Содержание
- 2. Network “ ... communication system for connecting end-systems” End-systems a.k.a. “hosts” PCs, workstations dedicated computers network
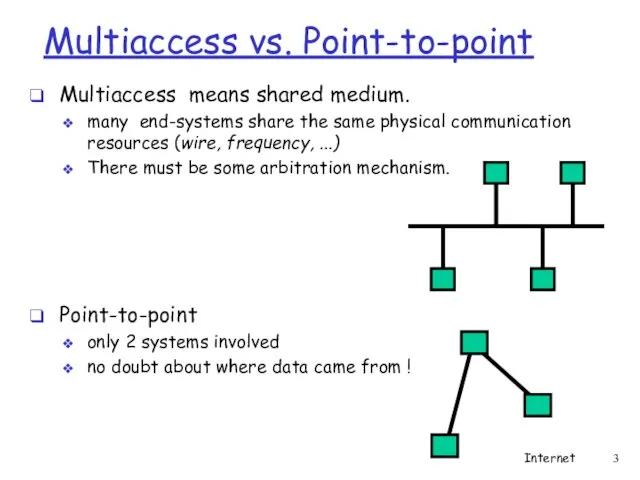
- 3. Multiaccess vs. Point-to-point Multiaccess means shared medium. many end-systems share the same physical communication resources (wire,
- 4. LAN - Local Area Network connects computers that are physically close together ( high speed multi-access
- 5. WAN - Wide Area Network connects computers that are physically far apart. “long-haul network”. typically slower
- 6. MAN - Metropolitan Area Network Larger than a LAN and smaller than a WAN - example:
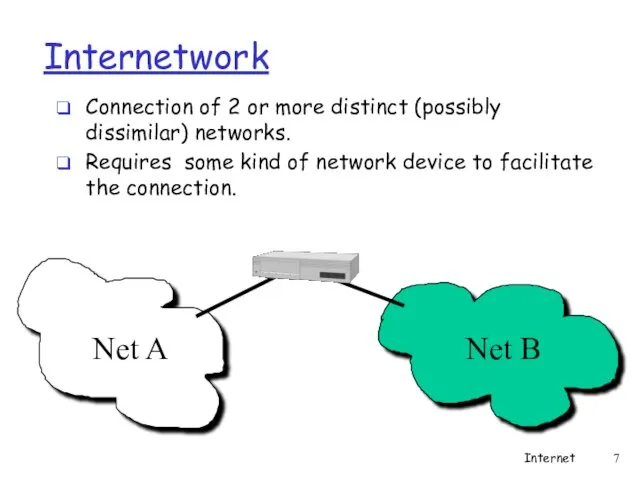
- 7. Internetwork Connection of 2 or more distinct (possibly dissimilar) networks. Requires some kind of network device
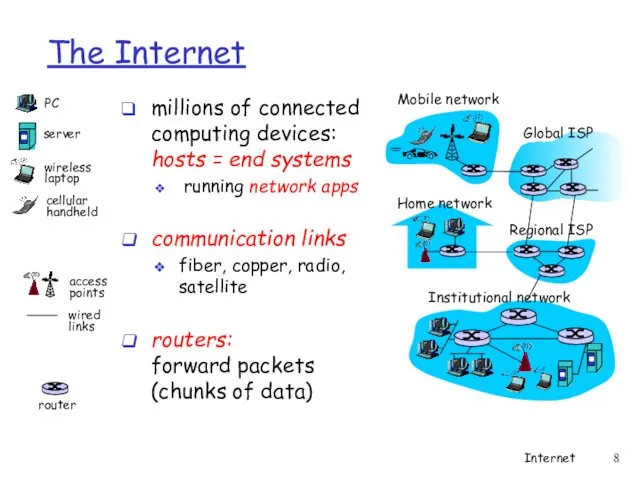
- 8. The Internet millions of connected computing devices: hosts = end systems running network apps communication links
- 9. The Internet Internet Internet Mapping Project, Bill Cheswick
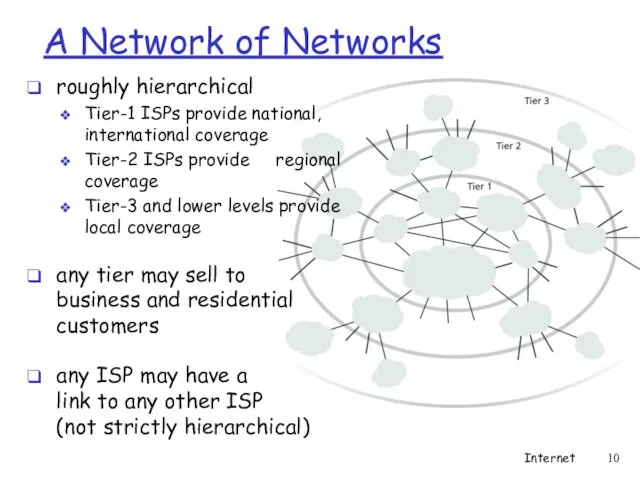
- 10. A Network of Networks roughly hierarchical Tier-1 ISPs provide national, international coverage Tier-2 ISPs provide regional
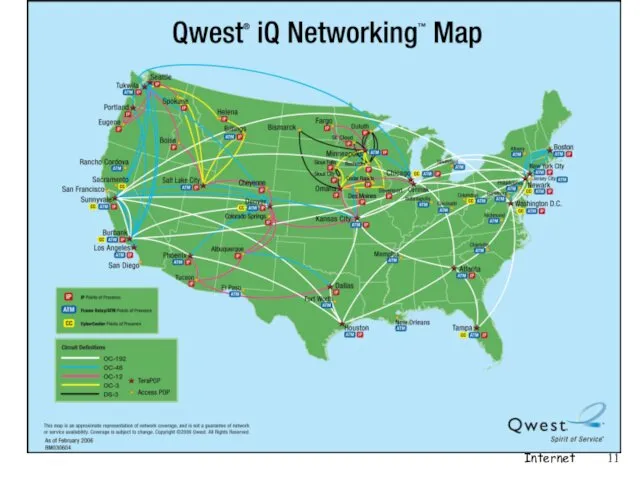
- 11. Internet
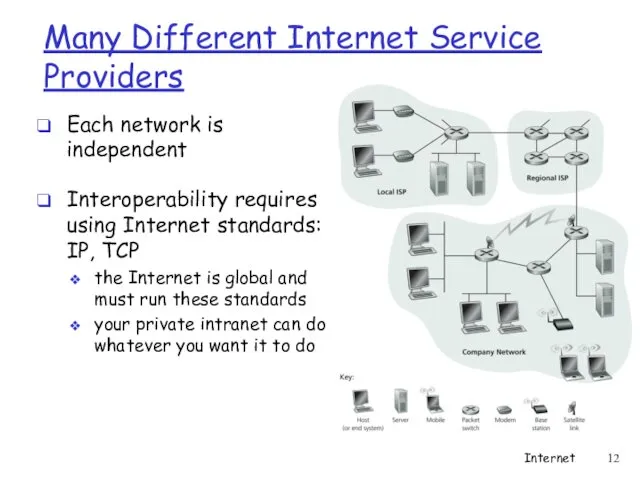
- 12. Many Different Internet Service Providers Each network is independent Interoperability requires using Internet standards: IP, TCP
- 13. Internet Design Goals primary goal: interoperability among existing networks a network of networks obey administrative boundaries
