Содержание
- 2. Getting Acquainted The Developer Technical Services Group About You?
- 3. Developer Technical Services Worldwide Workgroup Over 25 Specialists World Wide Virtually 24 hour support, 5 days
- 4. Getting Support http://www.autodesk.com/adn-devhelp Provides access to On-line knowledge base Call submission Newsgroups Calls are logged automatically
- 5. Course Objective It is to understand: the fundamentals of the AutoCAD .NET API how to teach
- 6. Class Agenda Lectures with Labs Slides give an abstract overview Labs and discussion give a practical
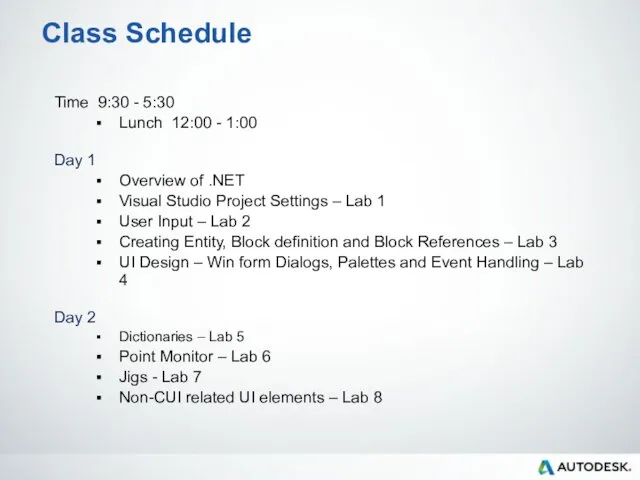
- 7. Class Schedule Time 9:30 - 5:30 Lunch 12:00 - 1:00 Day 1 Overview of .NET Visual
- 8. .NET Overview What is .NET? Benefits of programming in .NET Important Concepts
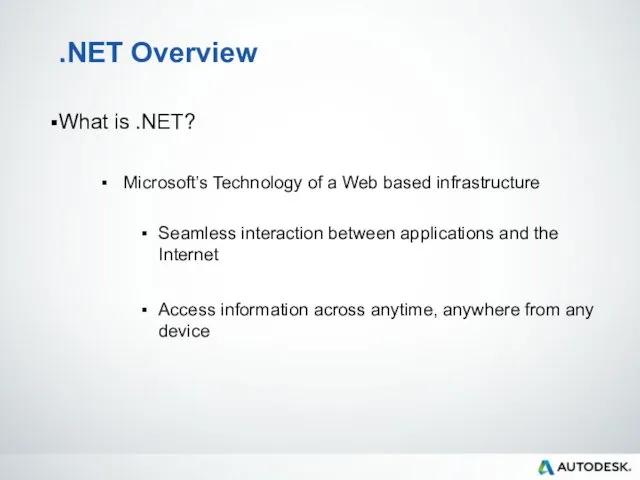
- 9. .NET Overview What is .NET? Microsoft’s Technology of a Web based infrastructure Seamless interaction between applications
- 10. .NET Overview What is .NET? Components of .NET The .NET Framework used for building and running
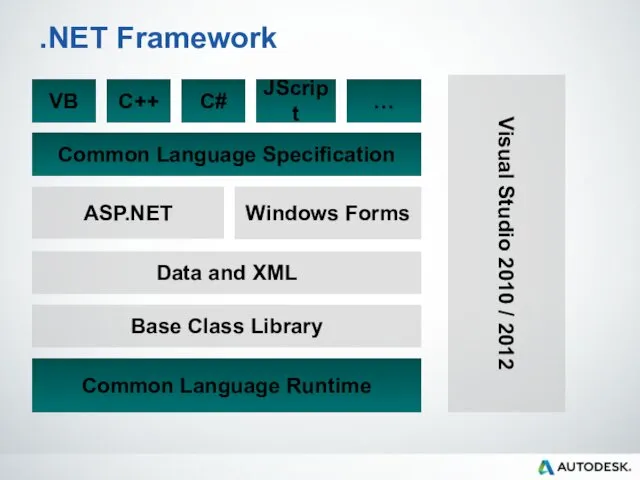
- 11. .NET Framework Base Class Library Common Language Runtime Data and XML Visual Studio 2010 / 2012
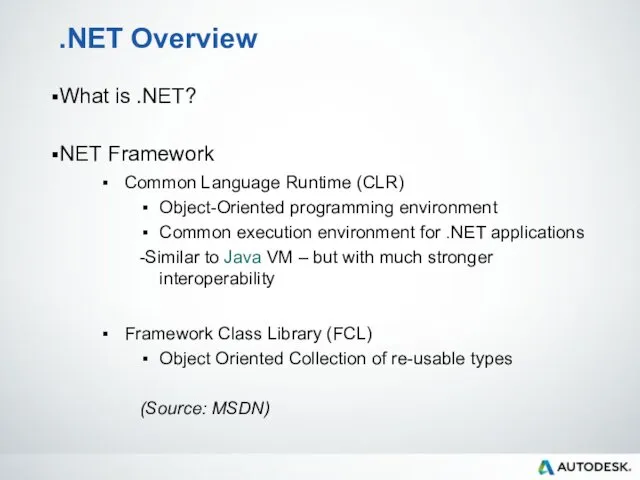
- 12. .NET Overview What is .NET? NET Framework Common Language Runtime (CLR) Object-Oriented programming environment Common execution
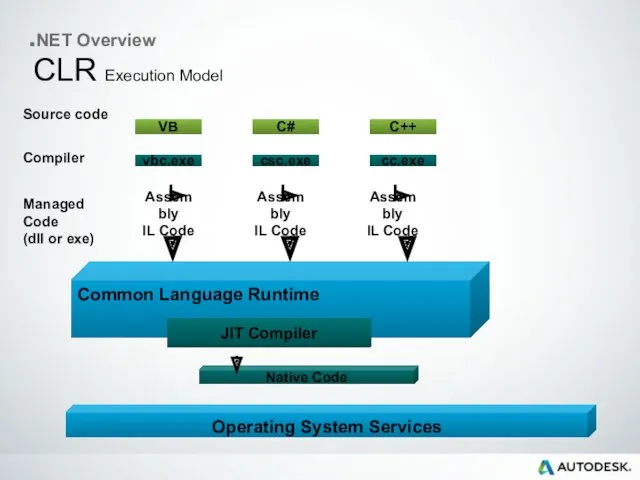
- 13. .NET Overview VB Source code vbc.exe C++ C# cc.exe csc.exe Operating System Services Common Language Runtime
- 14. What is Microsoft .NET? What we know from our experience so far… Intelligent symbolic representation Mature
