Содержание
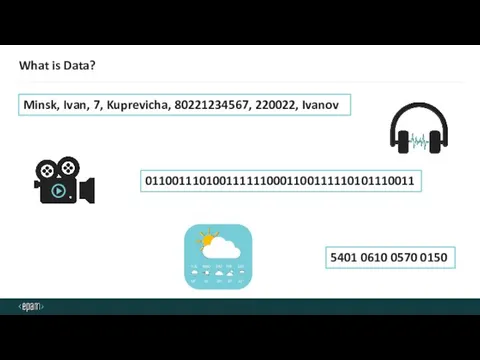
- 2. What is Data? Minsk, Ivan, 7, Kuprevicha, 80221234567, 220022, Ivanov 5401 0610 0570 0150 0110011101001111110001100111110101110011
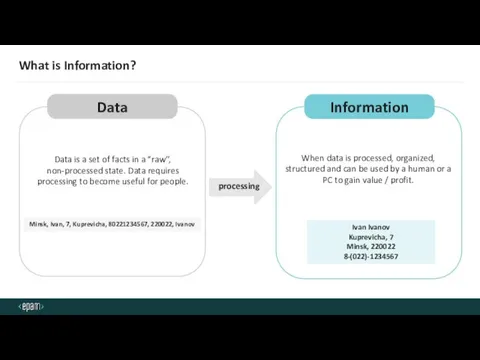
- 3. What is Information?
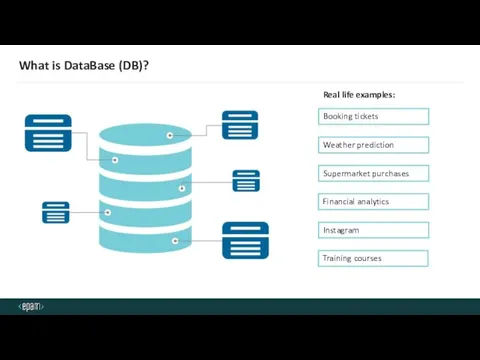
- 4. What is DataBase (DB)? Real life examples: Financial analytics Weather prediction Training courses Supermarket purchases Booking
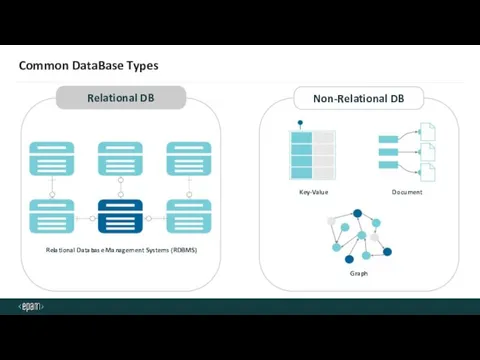
- 5. Common DataBase Types
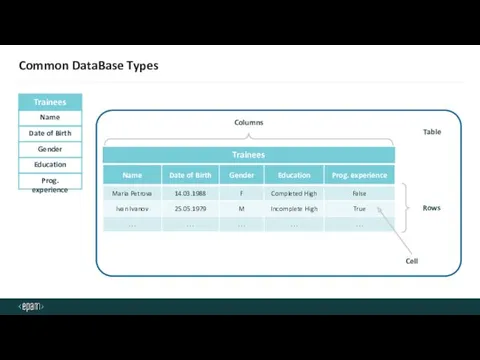
- 6. Common DataBase Types Date of Birth Gender Education Prog. experience Trainees Trainees Columns Rows Table Cell
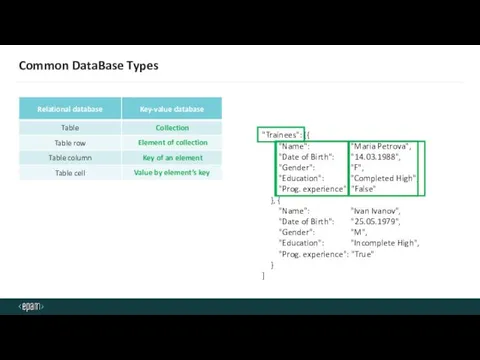
- 7. Common DataBase Types Collection Element of collection Key of an element Value by element’s key "Trainees":
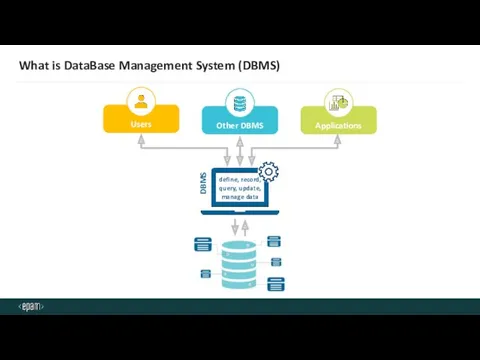
- 8. What is DataBase Management System (DBMS)
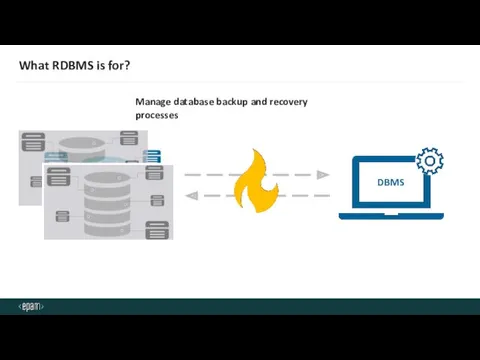
- 9. What RDBMS is for? Manage database backup and recovery processes
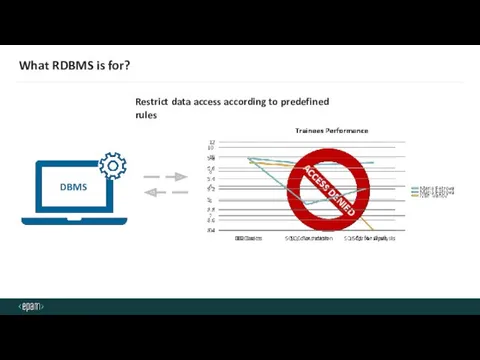
- 10. What RDBMS is for? Restrict data access according to predefined rules
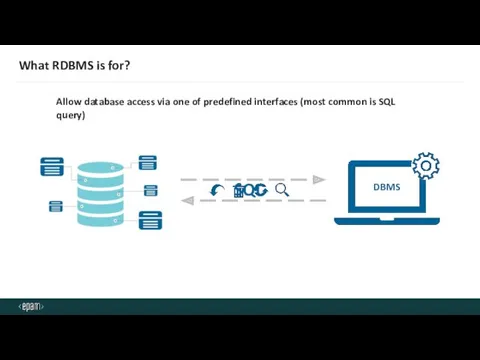
