Содержание
- 2. CLASSIFICATION OF ACCESS SYSTEMS AND NETWORKS (continuation) Lecture 2
- 3. The classification of AN can be done by the following features: - by the type of
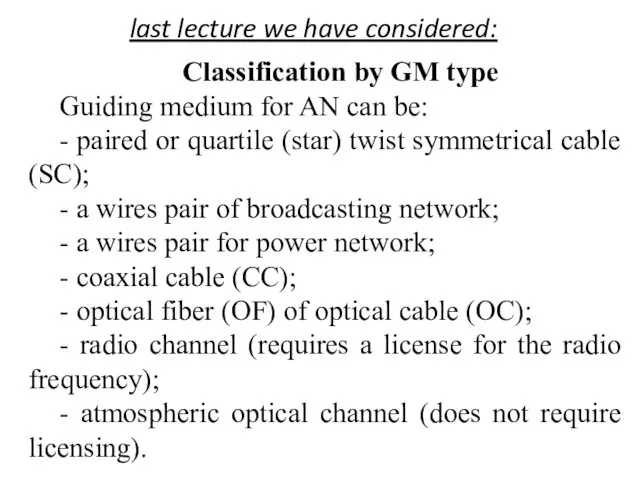
- 4. Classification by GM type Guiding medium for AN can be: - paired or quartile (star) twist
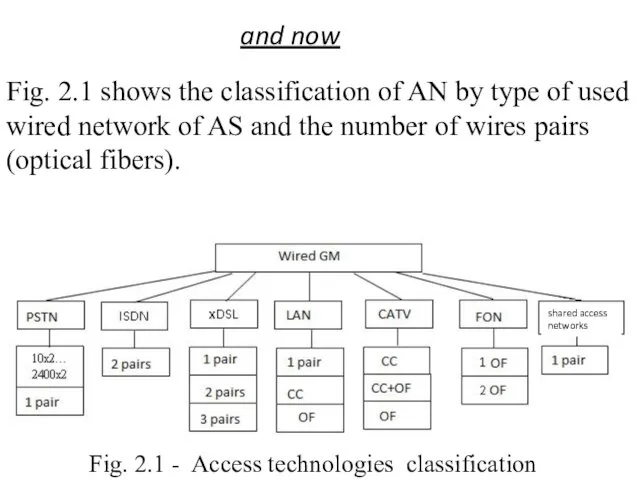
- 5. Fig. 2.1 shows the classification of AN by type of used wired network of AS and
- 6. Notes to Fig. 2.1: 1. In PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) cables with twisted pair conductors
- 7. 4. LAN - Local Area Network may be constructed on the basis of the special symmetrical
- 8. 6. In fiber optic networks optical fiber is used; 7. To shared access networks except the
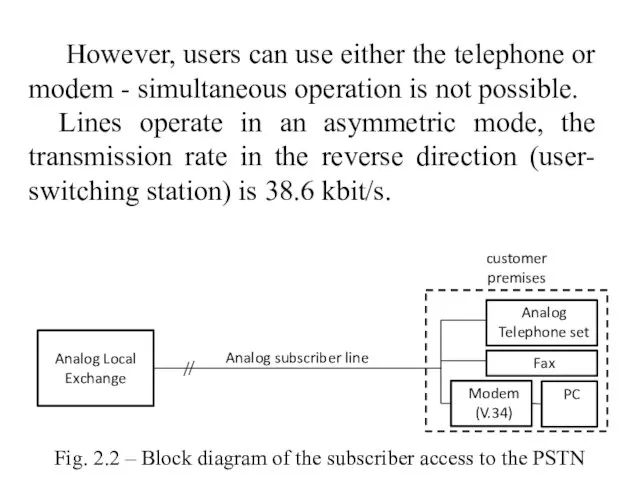
- 9. Narrowband access using the PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) Here, as the equipment located at the
- 10. However, users can use either the telephone or modem - simultaneous operation is not possible. Lines
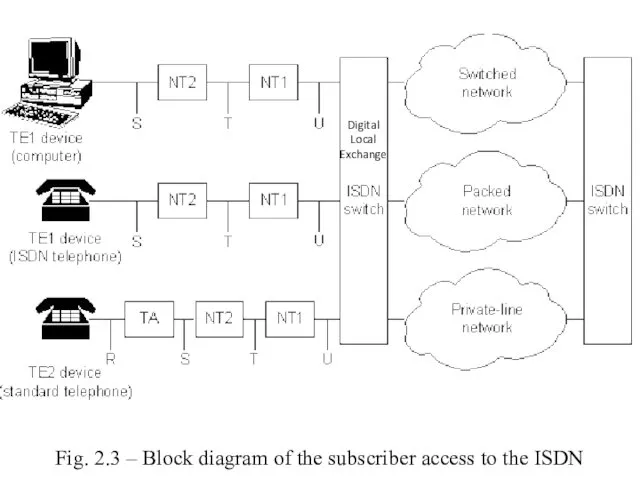
- 11. ISDN Access Technologies With such a standard two pairs of conductors are used, so they are
- 12. Fig. 2.3 – Block diagram of the subscriber access to the ISDN Digital Local Exchange
- 13. Broadband access technologies xDSL Simplex, half-duplex and full-duplex transmission of xDSL technologies are also different in
- 14. The majority of xDSL technology is a duplex, ie, transmission takes place in one pair in
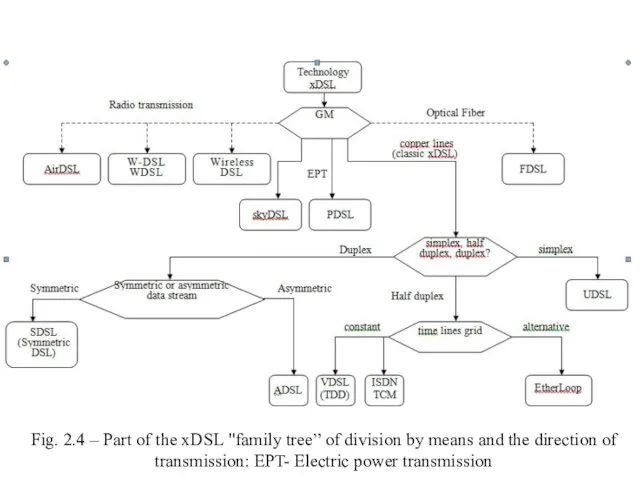
- 15. Fig. 2.4 – Part of the xDSL "family tree” of division by means and the direction
- 16. Classification by transmission rate in forward and reverse directions Duplex xDSL technology can be divided by
