Содержание
- 2. Learning objectives describe relational databases and their use use the terms attribute, entity, index record, table
- 3. Success criteria knows and understands the purpose of using the database can provide examples of the
- 4. A database is a collection of information that is organized so that it can be easily
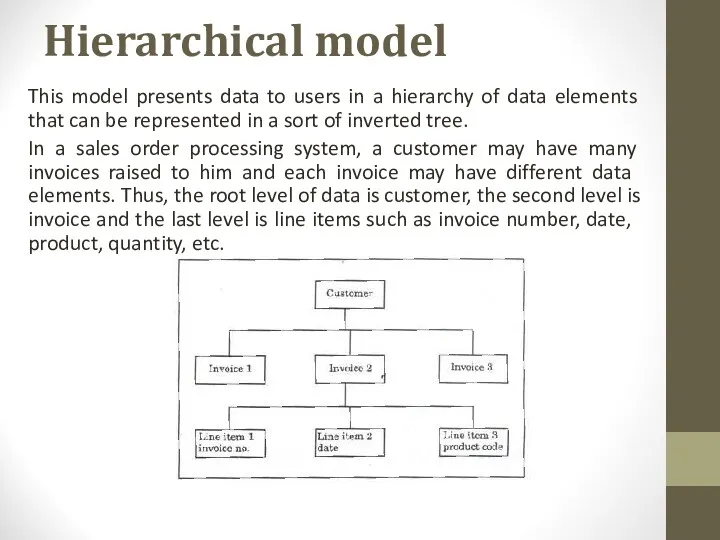
- 5. Hierarchical model This model presents data to users in a hierarchy of data elements that can
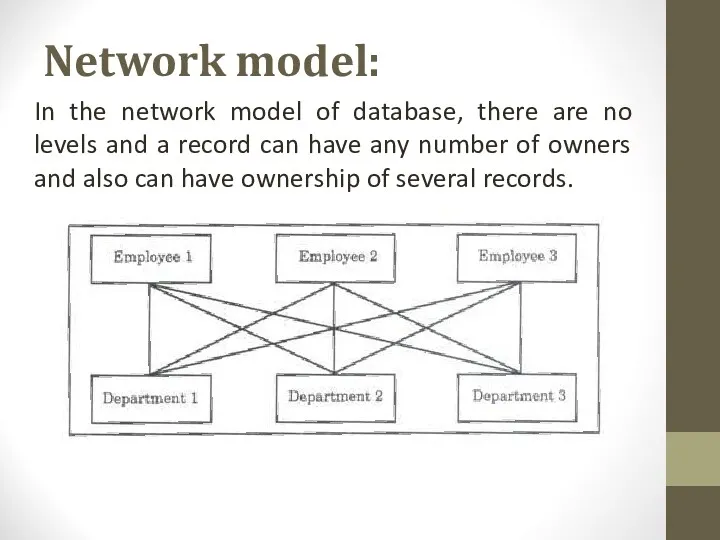
- 6. Network model: In the network model of database, there are no levels and a record can
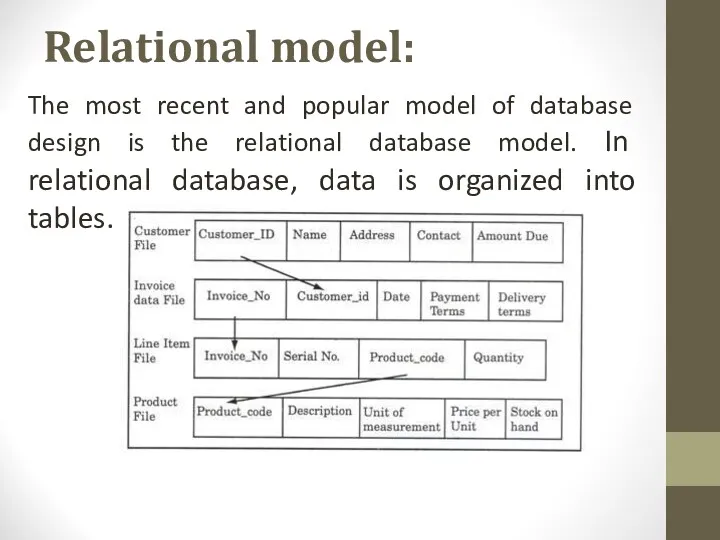
- 7. Relational model: The most recent and popular model of database design is the relational database model.
