Содержание
- 2. Main points What is an object ? What is a class ? What are messages ?
- 3. Object An object is an instance of a class. Objects have states and behaviors. Best practice:
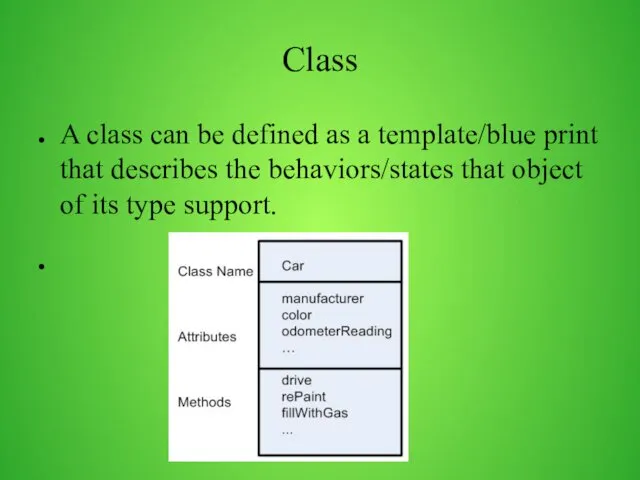
- 4. Class A class can be defined as a template/blue print that describes the behaviors/states that object
- 5. Messages Objects interact and communicate with each other using messages. You are able to send message
- 6. Inheritance Inheritance, therefore, defines an "is a" hierarchy among classes, in which subclass inherits from one
- 7. Polymorphism Polymorphism is the ability of an object to take on many forms. Polymorphism allows us
- 8. Encapsulation Change state of object using methods provided by object. Best practices: keep fields as private
- 9. S.O.L.I.D. principles SRP - a class should have only a single responsibility OCP - software entities
- 11. Скачать презентацию







 Мобильные приложения. Шаблоны проектирования
Мобильные приложения. Шаблоны проектирования Трассировка. Цикл DO While. Лабораторная работа №4
Трассировка. Цикл DO While. Лабораторная работа №4 Введение в C#. Новый язык от Microsoft
Введение в C#. Новый язык от Microsoft Компьютерные сети, Интернет и мультимедиа технологии. Основы сетей передачи данных
Компьютерные сети, Интернет и мультимедиа технологии. Основы сетей передачи данных The online gold shop
The online gold shop Логические элементы
Логические элементы Dota 2 — компьютерная многопользовательская командная игра
Dota 2 — компьютерная многопользовательская командная игра DTP — собственный протокол компании Cisco
DTP — собственный протокол компании Cisco Информационная система
Информационная система Базы данных
Базы данных Кібербулінг. Запобігання впливу шкідливої інформації
Кібербулінг. Запобігання впливу шкідливої інформації Библиографическое описание. Правила составления. (Тема 6)
Библиографическое описание. Правила составления. (Тема 6) Интерфейс мобильных приложений
Интерфейс мобильных приложений Что могут роботы
Что могут роботы CiGe Update firmware Using the tutorial
CiGe Update firmware Using the tutorial Моя будущая профессия - разработчик игр
Моя будущая профессия - разработчик игр Системы счисления
Системы счисления Введение в поисковое продвижение
Введение в поисковое продвижение Слой приложений
Слой приложений Использование электронной почты для организации электронного документооборота
Использование электронной почты для организации электронного документооборота Что такое UML
Что такое UML Сортировка массивов. Основы программирования
Сортировка массивов. Основы программирования Введение в профессию. Понятия информации, сообщения и сигнала
Введение в профессию. Понятия информации, сообщения и сигнала Multithreading (Java, C#, C++)
Multithreading (Java, C#, C++) Игра по информатике Умники и умницы
Игра по информатике Умники и умницы Современные информационные технологии в дипломатии
Современные информационные технологии в дипломатии Адаптеры Ethernet и Fast Ethernet
Адаптеры Ethernet и Fast Ethernet Работа с данными в Entity Framework Core. Проектирование и разработка веб-сервисов
Работа с данными в Entity Framework Core. Проектирование и разработка веб-сервисов