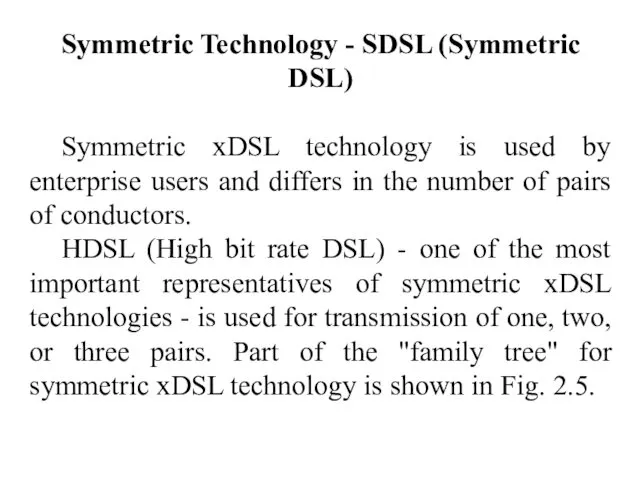
- 17. Symmetric Technology - SDSL (Symmetric DSL) Symmetric xDSL technology is used by enterprise users and differs
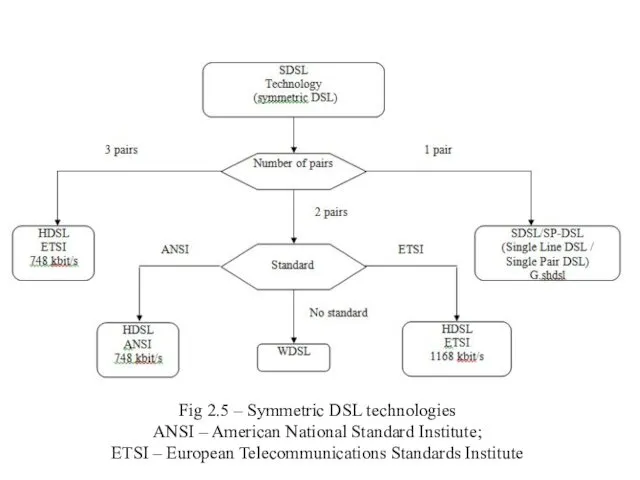
- 18. Fig 2.5 – Symmetric DSL technologies ANSI – American National Standard Institute; ETSI – European Telecommunications
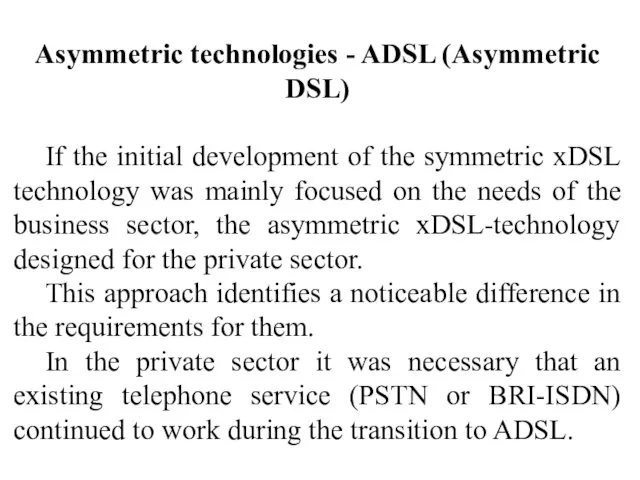
- 19. Asymmetric technologies - ADSL (Asymmetric DSL) If the initial development of the symmetric xDSL technology was
- 20. In other words, in addition to telephone services was necessary to provide data transfer. In order
- 22. Скачать презентацию







 Стандартизация ИТ
Стандартизация ИТ Ақпараттық технологиялардың математикалық негіздері
Ақпараттық технологиялардың математикалық негіздері Системы управления базами данных (СУБД) MS Access
Системы управления базами данных (СУБД) MS Access Информационные жанры в СМИ
Информационные жанры в СМИ Презентация бинарного урока информатика +экономикаДеньги3 класс
Презентация бинарного урока информатика +экономикаДеньги3 класс Codecraft PHP. PHP - PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor предварительный обработчик гипертекста. (Урок 1)
Codecraft PHP. PHP - PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor предварительный обработчик гипертекста. (Урок 1) Библиографическое описание источников информации
Библиографическое описание источников информации Топ-5 приложений для изучения иностранных языков для iOS и Android
Топ-5 приложений для изучения иностранных языков для iOS и Android 2010-2020 years in the world
2010-2020 years in the world Информатика. Формы информации по способу кодирования
