Содержание
- 2. 07/25/2022 Temperature Variation of Resistance The resistivity of a metal depends on many (environmental) factors. The
- 3. 07/25/2022 For most metals, resistivity increases approx. linearly with temperature. ρ is the resistivity at temperature
- 4. 07/25/2022 Example: A resistance thermometer, which measures temperature by measuring the change in the resistance of
- 5. 07/25/2022 [Q] A resistance thermometer using a platinum wire is used to measure the temperature of
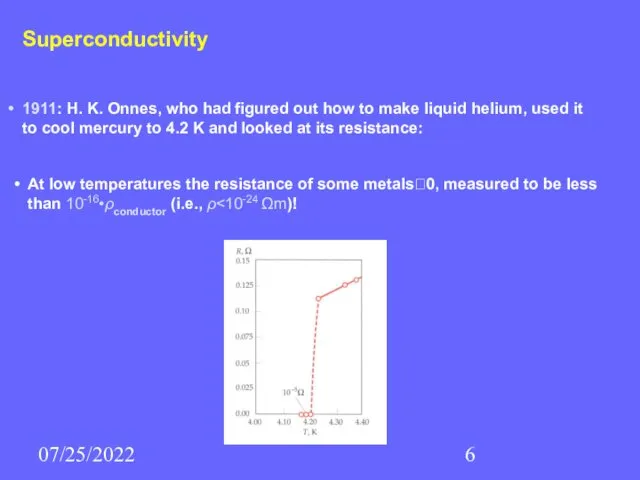
- 6. 07/25/2022 Superconductivity 1911: H. K. Onnes, who had figured out how to make liquid helium, used
- 7. 07/25/2022 Electrical energy and power In any circuit, battery is used to induce electrical current chemical
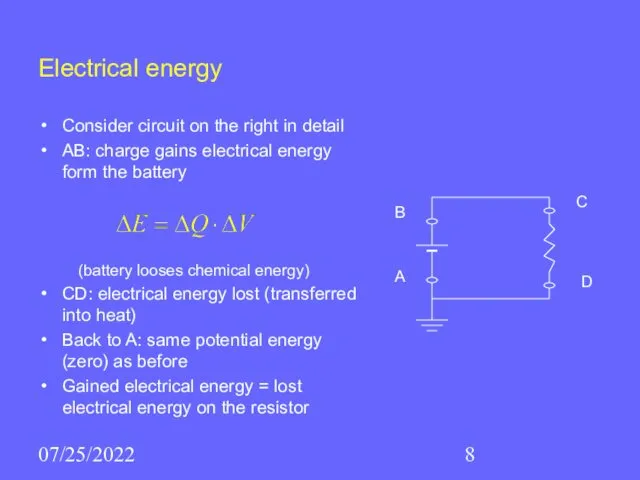
- 8. 07/25/2022 Electrical energy Consider circuit on the right in detail AB: charge gains electrical energy form
- 9. 07/25/2022 Power Compute rate of energy loss (power dissipated on the resistor) Use Ohm’s law Units
- 10. 07/25/2022 [Q] Calculate the total current drawn by all the devices in the circuit in the
- 11. 07/25/2022 Example A high-voltage transmission line with resistance of 0.31 Ω/km carries 1000A , starting at
- 12. 07/25/2022 (1) An aluminum wire carrying a current has a diameter 0.800 mm. The electric field
- 13. 07/25/2022 (5) Thermal energy is developed in a resistor at a rate of 100W when the
- 14. What is emf? A current is maintained in a closed circuit by a source of emf.
