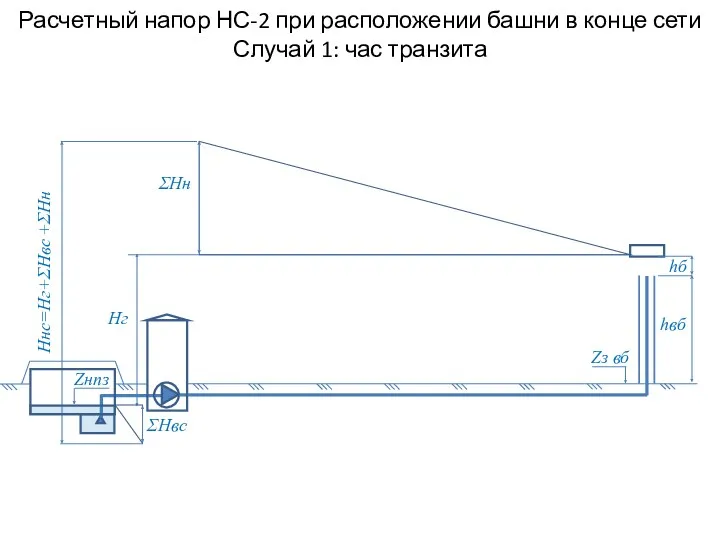 Расчетный напор НС-2 при расположении башни в конце сети. Случай 1: час транзита
Расчетный напор НС-2 при расположении башни в конце сети. Случай 1: час транзита Методы обнаружения скрытых дефектов
Методы обнаружения скрытых дефектов Зеркало
Зеркало Магнитное поле. Вектор магнитной индукции
Магнитное поле. Вектор магнитной индукции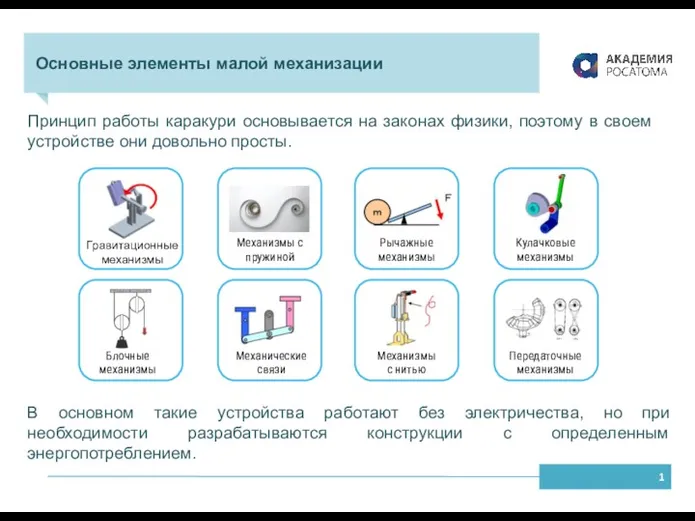 Базовые механизмы каракури. Основные элементы малой механизации
Базовые механизмы каракури. Основные элементы малой механизации Резка металла
Резка металла Своя игра по физике
Своя игра по физике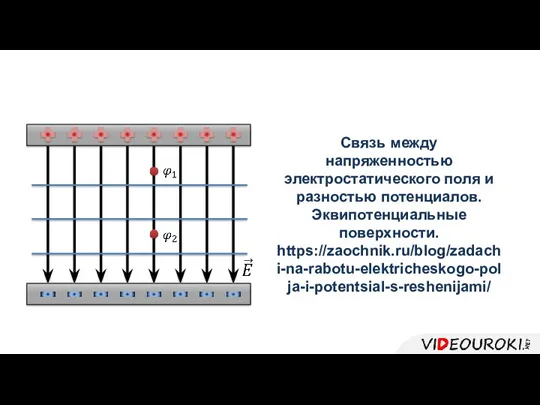 Связь между напряженностью электростатического поля и разностью потенциалов. Эквипотенциальные поверхности
Связь между напряженностью электростатического поля и разностью потенциалов. Эквипотенциальные поверхности Молекулярная физика. Термодинамика
Молекулярная физика. Термодинамика