Содержание
- 2. JDBC Basics The JDBC API is a Java API that can access any kind of tabular
- 3. Eclipse & Derby Projects Eclipse: New -> Java Project Fill project name and click next Click
- 4. Processing SQL Statements with JDBC Establishing a connection Create a statement Execute the query Process the
- 5. Basic Example I package app; import java.sql.*; public class E721JDBCBasics { public static void main(String[] args)
- 6. Basic Example II Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection ("jdbc:derby:C:\\VMO\\Курсы\\Projects\\CM"); Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(
- 7. Processing SQL Statements with JDBC Establishing a connection Create a statement Execute the query Process the
- 8. Establishing a connection. A JDBC application connects to a target data source using one of two
- 9. Connection example public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException, SQLException{ Connection conn = null; Properties props =
- 10. Processing SQL Statements with JDBC Establishing a connection Create a statement Execute the query Process the
- 11. Creating Statements Kinds of statements: Statement - simple SQL statements with no parameters PreparedStatement (extends Statement)
- 12. Insert New Customer Example I Connection con = getConnection(); String sql = "INSERT INTO customer (name,
- 13. Prepared Statements Usually reduces execution time (the DBMS can just run the PreparedStatement SQL statement without
- 14. Insert New Customer Example II public void addCustomer(String name, String address, String email, String ccNo, String
- 15. SQL Date From GregorianCalendar: GregorianCalendar c = new GregorianCalendar(2012, 03, 31); java.util.Date dt = c.getTime(); java.sql.Date
- 16. Processing SQL Statements with JDBC Establishing a connection Create a statement Execute the query Process the
- 17. Executing Queries executeQuery: Returns one ResultSet object executeUpdate: Returns an integer representing the number of rows
- 18. Exercise: Get Merchant’s Total Show total for a merchant which id is given in the first
- 19. Exercise: Get Merchant’s Total See 725Query project for the full text. * Infopulse Training Center
- 20. Processing SQL Statements with JDBC Establishing a connection Create a statement Execute the query Process the
- 21. Processing ResultSet Objects You access the data in a ResultSet object through a cursor Note that
- 22. Exercise: List of Merchants Create an application to display list of merchants: Create a Merchant class
- 23. Exercise: List of Merchants See 726MerchList project for the full text. * Infopulse Training Center
- 24. Processing SQL Statements with JDBC Establishing a connection Create a statement Execute the query Process the
- 25. Closing Connections Call the method Statement.close to immediately release the resources it is using. When you
- 26. Closing Connections in Java 7 Use a try-with-resources statement to automatically close Connection, Statement, and ResultSet
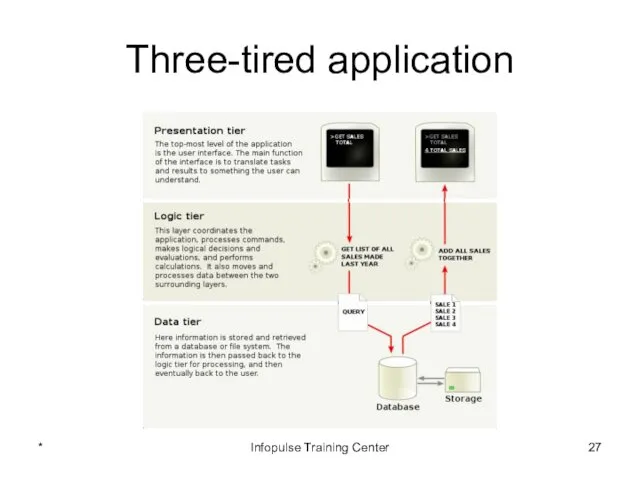
- 27. Three-tired application * Infopulse Training Center
- 28. Handling SQLExceptions The SQLException contains the following information A description of the error - getMessage() A
- 29. Data Tier Separation of concerns principle: business and presentation tiers should not know anything about database
- 30. Exercise: Add Payment Create a method to add new payment info to the database * Infopulse
