Содержание
- 2. Communicating in a Network-Centric World
- 3. Global Access The globalization of the Internet has succeeded faster than anyone could have imagined. The
- 4. Networks – Behind the Scenes Networks are more than just connecting cables. They are a complex
- 5. Networks – The Early Days Early communication relied on face-to-face conversations. The telephone was used for
- 6. Networks – The Early Days Early networks were limited to character based information. Communications between computers
- 7. Networks – Today Today’s networks carry multiple types of information through many types of devices -
- 8. Networks – Today – A Global Community
- 9. Networks Supporting The Way We Live The Internet has quickly become an integral part of our
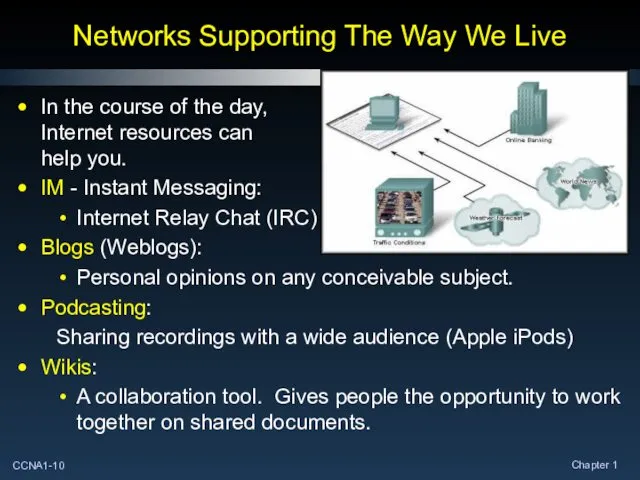
- 10. Networks Supporting The Way We Live In the course of the day, Internet resources can help
- 11. Networks Supporting The Way We Learn E-Learning
