Содержание
- 2. Two Antennas got married - the wedding was lousy, but the reception was outstanding THINK ABOUT
- 3. Define computer bridges Explain the function of BIOS Distinguish among various CMOS setup utility options Troubleshoot
- 4. BIOS AND CMOS
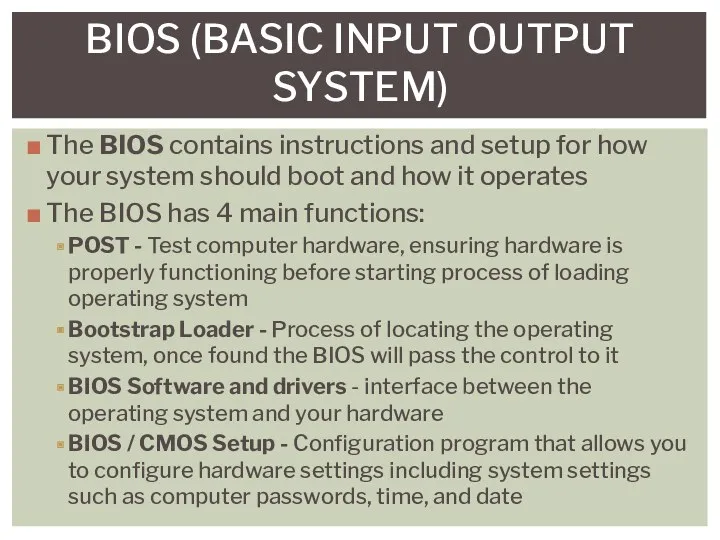
- 5. BIOS (BASIC INPUT OUTPUT SYSTEM) The BIOS contains instructions and setup for how your system should
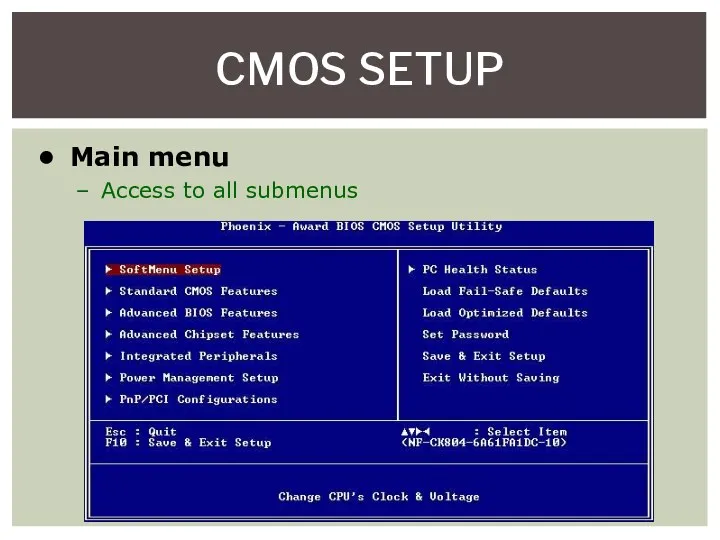
- 6. CMOS SETUP Main menu Access to all submenus
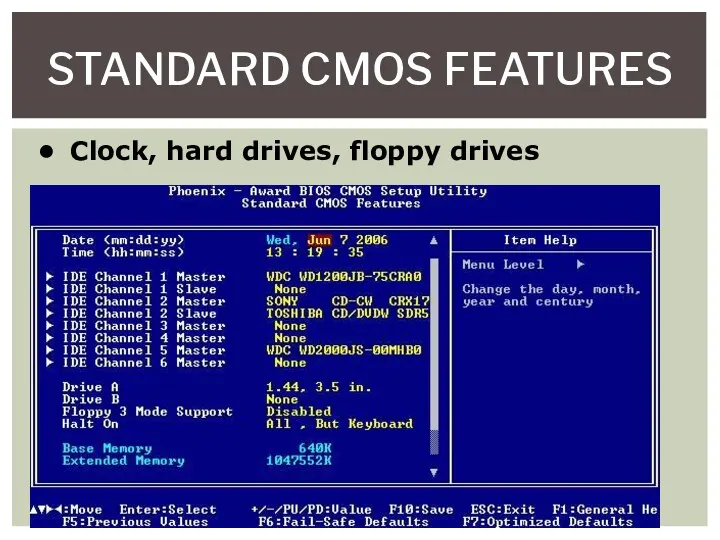
- 7. STANDARD CMOS FEATURES Clock, hard drives, floppy drives
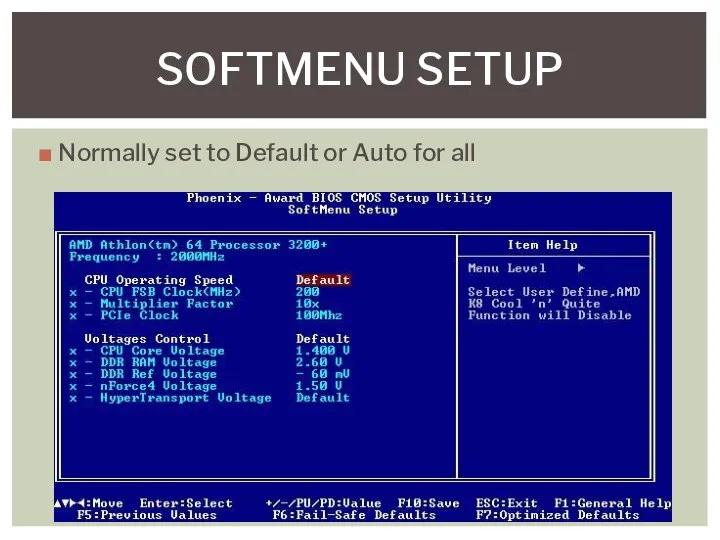
- 8. Normally set to Default or Auto for all SOFTMENU SETUP
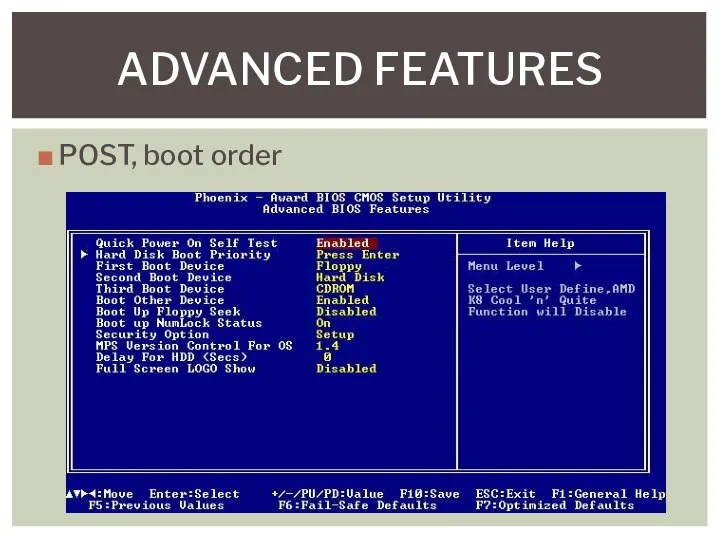
- 9. POST, boot order ADVANCED FEATURES
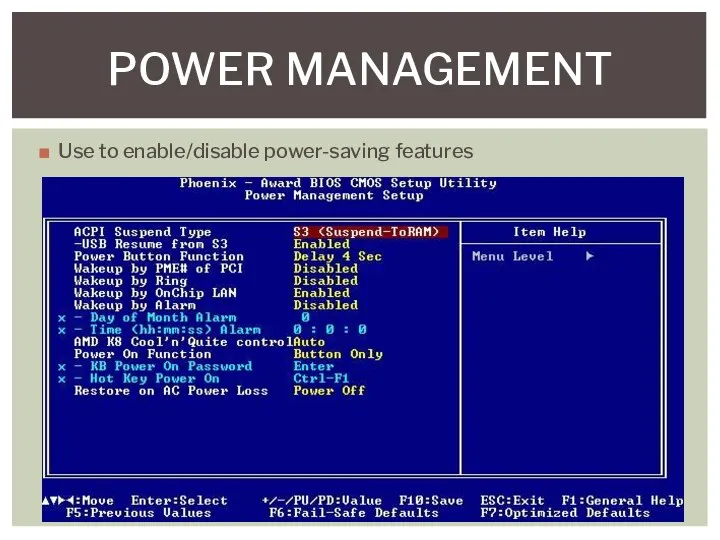
- 10. Use to enable/disable power-saving features POWER MANAGEMENT
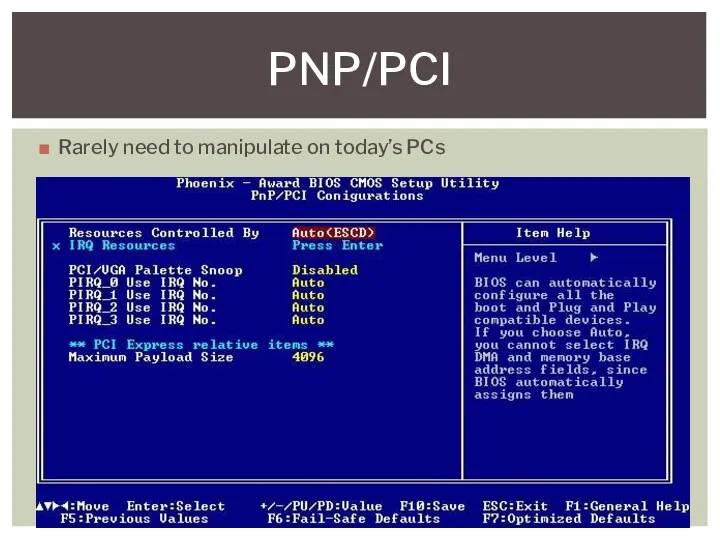
- 11. Rarely need to manipulate on today’s PCs PNP/PCI
- 12. The power-on self test (POST) is a special program stored on the ROM chip Initiated when
