Содержание
- 2. First Example of 3rd Law A horse harnessed to a cart exerts an equal and opposite
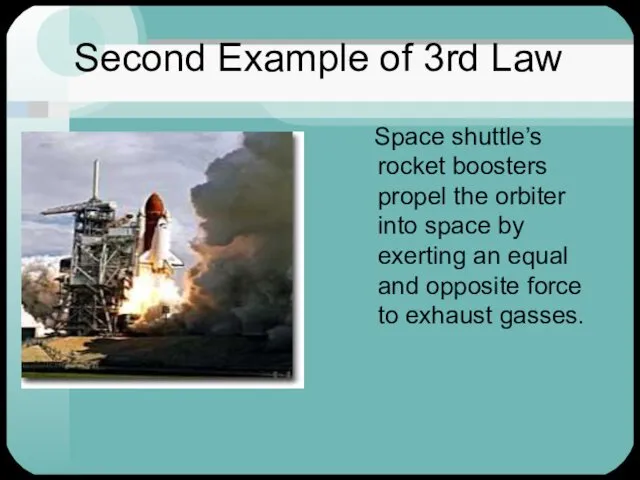
- 3. Second Example of 3rd Law Space shuttle’s rocket boosters propel the orbiter into space by exerting
- 4. Concept Question 1 Why are we able to walk?
- 5. Concept Question Answer We walk forward because when one foot pushes backward against the ground, the
- 6. Concept Question 2 What makes a car go forward?
- 7. Concept Question answer By Newton’s third law, the ground pushes on the tires in the opposite
- 8. Concept Question Which is stronger, the Earth’s pull on an orbiting space shuttle or the space
- 9. Concept Question Answer According to Newton’s Third Law, the two forces are equal and opposite. Because
- 10. Problem 1 What force is needed to accelerate the 60 kg cart at 2m/s^2?
- 11. How to solve Problem 1 What force is needed to accelerate the 60kg cart at 2
- 12. Problem 2 A force of 200 N accelerates a bike and rider at 2 m/s^2. What
- 14. Скачать презентацию










 Волновая оптика
Волновая оптика Системы управления автомобилем
Системы управления автомобилем Увеличение мощности автомобильного двигателя
Увеличение мощности автомобильного двигателя Равномерное движение по окружности
Равномерное движение по окружности Резерфорд тәжірибесі. Атомның планетарлық моделі
Резерфорд тәжірибесі. Атомның планетарлық моделі Насыщенный пар
Насыщенный пар 濽á ÒÓÒúßÔ¿ ºá¬¡ âÒ¬á
濽á ÒÓÒúßÔ¿ ºá¬¡ âÒ¬á Газораспределительный механизм
Газораспределительный механизм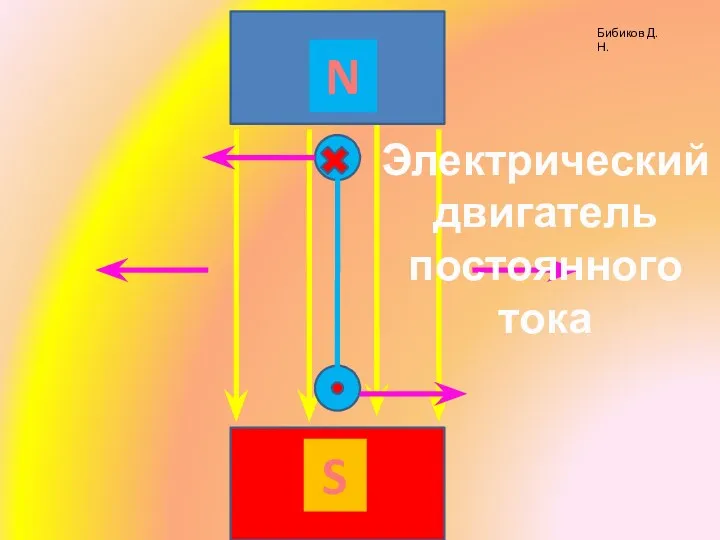 Электрические машины постоянного тока
Электрические машины постоянного тока Фізичні й хімічні явища у природі
Фізичні й хімічні явища у природі Урок повторения и обобщения 7 класс по теме: Давление
Урок повторения и обобщения 7 класс по теме: Давление Испарение и конденсация
Испарение и конденсация Общее устройство тракторов
Общее устройство тракторов Дифракция құбылысы. Френел және Фраунгофер жуықтаулары. Амплитудалық және фазалық дифракциялық торлар
Дифракция құбылысы. Френел және Фраунгофер жуықтаулары. Амплитудалық және фазалық дифракциялық торлар Элементтердің периодтық жүйесі және оның физикалық түсіндірілуі. Паули принципі. Хунд ережесі
Элементтердің периодтық жүйесі және оның физикалық түсіндірілуі. Паули принципі. Хунд ережесі Прочность, совместимость и радиационная стойкость реакторных материалов. Тема 3
Прочность, совместимость и радиационная стойкость реакторных материалов. Тема 3 Организация проектной деятельности учащихся
Организация проектной деятельности учащихся Электродинамика. Электростатика. Закон сохранения электрического заряда. Закон Кулона
Электродинамика. Электростатика. Закон сохранения электрического заряда. Закон Кулона Оценка последствий взрыва
Оценка последствий взрыва Повышение качества обработки колец подшипников
Повышение качества обработки колец подшипников Закон Ома для участка электрической цепи
Закон Ома для участка электрической цепи Investigation, of the use of planetary-circular gears in machine. Tool drives
Investigation, of the use of planetary-circular gears in machine. Tool drives Валы и оси
Валы и оси Организация технического обслуживания и ремонта автомобиля Шевроле Нива
Организация технического обслуживания и ремонта автомобиля Шевроле Нива Магнитное поле в вакууме
Магнитное поле в вакууме Машины постоянного тока. Устройство, материалы и принцип действия. Карточка 16
Машины постоянного тока. Устройство, материалы и принцип действия. Карточка 16 Механические передачи. Ременные передачи
Механические передачи. Ременные передачи Моделирование электрофизических свойств gaas методом монте-карло
Моделирование электрофизических свойств gaas методом монте-карло