- 15. .NET Overview What is .NET? Benefits of programming in .NET Important Concepts
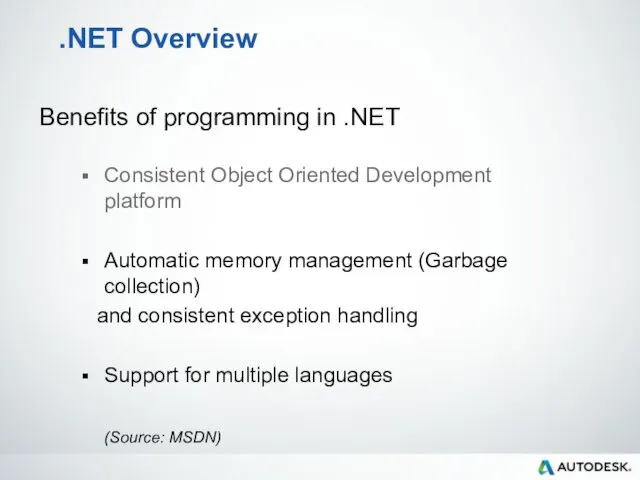
- 16. .NET Overview Benefits of programming in .NET Consistent Object Oriented Development platform Automatic memory management –
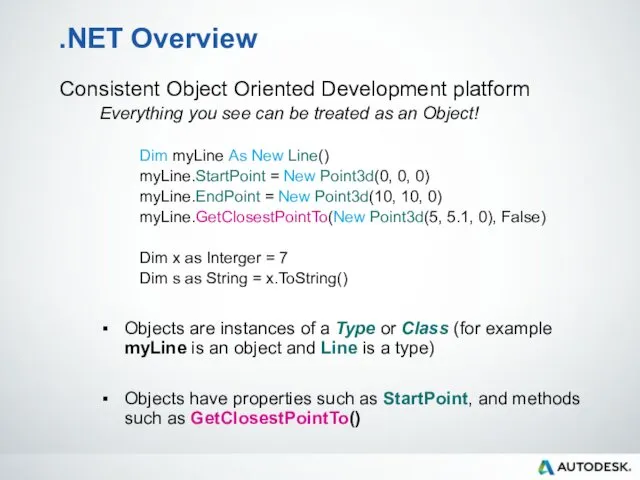
- 17. .NET Overview Consistent Object Oriented Development platform Everything you see can be treated as an Object!
- 18. .NET Overview Consistent Object Oriented Development platform Mature API Constructs What’s wrong with this function? int
- 19. .NET Overview Consistent Object Oriented Development platform Mature API Constructs Some 6 new classes defined to
- 20. .NET Overview Benefits of programming in .NET Consistent Object Oriented Development platform Automatic memory management (Garbage
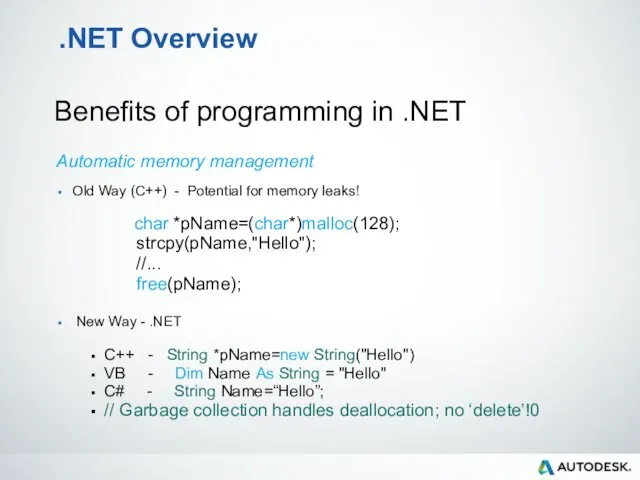
- 21. .NET Overview Benefits of programming in .NET Automatic memory management Old Way (C++) - Potential for
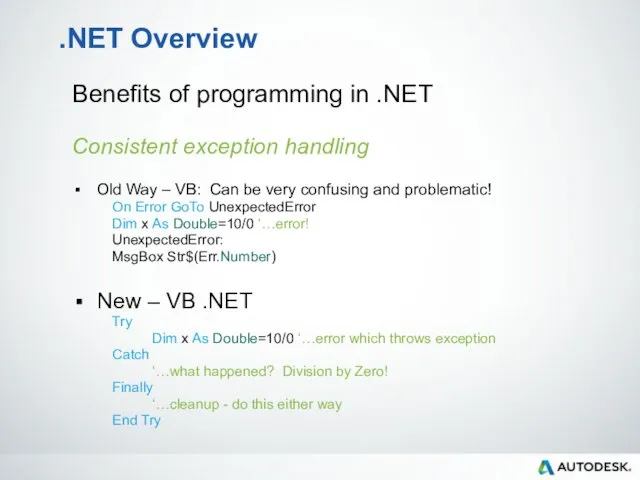
- 22. .NET Overview Benefits of programming in .NET Consistent exception handling Old Way – VB: Can be
- 23. .NET Overview Benefits of programming in .NET Consistent Object Oriented Development platform Automatic memory management (Garbage
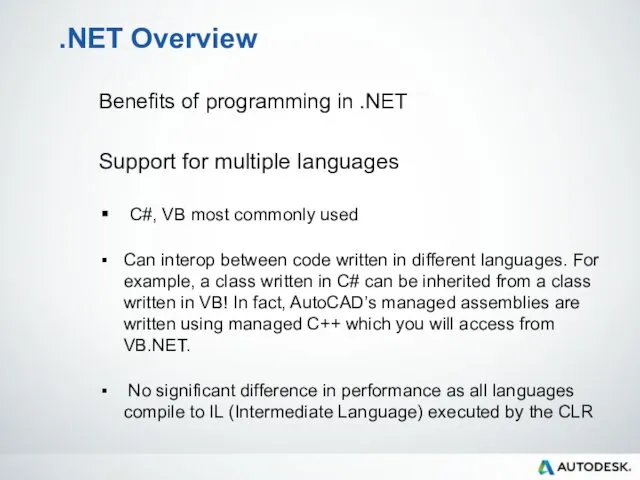
- 24. .NET Overview Benefits of programming in .NET Support for multiple languages C#, VB most commonly used
- 25. .NET Overview What is .NET? Benefits of programming in .NET Important Concepts
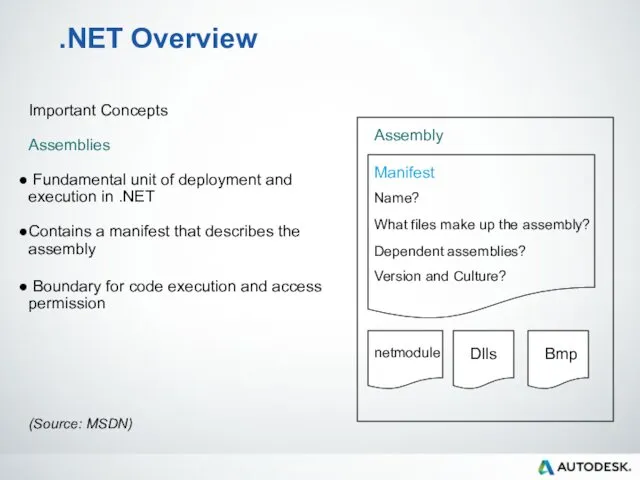
- 26. .NET Overview Important Concepts Assemblies Fundamental unit of deployment and execution in .NET Contains a manifest
- 27. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