- 31. Exercise: Add Payment See 727AddPayment project for the full text. * Infopulse Training Center
- 32. Transactions These statements should take effect only together: // Insert new record into PAYMENT table //
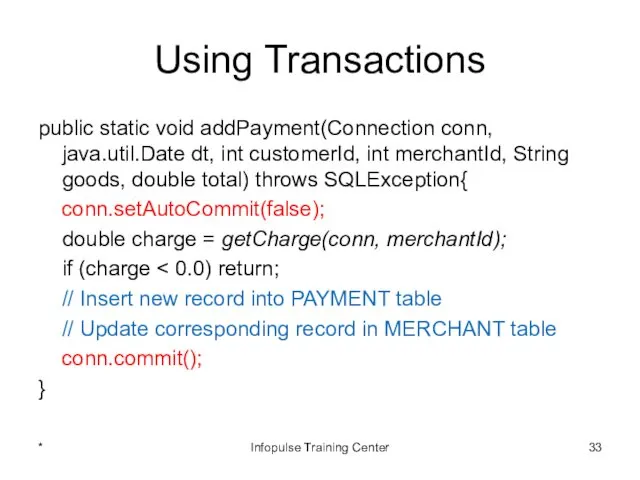
- 33. Using Transactions public static void addPayment(Connection conn, java.util.Date dt, int customerId, int merchantId, String goods, double
- 34. Rollback Method Calling the method rollback terminates a transaction and returns any values that were modified
- 35. Exercise: Get Income Report Create a report about CM system’s income got from each merchant. *
- 36. Exercise: Get Income Report See 728MerchantCharge project for the full text. * Infopulse Training Center
- 37. Object-Relational Mapping SQL DBMS can only store and manipulate scalar values such as integers and strings
- 38. ORM Advantages&Disadvantages Advantage: often reduces the amount of code that needs to be written Disadvantage: performance
- 39. Some Java ORM Systems Hibernate, open source ORM framework, widely used MyBatis, formerly named iBATIS, has
- 41. Скачать презентацию





























 Решение задач ЕГЭ типа В2
Решение задач ЕГЭ типа В2 Абстрактні типи даних
Абстрактні типи даних Дербес компьютерлер туралы жалпы мәліметтер
Дербес компьютерлер туралы жалпы мәліметтер Двоичное кодирование текстовой информации
Двоичное кодирование текстовой информации Поиск и работа в интернете: прикладные и теоретические аспекты
Поиск и работа в интернете: прикладные и теоретические аспекты Життя з Інформаційними технологіями
Життя з Інформаційними технологіями Машина Тьюринга
Машина Тьюринга Интегрированный урок информатики и русского языка в 10 классе
Интегрированный урок информатики и русского языка в 10 классе Смешарики : London Gloom – 3 эпизод
Смешарики : London Gloom – 3 эпизод Модель вариантов использования в Rose. (Тема 4)
Модель вариантов использования в Rose. (Тема 4) Paint графикалық редакторы
Paint графикалық редакторы Цикли з лічильником у середовищі скретч
Цикли з лічильником у середовищі скретч Физический уровень
Физический уровень Құрылымдық схема және ДК құрылғылары
Құрылымдық схема және ДК құрылғылары Интернет: общая характеристика
Интернет: общая характеристика Своя игра. Мир информатики
Своя игра. Мир информатики Набор текстовых файлов
Набор текстовых файлов Запросы к нескольким таблицам. Работа с SQL
Запросы к нескольким таблицам. Работа с SQL HTML – язык гипертекстовой разметки Webстраниц
HTML – язык гипертекстовой разметки Webстраниц Газета Известия
Газета Известия Презентация к уроку информатики по теме: Текст как форма представления информации
Презентация к уроку информатики по теме: Текст как форма представления информации Внедрение CRM на предприятии
Внедрение CRM на предприятии Сети и системы телекоммуникаций. Транспортный уровень
Сети и системы телекоммуникаций. Транспортный уровень Введение в программную инженерию. Управление рисками проекта
Введение в программную инженерию. Управление рисками проекта Сравнение нотаций ВS с ARIS и BPMN 2022
Сравнение нотаций ВS с ARIS и BPMN 2022 Операционная система Windows
Операционная система Windows СЕТИ (ПРОТОКОЛЫ СЕТЕВОГО ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЯ) SOFTWARE
СЕТИ (ПРОТОКОЛЫ СЕТЕВОГО ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЯ) SOFTWARE Текстовый процессор OpenOffice.org Writer
Текстовый процессор OpenOffice.org Writer