Содержание
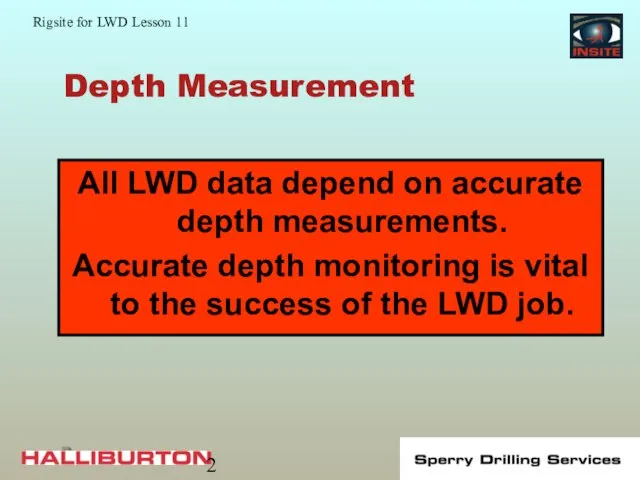
- 2. Depth Measurement All LWD data depend on accurate depth measurements. Accurate depth monitoring is vital to
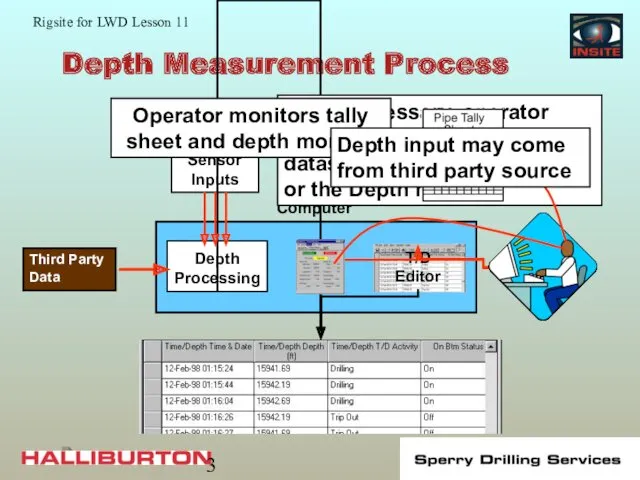
- 3. Depth Measurement Process Computer Depth sensors data are processed and added to the T/D dataset
- 4. Types of Failure or Error Mechanical failure Software failure Human Error Three possible ways to introduce
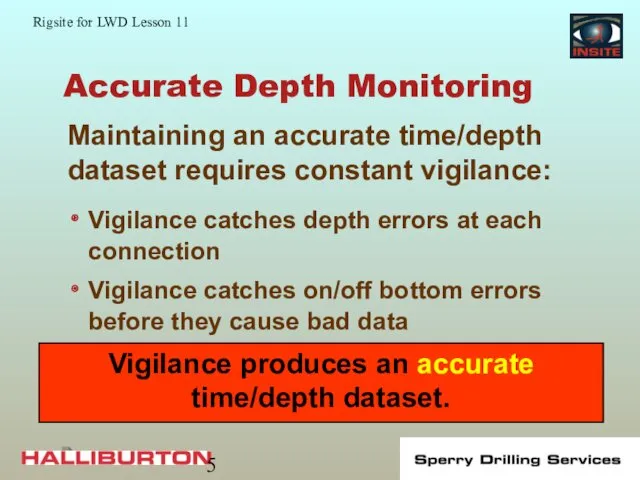
- 5. Accurate Depth Monitoring Vigilance catches depth errors at each connection Vigilance catches on/off bottom errors before
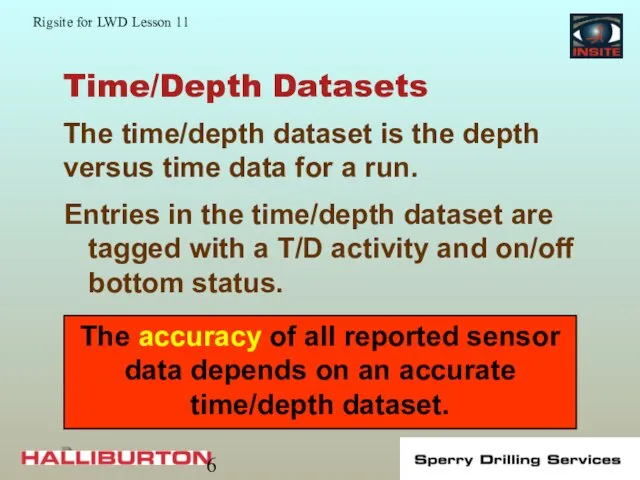
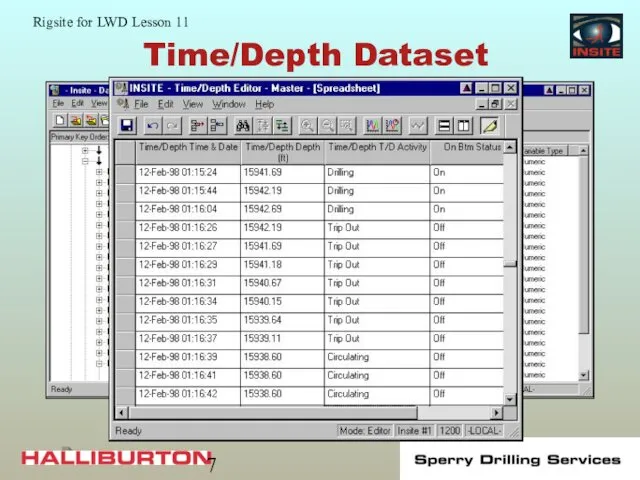