- 28. AutoCAD .NET API Documentation How do I get started? ObjectARX SDK Includes: SDK Samples! ObjectARX Developer’s
- 29. Development Environment Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 (SP1) or Microsoft Visual Studio 2012 AutoCAD 2014 Microsoft Windows
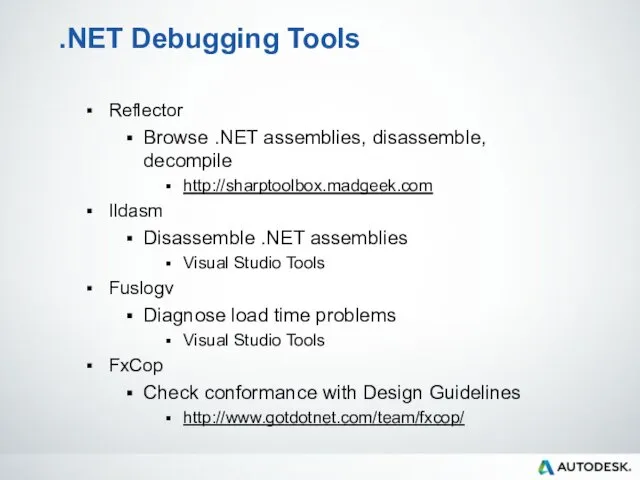
- 30. .NET Debugging Tools Reflector Browse .NET assemblies, disassemble, decompile http://sharptoolbox.madgeek.com Ildasm Disassemble .NET assemblies Visual Studio
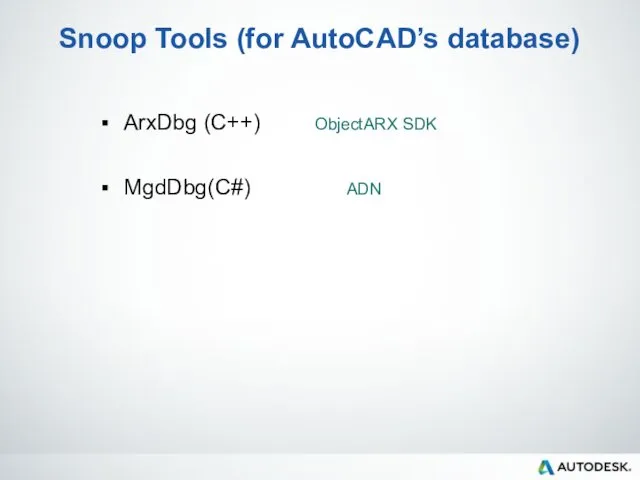
- 31. Snoop Tools (for AutoCAD’s database) ArxDbg (C++) ObjectARX SDK MgdDbg(C#) ADN
- 32. Visual Studio project settings– Hello World! Start with a Class Library application type with DLL output.
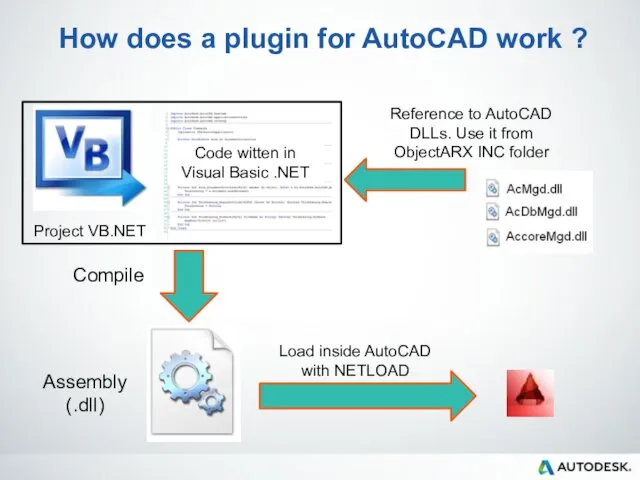
- 33. How does a plugin for AutoCAD work ? Assembly (.dll) Compile Code witten in Visual Basic
- 34. Visual Studio project settings– Hello World! Reference namespaces you will use in your project In VB.NET
- 35. Visual Studio project settings– Hello World! Add a simple command – HelloWorld Make a function an
- 36. Visual Studio project settings– Hello World! To print a string to command line Get the editor
- 37. Loading .NET assembly NETLOAD command AUTOLOADER Startup On command invocation Demand Load (Registry) Startup On command
- 38. AutoLoader AutoCAD loads “bundles” from %appdata%\Autodesk\ApplicationPlugins Each bundle has “PackageContents.xml”
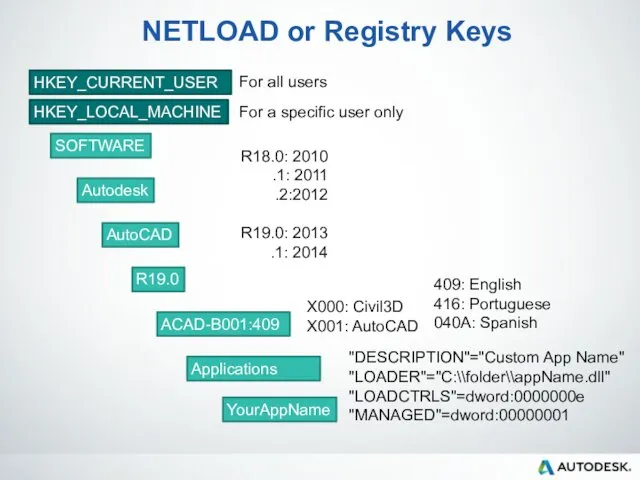
- 39. NETLOAD or Registry Keys HKEY_CURRENT_USER HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SOFTWARE Autodesk AutoCAD R19.0 ACAD-B001:409 Applications YourAppName R18.0: 2010 .1:
- 40. Lab 1 – Hello World!
