What Makes
Materials Change State?
When a liquid turns into a solid it
is called freezing.
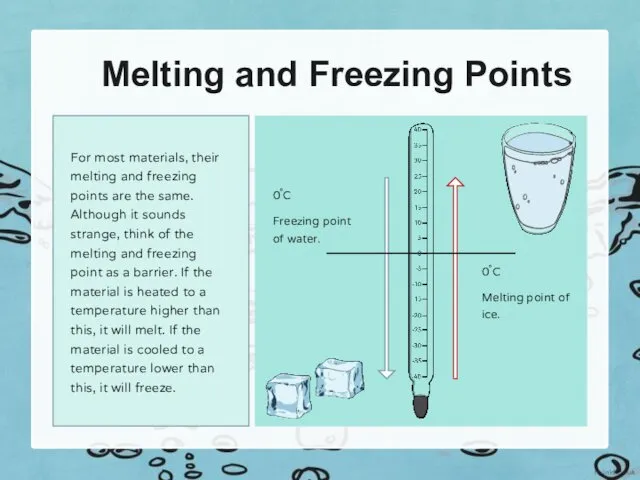
The temperature at which a liquid material freezes is called its
freezing point. Different materials have different freezing points.
It is important to remember that some materials have freezing
points above 0°C. For example, the freezing point of iron is
around 1550°C! Interestingly, this means its melting point is also
its freezing point, just in reverse! Above this temperature, it will be
liquid iron. Below this temperature, it will be solid iron.
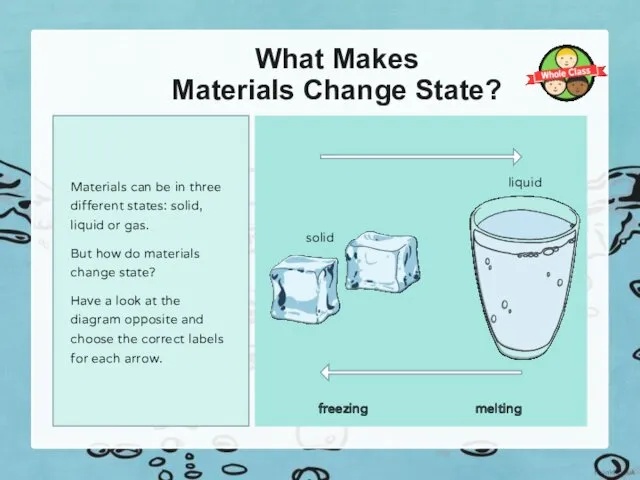
If a liquid material is cooled to its freezing point, it will turn from a
liquid to a solid.
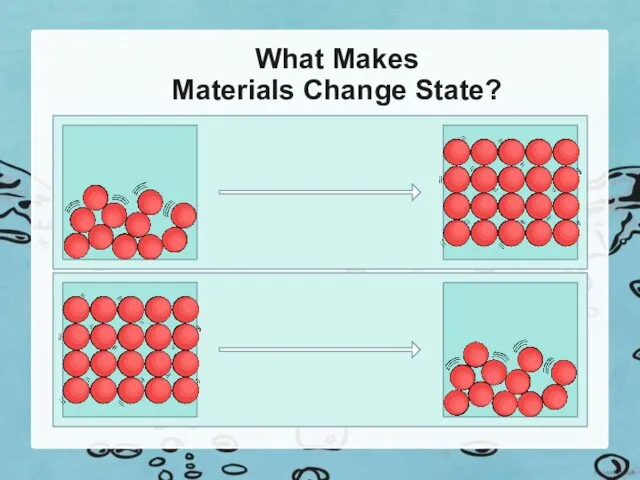
The particles in a liquid are close together, but can move quite quickly around and over each other. As it is cooled, the particles start to slow down. Eventually, they slow down so much that they only move gently on the spot, and a solid structure is formed. The material has frozen.




