Содержание
- 2. Introduction to Cloud Computing Basics of cloud computing Architecture: Layers of Cloud Computing Types of cloud
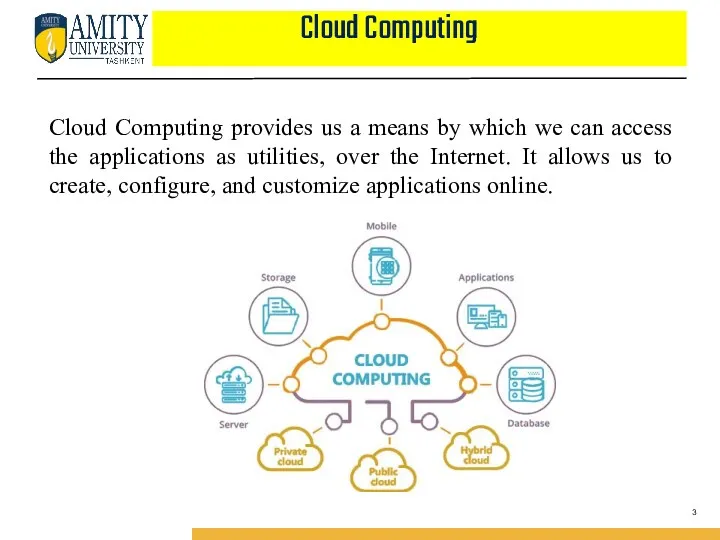
- 3. Cloud Computing Cloud Computing provides us a means by which we can access the applications as
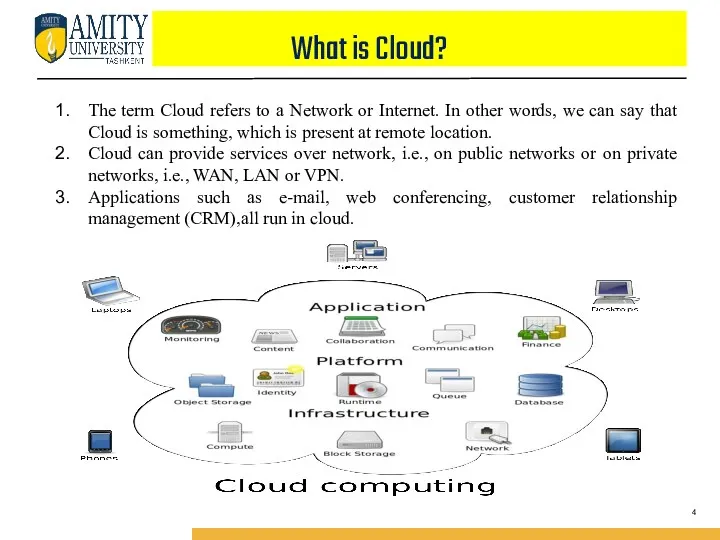
- 4. What is Cloud? The term Cloud refers to a Network or Internet. In other words, we
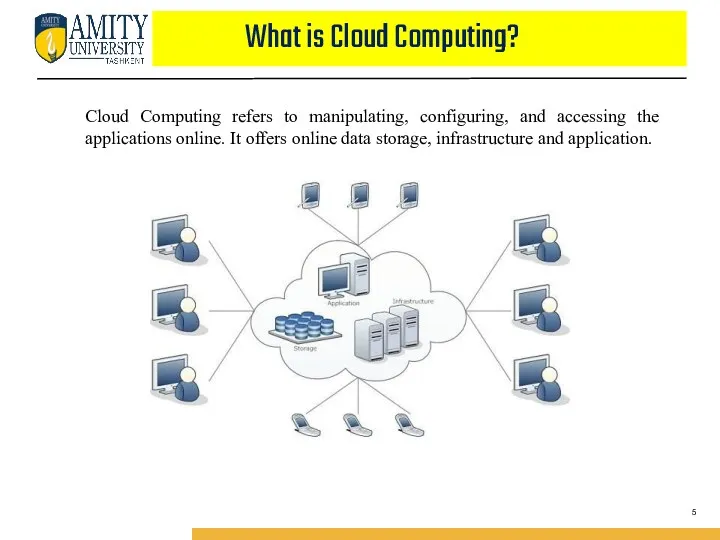
- 5. What is Cloud Computing? Cloud Computing refers to manipulating, configuring, and accessing the applications online. It
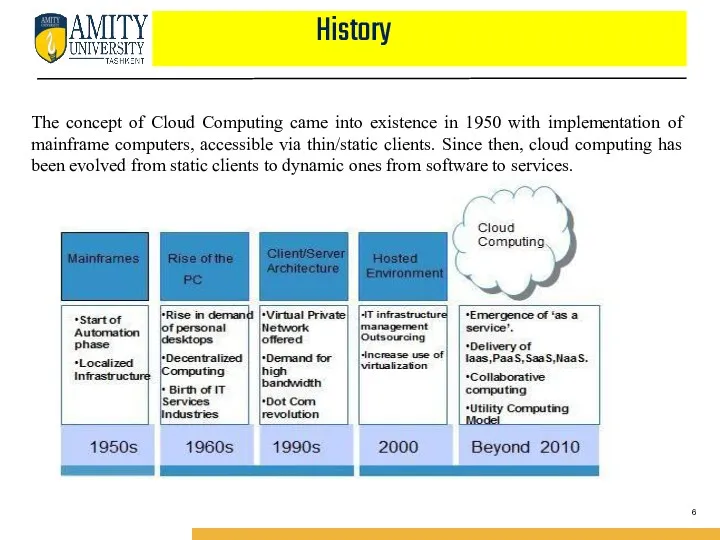
- 6. History The concept of Cloud Computing came into existence in 1950 with implementation of mainframe computers,
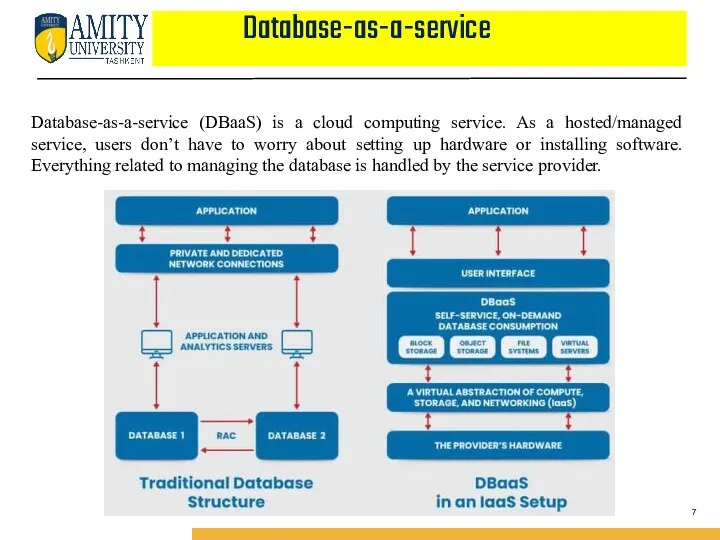
- 7. Database-as-a-service Database-as-a-service (DBaaS) is a cloud computing service. As a hosted/managed service, users don’t have to
- 8. Database-as-a-service DBaaS (also known as managed database service) is a cloud computing service that lets users
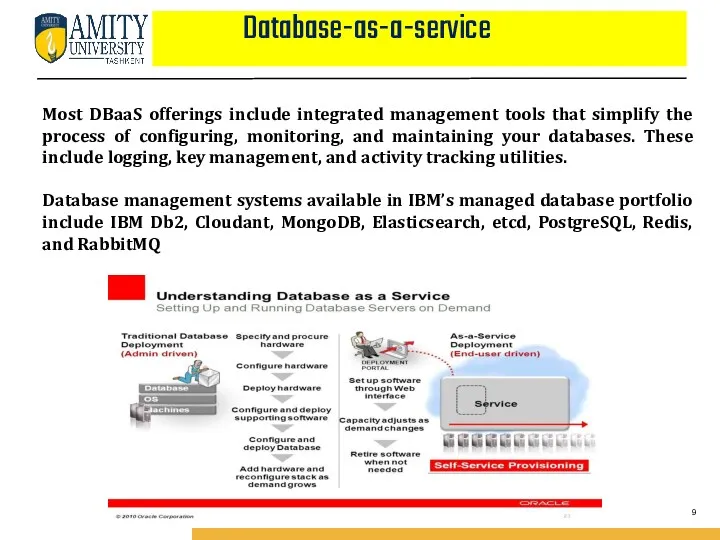
- 9. Database-as-a-service Most DBaaS offerings include integrated management tools that simplify the process of configuring, monitoring, and