- 6. Time/Depth Datasets Entries in the time/depth dataset are tagged with a T/D activity and on/off bottom
- 7. Time/Depth Dataset
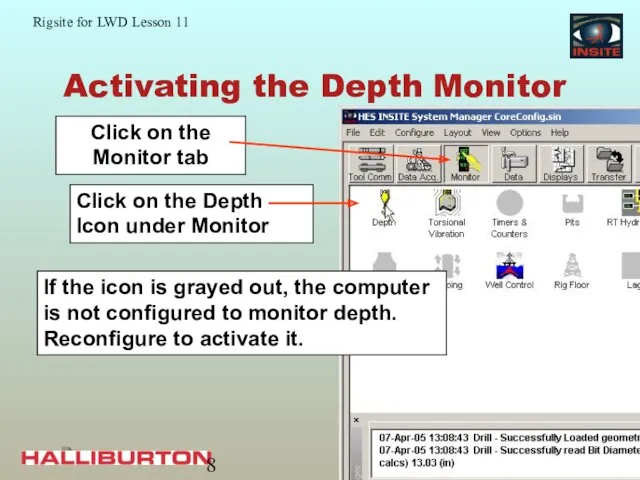
- 8. Activating the Depth Monitor If the icon is grayed out, the computer is not configured to
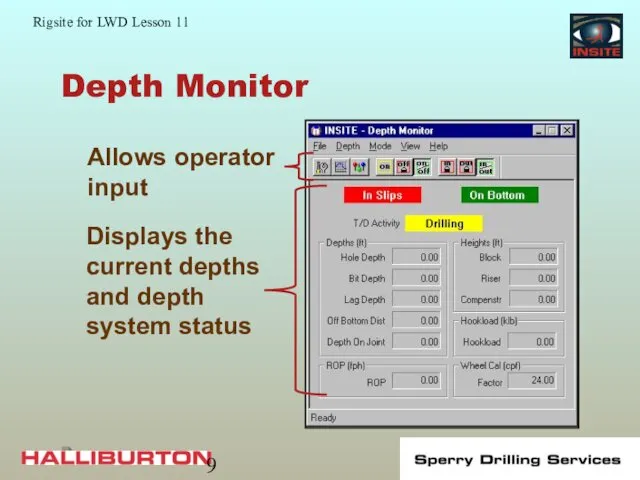
- 9. Depth Monitor
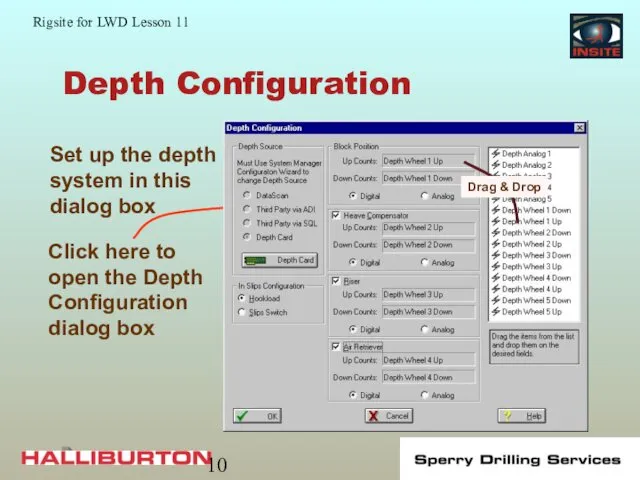
- 10. Depth Configuration
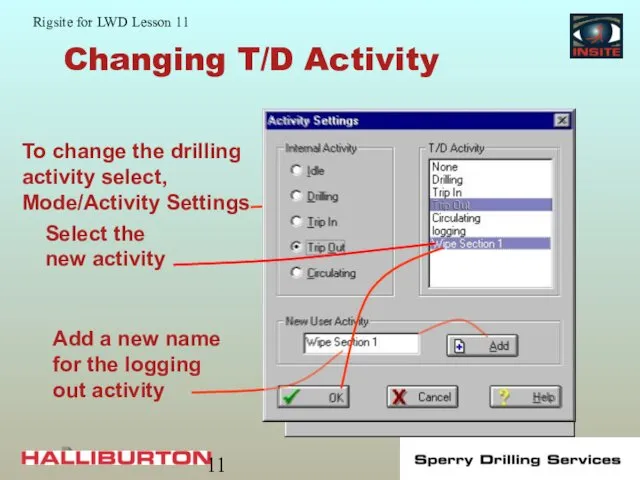
- 11. Changing T/D Activity
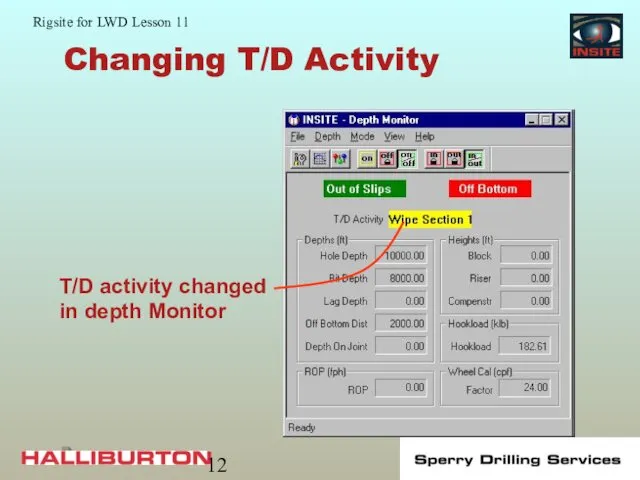
- 12. Changing T/D Activity
- 13. Logging Out of the Hole Set a new T/D activity in the depth monitor Used until
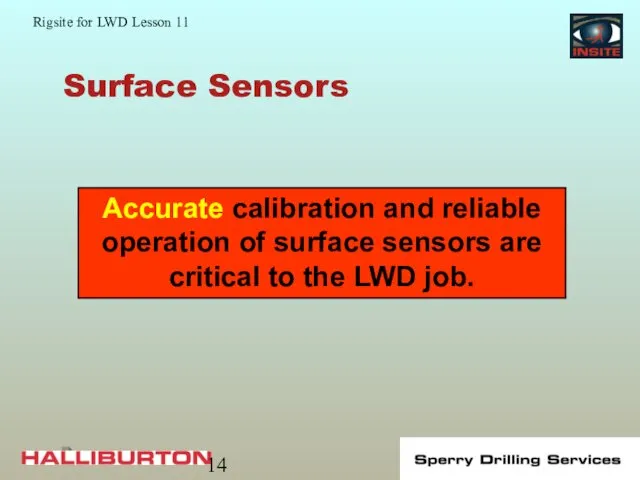
- 14. Surface Sensors Accurate calibration and reliable operation of surface sensors are critical to the LWD job.