- 12. Networks Supporting The Way We Learn Online discussions and access to resources.
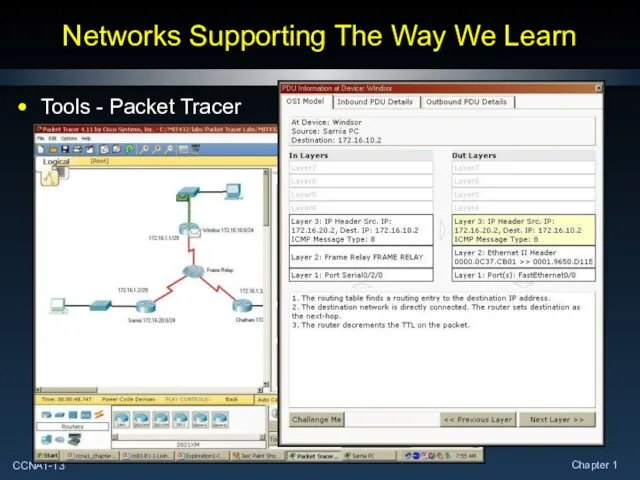
- 13. Networks Supporting The Way We Learn Tools - Packet Tracer
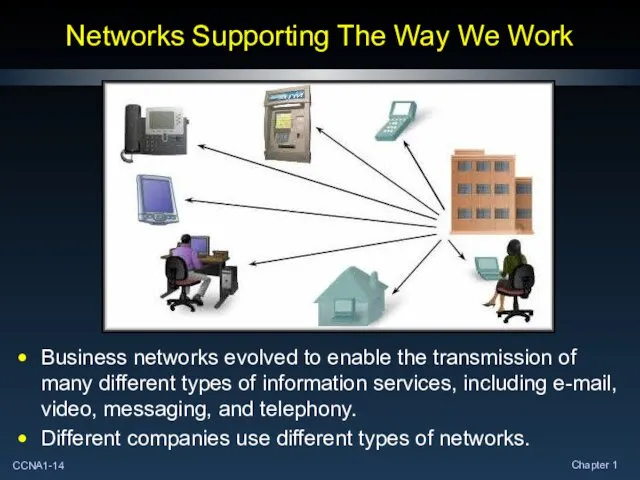
- 14. Networks Supporting The Way We Work Business networks evolved to enable the transmission of many different
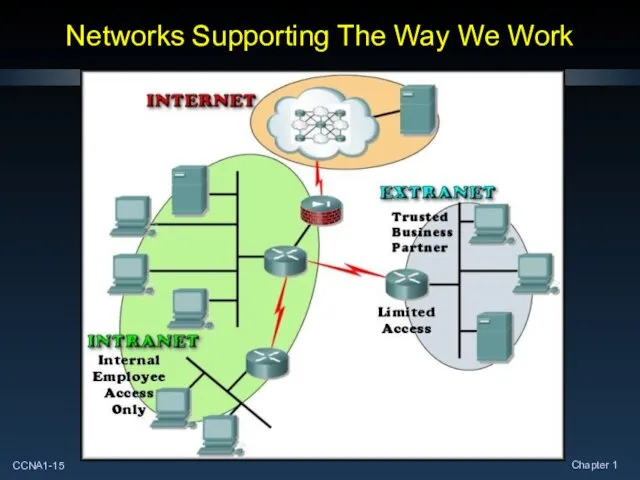
- 15. Networks Supporting The Way We Work
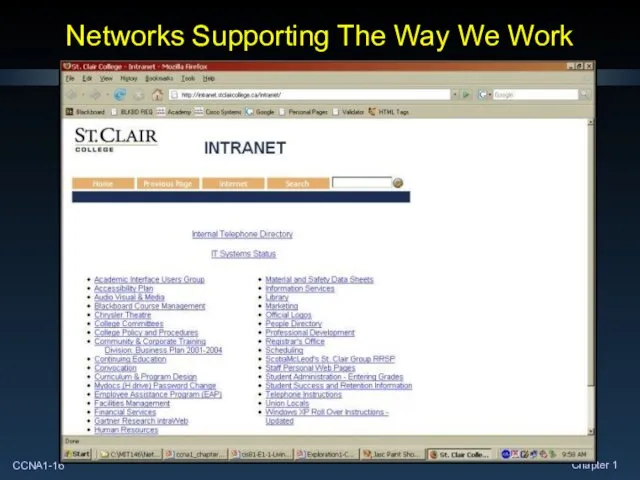
- 16. Networks Supporting The Way We Work
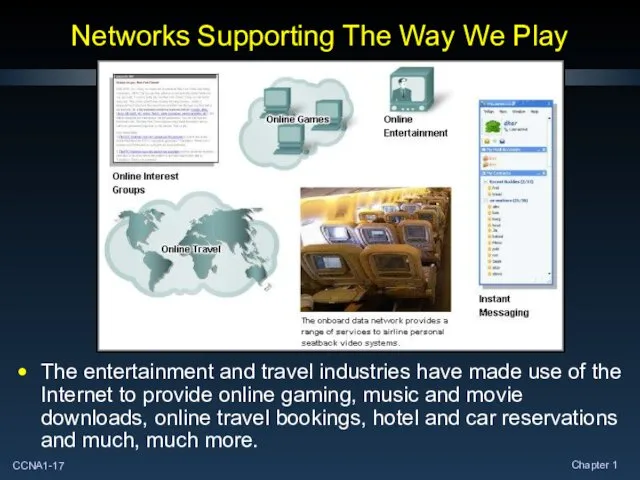
- 17. Networks Supporting The Way We Play The entertainment and travel industries have made use of the
- 18. Networks Supporting The Way We Play Some of the most innovative developments in network technology have
- 19. Communications – What is it? Communications can take many forms and occurs in many different environments.
- 20. Communications - Quality For data networks, we use the same basic criteria to judge successful communication.