- 10. Benefits of DBaaS DBaaS offers your organization significant financial, operational, and strategic benefits: Cost Savings: Laying
- 11. Benefits of DBaaS Data and Application Security: Cloud database providers typically offer enterprise grade security, including
- 12. Governance / Management as a Service Governance as a Service is an integrated governance platform. An
- 13. Benefits of GaaS /MaaS Benefits of GaaS / MaaS are as follows: Regulation Monitoring and Reporting
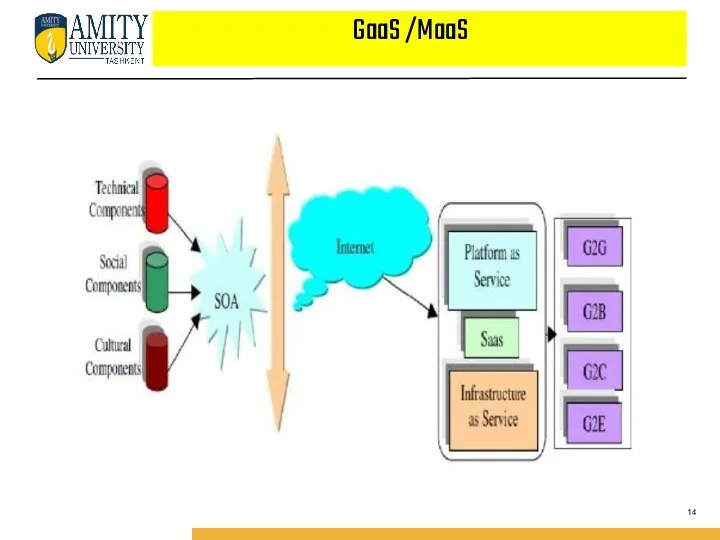
- 14. GaaS /MaaS
- 15. Storage as a Service Storage as a service (SaaS) is a cloud business model in which
- 16. Benefits of SaaS Top 10 advantage of Storage as a Services: Cost– factually speaking, backing up
- 17. Benefits of SaaS Syncing – Syncing ensures your files are automatically updated across all of your
- 18. Storage as a Service
- 19. Testing as a Service (TaaS) TESTING AS A SERVICE (TaaS) is an outsourcing model, in which
- 20. Testing as a Service (TaaS) Performance Testing as a Service: Multiple users are accessing the application
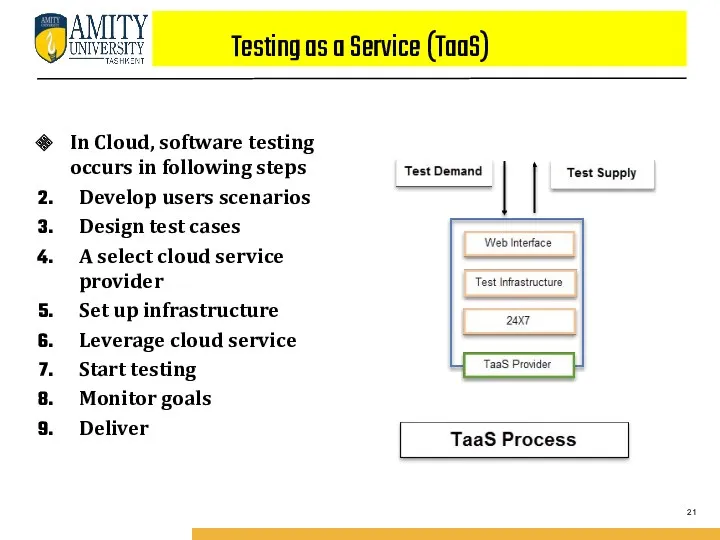
- 21. Testing as a Service (TaaS) In Cloud, software testing occurs in following steps Develop users scenarios
- 22. Benefits of Cloud Computing
- 23. Benefits Cloud Computing has numerous advantages. Some of them are listed below: One can access applications