- 14. Internet Design Principles minimal assumptions about services network should support ability to send packets no reliability
- 15. Network Models Using a formal model allows us to deal with various aspects of Networks abstractly.
- 16. Layering Divide a task into pieces and then solve each piece independently (or nearly so). Establishing
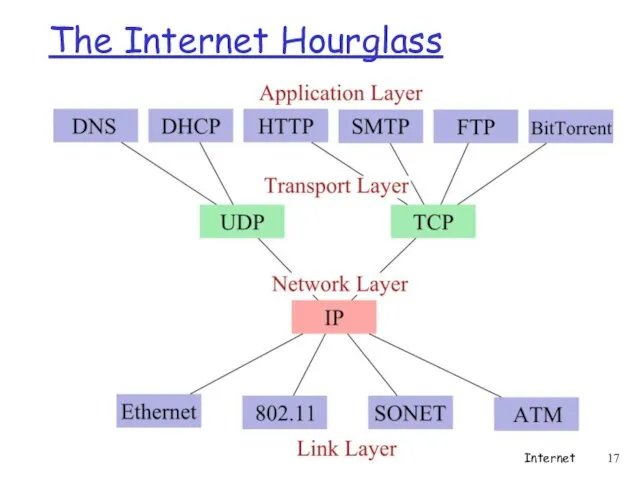
- 17. The Internet Hourglass Internet
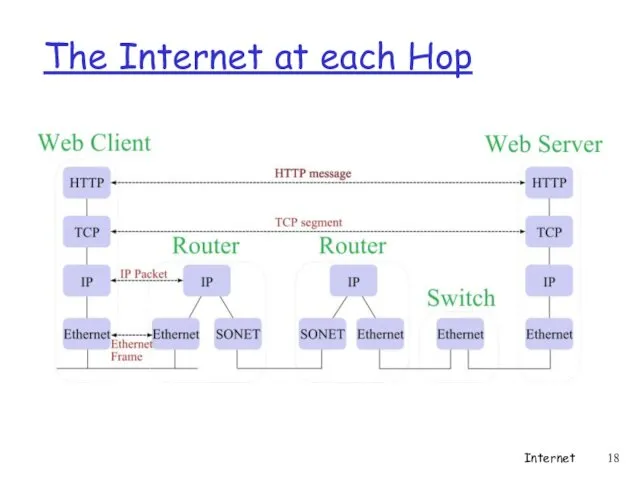
- 18. The Internet at each Hop Internet
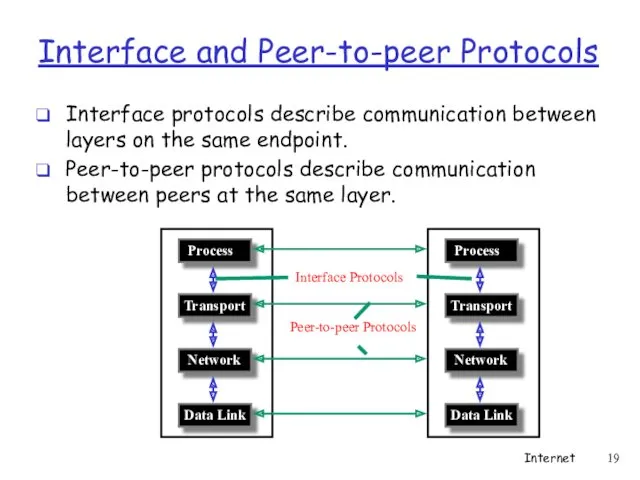
- 19. Interface protocols describe communication between layers on the same endpoint. Peer-to-peer protocols describe communication between peers
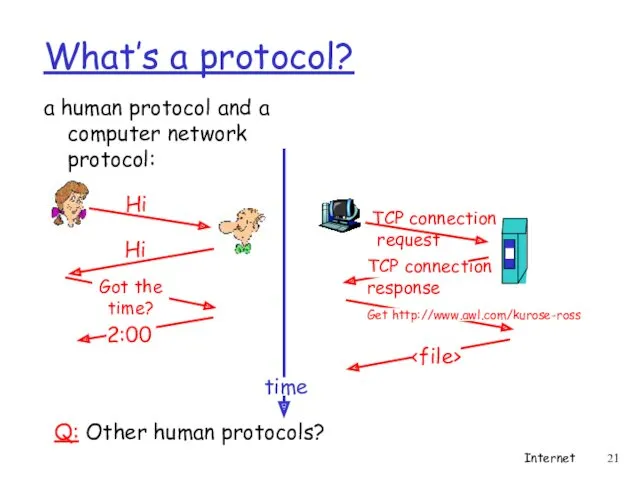
- 20. What’s a protocol? human protocols: “what’s the time?” “I have a question” introductions … specific msgs
- 21. What’s a protocol? a human protocol and a computer network protocol: Internet Q: Other human protocols?
- 22. Protocol An agreed upon convention for communication. both endpoints need to understand the protocol. Protocols must
- 23. Programs & Processes A program is an executable file. A process or task is an instance
- 24. Client - Server A server is a process - not a machine ! A server waits
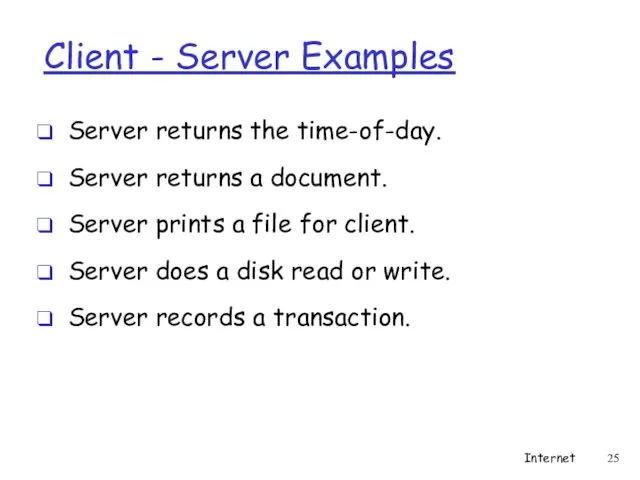
- 25. Client - Server Examples Server returns the time-of-day. Server returns a document. Server prints a file
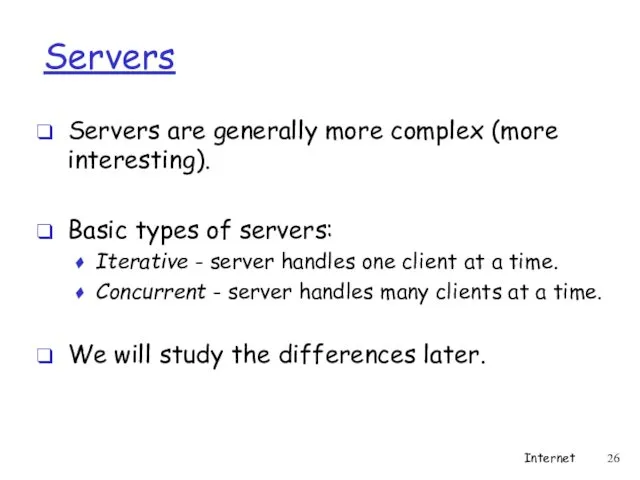
- 26. Servers Servers are generally more complex (more interesting). Basic types of servers: Iterative - server handles
