Содержание
- 2. Overview Summary Analysis Discussion
- 3. Publication Information Author: Stephen Marche Magazine: The Atlantic Issue: May 2012
- 4. Paradox of Connectivity Marche identifies a paradox at the heart of the digital age. Marche describes
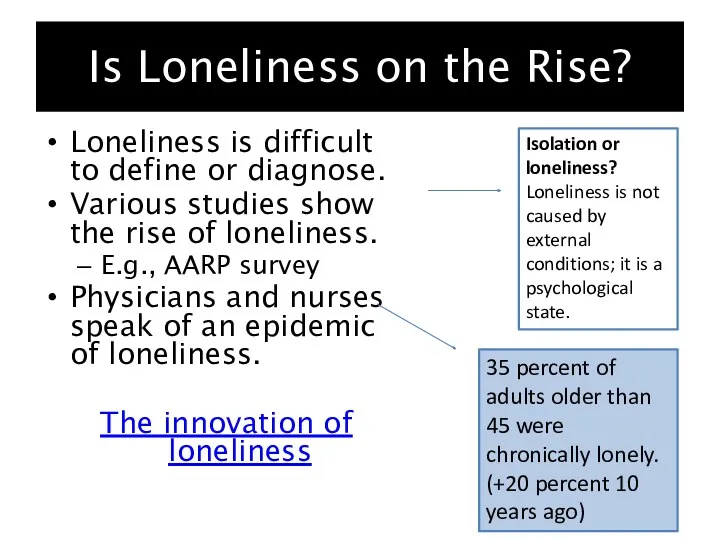
- 5. Is Loneliness on the Rise? Loneliness is difficult to define or diagnose. Various studies show the
- 6. Lack of Meaningful Social Interaction Marche argues that we engage in less meaningful social interaction. He
- 7. Before Facebook Digital technology has enabled our tendency for isolation. Some studies suggest a link between
- 8. “Who Uses Facebook?” Facebook had slightly lower levels of “social loneliness” but “significantly higher levels of
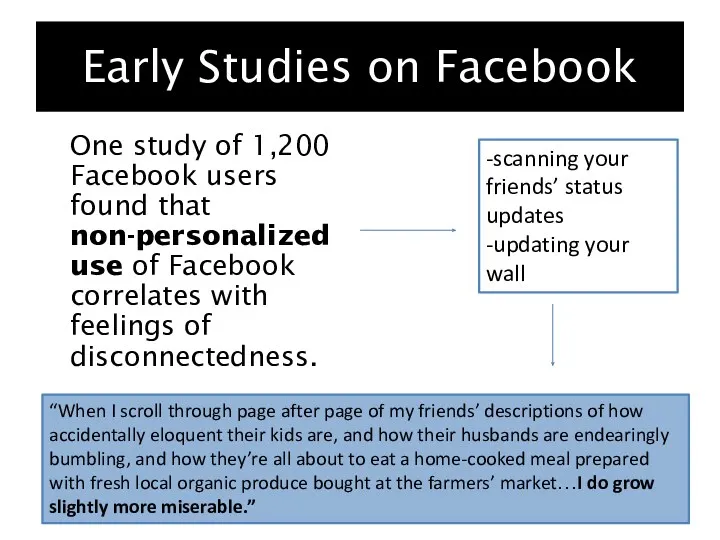
- 9. Early Studies on Facebook One study of 1,200 Facebook users found that non-personalized use of Facebook
- 10. Marche’s Conclusion Early research does not support the assertion that Facebook creates loneliness. There may be
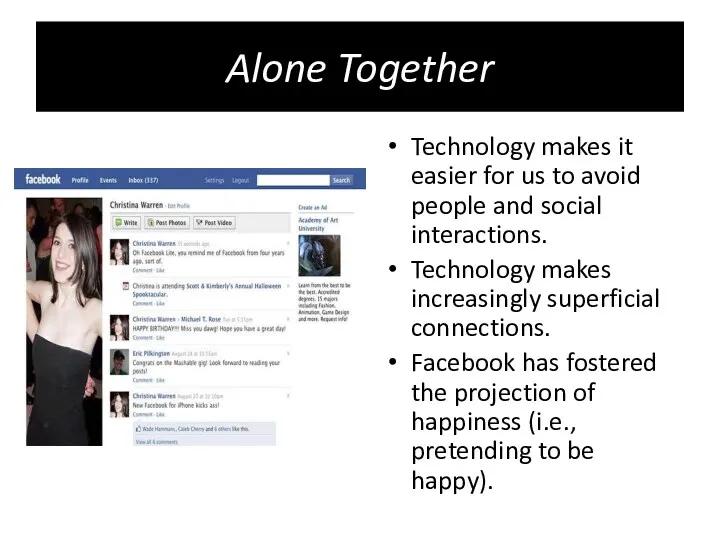
- 11. Alone Together Technology makes it easier for us to avoid people and social interactions. Technology makes
- 12. Facebook and Narcissism “Who Uses Facebook?” identified a correlation between Facebook use and narcissism. Narcissism is
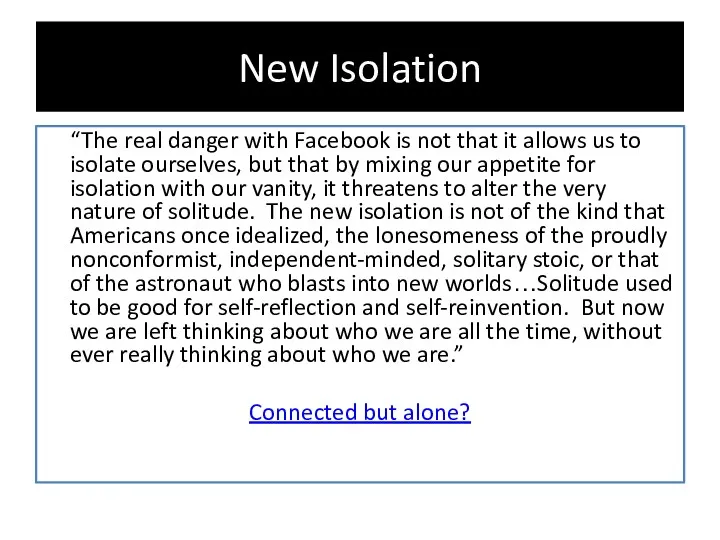
- 13. New Isolation “The real danger with Facebook is not that it allows us to isolate ourselves,
- 14. Strengths The article presents early studies on Facebook. The article is focussed on a simple yet
- 15. Strengths The article raises many questions that could lead to future inquiries: Is Facebook linked to
- 17. Скачать презентацию









 Нейросети. Практическое применение нейросетей в жизни
Нейросети. Практическое применение нейросетей в жизни Технология оцифровки архивных документов. Теория и практика
Технология оцифровки архивных документов. Теория и практика Order of placing an order
Order of placing an order Электронные системы тестирования