- 11. What RDBMS is for? Allow database access via one of predefined interfaces (most common is SQL
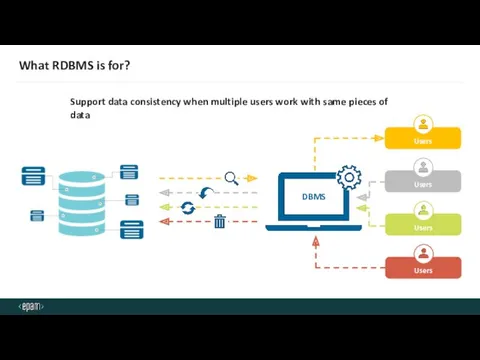
- 12. What RDBMS is for? Support data consistency when multiple users work with same pieces of data
- 13. DB Components DB Basics
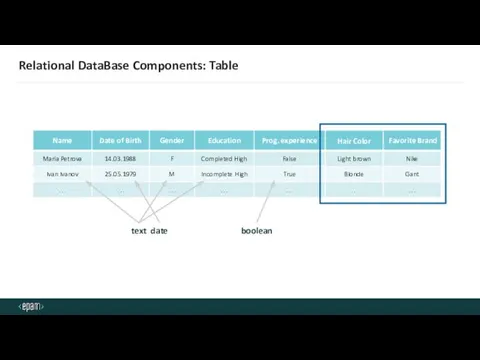
- 14. Relational DataBase Components: Table text boolean date
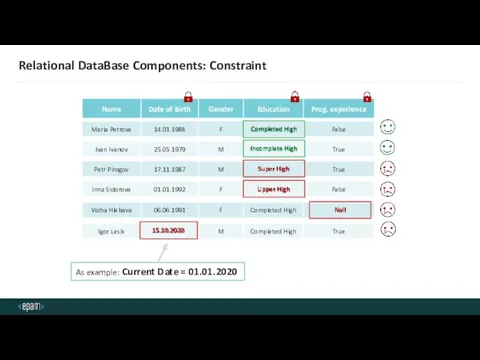
- 15. Relational DataBase Components: Constraint Completed High Completed High Incomplete High Incomplete High Super High Super High
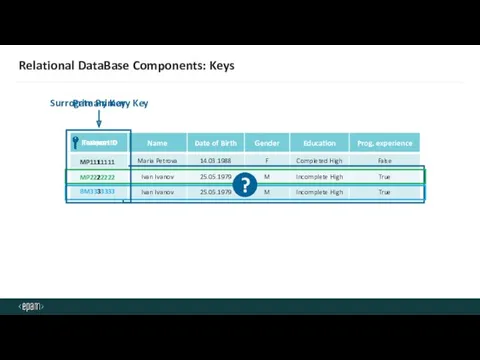
- 16. Relational DataBase Components: Keys MP2222222 BM3333333 MP1111111 Primary Key 1 2 3 PassportID TraineesID Surrogate Primary
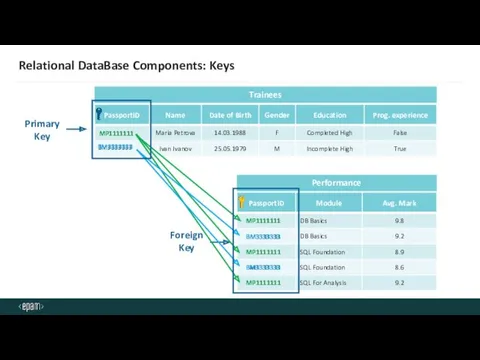
- 17. Relational DataBase Components: Keys Primary Key Foreign Key MP1111111 BM3333333 MP1111111 BM3333333 MP1111111 MP1111111 MP1111111 BM3333333
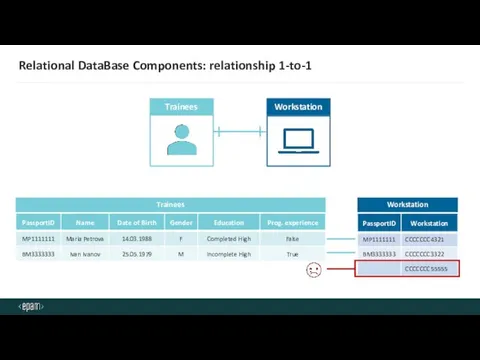
- 18. Relational DataBase Components: relationship 1-to-1 Trainees Workstation
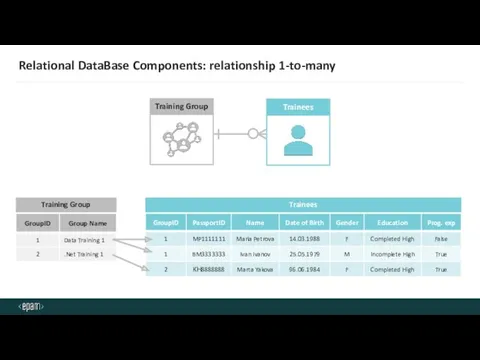
- 19. Relational DataBase Components: relationship 1-to-many Trainees Training Group