- 24. Risks of Cloud Computing SECURITY & PRIVACY It is the biggest concern about cloud computing. Since
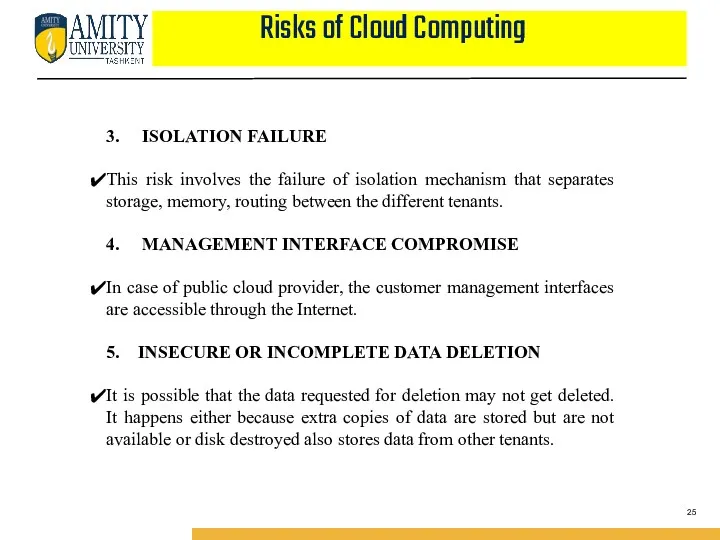
- 25. Risks of Cloud Computing 3. ISOLATION FAILURE This risk involves the failure of isolation mechanism that
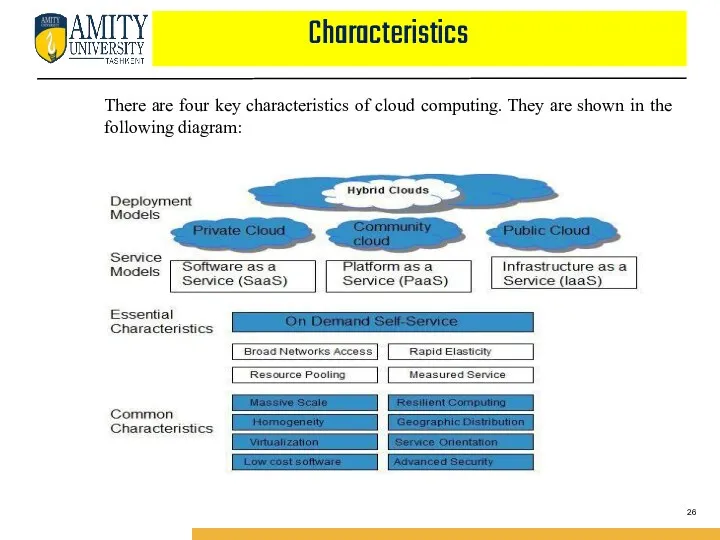
- 26. Characteristics There are four key characteristics of cloud computing. They are shown in the following diagram:
- 27. Characteristics ON DEMAND SELF-SERVICE Cloud Computing allows the users to use web services and resources on
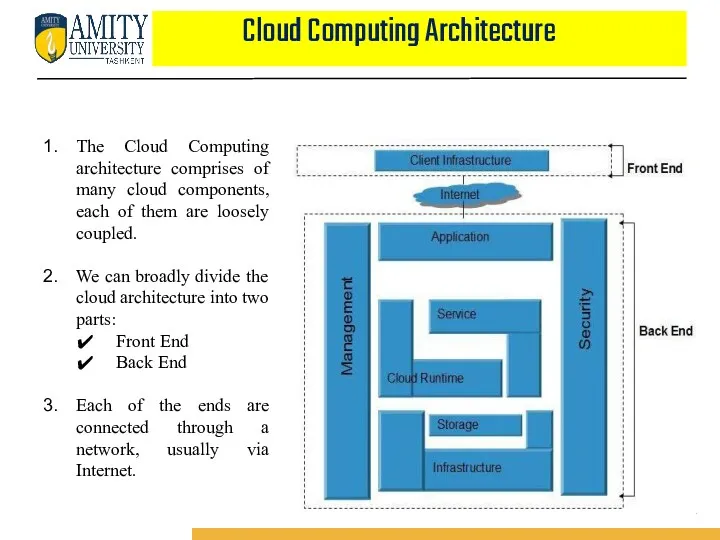
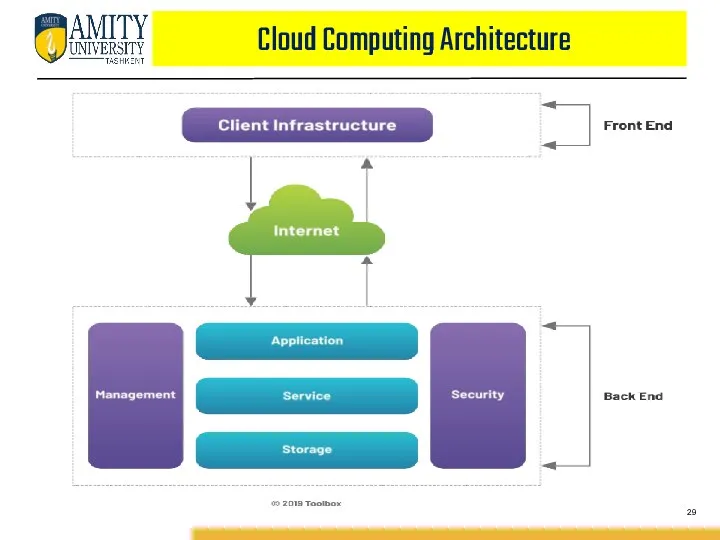
- 28. Cloud Computing Architecture The Cloud Computing architecture comprises of many cloud components, each of them are
- 29. Cloud Computing Architecture
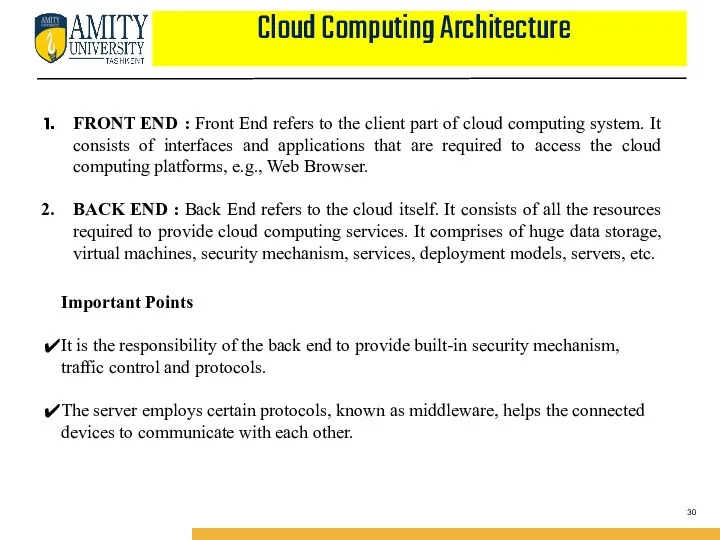
- 30. Cloud Computing Architecture FRONT END : Front End refers to the client part of cloud computing
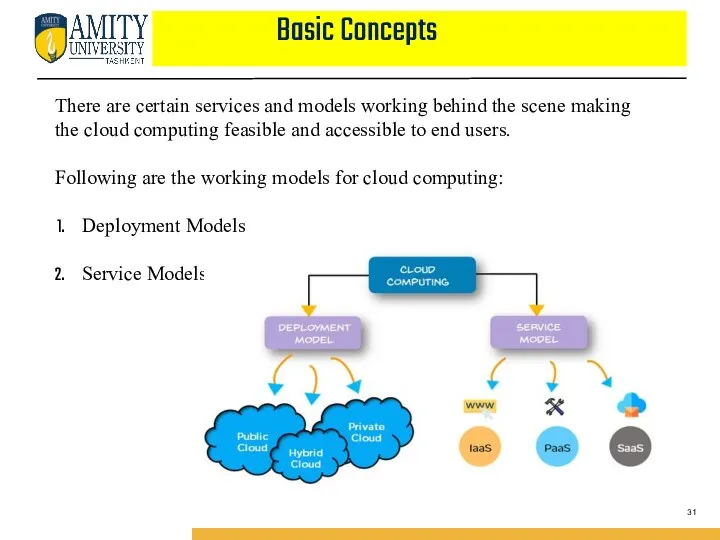
- 31. Basic Concepts There are certain services and models working behind the scene making the cloud computing
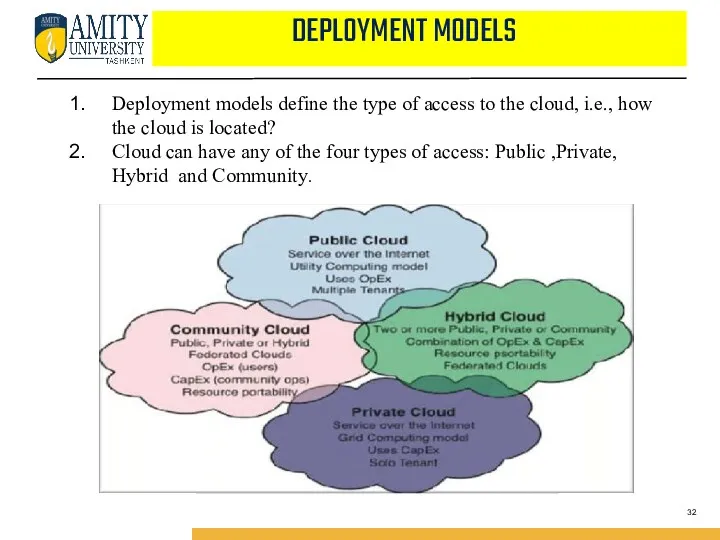
- 32. DEPLOYMENT MODELS Deployment models define the type of access to the cloud, i.e., how the cloud
