Содержание
- 2. Learning objectives: understand that there are several lifecycle models that can be used (eg cyclical, waterfall,
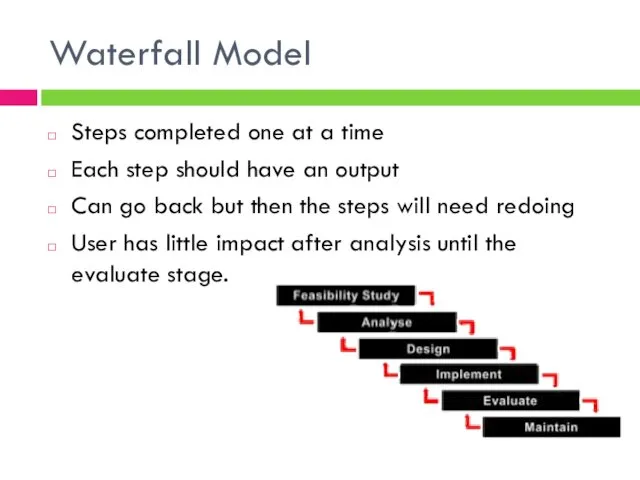
- 3. Waterfall Model Steps completed one at a time Each step should have an output Can go
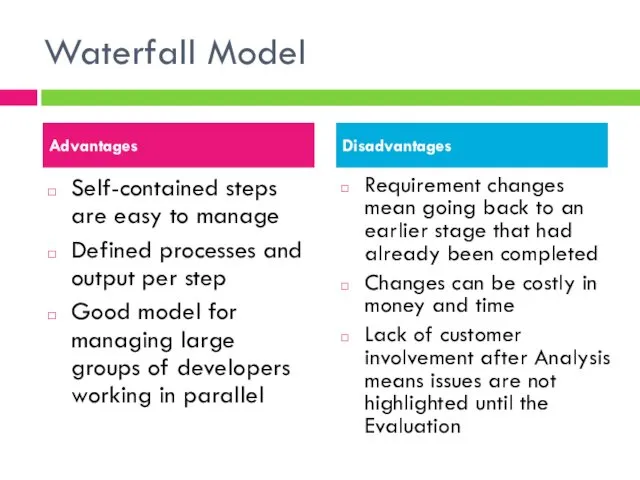
- 4. Waterfall Model Self-contained steps are easy to manage Defined processes and output per step Good model
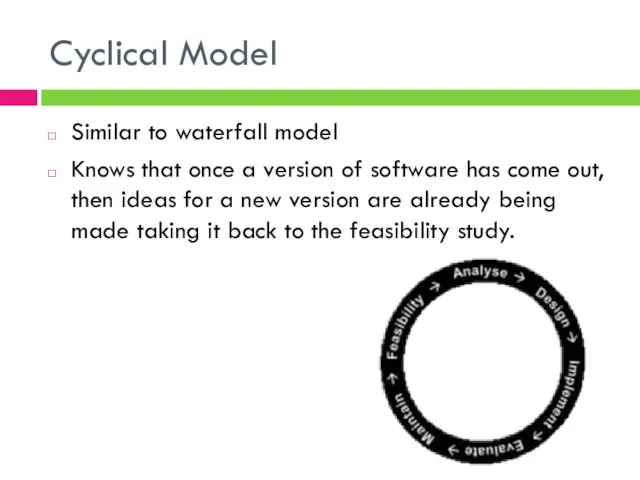
- 5. Cyclical Model Similar to waterfall model Knows that once a version of software has come out,
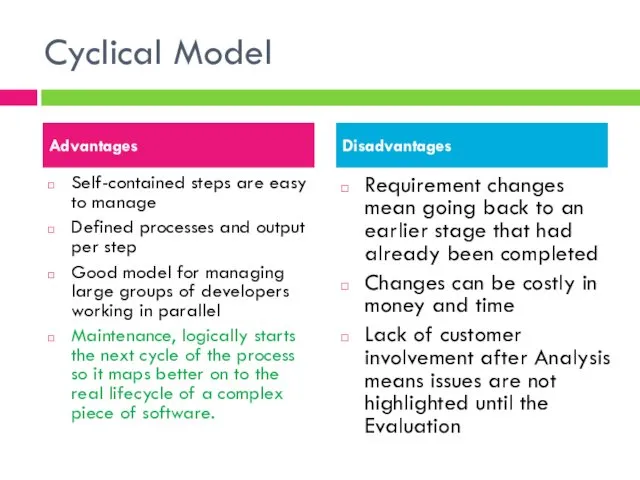
- 6. Cyclical Model Self-contained steps are easy to manage Defined processes and output per step Good model
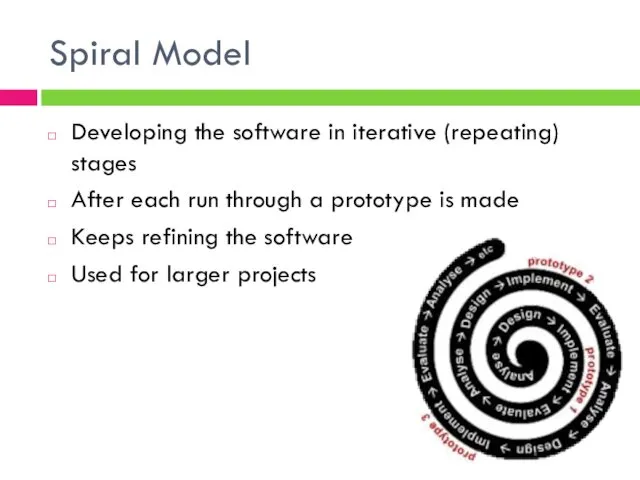
- 7. Spiral Model Developing the software in iterative (repeating) stages After each run through a prototype is
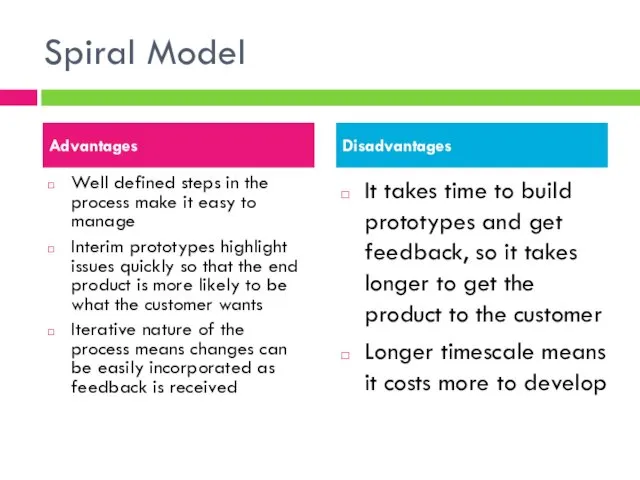
- 8. Spiral Model Well defined steps in the process make it easy to manage Interim prototypes highlight
- 9. Agile Model Similar to spiral in making prototypes Customer then evaluates each prototype and gives feedback
- 10. Agile Model Essentially the same as the Spiral Model with the following addition: Small multitasking groups
- 11. Review Can you simplify each model to 10 words? Now 5? Agile
- 12. Prototype – опытный образец In the spiral life-cycle model at the stage of analysis and design
- 13. Prototype – опытный образец advantages of prototyping: Enable the system to be reviewed by the
- 15. Скачать презентацию




 Единицы измерения информации
Единицы измерения информации Освещение и камеры в Blender
Освещение и камеры в Blender Информационная безопасность предприятия
Информационная безопасность предприятия Анимации в презентации
Анимации в презентации 3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный)
3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный) Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома)
Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома) Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики
Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики Распределенные вычисления в Интернет
Распределенные вычисления в Интернет HTML/ CSS Base
HTML/ CSS Base Разработка и эксплуатация АИС
Разработка и эксплуатация АИС Getting more physical in Call of Duty
Getting more physical in Call of Duty Коллекции Python
Коллекции Python Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей
Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии
Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии 9 класс. Алгоритмизация.
9 класс. Алгоритмизация. История развития Интернета
История развития Интернета Service Tool
Service Tool Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия
Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2)
Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2) Искусственный интеллект
Искусственный интеллект Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных
Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных Теория нейронных сетей
Теория нейронных сетей Интернет в работе переводчика
Интернет в работе переводчика Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа
Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word
Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы
MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы Поняття про мультимедіа
Поняття про мультимедіа Independent Component Analysis
Independent Component Analysis