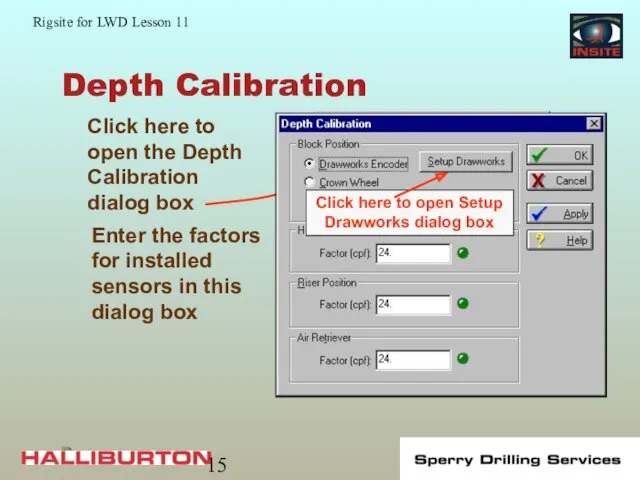
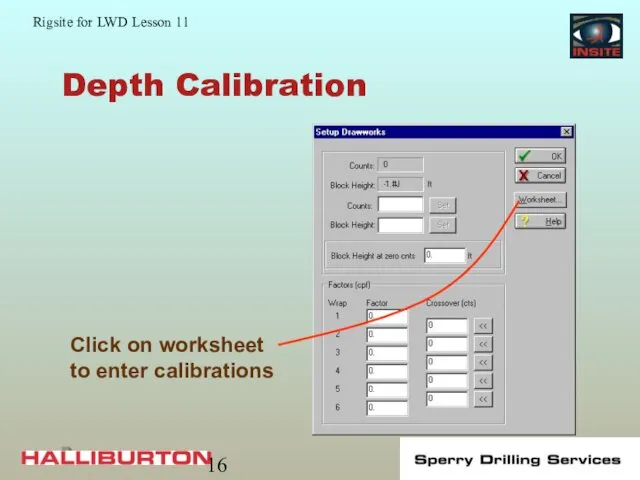
- 15. Depth Calibration Enter the factors for installed sensors in this dialog box
- 16. Depth Calibration
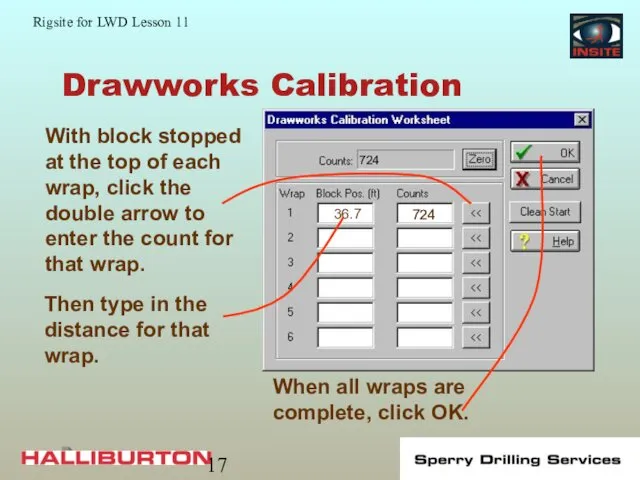
- 17. Drawworks Calibration
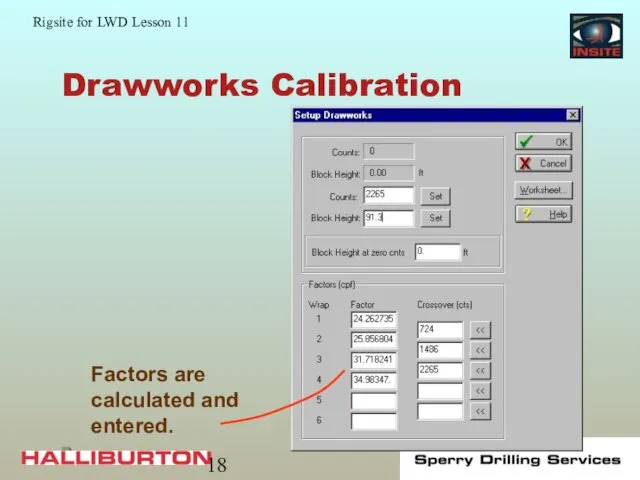
- 18. Drawworks Calibration
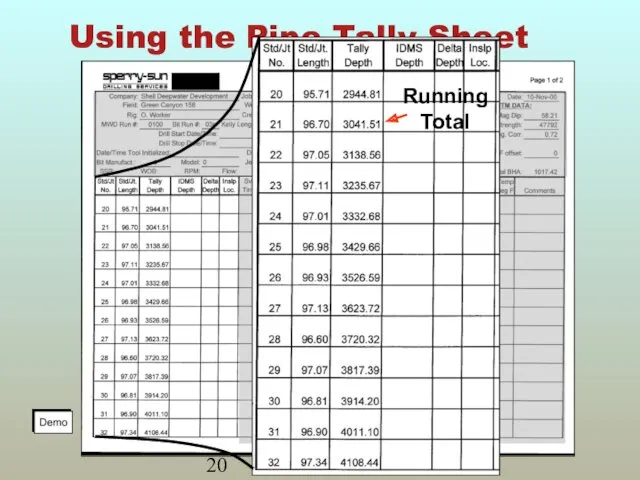
- 19. Pipe Tally Sheet Copy the pipe joint lengths from the driller's pipe tally to the LWD
- 20. Using the Pipe Tally Sheet
- 21. Depth Control Review Importance of depth monitoring T/D dataset Depth monitor Depth configuration Depth calibration Pipe
- 22. Sources of Depth Errors Incorrect entry in tally sheet Driller used pipe out of order Not
- 23. Incorrect Entry in Tally Sheet First, check for errors in the tally sheet Possible sources of
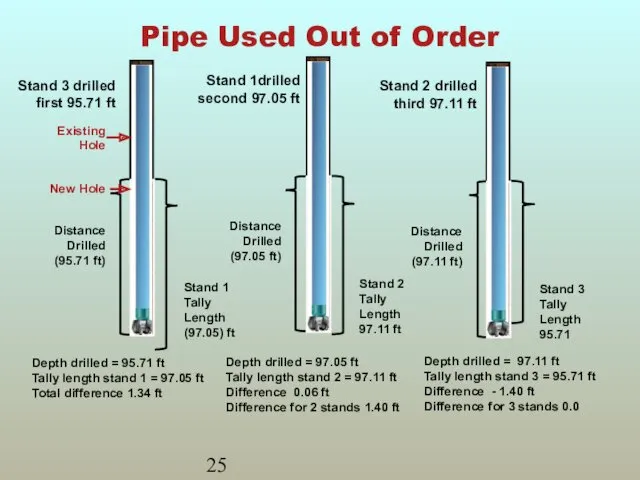
- 24. Driller Used Pipe Out of Order The depth differences will even out after two or three
- 25. Pipe Used Out of Order Depth drilled = 95.71 ft Tally length stand 1 = 97.05
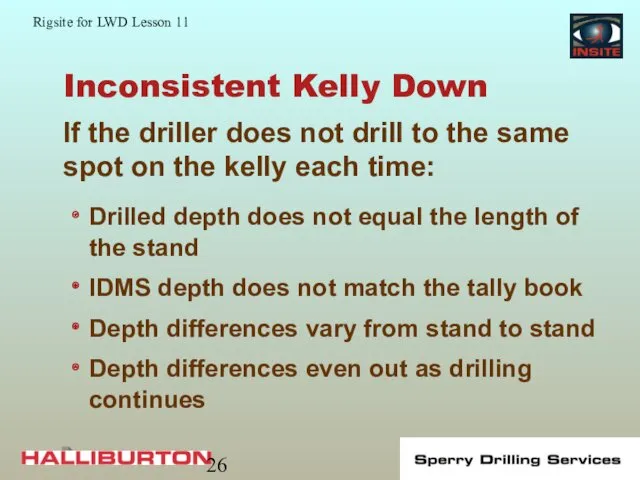
- 26. Inconsistent Kelly Down Drilled depth does not equal the length of the stand IDMS depth does