- 13. If video is determined to be missing or faulty One long beep followed by three short
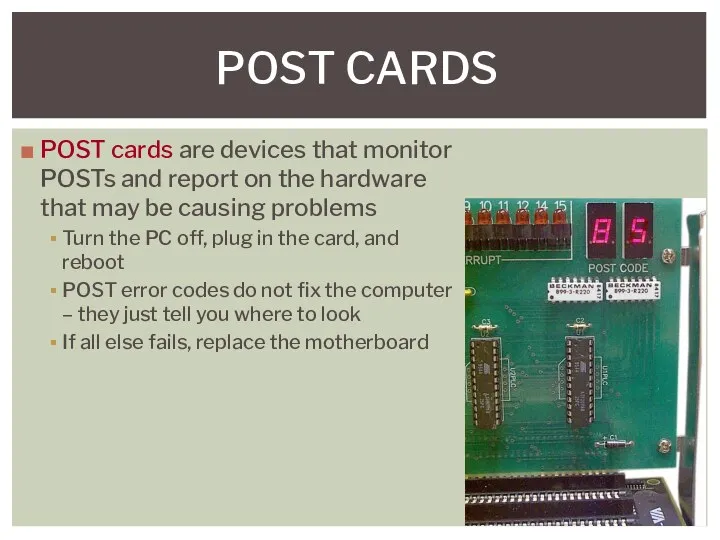
- 14. POST CARDS POST cards are devices that monitor POSTs and report on the hardware that may
- 15. UPDATING/FLASHING THE BIOS Flashing your BIOS to the latest release is crucial because it enhances your
- 16. To clear the CMOS settings, place the shunt on the CMOS jumper Resets to factory settings
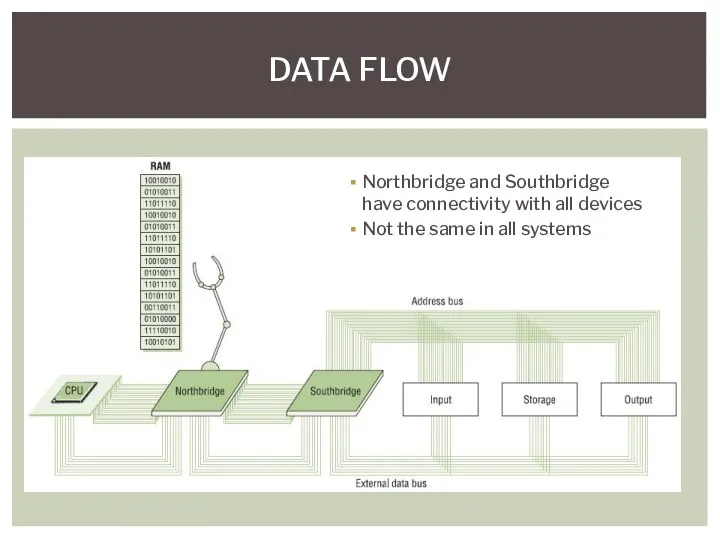
- 17. Data flows through the computer Between CPU and RAM Between CPU and video Between CPU and
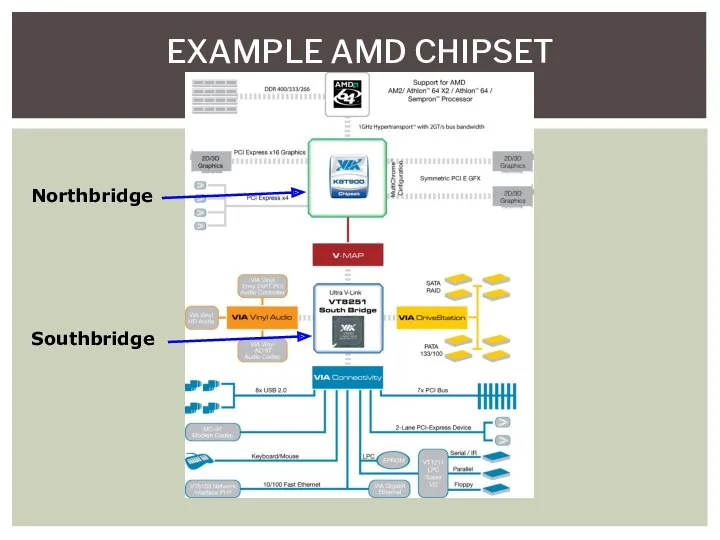
- 18. Northbridge Chip or chips that connect the CPU to video and/or memory Southbridge Handles all of
- 19. DATA FLOW Northbridge and Southbridge have connectivity with all devices Not the same in all systems
- 20. EXAMPLE AMD CHIPSET Northbridge Southbridge
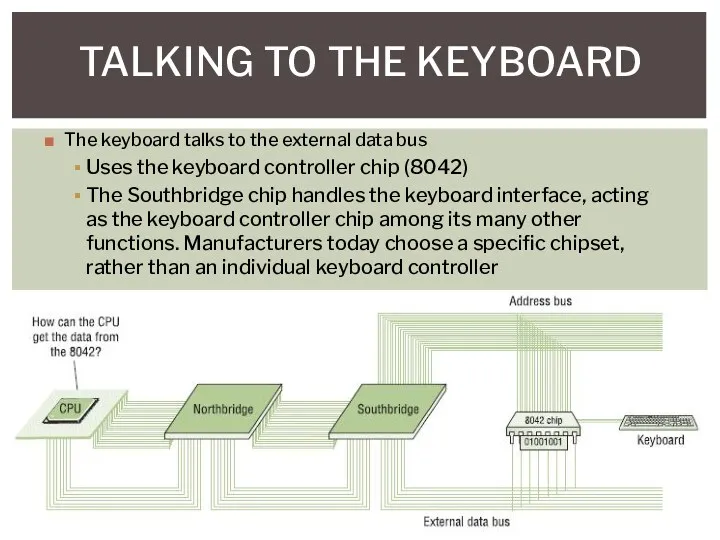
- 21. TALKING TO THE KEYBOARD The keyboard talks to the external data bus Uses the keyboard controller