- 41. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
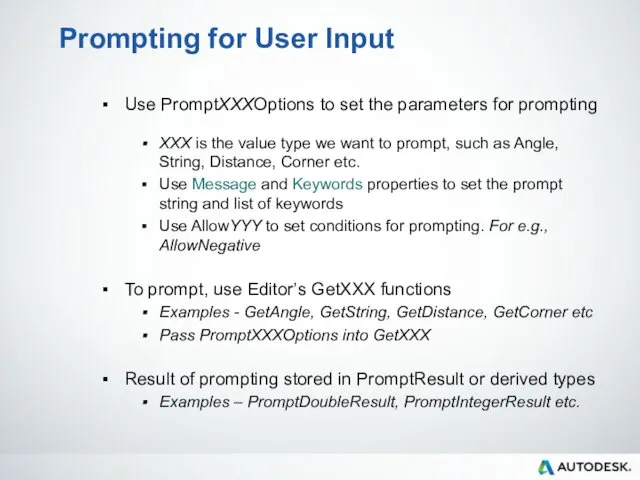
- 42. Prompting for User Input Use PromptXXXOptions to set the parameters for prompting XXX is the value
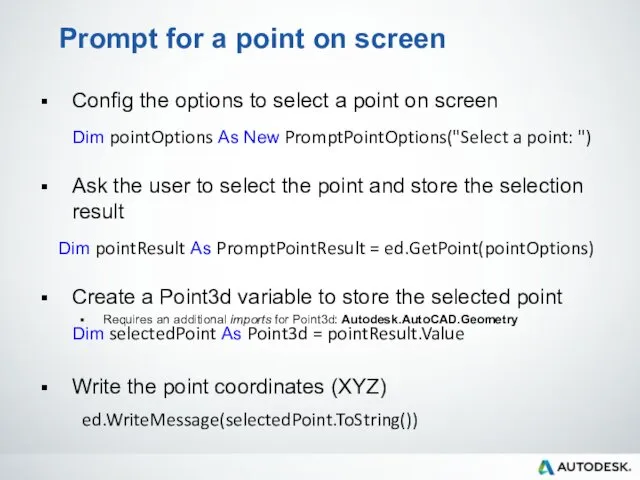
- 43. Prompt for a point on screen Config the options to select a point on screen Ask
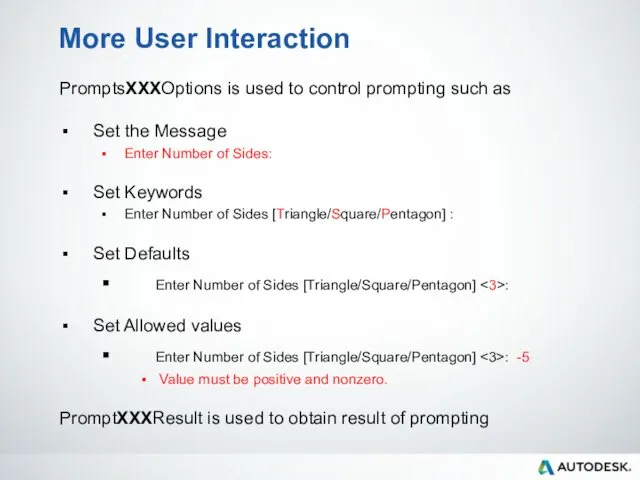
- 44. More User Interaction PromptsXXXOptions is used to control prompting such as Set the Message Enter Number
- 45. Additional prompts Types: PromptPointOptions PromptStringOptions PromptDoubleOptions PromptAngleOptions PromptCornerOptions PromptDistanceOptions PromptEntityOptions PromptIntegerOptions PromptKeywordOptions PromptNestedEntityOptions PromptSelectionOptions Etc. Help
- 46. Dotnet 2014 Wizards AppWizard – Templates for a VB.NET or C# application
- 47. Lab 2 –User Input
- 48. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
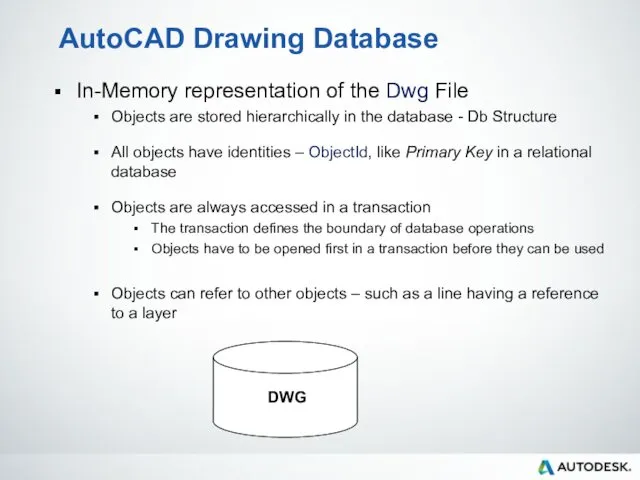
- 49. AutoCAD Drawing Database In-Memory representation of the Dwg File Objects are stored hierarchically in the database
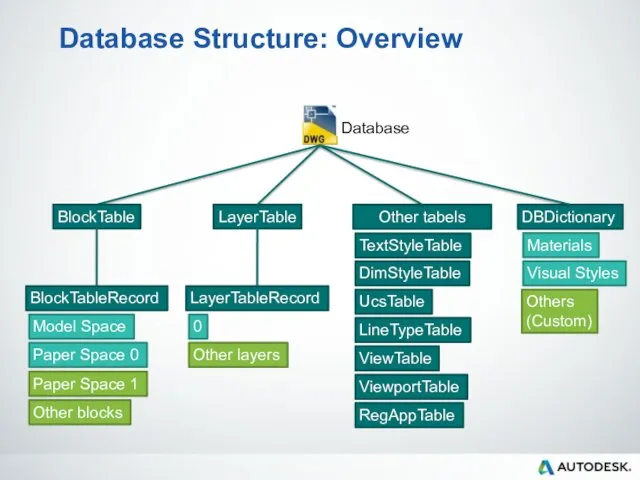
- 50. Database Structure: Overview Database BlockTable LayerTable Other tabels Model Space Paper Space 0 BlockTableRecord Other blocks
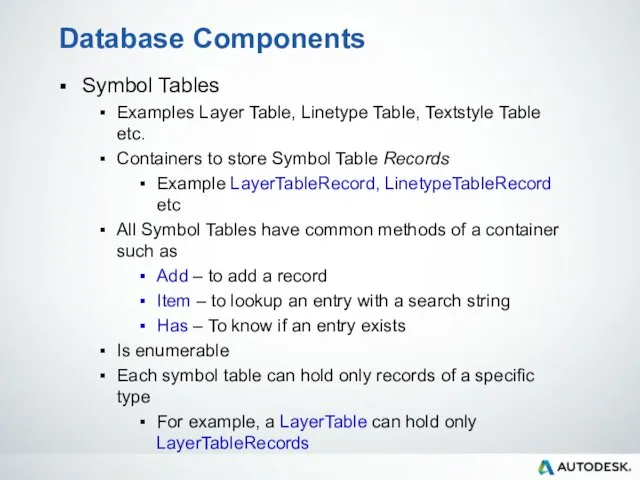
- 51. Database Components Symbol Tables Examples Layer Table, Linetype Table, Textstyle Table etc. Containers to store Symbol
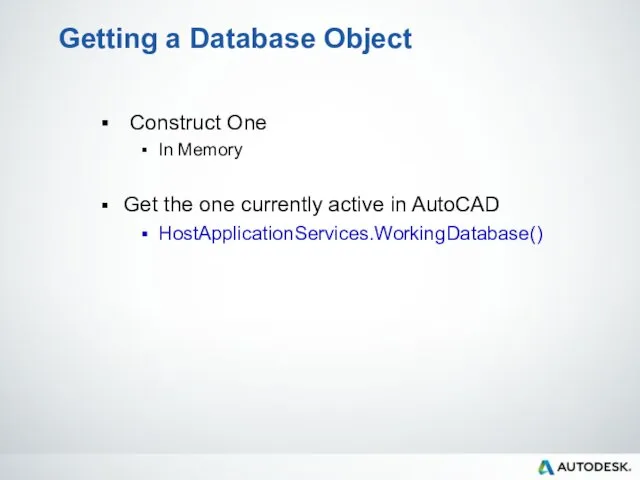
- 52. Getting a Database Object Construct One In Memory Get the one currently active in AutoCAD HostApplicationServices.WorkingDatabase()
- 53. Object Identity - ObjectID All Objects that exist in the database have an ObjectId Is unique
- 54. Transactions Transactions Sets the boundary for database operations Handles exception cleanly Operates with a single Undo
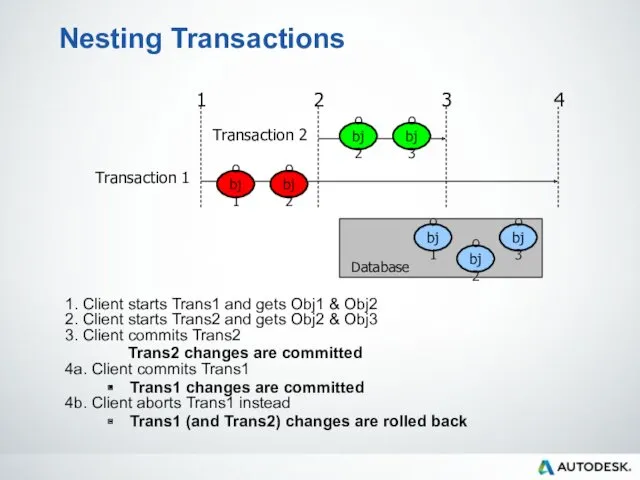
- 55. Nesting Transactions 1. Client starts Trans1 and gets Obj1 & Obj2 2. Client starts Trans2 and
- 56. Transactions Standard db access with Transactions Public Function MyFunc() ‘Get the database current in AutoCAD Dim
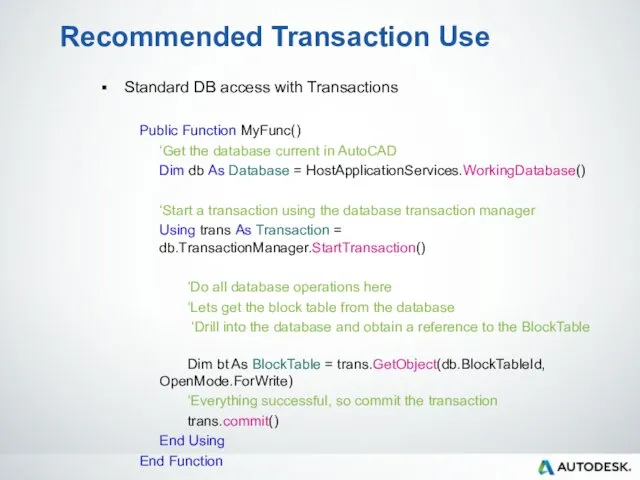