- 27. Thought Exercise Come up with an example of a layered system. Describe the interface and peer-to-peer
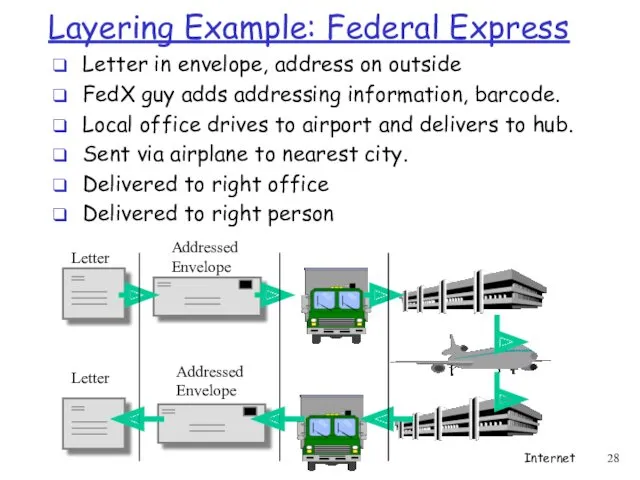
- 28. Layering Example: Federal Express Letter in envelope, address on outside FedX guy adds addressing information, barcode.
- 29. Layered Software Systems Network software Operating systems Windowing systems Internet
- 31. Скачать презентацию













 Массивы
Массивы Қазақстан мен сыртқы әлем арасындағы байланыс құралдары
Қазақстан мен сыртқы әлем арасындағы байланыс құралдары Принципы представления данных и команд в компьютере
Принципы представления данных и команд в компьютере Переферійні пристрої
Переферійні пристрої Таргетированная реклама Вконтакте. Вводный курс
Таргетированная реклама Вконтакте. Вводный курс Анонс новой редакции 1С:Университет ПРОФ
Анонс новой редакции 1С:Университет ПРОФ Особенности восприятия графики посетителями сайтов
Особенности восприятия графики посетителями сайтов Автоматизированное тестирование
Автоматизированное тестирование Таблиці. Електронні таблиці. Формати даних та форматування таблиць
Таблиці. Електронні таблиці. Формати даних та форматування таблиць Внедрение в практику преподавания учителей-предметников технологии Web 2.0. с целью повышения эффективности урока
Внедрение в практику преподавания учителей-предметников технологии Web 2.0. с целью повышения эффективности урока Word мәтінідік құжатына графикалық кескіндерді кірістіру
Word мәтінідік құжатына графикалық кескіндерді кірістіру Проектирование баз данных и работа с ними веб-приложений. (Лекция 8)