Информатика. Формы информации по способу кодирования 27 ноября 2014 года. Районный конкурс Учитель года. Невский район. 8 класс. Логические операции Технологические этапы Фаза вызова Фаза осмысления содержания Фаза рефлексии Ход урока
27 ноября 2014 года. Районный конкурс Учитель года. Невский район. 8 класс. Логические операции Технологические этапы Фаза вызова Фаза осмысления содержания Фаза рефлексии Ход урока Использование динамически выделяемой памяти
Использование динамически выделяемой памяти Организация данных в базах данных
Организация данных в базах данных Новая функциональность
Новая функциональность Современные веб-технологии
Современные веб-технологии Команда если (неполное ветвление) 6 класс
Команда если (неполное ветвление) 6 класс HTML программирование
HTML программирование ECM-технологии интеграции информационных систем
ECM-технологии интеграции информационных систем Циклы с пред- и постусловием
Циклы с пред- и постусловием Нормализация баз данных
Нормализация баз данных Мәліметтер қоры (МҚ)
Мәліметтер қоры (МҚ) Архитектура персонального компьютера
Архитектура персонального компьютера Государственная система обеспечения информационной безопасности РФ. (Лекция 3)
Государственная система обеспечения информационной безопасности РФ. (Лекция 3) Контент-анализ: количественный и качественный
Контент-анализ: количественный и качественный Форматування даних в MS Excel
Форматування даних в MS Excel SOLID (single responsibility, openclosed, Liskov substitution, interface segregation, dependency inversion)
SOLID (single responsibility, openclosed, Liskov substitution, interface segregation, dependency inversion) Ensuring the security of information networks
Ensuring the security of information networks Нормализация базы данных
Нормализация базы данных