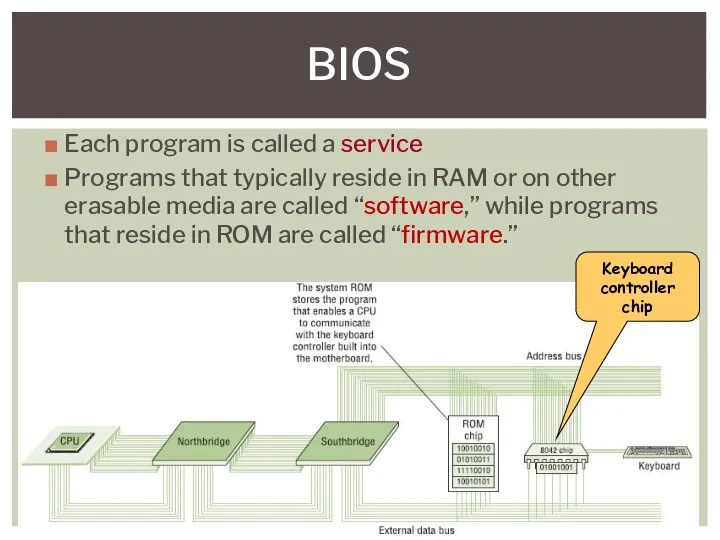
- 22. BIOS Each program is called a service Programs that typically reside in RAM or on other
- 23. BIOS Programs Non-volatile (stays same after power off) Can be changed by “flashing” Typically 64 K
- 24. Updating CMOS Updated via BIOS program Three primary BIOS brands American Megatrends (AMI), Award, Phoenix To
- 25. CMOS (COMPLEMENTARY METAL OXIDE SEMICONDUCTOR) The CMOS is powered by a CMOS battery and contains your
- 26. LOSING CMOS SETTINGS Common errors CMOS configuration mismatch CMOS date/time not set No boot device available
- 27. A PSU converts the 115-volt alternating current (AC) supplied by an electrical outlet into direct current
- 28. Every PSU in use today is either an AT or an ATX The main difference is
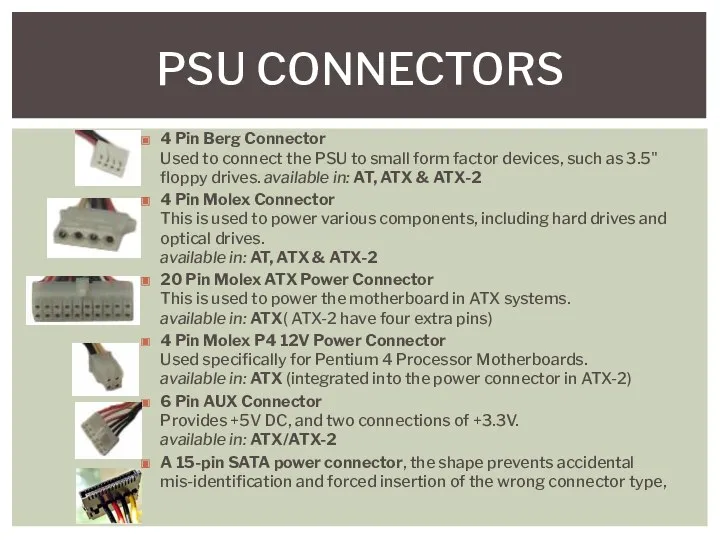
- 29. 4 Pin Berg Connector Used to connect the PSU to small form factor devices, such as
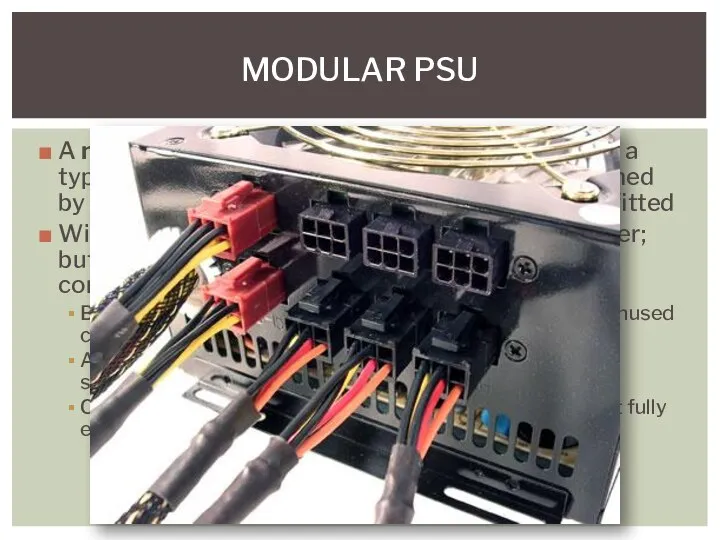
- 30. A modular power supply unit, abbreviated MPS, is a type of PSU with cables to powered