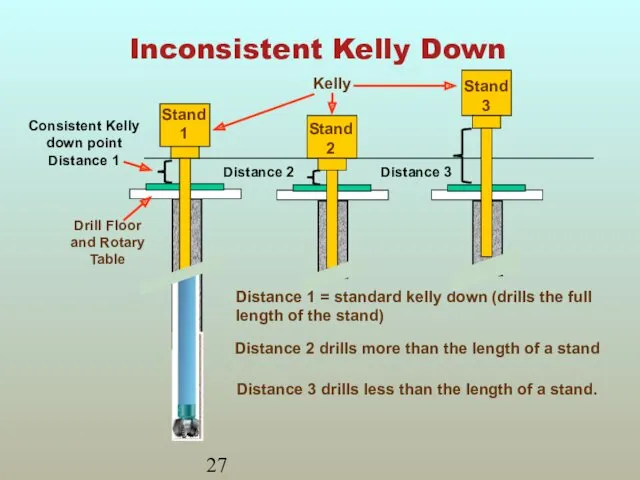
- 27. Inconsistent Kelly Down
- 28. Depth Calibration Error Same error showing up on each stand is a calibration error A small
- 29. Calibration Error Measurement Error - 0.58 ft Depth Error = - 0.58 ft Measurement Error -
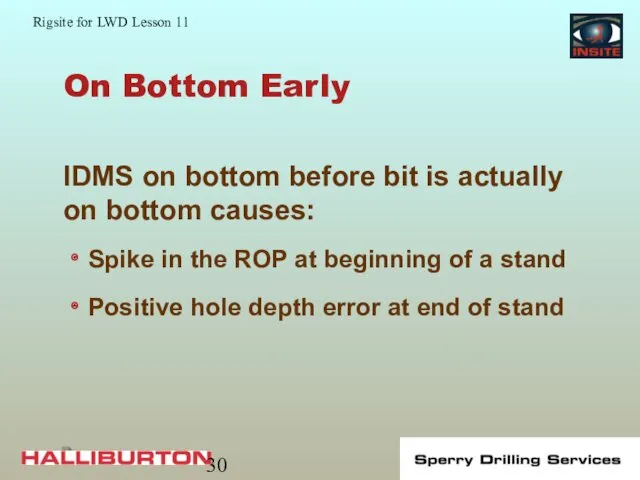
- 30. On Bottom Early Spike in the ROP at beginning of a stand Positive hole depth error
- 31. On Bottom Early 6.11 ft hole depth error
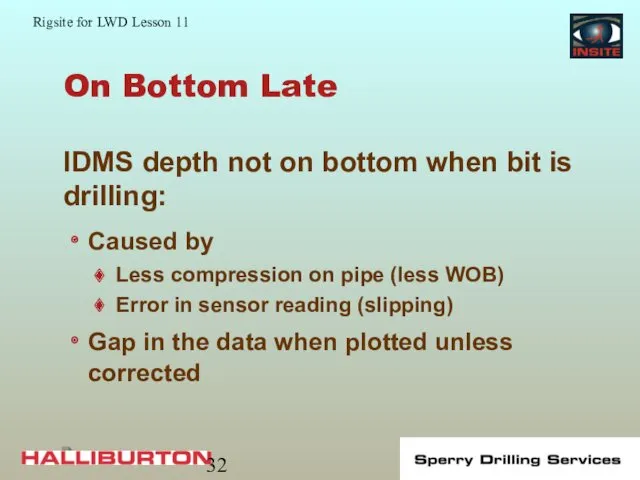
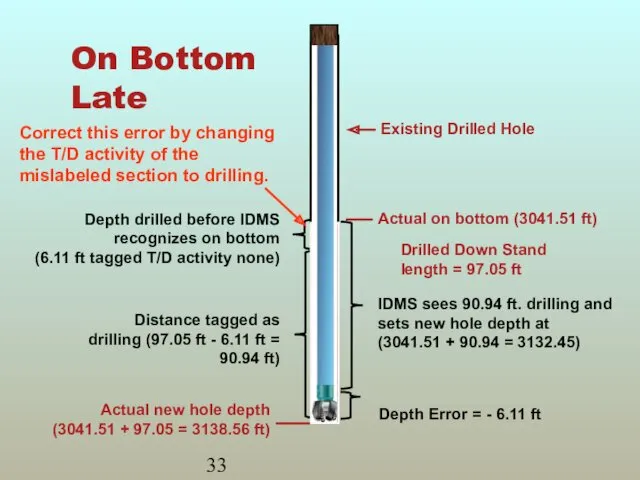
- 32. On Bottom Late Caused by Less compression on pipe (less WOB) Error in sensor reading (slipping)
- 33. On Bottom Late
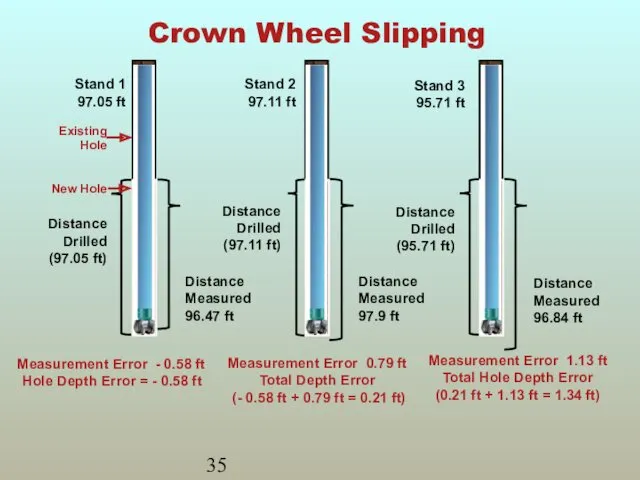
- 34. Crown Wheel Slipping Most likely to slip during fast movement of the drillstring Hot weather can
- 35. Crown Wheel Slipping Measurement Error - 0.58 ft Hole Depth Error = - 0.58 ft Measurement
- 36. Time/Depth Editor Functions Find Expand and compress Shift Insert and append Delete Edit single records Functions
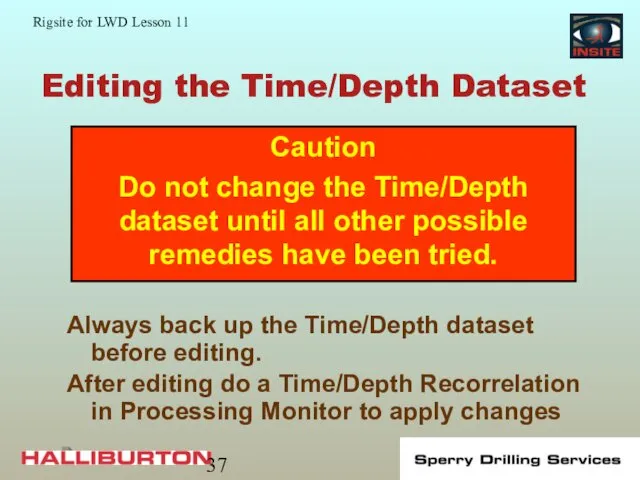
- 37. Editing the Time/Depth Dataset Always back up the Time/Depth dataset before editing. After editing do a
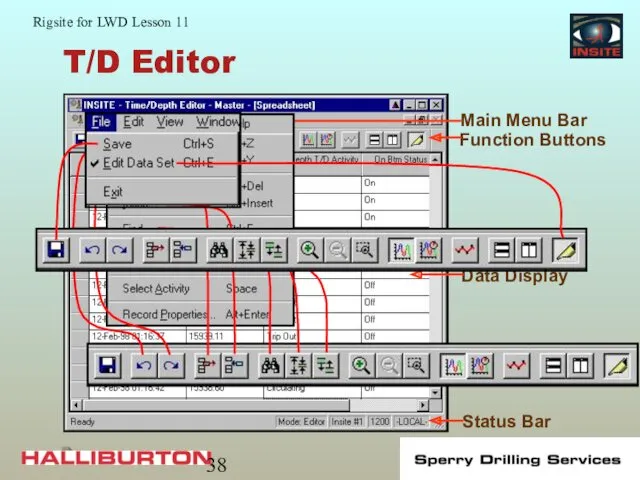