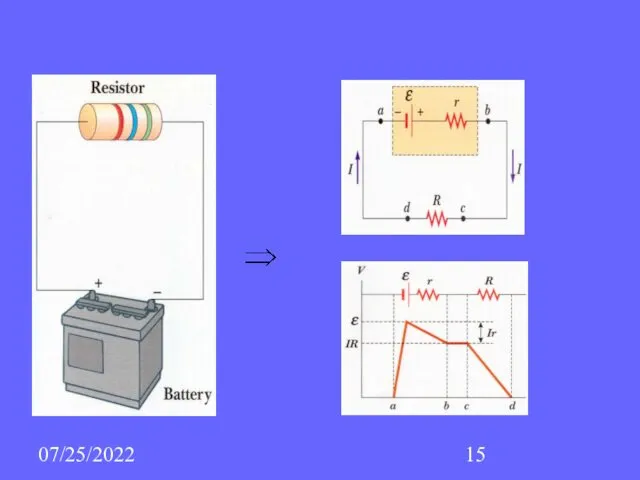
- 15. 07/25/2022
- 16. 07/25/2022 Each real battery has some internal resistance AB: potential increases by on the source of
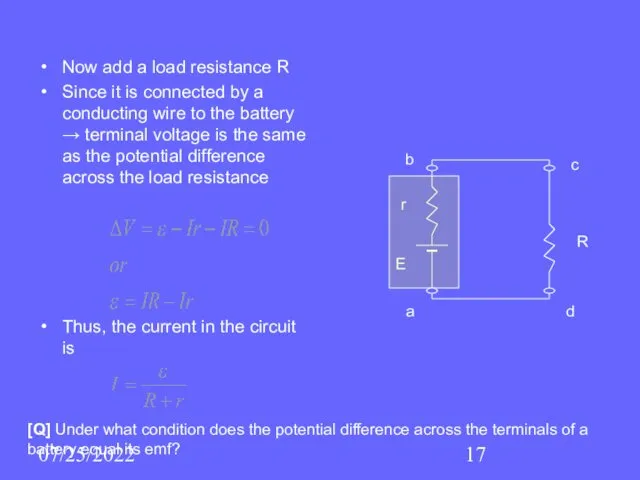
- 17. 07/25/2022 Now add a load resistance R Since it is connected by a conducting wire to
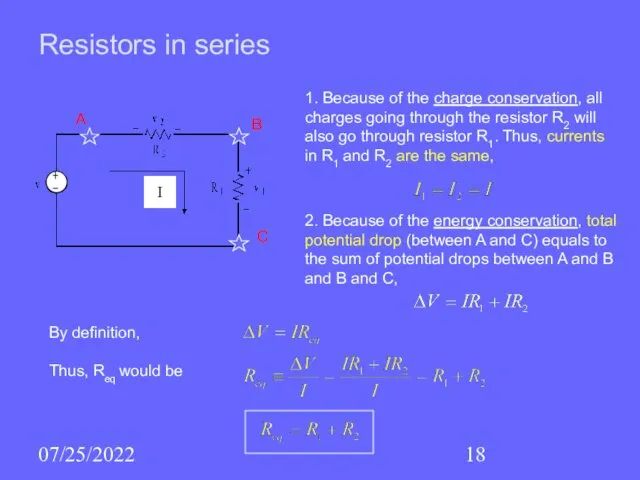
- 18. 07/25/2022 Resistors in series 1. Because of the charge conservation, all charges going through the resistor
- 19. 07/25/2022 Analogous formula is true for any number of resistors, It follows that the equivalent resistance
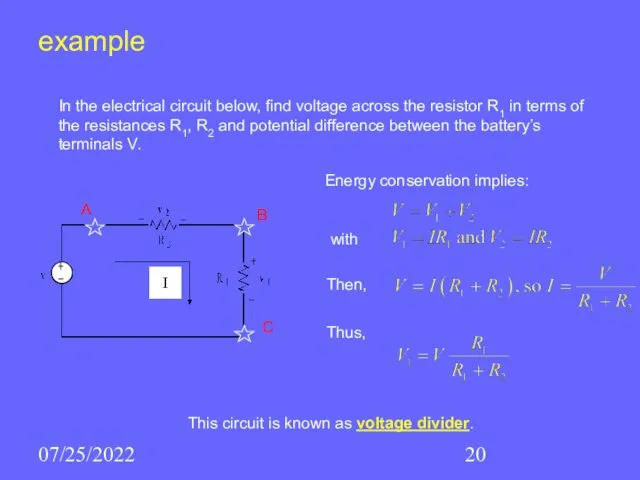
- 20. 07/25/2022 example A B C I In the electrical circuit below, find voltage across the resistor
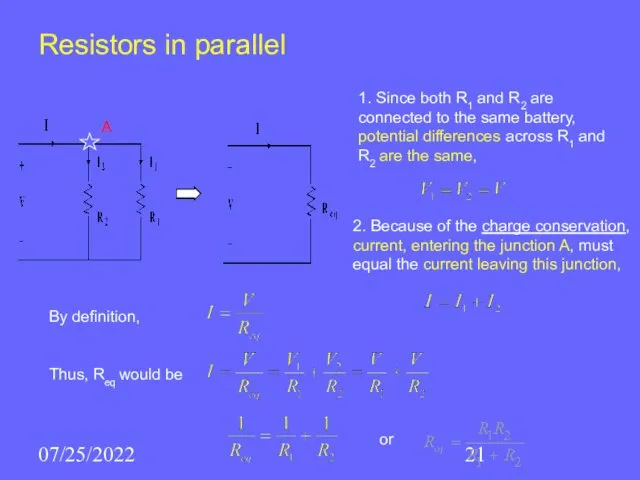
- 21. 07/25/2022 Resistors in parallel 1. Since both R1 and R2 are connected to the same battery,
- 22. 07/25/2022 Analogous formula is true for any number of resistors, It follows that the equivalent resistance
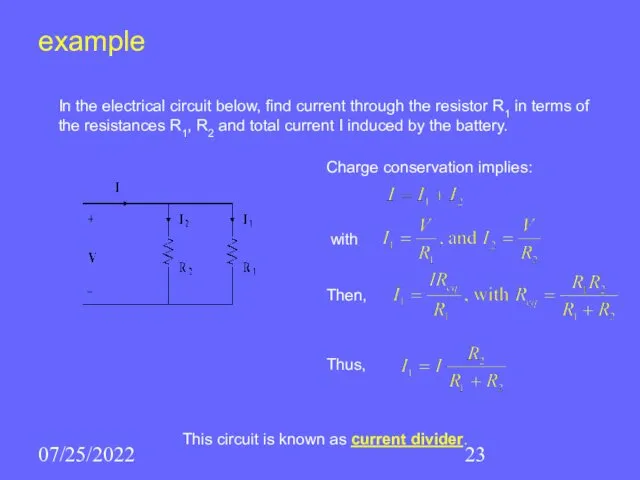
- 23. 07/25/2022 example In the electrical circuit below, find current through the resistor R1 in terms of
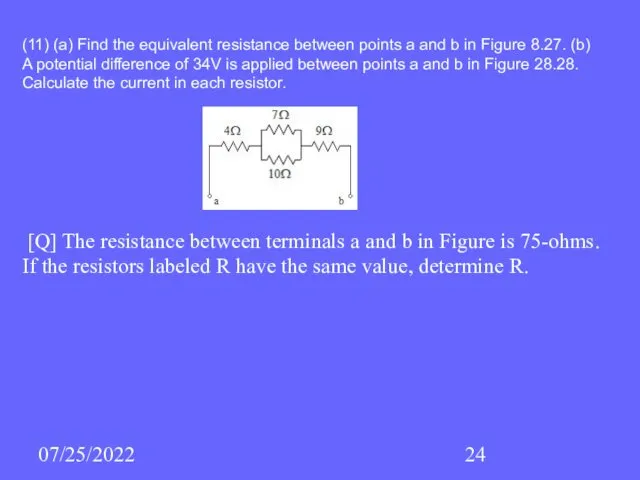
- 24. 07/25/2022 (11) (a) Find the equivalent resistance between points a and b in Figure 8.27. (b)
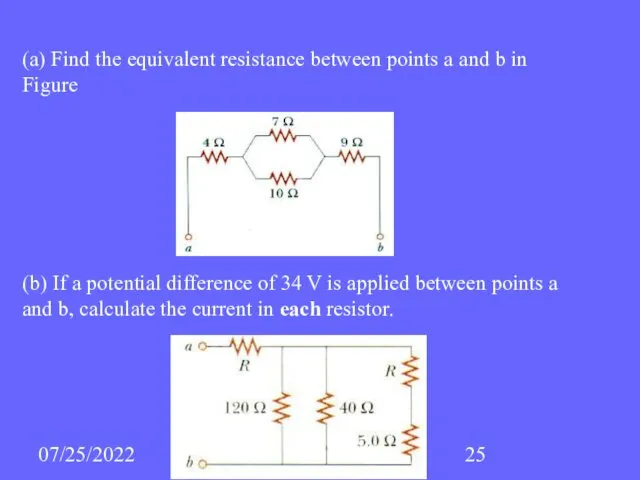
- 25. 07/25/2022 (a) Find the equivalent resistance between points a and b in Figure (b) If a
- 26. 07/25/2022 [Q] Determine the equivalent resistance between the terminals a and b for the network illustrated
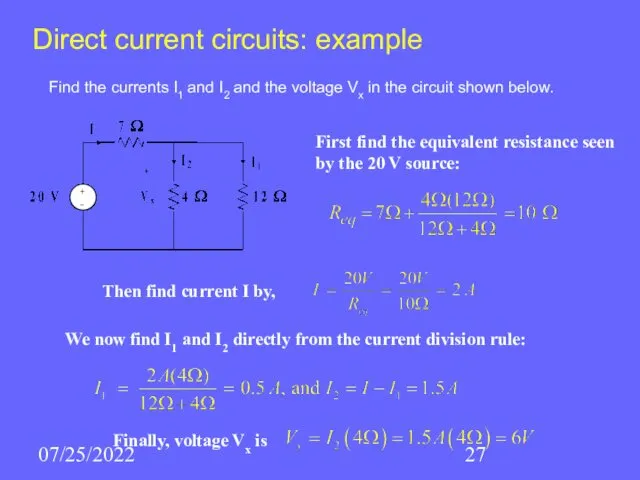
- 27. 07/25/2022 Direct current circuits: example Find the currents I1 and I2 and the voltage Vx in
- 28. 07/25/2022 A battery with an emf of 12V and internal resistance of 0.9W is connected across