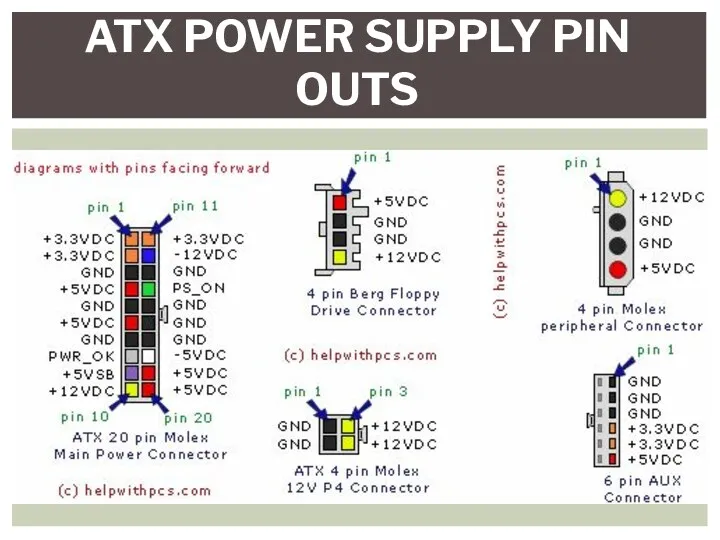
- 31. ATX POWER SUPPLY PIN OUTS
- 32. A multimeter measures electrical properties such as AC or DC voltage, current, and resistance Electricians and
- 33. A digital multimeter has an LCD screen that gives a straight forward decimal read out, while
- 34. THE PSU POWER ON TRICK First of all, find a paperclip and bend it to something
- 36. Скачать презентацию













 Множественное наследование. Лекция 18
Множественное наследование. Лекция 18 Справочные издания
Справочные издания Представления (VIEW). Лабораторная работа 7
Представления (VIEW). Лабораторная работа 7 Системы счисления. Представление чисел в компьютере
Системы счисления. Представление чисел в компьютере Эволюция операционных систем
Эволюция операционных систем Дерево целей - как метод исследования
Дерево целей - как метод исследования Этапы развития вычислительной техники в период 60-х – 70-х
Этапы развития вычислительной техники в период 60-х – 70-х Основные понятия криптографической защиты. Симметричные алгоритмы шифрования