- 33. Deployment Models PUBLIC CLOUD :The Public Cloud allows systems and services to be easily accessible to
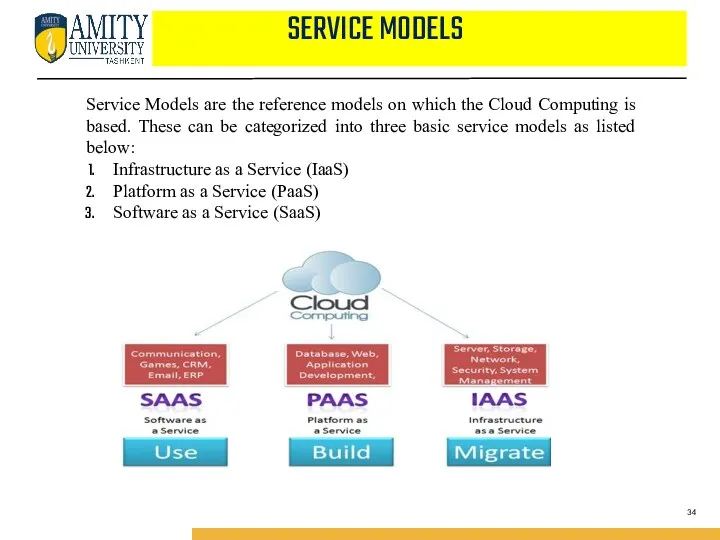
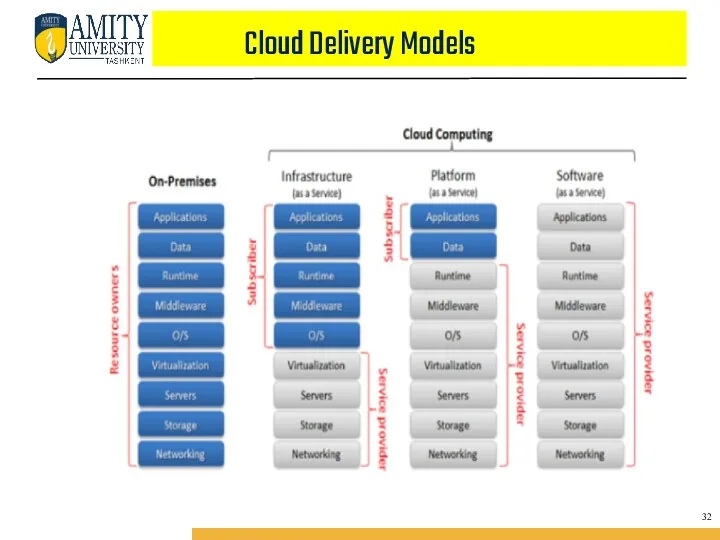
- 34. SERVICE MODELS Service Models are the reference models on which the Cloud Computing is based. These
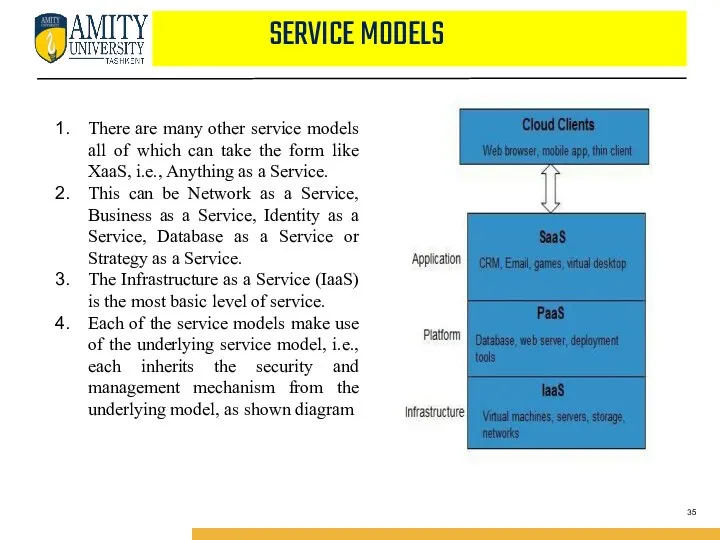
- 35. There are many other service models all of which can take the form like XaaS, i.e.,
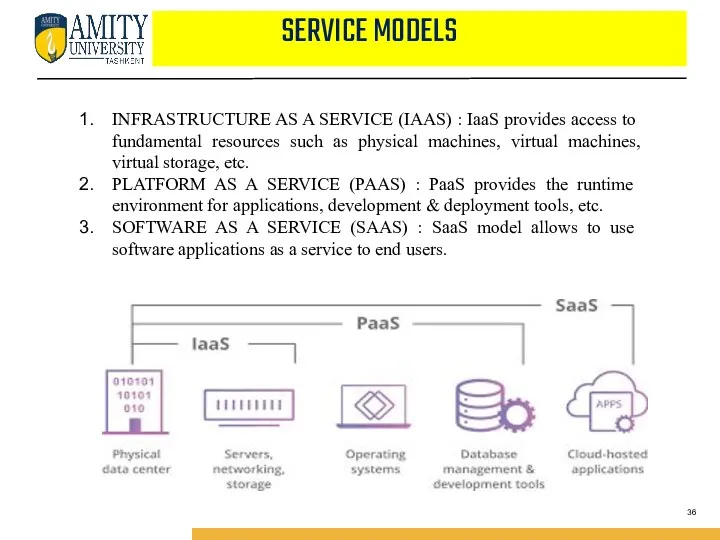
- 36. INFRASTRUCTURE AS A SERVICE (IAAS) : IaaS provides access to fundamental resources such as physical machines,
- 37. CLOUD DELIVERY MODELS There are three elementary cloud service delivery models which are denoted as SPI
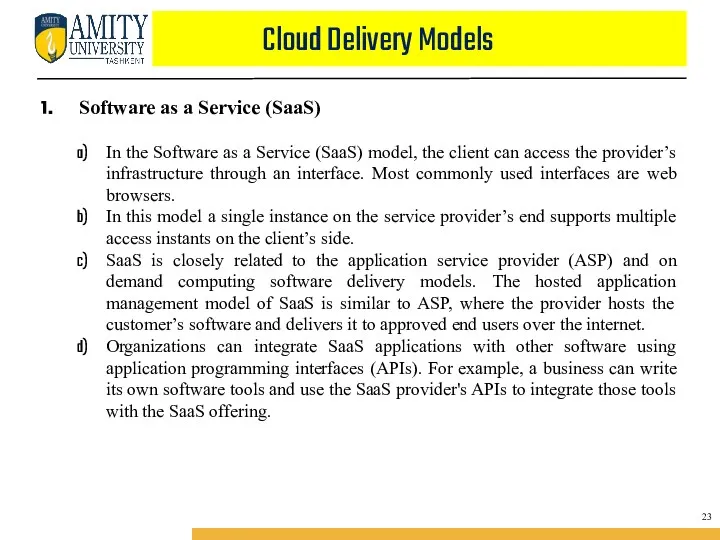
- 38. Cloud Delivery Models Software as a Service (SaaS) In the Software as a Service (SaaS) model,
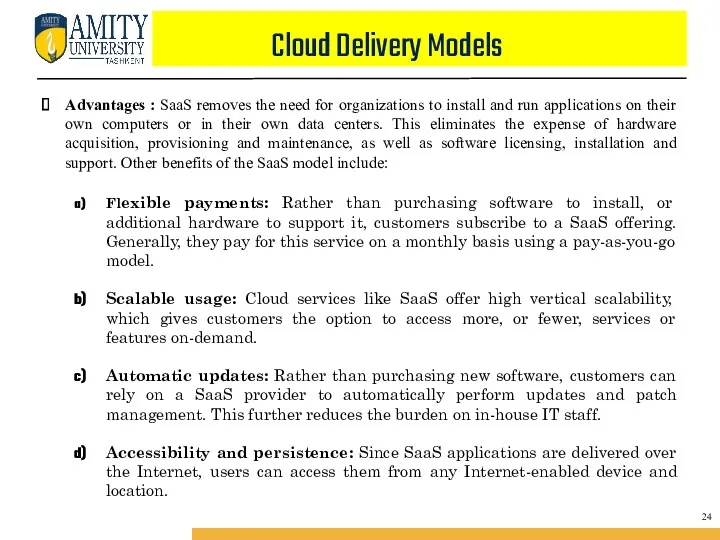
- 39. Cloud Delivery Models Advantages : SaaS removes the need for organizations to install and run applications
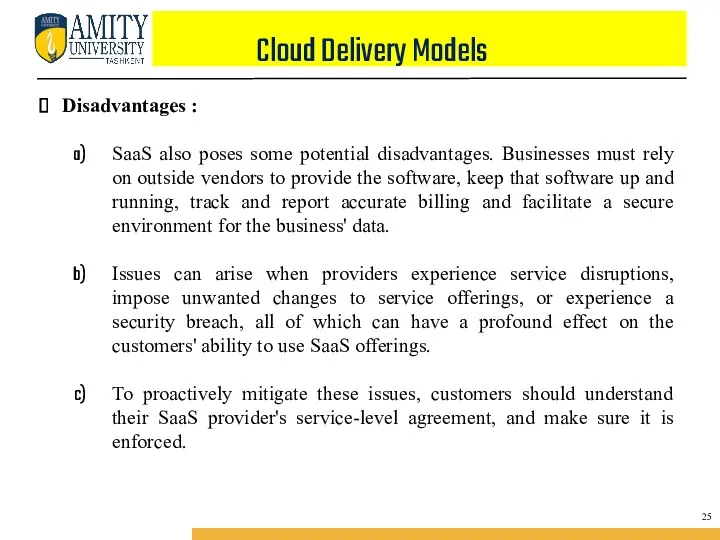
- 40. Cloud Delivery Models Disadvantages : SaaS also poses some potential disadvantages. Businesses must rely on outside
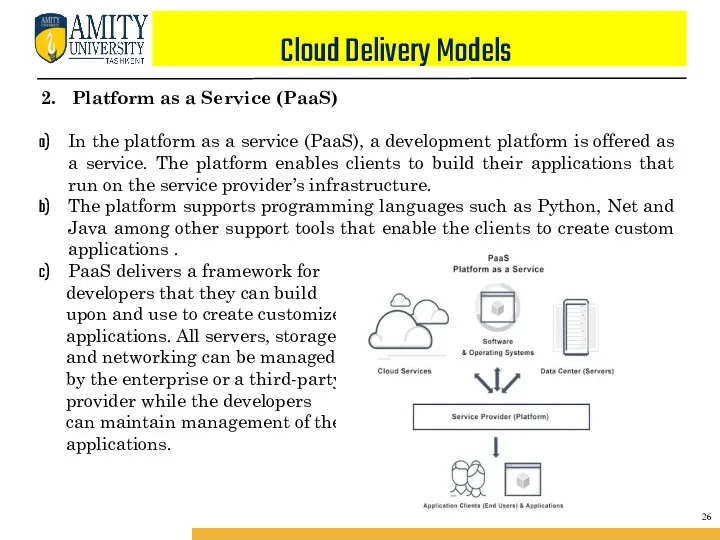
- 41. Cloud Delivery Models 2. Platform as a Service (PaaS) In the platform as a service (PaaS),