- 30. Скачать презентацию



![07/25/2022 [Q] A resistance thermometer using a platinum wire is](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/90090/slide-4.jpg)


![07/25/2022 [Q] Calculate the total current drawn by all the](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/90090/slide-9.jpg)







![07/25/2022 [Q] Determine the equivalent resistance between the terminals a](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/90090/slide-25.jpg)

 Презентация Недостаточно только получить знания: надо найти им приложение. И. Гете
Презентация Недостаточно только получить знания: надо найти им приложение. И. Гете Основные элементы подвески
Основные элементы подвески Оптика. Явление полного внутреннего отражения света. Рефрактометрия
Оптика. Явление полного внутреннего отражения света. Рефрактометрия Методы наблюдения и регистрации элементарных частиц
Методы наблюдения и регистрации элементарных частиц Волновая и квантовая оптика
Волновая и квантовая оптика Расчёт пути, скорости и времени движения тела. Решение задач
Расчёт пути, скорости и времени движения тела. Решение задач Контроль качества клеевых соединений
Контроль качества клеевых соединений Измерение работы силы тяги, расчет косвенных погрешностей. Лабораторная работа
Измерение работы силы тяги, расчет косвенных погрешностей. Лабораторная работа Радиоактивные превращения атомных ядер
Радиоактивные превращения атомных ядер Конденсаторы. Виды конденсаторов
Конденсаторы. Виды конденсаторов Газораспределительный механизм двигателя
Газораспределительный механизм двигателя Линзы. Построение изображения в собирающих линзах. (8 класс)