Основные понятия криптографической защиты. Симметричные алгоритмы шифрования Стандартные программы Windows 7. (Лекция 7)
Стандартные программы Windows 7. (Лекция 7) Основные принципы работы в программе Cisco Packet Tracer
Основные принципы работы в программе Cisco Packet Tracer Архитектура крупных систем информационного обеспечения
Архитектура крупных систем информационного обеспечения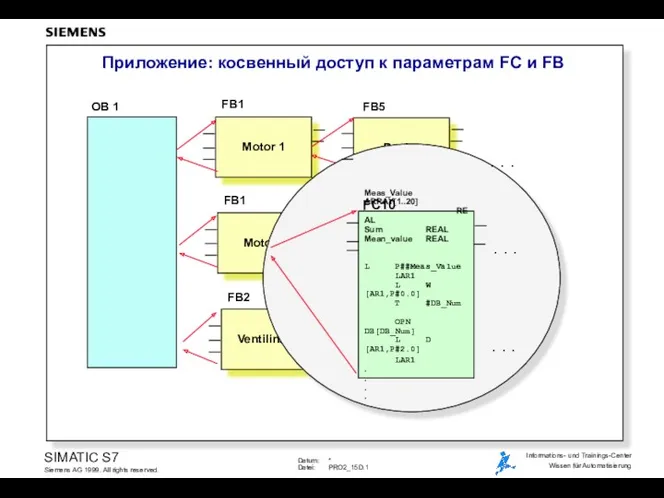 Приложение: косвенный доступ к параметрам FC и FB
Приложение: косвенный доступ к параметрам FC и FB презентация к уроку Глобальная компьютерная сеть Интернет
презентация к уроку Глобальная компьютерная сеть Интернет Оптимізація топології гетерогенної комп’ютерної мережі навчального закладу
Оптимізація топології гетерогенної комп’ютерної мережі навчального закладу Средства коммуникационной техники. Средства и системы телефонной связи
Средства коммуникационной техники. Средства и системы телефонной связи Влияние современных СМИ на молодёжь
Влияние современных СМИ на молодёжь Розвиток інформатики в Україні
Розвиток інформатики в Україні Урок по теме Устройства компьютера
Урок по теме Устройства компьютера Основные понятия и задачи моделирования процессов и систем
Основные понятия и задачи моделирования процессов и систем Структура компьютера. Понятие вычислительной системы
Структура компьютера. Понятие вычислительной системы Основы гидродинамического моделирования
Основы гидродинамического моделирования Классификация программного обеспечения
Классификация программного обеспечения Кибербезопасность для младших школьников
Кибербезопасность для младших школьников Язык PHP
Язык PHP Введение в SDH
Введение в SDH Библиотеки PID_Regulators и PID_Reg2. Программные ПИД-регуляторы (на примере пакета CoDeSys)
Библиотеки PID_Regulators и PID_Reg2. Программные ПИД-регуляторы (на примере пакета CoDeSys) Как найти информацию о стажировках
Как найти информацию о стажировках Понятие сетевой модели. Сетевая модель OSI. (Тема 8)
Понятие сетевой модели. Сетевая модель OSI. (Тема 8)