- 38. T/D Editor
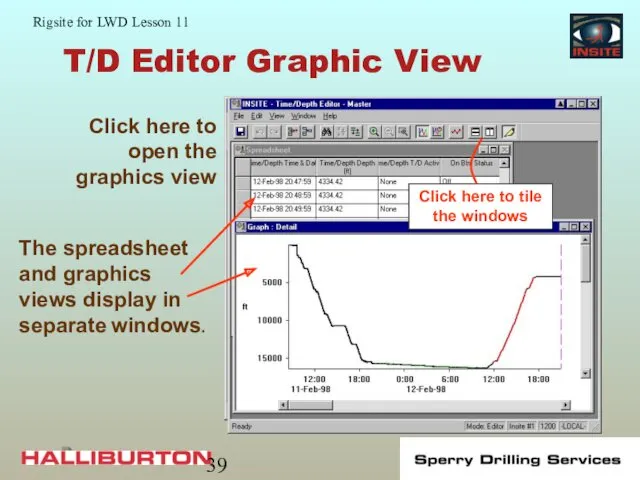
- 39. T/D Editor Graphic View
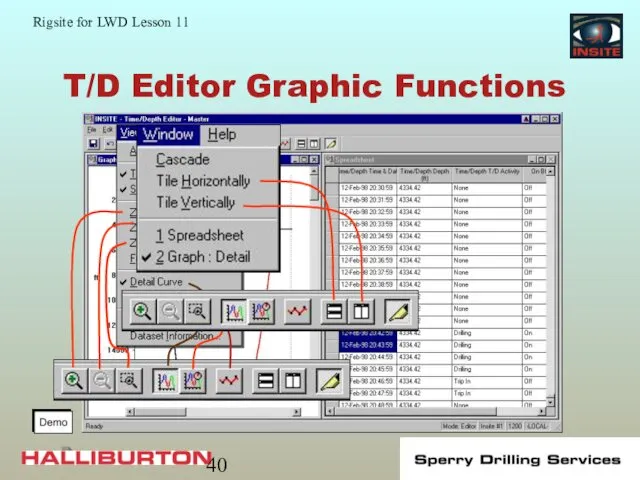
- 40. T/D Editor Graphic Functions
- 41. Time/Depth Review Sources of depth error Time/Depth editor layout Editing functions and when to use them
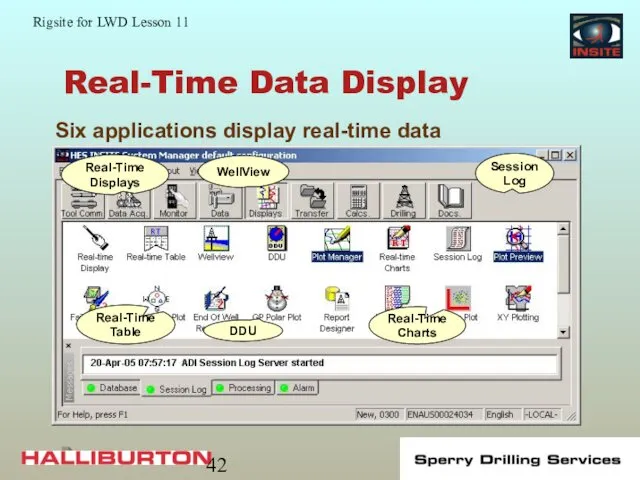
- 42. Real-Time Data Display Six applications display real-time data Real-Time Displays WellView Session Log Real-Time Table DDU
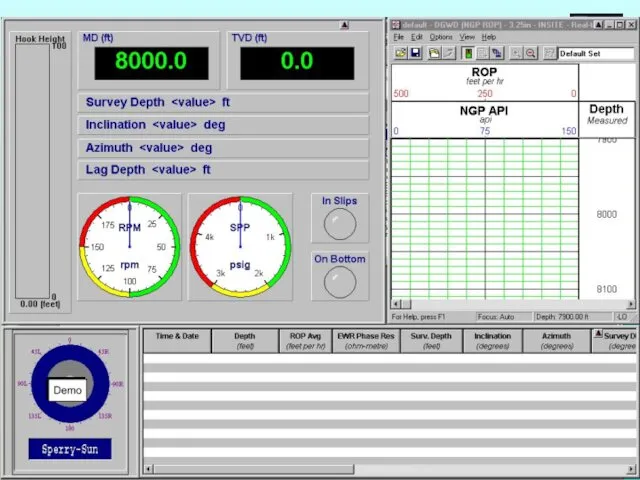
- 43. Real-Time Displays Real-time displays are customized for specific tools or situations: Built up from elements called
- 44. Real-Time Setup Files Applications with real-time displays (except DDU and WellView) can save the setup parameters:
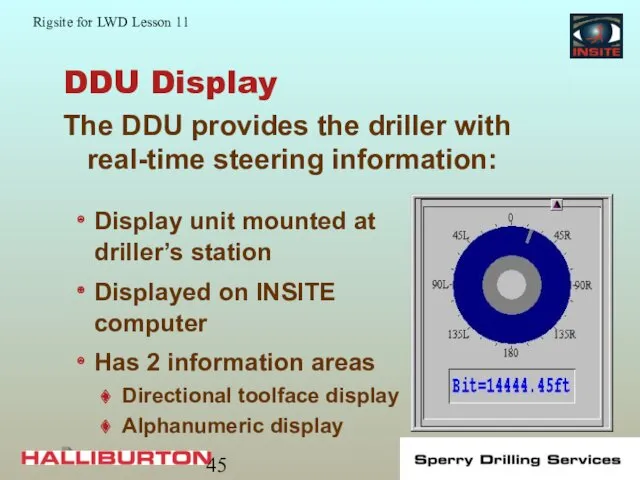
- 45. DDU Display The DDU provides the driller with real-time steering information: Display unit mounted at driller’s
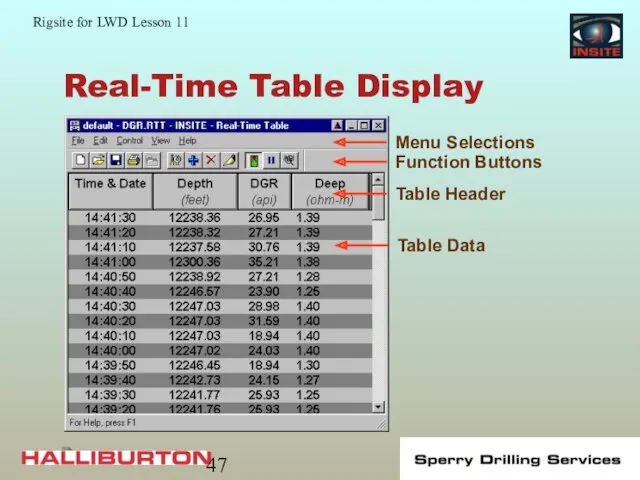
- 46. Real-Time Table Real-time tables are customized for specific tools or situations: Easier to read actual values
- 47. Real-Time Table Display
- 48. Real-Time Charts Real-time Charts: X,Y plot or bar chart of selected data Used to monitor critical