- 42. Cloud Delivery Models Advantages : No matter the size of your company, using PaaS offers numerous
- 43. Cloud Delivery Models Disadvantages: Data security : Organizations can run their own apps and services using
- 44. Cloud Delivery Models 3. Infrastructure as a Service Model (IaaS) For the Infrastructure as a service
- 45. Cloud Delivery Models Advantages: IaaS offers many advantages, including: The most flexible cloud computing model Easy
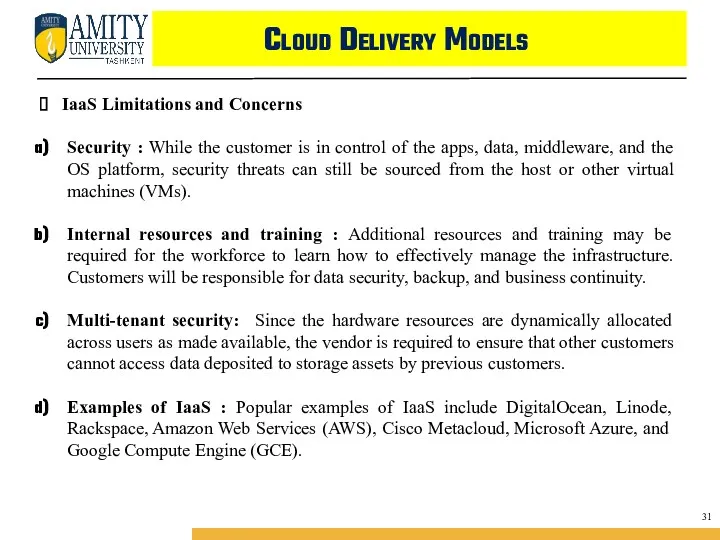
- 46. Cloud Delivery Models IaaS Limitations and Concerns Security : While the customer is in control of
- 47. Cloud Delivery Models 32
- 48. security issues cloud computing Security issues experienced with software-as-a-service (SaaS) Lack of visibility into what data
- 49. security issues cloud computing Security issues experienced with infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) Cloud workloads and accounts being created
- 50. security issues cloud computing Security issues experienced with platform-as-a-service (PaaS) Lack of interoperability: Diverse computational resources
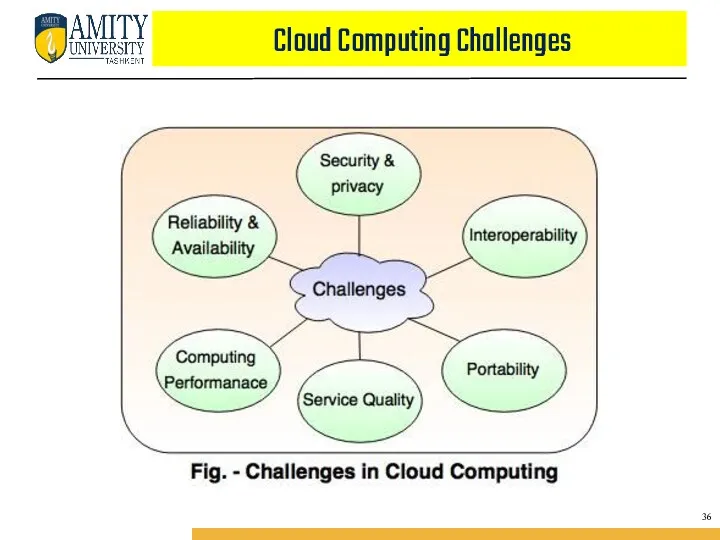
- 51. Cloud Computing Challenges 36
- 52. Cloud Computing Risks & Challenges Security issues : To ensure your organization’s privacy and security is