- 57. Recommended Transaction Use Standard DB access with Transactions Public Function MyFunc() ‘Get the database current in
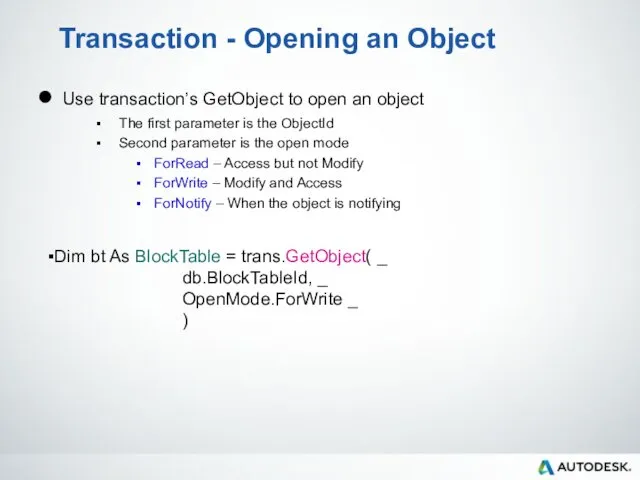
- 58. Transaction - Opening an Object Use transaction’s GetObject to open an object The first parameter is
- 59. Adding an Object to the database Find the right owner to add a newly created object
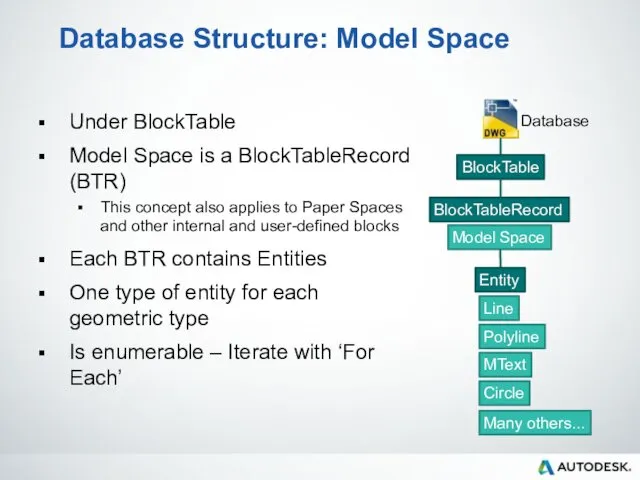
- 60. Database Structure: Model Space Under BlockTable Model Space is a BlockTableRecord (BTR) This concept also applies
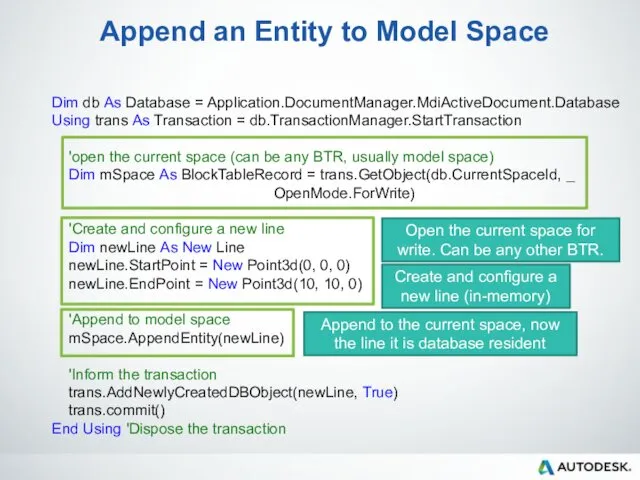
- 61. Append an Entity to Model Space Dim db As Database = Application.DocumentManager.MdiActiveDocument.Database Using trans As Transaction
- 62. Object memory management Note managed objects wrap an unmanaged C++ object! So we create them with
- 63. Object Model Overview classmap.dwg in ObjectARX distribution
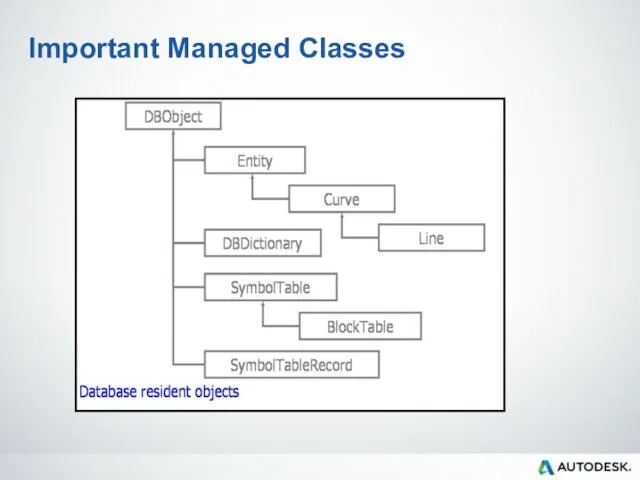
- 64. Important Managed Classes
- 65. Lab 3 Create Entity, Block and Block Reference
- 66. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
- 67. Forms and UI Basics Win Form API basics How create a form Common used controls Respond
- 68. Windows® OS is based on windows Everything on screen is some type of window You move
- 69. Forms with WinForms API Require reference to System.Windows.dll Namespace System.Windows.Forms Main features Forms Controls for forms
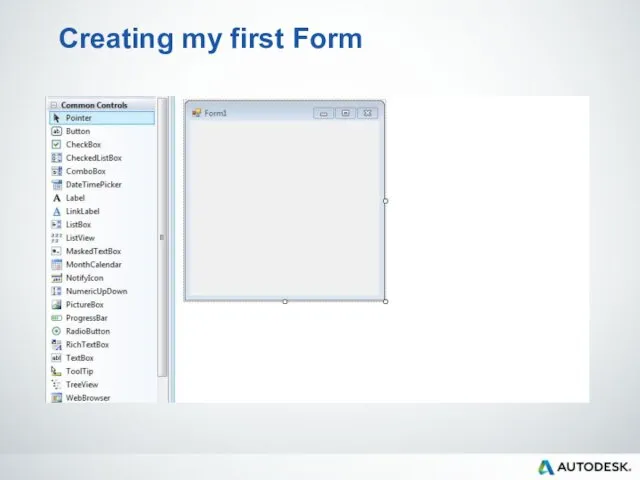
- 70. Creating my first Form Add a Windows Form Add controls for the form
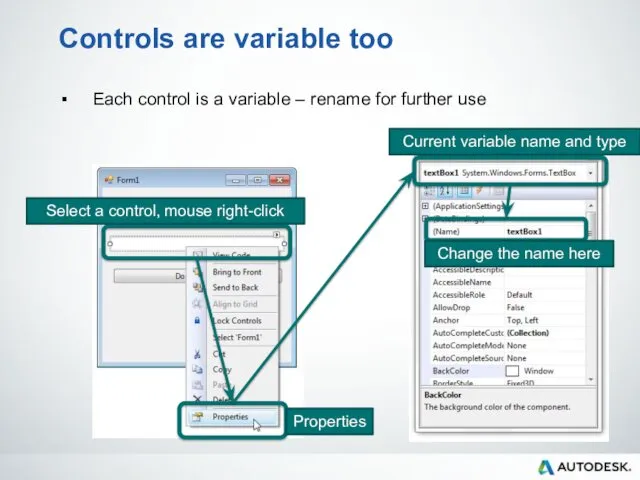
- 71. Controls are variable too Each control is a variable – rename for further use Select a
- 72. Do something when the user click! For some controls we need execute something when the user
- 73. Create the control events TIP
- 74. User Interface Design AutoCAD Defined Menus – Application level menu, Context menu Dialogs AutoCAD’s Enhanced Secondary
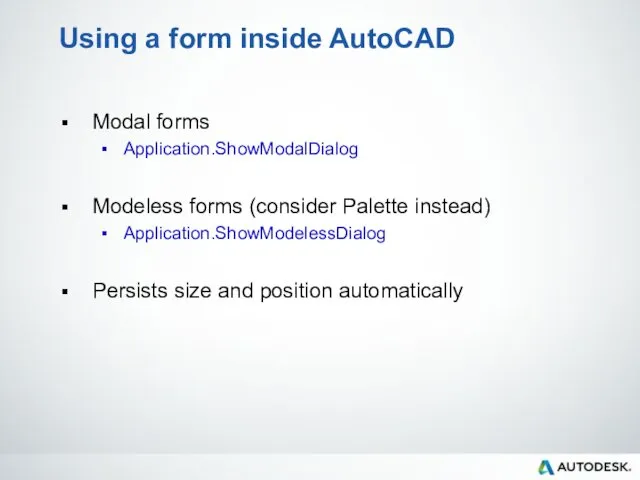
- 75. Using a form inside AutoCAD Modal forms Application.ShowModalDialog Modeless forms (consider Palette instead) Application.ShowModelessDialog Persists size