Линзы. Построение изображения в собирающих линзах. (8 класс) Антенно-фидерные устройства и распространение радиоволн
Антенно-фидерные устройства и распространение радиоволн Воздействия на современные объекты ракетно-космической техники. Тепловые нагрузки
Воздействия на современные объекты ракетно-космической техники. Тепловые нагрузки Количество теплоты. Внутренняя энергия тела
Количество теплоты. Внутренняя энергия тела Информационный материал для стенда в кабинет физики
Информационный материал для стенда в кабинет физики Презентация Основные положения молекулярно-кинетической теории и их опытные подтверждения
Презентация Основные положения молекулярно-кинетической теории и их опытные подтверждения Магнитное поле. Обобщение темы.
Магнитное поле. Обобщение темы. Техническое обслуживание и ремонт газораспределительного механизма двигателя А-41
Техническое обслуживание и ремонт газораспределительного механизма двигателя А-41 Спектрофотометрия и спектрофлуориметрия
Спектрофотометрия и спектрофлуориметрия Колебания и волны. Механические гармонические колебания (на примере маятников)
Колебания и волны. Механические гармонические колебания (на примере маятников) Динамика материальной точки и абсолютно твердого тела
Динамика материальной точки и абсолютно твердого тела Корабельные гироскопические системы. (Тема 2)
Корабельные гироскопические системы. (Тема 2) метод разработка мех колебания
метод разработка мех колебания Атомные спектры
Атомные спектры ТРИЗ Основные понятия теории систем
ТРИЗ Основные понятия теории систем Движение небесных тел под действием сил тяготения. Строение Солнечной системы
Движение небесных тел под действием сил тяготения. Строение Солнечной системы Трехфазный ток
Трехфазный ток