Проектирование баз данных и работа с ними веб-приложений. (Лекция 8) JavaScript Basics
JavaScript Basics СУБД MS Access
СУБД MS Access Множества. Массивы (Delphi)
Множества. Массивы (Delphi) Система CRM - твой верный помощник
Система CRM - твой верный помощник Система сбора и анализа сведений о преподавателях
Система сбора и анализа сведений о преподавателях Створення розкладу
Створення розкладу Методи equals та hashcode
Методи equals та hashcode Ерекшеліктерді өңдеу. Java
Ерекшеліктерді өңдеу. Java Презентация по теме Табличные вычисления на компьютере к учебнику Семакина. 9 класс.
Презентация по теме Табличные вычисления на компьютере к учебнику Семакина. 9 класс. Отчет о прохождении учебной практики по модулю Эксплуатация и модификация информационных систем
Отчет о прохождении учебной практики по модулю Эксплуатация и модификация информационных систем Локальные компьютерные сети
Локальные компьютерные сети Module 28: Digital Forensics and Incident Analysis and Response
Module 28: Digital Forensics and Incident Analysis and Response Компьютерная грамотность и информационная культура
Компьютерная грамотность и информационная культура Презентация к уроку информатики в 9 классе по теме Информационное общество
Презентация к уроку информатики в 9 классе по теме Информационное общество викторина по информатике для 5-6 классов Информашка
викторина по информатике для 5-6 классов Информашка Антивирусные программы. Антивирусная защита информации
Антивирусные программы. Антивирусная защита информации