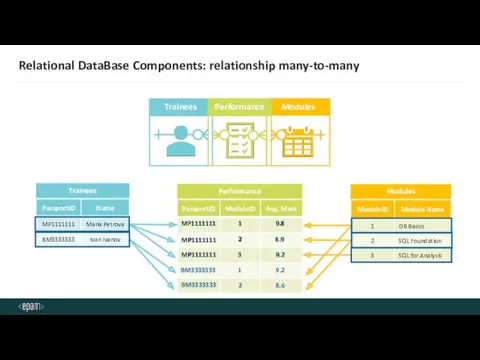
- 20. Relational DataBase Components: relationship many-to-many Trainees Modules Performance MP1111111 BM3333333 1 9.8 8.9 9.2 9.2 8.6
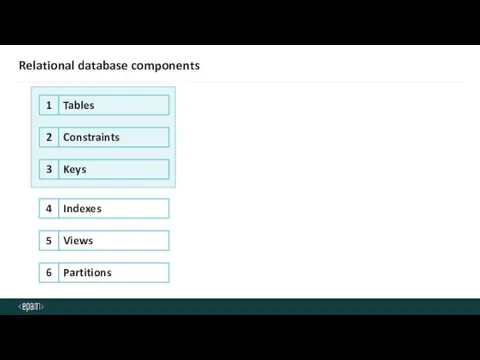
- 21. Relational database components 1 Indexes 4 Views 5 Partitions 6 Constraints Keys Tables 2 3
- 22. DB Modeling DB Basics
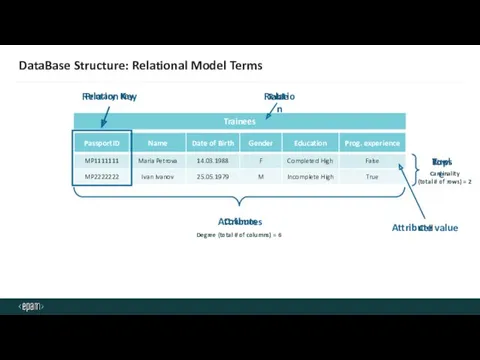
- 23. DataBase Structure: Relational Model Terms Trainees Columns Rows Table Cell Relation Cardinality (total # of rows)
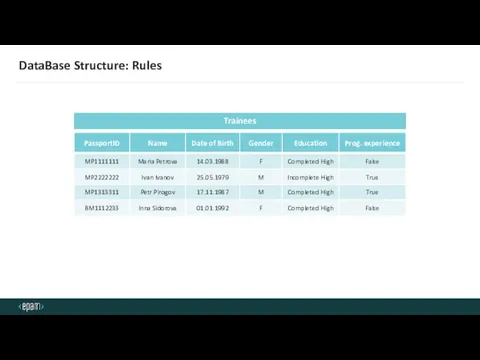
- 24. DataBase Structure: Rules Trainees
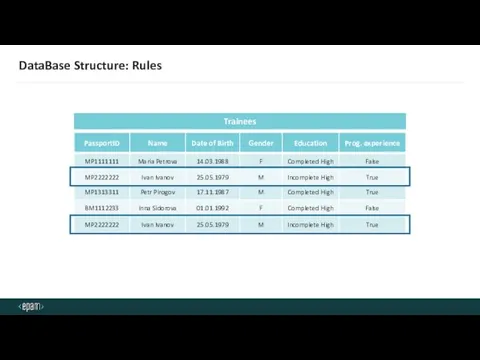
- 25. DataBase Structure: Rules Trainees
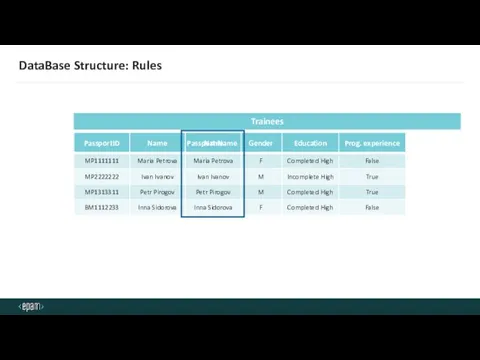
- 26. DataBase Structure: Rules Trainees Trainees Passport Name Name
- 27. DataBase Structure: Rules Trainings Participations Trainings Participations
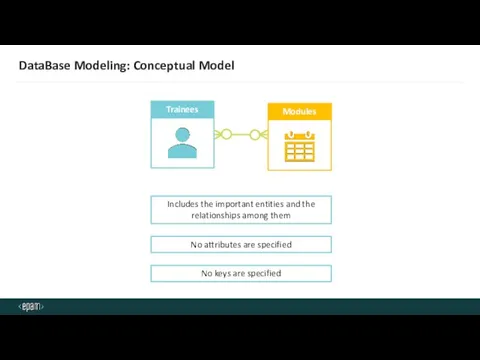
- 28. DataBase Modeling: Conceptual Model No attributes are specified No keys are specified Includes the important entities
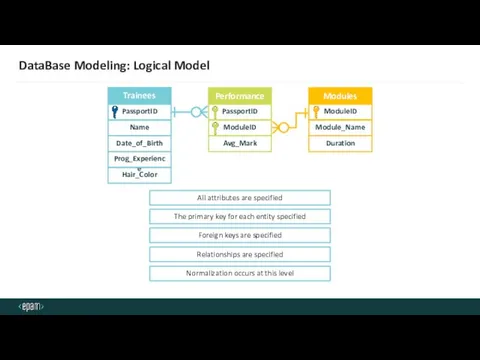
- 29. DataBase Modeling: Logical Model Name Date_of_Birth Prog_Experience Hair_Color Trainees PassportID Module_Name Duration Modules ModuleID ModuleID Avg_Mark