- 76. Palette in AutoCAD Create a user control Create a PaletteSet Add the user control to the
- 77. Handling Events Event message sent by an object to notify something has happened message is received
- 78. Using Delegates Delegates in AutoCAD’s .NET API usually have ‘EventHandler’ suffix Lookup the signature of the
- 79. Event Handling - Example Create the event handler (callback) Sub objAppended(ByVal o As Object, ByVal e
- 80. Lab 4 PaletteSet and DB Events
- 81. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
- 82. Dictionaries and XRecords Dictionaries (Type DbDictionary) Containers to hold data only Holds other Dictionaries Holds non-graphical
- 83. Dictionaries and XRecords XRecord Data containers Holds data in a Resbuf chain (Result Buffer) Resbuf –
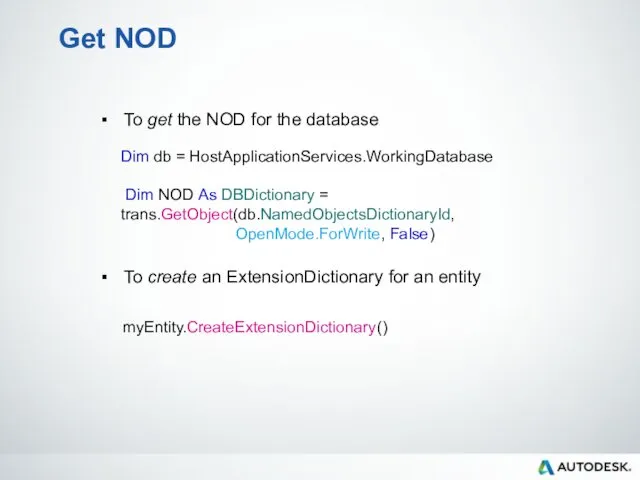
- 84. Get NOD To get the NOD for the database Dim db = HostApplicationServices.WorkingDatabase Dim NOD As
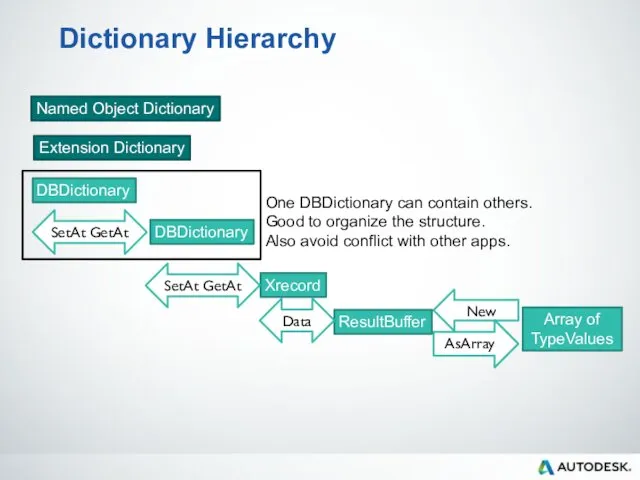
- 85. Dictionary Hierarchy Named Object Dictionary Extension Dictionary DBDictionary Xrecord DBDictionary ResultBuffer Array of TypeValues New AsArray
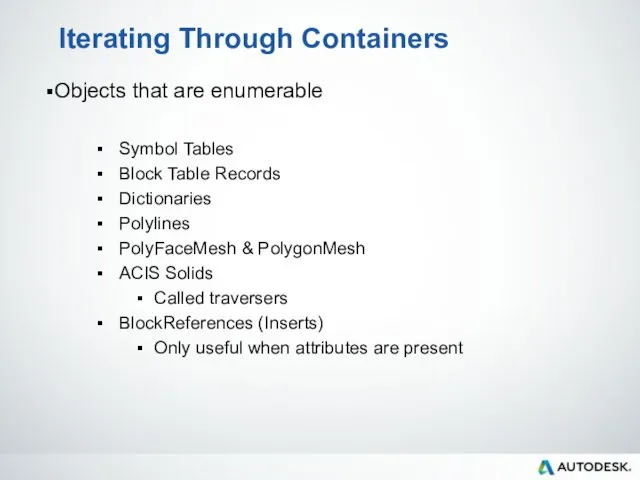
- 86. Iterating Through Containers Objects that are enumerable Symbol Tables Block Table Records Dictionaries Polylines PolyFaceMesh &
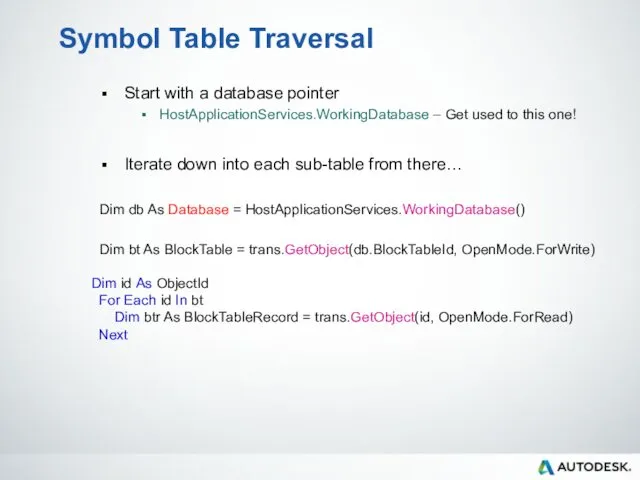
- 87. Symbol Table Traversal Start with a database pointer HostApplicationServices.WorkingDatabase – Get used to this one! Iterate
- 88. Lab 5 Adding Custom Data
- 89. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
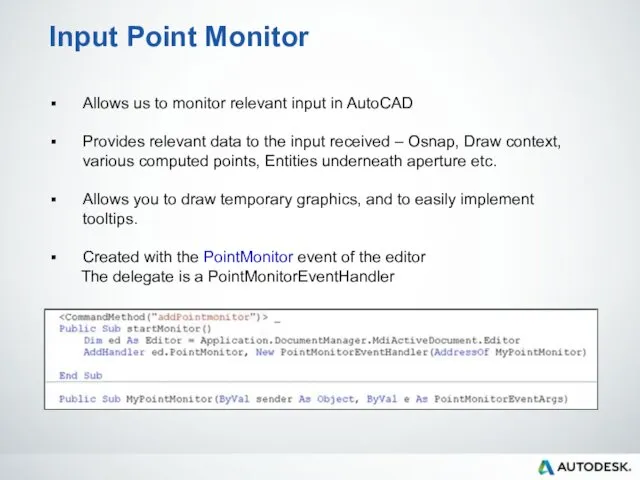
- 90. Input Point Monitor Allows us to monitor relevant input in AutoCAD Provides relevant data to the
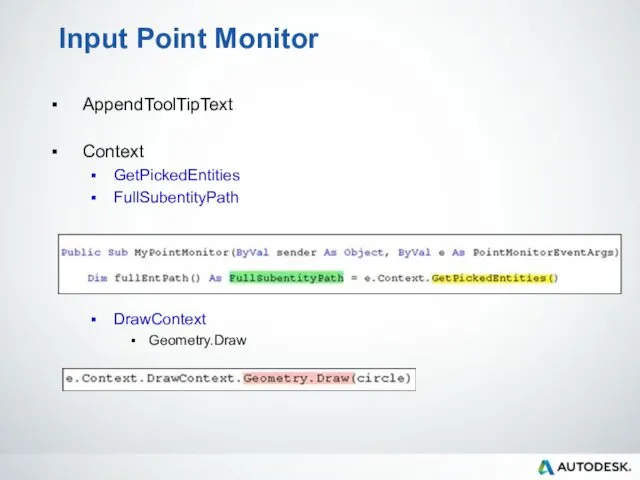
- 91. Input Point Monitor AppendToolTipText Context GetPickedEntities FullSubentityPath DrawContext Geometry.Draw
- 92. Lab 6 PointMonitor
- 93. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
- 94. Jigs Allows you to graphically manipulate and form an Entity in real time. Two types of
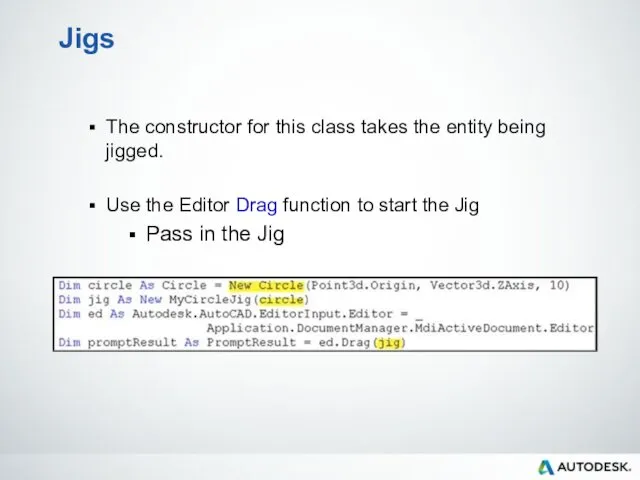
- 95. Jigs The constructor for this class takes the entity being jigged. Use the Editor Drag function