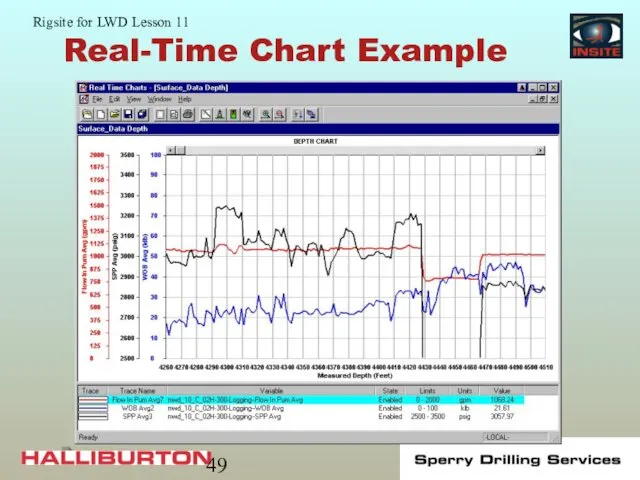
- 49. Real-Time Chart Example
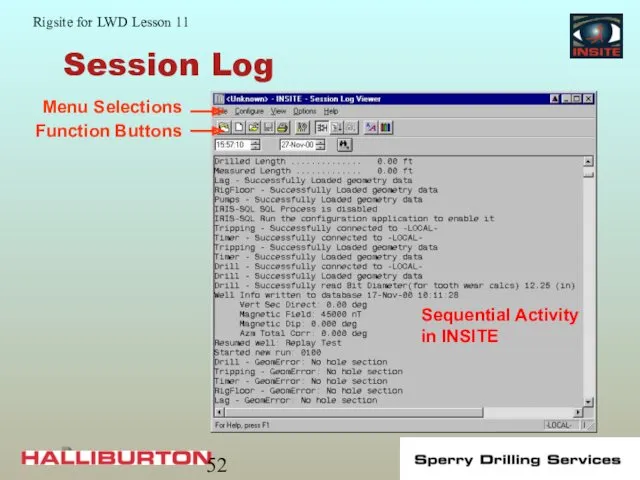
- 50. Session Log Record of all information received and operations performed by INSITE: Scrolling sequential record of
- 51. Session Log continued Realtime or historical mode Can view previous Session Logs Previous Session Log files
- 52. Session Log Sequential Activity in INSITE
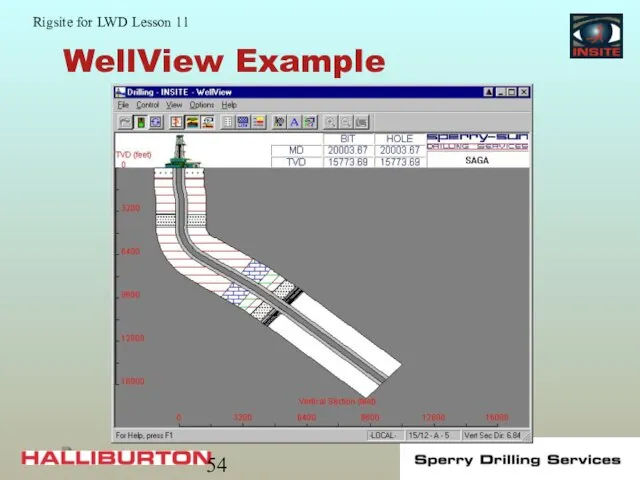
- 53. WellView WellView is a graphic presentation of the drilling track: Provides a visual display of well
- 54. WellView Example
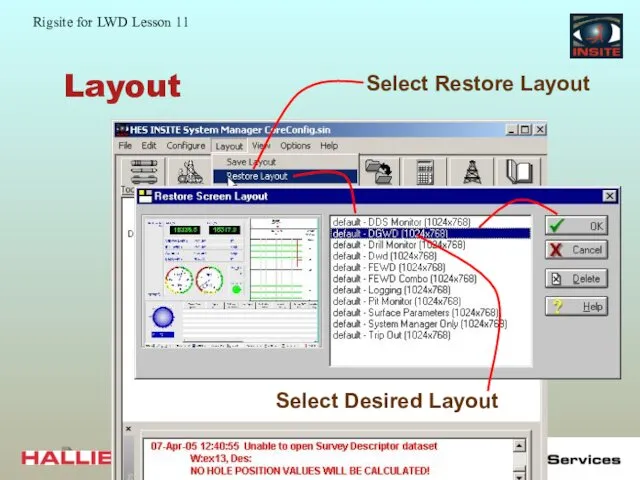
- 55. Layout Layout provides a set up of real-time displays: Contains templates for different job situations Templates
- 56. Layout
- 57. Layout
- 58. Real-time Display Review DDU Tables Plots Session log Layout
- 60. Скачать презентацию


















 Язык HTML
Язык HTML WSDL - Web Services Description Language
WSDL - Web Services Description Language Канальный уровень функциональной архитектуры телекоммуникационных сетей
Канальный уровень функциональной архитектуры телекоммуникационных сетей Точні та наближені алгоритми мінімізації числа виконавців при заданих директивних термінах