- 8. Main database objects Tables – Data collection objects Queries – Questions of your data Forms –
- 9. Main objects Field (attribute): a single piece of information. Could be a name, or a number.
- 10. MySQL is an open source relational database management system (RDBMS) based on Structured Query Language (SQL).
- 11. SQL Commands: SQL commands are instructions, coded into SQL statements, which are used to communicate with
- 12. Data Definition Language (DDL) - These SQL commands are used for creating, modifying, and dropping the
- 13. Transaction Control Language (TCL) - These SQL commands are used for managing changes affecting the data.
- 14. SQL Create DataBase CREATE DATABASE database_name SQL Alter DataBase The ALTER DATABASE Statement is used to
- 15. SQL CREATE TABLE CREATE TABLE table_name (column_name1 datatype, column_name2 datatype, ... column_nameN datatype ); CREATE TABLE
- 16. SQL ALTER TABLE Statement The SQL ALTER TABLE command is used to modify the definition (structure)
- 17. Local server XAMPP XAMPP is a free and open source cross-platform web server solution stack package
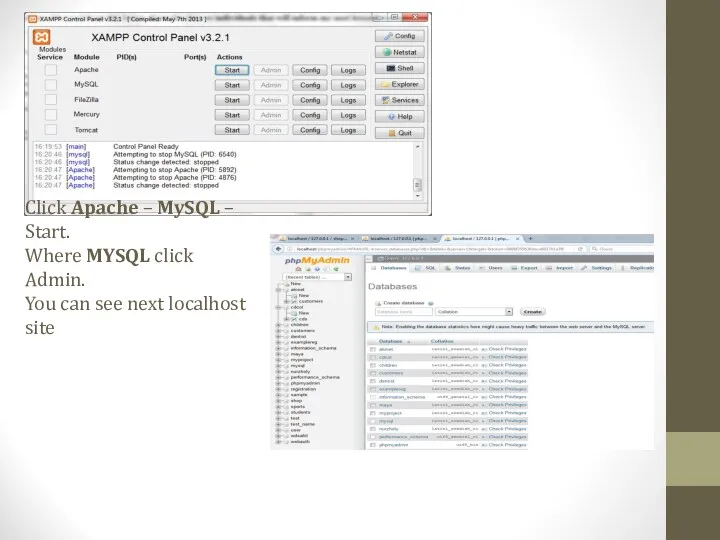
- 18. Click Apache – MySQL – Start. Where MYSQL click Admin. You can see next localhost site
- 20. Скачать презентацию












 Единицы измерения информации
Единицы измерения информации Освещение и камеры в Blender
Освещение и камеры в Blender Информационная безопасность предприятия
Информационная безопасность предприятия Анимации в презентации
Анимации в презентации 3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный)
3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный) Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома)
Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома) Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики
Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики Распределенные вычисления в Интернет
Распределенные вычисления в Интернет HTML/ CSS Base
HTML/ CSS Base Разработка и эксплуатация АИС
Разработка и эксплуатация АИС Getting more physical in Call of Duty
Getting more physical in Call of Duty Коллекции Python
Коллекции Python Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей
Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии
Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии 9 класс. Алгоритмизация.
9 класс. Алгоритмизация. История развития Интернета
История развития Интернета Service Tool
Service Tool Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия
Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2)
Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2) Искусственный интеллект
Искусственный интеллект Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных
Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных Теория нейронных сетей
Теория нейронных сетей Интернет в работе переводчика
Интернет в работе переводчика Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа
Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word
Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы
MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы Поняття про мультимедіа
Поняття про мультимедіа Independent Component Analysis
Independent Component Analysis