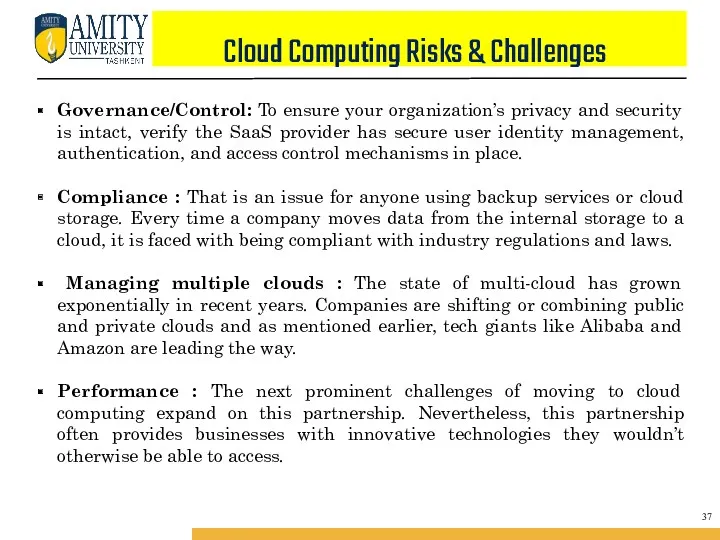
- 53. Cloud Computing Risks & Challenges Governance/Control: To ensure your organization’s privacy and security is intact, verify
- 54. Cloud service development Cloud application development services aim to provide assistance with developing, migrating or otherwise
- 55. Deployment challenges Privacy and Security : Cloud architecture do not automatically grant security compliance for the
- 56. Cloud Computing Risks & Challenges Building a private cloud : Creating an internal or private cloud
- 57. Deployment challenges 3. Data Security : One of the major concerns associated with cloud computing is
- 58. Deployment challenges 6. Performance and Bandwidth Cost : Businesses can save money on hardware but they
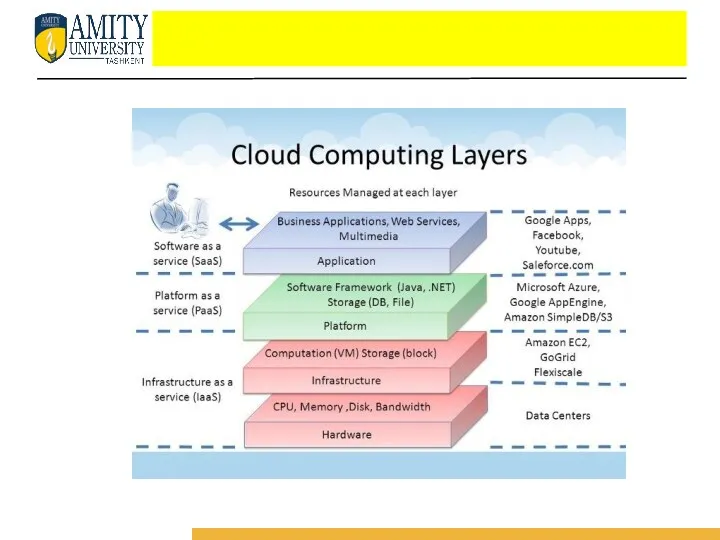
- 59. To gain a better understanding of the aforementioned terms, it is important to understand the underlying
- 61. There are many different types of cloud computing used by companies around the world. The most
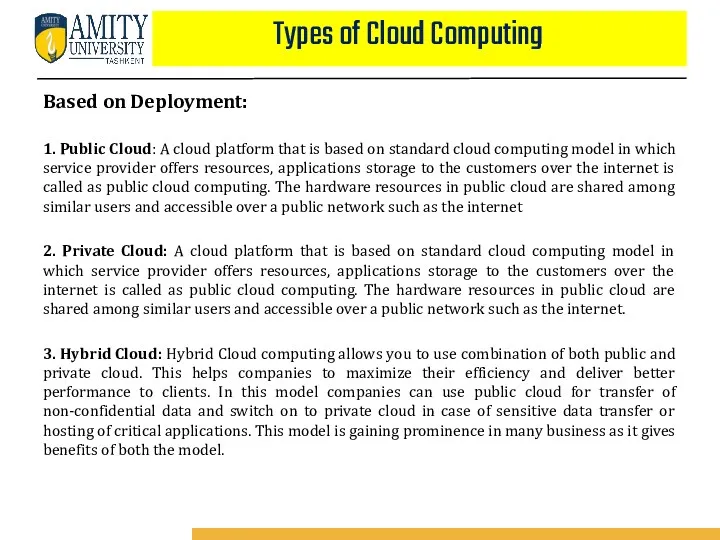
- 62. Based on Deployment: 1. Public Cloud: A cloud platform that is based on standard cloud computing
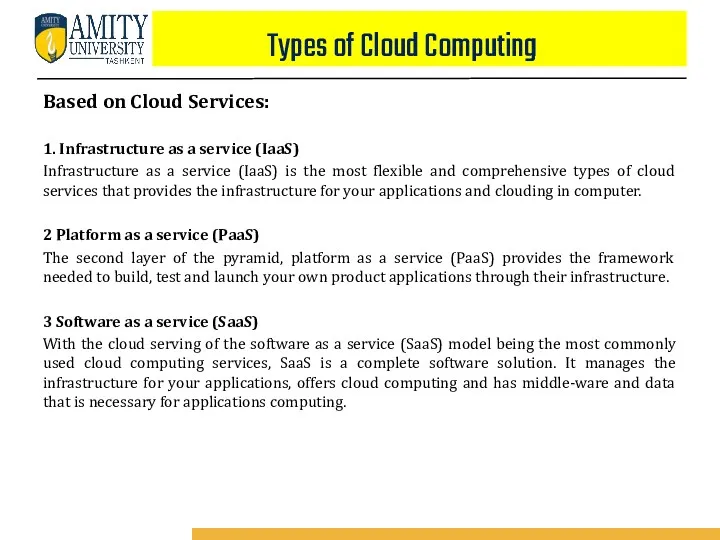
