Содержание
- 2. Contents Introduction to structured exception handling Construct «try..catch» «Exception» class and exception hierarchy in.NET Framework Exception
- 3. 1. Introduction to structured exception handling
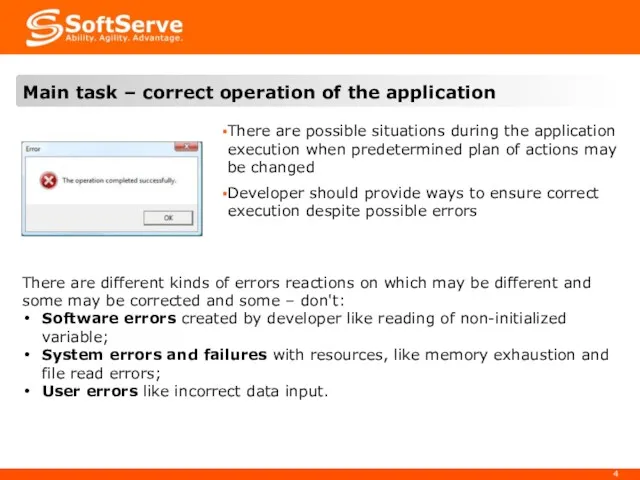
- 4. There are possible situations during the application execution when predetermined plan of actions may be changed
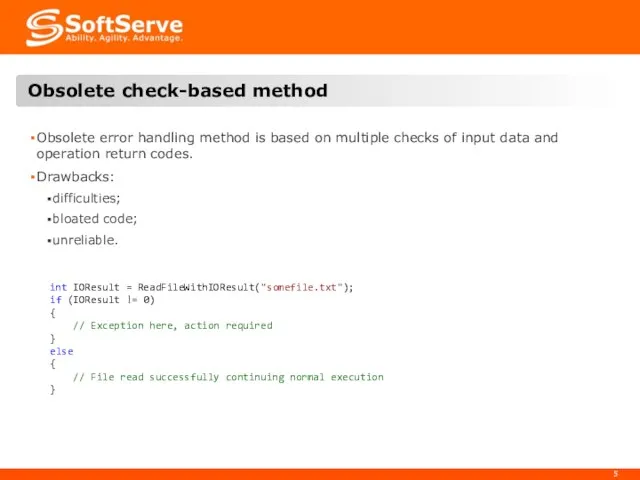
- 5. Obsolete error handling method is based on multiple checks of input data and operation return codes.
- 6. Modern way to handle errors provides using of special mechanism – structured exception handling which is
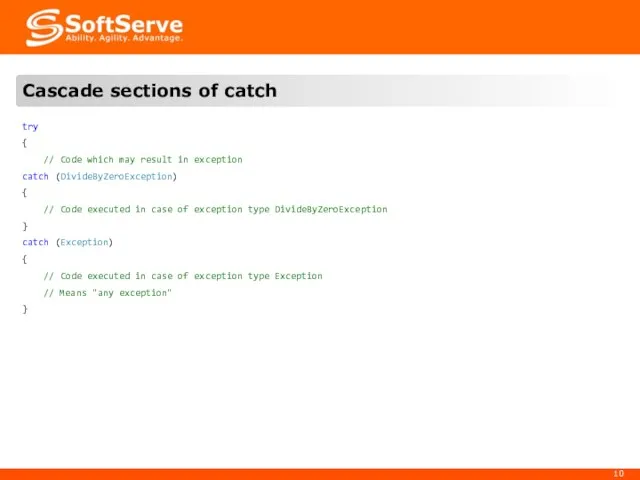
- 7. 2. Construct «try..catch»
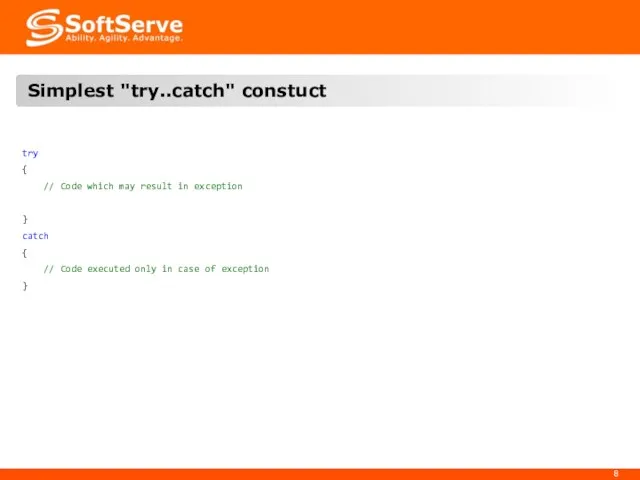
- 8. try { // Code which may result in exception } catch { // Code executed only
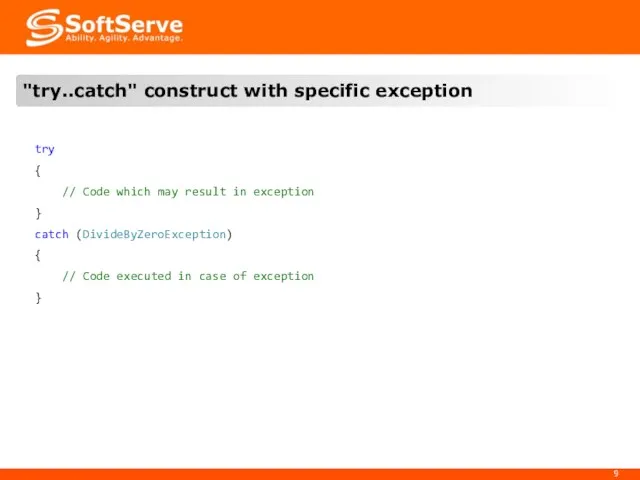
- 9. try { // Code which may result in exception } catch (DivideByZeroException) { // Code executed
- 10. try { // Code which may result in exception catch (DivideByZeroException) { // Code executed in
- 11. "try..catch" construct with instance of exception try { // Code which may result in exception }
- 12. 3. «Exception» class and exception hierarchy in.NET Framework
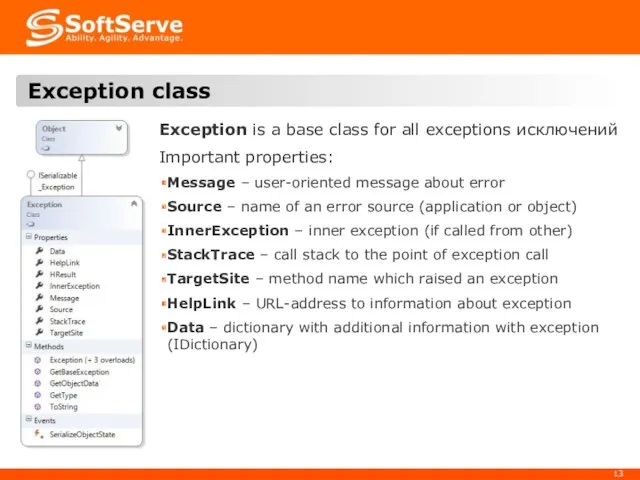