Точні та наближені алгоритми мінімізації числа виконавців при заданих директивних термінах Абсолютная и относительная адресация ячеек MS Excel
Абсолютная и относительная адресация ячеек MS Excel Теория и практика информационно-аналитической работы. Семинар
Теория и практика информационно-аналитической работы. Семинар История создания UNIX-систем. (Занятия 3 и 4)
История создания UNIX-систем. (Занятия 3 и 4) Программа Microsoft Excel. Электронные таблицы
Программа Microsoft Excel. Электронные таблицы Создание игр в Scratch - 24 - Trex (часть 2)
Создание игр в Scratch - 24 - Trex (часть 2) Журналистика деген не?
Журналистика деген не? Типология информационных ресурсов Интернет
Типология информационных ресурсов Интернет Создателям презентаций. Советы по составлению
Создателям презентаций. Советы по составлению Интерактивная презентация Кроссворд Компьютерные устройства
Интерактивная презентация Кроссворд Компьютерные устройства Web-страницы. Язык HTML и др
Web-страницы. Язык HTML и др Мультимедиа технологии
Мультимедиа технологии Автоматизированная система Музей-3
Автоматизированная система Музей-3 Количество информации
Количество информации Розробка Web-сайту кафедри біомедичної інженерії
Розробка Web-сайту кафедри біомедичної інженерії Безопасность данных и информационная защита
Безопасность данных и информационная защита Компьютерные вирусы и антивирусные программы
Компьютерные вирусы и антивирусные программы Знакомство с алгоритмическим языком стрелок
Знакомство с алгоритмическим языком стрелок Основы кибербезопасности. Лекция 4.1. Понятие об источниках и каналах утечки информации; основы технической защиты информации
Основы кибербезопасности. Лекция 4.1. Понятие об источниках и каналах утечки информации; основы технической защиты информации Файл. Файловая система
Файл. Файловая система Основы программирования станков с ЧПУ и программоносители
Основы программирования станков с ЧПУ и программоносители Управление в автоматизированном производстве (01)
Управление в автоматизированном производстве (01) Знакомство с библиотекой
Знакомство с библиотекой Простейшие программы
Простейшие программы Оперативно-информационный комплекс СК-2007 для диспетчерского управления электроэнергетическими системами. Монитор Электрик
Оперативно-информационный комплекс СК-2007 для диспетчерского управления электроэнергетическими системами. Монитор Электрик