Электронные системы тестирования Программирование на языке Visual Basic for Applications (VBA)
Программирование на языке Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) Пристрій керування
Пристрій керування Объекты и их имена
Объекты и их имена Алгоритми з розгалуженнями для опрацювання величин
Алгоритми з розгалуженнями для опрацювання величин Важность сюжета в онлайн-играх
Важность сюжета в онлайн-играх Процессоры электронных таблиц. Электронные таблицы MS Excel
Процессоры электронных таблиц. Электронные таблицы MS Excel Защита информации
Защита информации Заводская дверь
Заводская дверь Умное зеркало
Умное зеркало Обзор алгоритмов и систем шифрования
Обзор алгоритмов и систем шифрования Графический дизайнер
Графический дизайнер Види і типи сайтів. Цільова аудиторія. Урок 1. 10 (11) клас
Види і типи сайтів. Цільова аудиторія. Урок 1. 10 (11) клас Rigsite for LWD. (Lesson 11)
Rigsite for LWD. (Lesson 11) تعريف تصوير : تصویر به معنی نمايش يك جسم برروى صفحه است
تعريف تصوير : تصویر به معنی نمايش يك جسم برروى صفحه است Поисковая система Bing
Поисковая система Bing Информационное общество
Информационное общество Что такое персональные данные? Какими бывают персональные данные?
Что такое персональные данные? Какими бывают персональные данные? Условный оператор
Условный оператор Административно-правовые формы и методы реализации исполнительной власти
Административно-правовые формы и методы реализации исполнительной власти 20231001_prezentatsiya
20231001_prezentatsiya Информатика для СПО Базы данных. Системы управления базами данных (СУБД). Основные понятия
Информатика для СПО Базы данных. Системы управления базами данных (СУБД). Основные понятия Двоичное кодирование. Информация и информационные процессы. 7 класс
Двоичное кодирование. Информация и информационные процессы. 7 класс Operating systems. Threads. (Section 4)
Operating systems. Threads. (Section 4) Обзор интернет аудитории Украины
Обзор интернет аудитории Украины