- 21. Communications - Quality There are also internal factors that can affect successful communication. Message Complexity Message
- 22. Communications - Quality It is also more difficult to deliver a large, bulky package successfully and
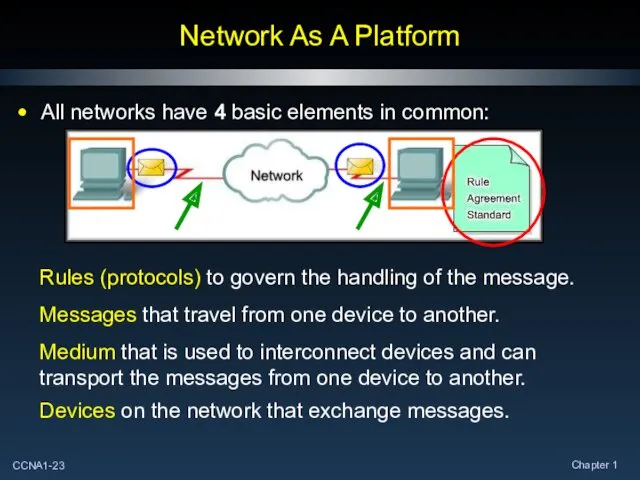
- 23. Network As A Platform All networks have 4 basic elements in common:
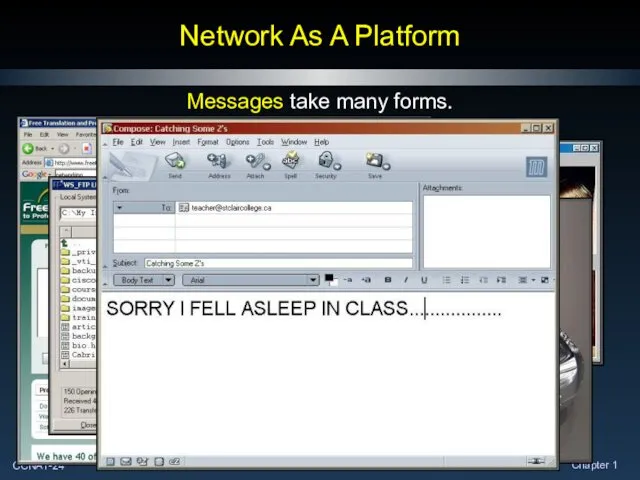
- 24. Network As A Platform Messages take many forms.
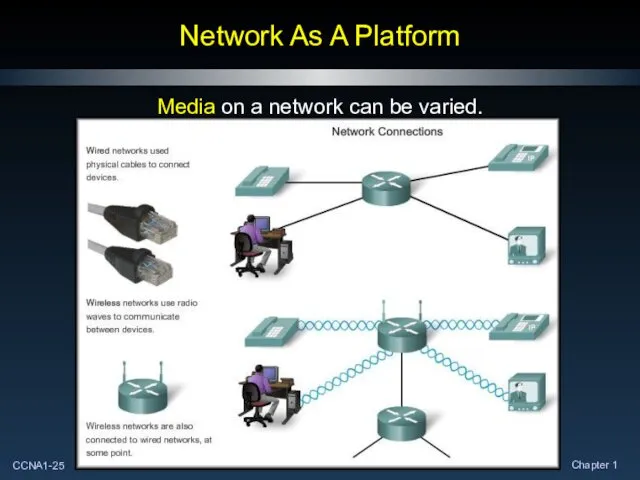
- 25. Network As A Platform Media on a network can be varied.
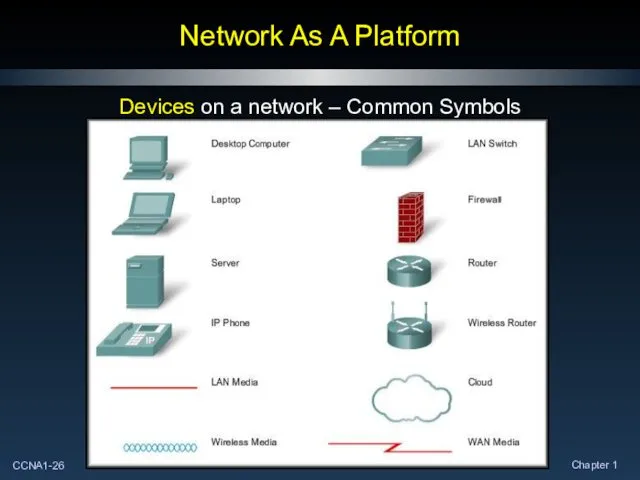