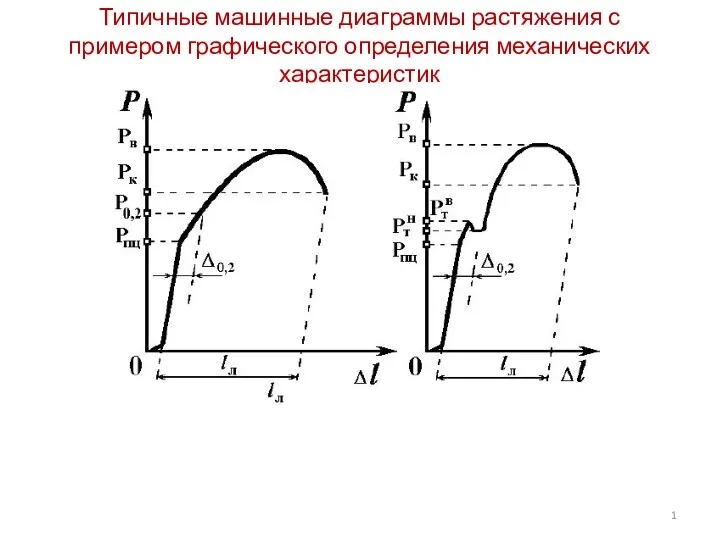 Типичные машинные диаграммы растяжения с примером графического определения механических характеристик
Типичные машинные диаграммы растяжения с примером графического определения механических характеристик Электричество. Работа электрического тока
Электричество. Работа электрического тока Кинематика. 10 класс
Кинематика. 10 класс Лекция № 5,6 РБ. Цепная реакция деления тяжелых ядер
Лекция № 5,6 РБ. Цепная реакция деления тяжелых ядер Молекулярно-кинетическая теория идеальных газов
Молекулярно-кинетическая теория идеальных газов Учебный курс Термодинамика и теплопередача. Практическое занятие 2
Учебный курс Термодинамика и теплопередача. Практическое занятие 2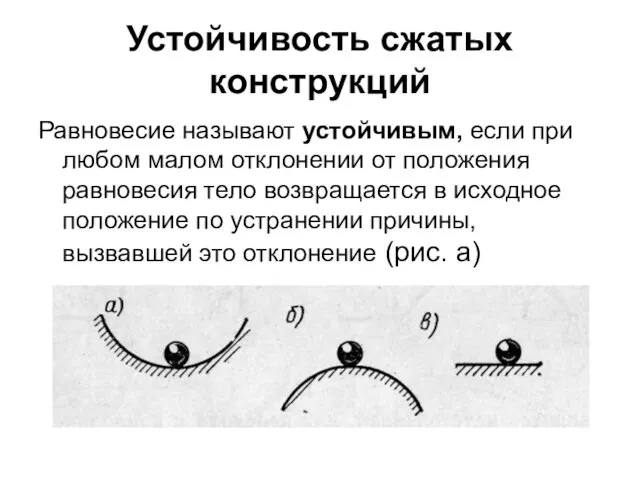 Устойчивость сжатых конструкций
Устойчивость сжатых конструкций Экспериментальные методы исследования частиц
Экспериментальные методы исследования частиц Анализ вариантов составляющих конструкции из КМ силового элемента втулки РВ вертолета
Анализ вариантов составляющих конструкции из КМ силового элемента втулки РВ вертолета Методы эффективного управления инверторами напряжения в приводах переменного тока
Методы эффективного управления инверторами напряжения в приводах переменного тока Forces and Motion If I were…
Forces and Motion If I were… Фізика в житті сучасної людини
Фізика в житті сучасної людини Центр тяжести. Равновесие тел
Центр тяжести. Равновесие тел Определение стоимости и расхода электроэнергии
Определение стоимости и расхода электроэнергии Методы регистрации заряженных частиц
Методы регистрации заряженных частиц Солнечная батарея
Солнечная батарея Источники электрического тока. Физика. 8 класс
Источники электрического тока. Физика. 8 класс Неоднородное одномерное уравнение теплопроводности
Неоднородное одномерное уравнение теплопроводности Заттың құрылысы
Заттың құрылысы Лампа накаливания
Лампа накаливания Жидкое и твердое состояния вещества
Жидкое и твердое состояния вещества Законы постоянного тока
Законы постоянного тока Технологии выращивания кристаллов. Технология полупроводниковых материалов
Технологии выращивания кристаллов. Технология полупроводниковых материалов Организация работ по ТО и ТР автомобилей Lada Granta с детальной разработкой участка покраски
Организация работ по ТО и ТР автомобилей Lada Granta с детальной разработкой участка покраски Деление атомных ядер. (Тема 2.7)
Деление атомных ядер. (Тема 2.7) Архимед и его мудрое открытие (287 - 212 до н.э.)
Архимед и его мудрое открытие (287 - 212 до н.э.) Влияние билингвизма на способности по физике
Влияние билингвизма на способности по физике Каталитические нейтрализаторы отработавших газов бензиновых двигателей внутреннего сгорания
Каталитические нейтрализаторы отработавших газов бензиновых двигателей внутреннего сгорания