- 13. Exception is a base class for all exceptions исключений Important properties: Message – user-oriented message about
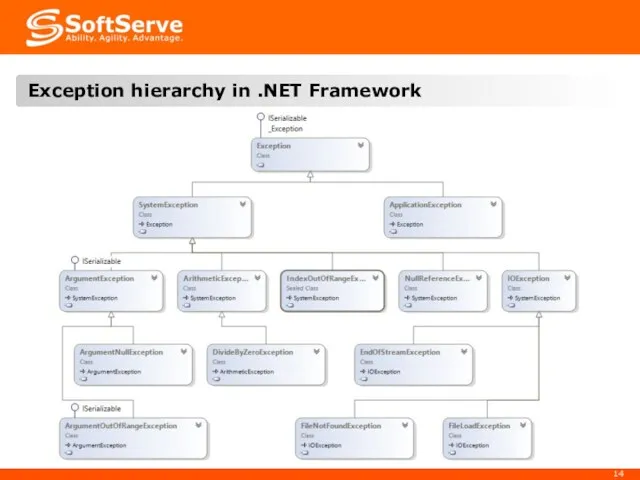
- 14. Exception hierarchy in .NET Framework
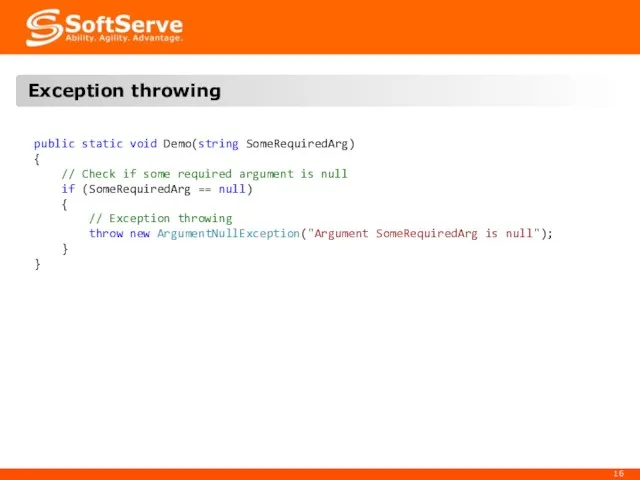
- 15. 4. Exception throwing and re-rising
- 16. Exception throwing public static void Demo(string SomeRequiredArg) { // Check if some required argument is null
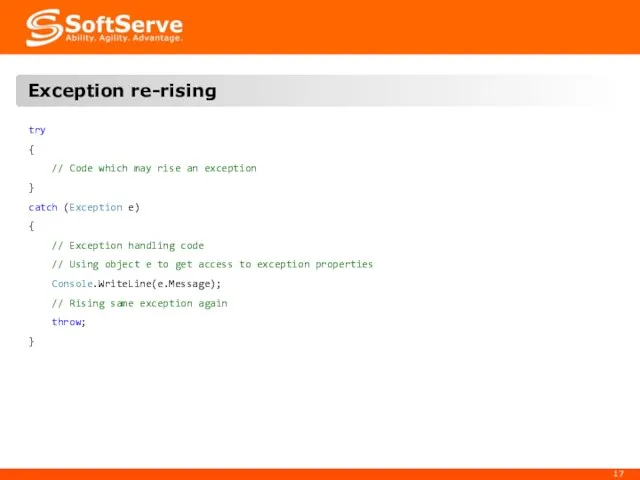
- 17. Exception re-rising try { // Code which may rise an exception } catch (Exception e) {
- 18. 5. Creating own exceptions
- 19. Exception declaration class SampleException: ApplicationException { }; It is recommended to create own exceptions based on
- 20. MSDN recommendations for exception declarations Minimal possible declaration for exception declaration described in MSDN requires use
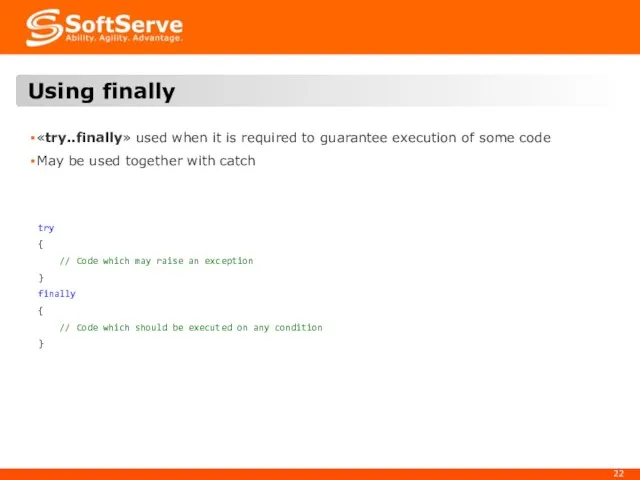
- 21. 6. Construct «try..finally»
- 22. «try..finally» used when it is required to guarantee execution of some code May be used together
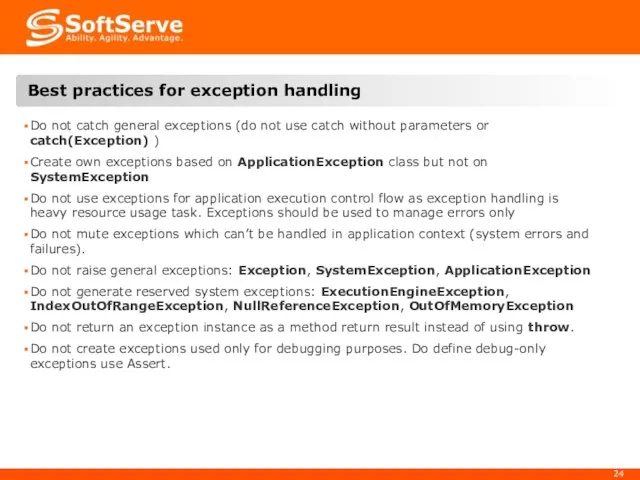
- 23. 7. Best practices for exception handling
- 24. Do not catch general exceptions (do not use catch without parameters or catch(Exception) ) Create own