- 63. Based on Cloud Services: 1. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is
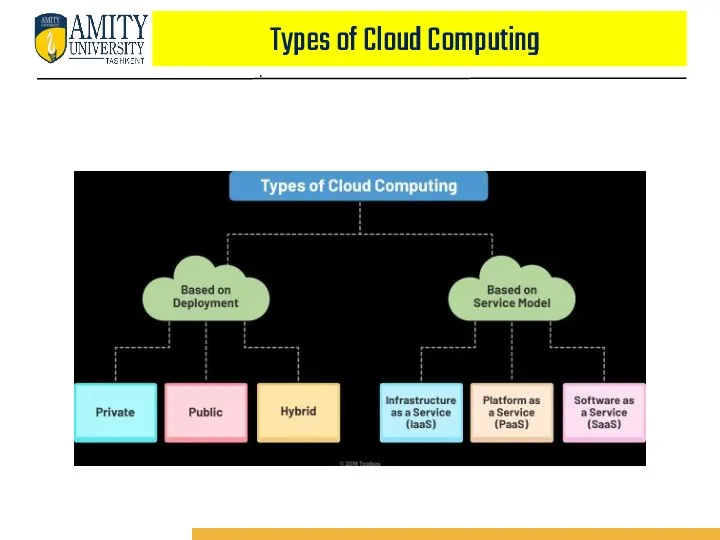
- 64. Types of Cloud Computing .
- 65. Some of the features that make cloud computing more suitable for the industries as well as
- 67. Скачать презентацию











 Виды аналоговых сигналов в канале телекоммуникационной системы. Практическая работа
Виды аналоговых сигналов в канале телекоммуникационной системы. Практическая работа Основы языка VB Урок 1: Данные
Основы языка VB Урок 1: Данные Programming Logic and Design Seventh Edition. Chapter 1. An Overview of Computers and Programming
Programming Logic and Design Seventh Edition. Chapter 1. An Overview of Computers and Programming Компьютерная графика
Компьютерная графика Управление ИТ-сервисами и контентом
Управление ИТ-сервисами и контентом The internet
The internet Оператор цикла с параметром
Оператор цикла с параметром Хакеризм. Понятие хакера
Хакеризм. Понятие хакера Программирование на языке Си++. Модуль №8
Программирование на языке Си++. Модуль №8 Уровни организации ЭВМ. Операционные системы
Уровни организации ЭВМ. Операционные системы Construct 2. Урок # 2
Construct 2. Урок # 2 Database 5.1
Database 5.1 Синхронизация потоков
Синхронизация потоков События. Лекция 6