- 96. Jig Functions Two functions that must be overridden Sampler Used to get input from the user
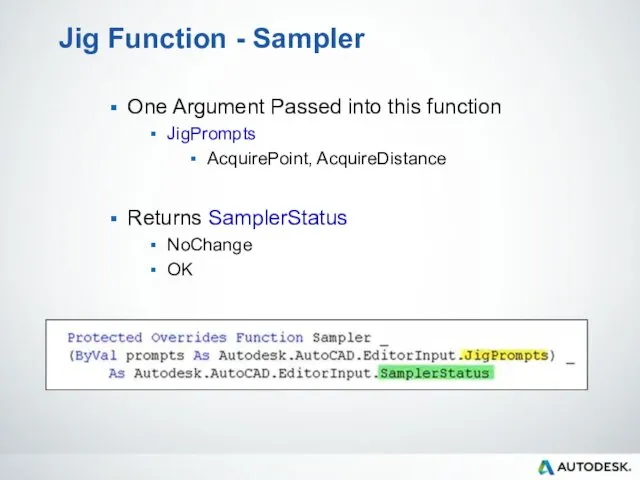
- 97. Jig Function - Sampler One Argument Passed into this function JigPrompts AcquirePoint, AcquireDistance Returns SamplerStatus NoChange
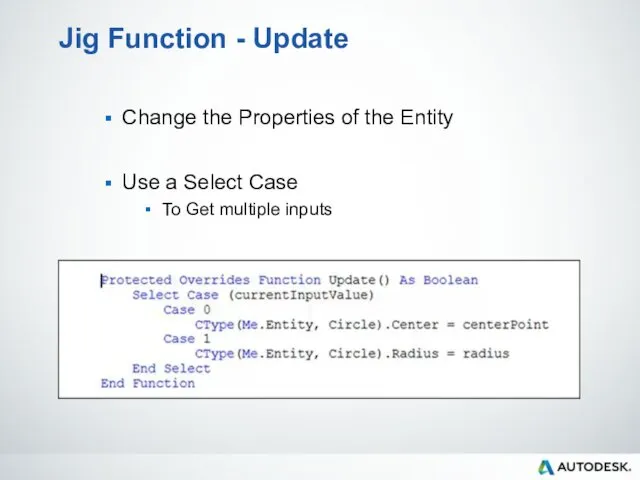
- 98. Jig Function - Update Change the Properties of the Entity Use a Select Case To Get
- 99. Lab 7 Jigs
- 100. Class Agenda Lectures and Labs Overview of .NET. AutoCAD .NET Visual Studio project settings – Hello
- 101. Context menu Application Level Application.AddDefaultContextMenuExtension Object Level Application. AddObjectContextMenuExtension –per RXClass
- 102. Tabbed Dialog Extensions Create a new tab inside Options dialog Create a user control Hook to
- 103. Drag and Drop Handle MouseMove Create an instance of your DropTarget class Call Application.DoDragDrop Application.DoDragDrop (
- 104. Lab 8 Additional User Interface Elements (Non CUI based)
- 105. More API Resources Blogs Through the Interface (AutoCAD.NET) http://through-the-interface.typepad.com/through_the_interface/ AutoCAD DevBlog http://adndevblog.typepad.com/autocad/ Developer Center : http://www.autodesk.com/developautocad
- 107. Скачать презентацию






















































 Позиционные системы счисления
Позиционные системы счисления Локальные сети. Параметры сетей и их стандарты
Локальные сети. Параметры сетей и их стандарты Сбор и подготовка данных
Сбор и подготовка данных Современные накопители информации, используемые в вычислительной технике
Современные накопители информации, используемые в вычислительной технике Использование технологии веб-квест как средство развития познавательных и творческих способностей учащихся
Использование технологии веб-квест как средство развития познавательных и творческих способностей учащихся Блочные алгоритмы. Блочное шифрование. Сравнение блочных и поточных шифров. Предпосылки создания шифра Фейстеля