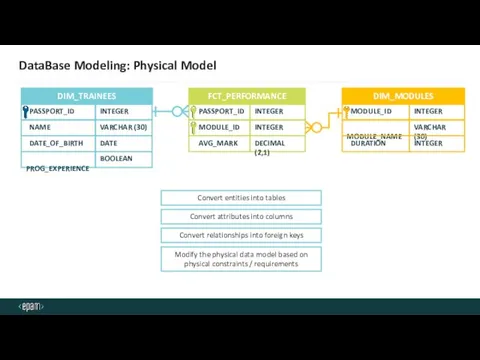
- 30. DATE DataBase Modeling: Physical Model NAME DATE_OF_BIRTH PROG_EXPERIENCE DIM_TRAINEES PASSPORT_ID MODULE_NAME DURATION DIM_MODULES MODULE_ID MODULE_ID AVG_MARK
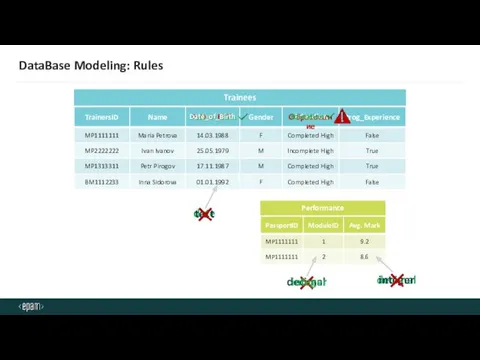
- 31. DataBase Modeling: Rules Trainees Образование Education Date of Birth Date of Birth date text Date_of_Birth Performance
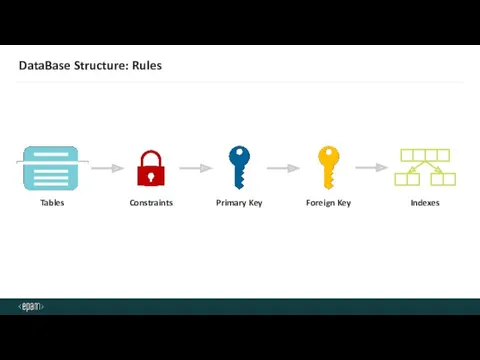
- 32. DataBase Structure: Rules
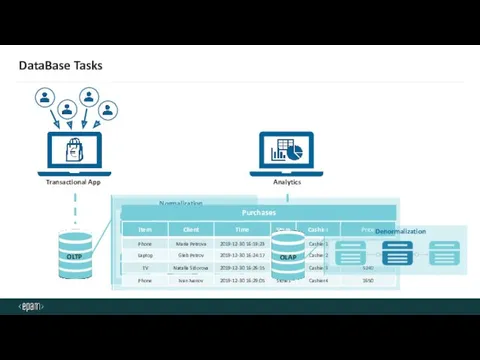
- 33. DataBase Tasks Purchases Transactional App OLTP OLAP
- 34. Normalization DB Basics
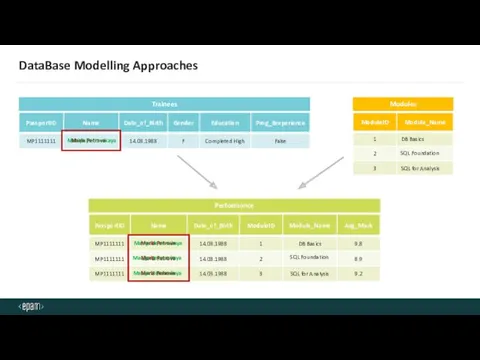
- 35. DataBase Modelling Approaches Trainees Modules Performance Maria Petrova Maria Petrova Maria Petrova Maria Petrova SQL Foundation
- 36. Conversion to 1NF Trainees Trainees
- 37. Conversion from 1NF to 2NF
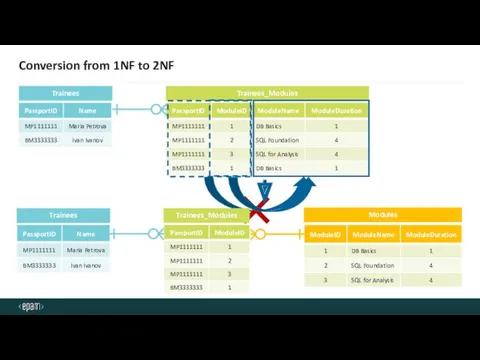
- 38. Conversion from 1NF to 2NF Trainees Trainees_Modules Modules Trainees Trainees_Modules
- 39. Conversion from 2NF to 3NF
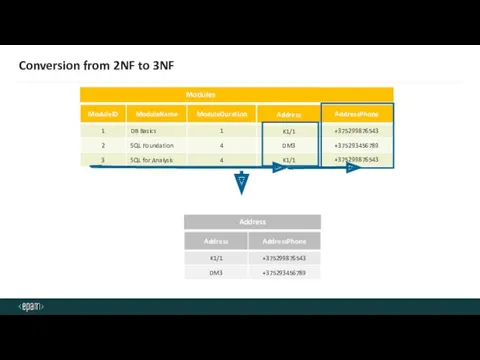
- 40. Conversion from 2NF to 3NF Modules Modules Address
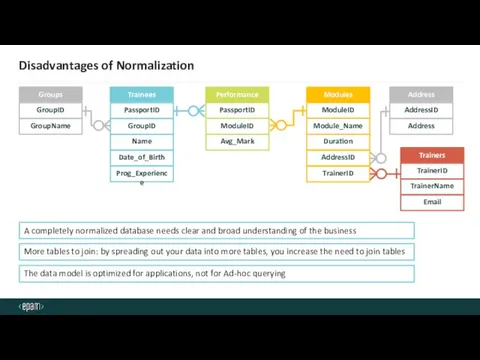