События. Лекция 6 Естественные и формальные языки. Язык, как способ представления информации
Естественные и формальные языки. Язык, как способ представления информации Краткое введение в NGN для NSS
Краткое введение в NGN для NSS Этические и правовые нормы информационной деятельности
Этические и правовые нормы информационной деятельности Сетевая журналистика
Сетевая журналистика Мультимедиа
Мультимедиа Динамические структуры данных (язык Си)
Динамические структуры данных (язык Си) Автоматизация ресторанного бизнеса
Автоматизация ресторанного бизнеса Computer vision for robotics
Computer vision for robotics Фон для презентации о мультфильмах. Диск
Фон для презентации о мультфильмах. Диск Электронные таблицы Excel
Электронные таблицы Excel Алгоритмы размещения конструктивных модулей различных уровней иерархии. Лекция 3
Алгоритмы размещения конструктивных модулей различных уровней иерархии. Лекция 3 Анализ данных в табличных процессорах
Анализ данных в табличных процессорах Программирование на Python. Создание Telegram-бота. Часть 5. 29 занятие. 5-8 классы
Программирование на Python. Создание Telegram-бота. Часть 5. 29 занятие. 5-8 классы 1C-Администратор. Новый сервис для продвинутых пользователей
1C-Администратор. Новый сервис для продвинутых пользователей