- 25. MSDN recommendations for creating exceptions: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms173163.aspx MSDN recommendation for exception generation: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms182338.aspx Full hierarchy of Microsoft
- 27. Скачать презентацию












 Гайд по настройке и использованию SSH - Secure Shell, сетевой протокол
Гайд по настройке и использованию SSH - Secure Shell, сетевой протокол Создание веб приложения Music Manager
Создание веб приложения Music Manager Компьютерные технологии на службе криминалистики
Компьютерные технологии на службе криминалистики Базовое Администрирование Linux
Базовое Администрирование Linux Збереження інформації
Збереження інформації Обобщенная линейная модель множественной регрессии с гетероскедастичными остатками. Лекция 8
Обобщенная линейная модель множественной регрессии с гетероскедастичными остатками. Лекция 8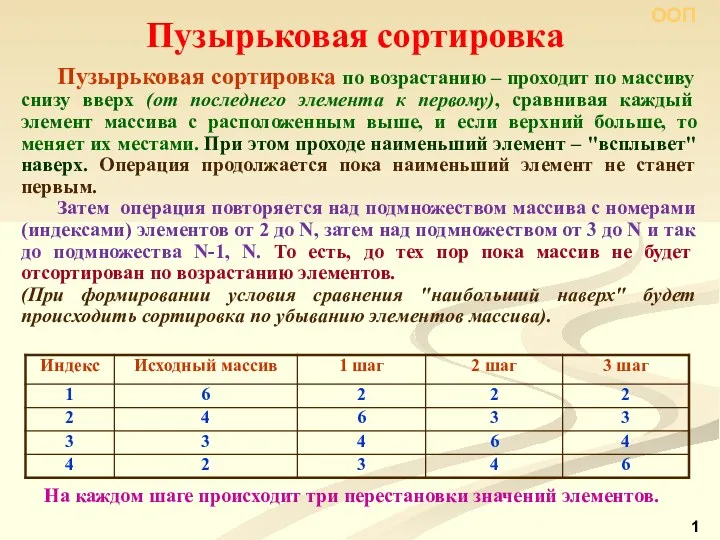 Пузырьковая сортировка
Пузырьковая сортировка Облачные технологии
Облачные технологии Четыре основных принципа объектно-ориентированного программирования
Четыре основных принципа объектно-ориентированного программирования Персональные компьютеры
Персональные компьютеры Методы сортировки и поиска
Методы сортировки и поиска Процедурные расширения SQL. Хранимые процедуры и триггеры
Процедурные расширения SQL. Хранимые процедуры и триггеры Классификация программных продуктов