- 41. Disadvantages of Normalization GroupID Name Date_of_Birth Prog_Experience Trainees PassportID Module_Name Duration Modules ModuleID ModuleID Avg_Mark Performance
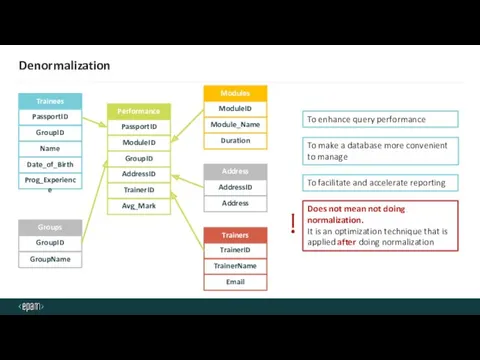
- 42. Denormalization GroupID Name Date_of_Birth Prog_Experience Trainees PassportID Module_Name Duration Modules ModuleID ModuleID GroupID Performance PassportID GroupName
- 44. Скачать презентацию





 Единицы измерения информации
Единицы измерения информации Освещение и камеры в Blender
Освещение и камеры в Blender Информационная безопасность предприятия
Информационная безопасность предприятия Анимации в презентации
Анимации в презентации 3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный)
3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный) Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома)
Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома) Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики
Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики Распределенные вычисления в Интернет
Распределенные вычисления в Интернет HTML/ CSS Base
HTML/ CSS Base Разработка и эксплуатация АИС
Разработка и эксплуатация АИС Getting more physical in Call of Duty
Getting more physical in Call of Duty Коллекции Python
Коллекции Python Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей
Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии
Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии 9 класс. Алгоритмизация.
9 класс. Алгоритмизация. История развития Интернета
История развития Интернета Service Tool
Service Tool Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия
Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2)
Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2) Искусственный интеллект
Искусственный интеллект Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных
Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных Теория нейронных сетей
Теория нейронных сетей Интернет в работе переводчика
Интернет в работе переводчика Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа
Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word
Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы
MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы Поняття про мультимедіа
Поняття про мультимедіа Independent Component Analysis
Independent Component Analysis