Блочные алгоритмы. Блочное шифрование. Сравнение блочных и поточных шифров. Предпосылки создания шифра Фейстеля Параллельное программирование. С++. Thread Support Library. Atomic Operations Library
Параллельное программирование. С++. Thread Support Library. Atomic Operations Library Функции в Excel
Функции в Excel Организация и средства информационных технологий обеспечения управленческой деятельности
Организация и средства информационных технологий обеспечения управленческой деятельности Поиск публикаций и показатели деятельности ученого в Web of Science
Поиск публикаций и показатели деятельности ученого в Web of Science Бездротові мережі
Бездротові мережі Занятие 1. Знакомство с программой Adobe Photoshop
Занятие 1. Знакомство с программой Adobe Photoshop Microsoft Visual Studio — линейка продуктов компании Microsoft
Microsoft Visual Studio — линейка продуктов компании Microsoft Операторы цикла
Операторы цикла Понятие об информации. Представление информации. Информационная деятельность человека.
Понятие об информации. Представление информации. Информационная деятельность человека. Автоматизоване створення запитів у базі даних
Автоматизоване створення запитів у базі даних Архітектура операційних систем
Архітектура операційних систем Windows System Programming
Windows System Programming Личный кабинет
Личный кабинет Мир станочника. Аддитивные технологии и 3D-сканирование
Мир станочника. Аддитивные технологии и 3D-сканирование Методы и средства защиты программ от компьютерных вирусов
Методы и средства защиты программ от компьютерных вирусов 46_Yaroslavskaya_Sasha
46_Yaroslavskaya_Sasha Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6)
Локальные и глобальные сети ЭВМ. Защита информации в сетях. (Тема 6) Godseeker. Игра
Godseeker. Игра Рабочий стол. Управление компьютером с помощью мыши
Рабочий стол. Управление компьютером с помощью мыши Проектирование изделий из листового металла в NX
Проектирование изделий из листового металла в NX Эти люди изменили мир
Эти люди изменили мир Электронные ресурсы для детей и юношества в общедоступных библиотеках: создание и использование
Электронные ресурсы для детей и юношества в общедоступных библиотеках: создание и использование