Классификация программных продуктов Welcome. Anti-virus
Welcome. Anti-virus Антивирусные программы
Антивирусные программы Сеть Ethernet. Построение коммутируемой сети
Сеть Ethernet. Построение коммутируемой сети Кейс сервисов Веб 2.0
Кейс сервисов Веб 2.0 Структура сайта школьного музея
Структура сайта школьного музея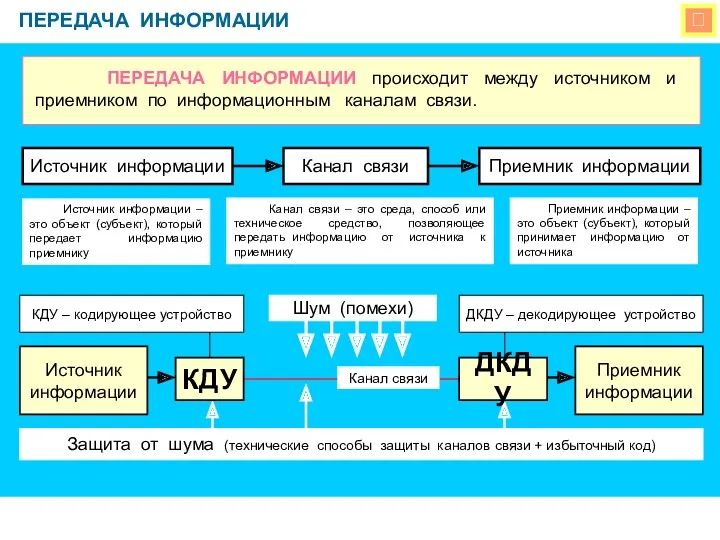 Передача информации.
Передача информации. Практическое применение 3D-моделирования
Практическое применение 3D-моделирования Справочно-библиографический аппарат Колмовской библиотеки, Великий Новгород
Справочно-библиографический аппарат Колмовской библиотеки, Великий Новгород Анализ данных в реляционных БД на примере СУБД MS Access. Создание запросов, изменяющих таблицы. Создание отчетов
Анализ данных в реляционных БД на примере СУБД MS Access. Создание запросов, изменяющих таблицы. Создание отчетов Команди для малювання в середовищі Scratch
Команди для малювання в середовищі Scratch Устройство компьютера
Устройство компьютера Безопасность систем баз данных. Обеспечение целостности
Безопасность систем баз данных. Обеспечение целостности Расширенный алгоритм Евклида. Разбор задач
Расширенный алгоритм Евклида. Разбор задач Программирование на языке C++
Программирование на языке C++ Информационная система Недра
Информационная система Недра