- 26. Network As A Platform Devices on a network – Common Symbols
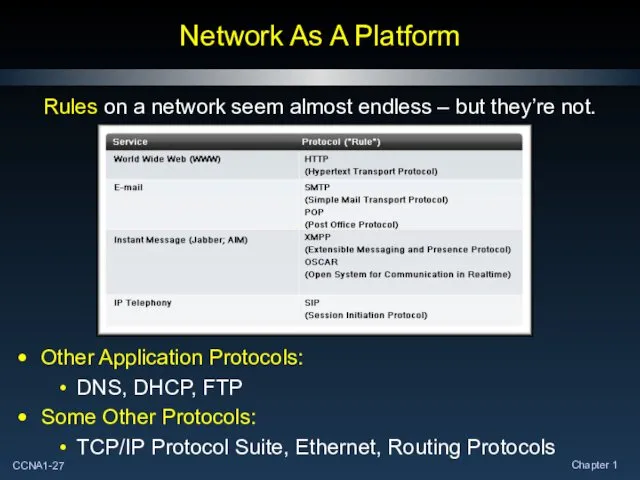
- 27. Network As A Platform Rules on a network seem almost endless – but they’re not. Other
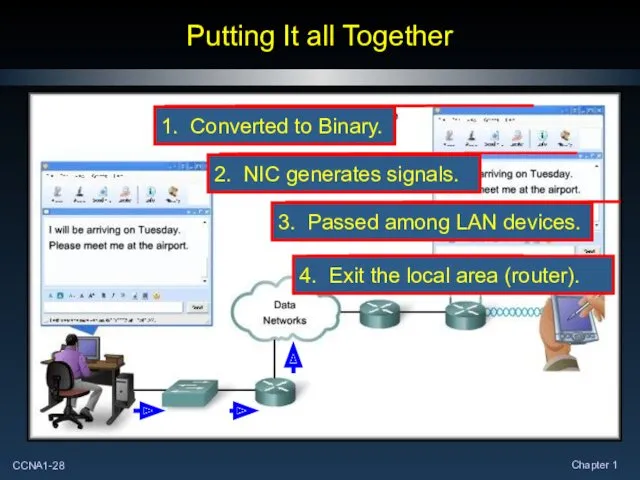
- 28. Putting It all Together 1. Converted to Binary.
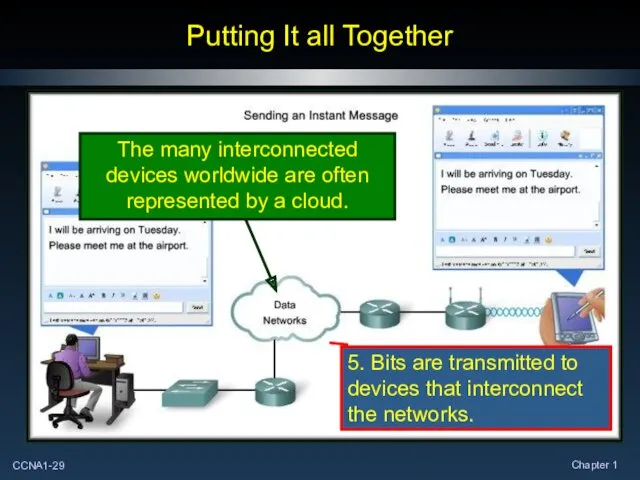
- 29. Putting It all Together 5. Bits are transmitted to devices that interconnect the networks.
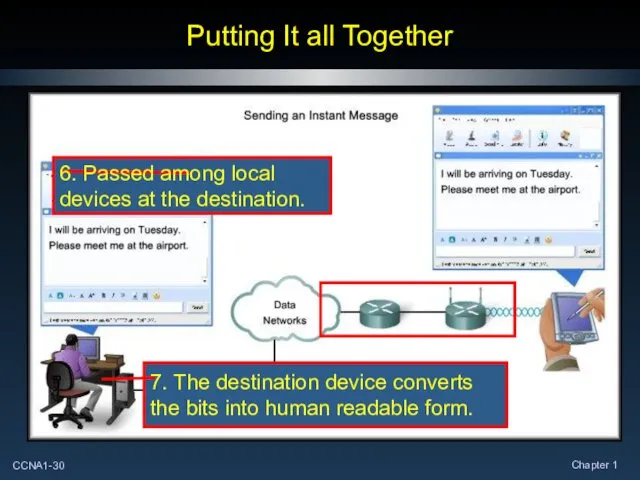
- 30. Putting It all Together 7. The destination device converts the bits into human readable form.
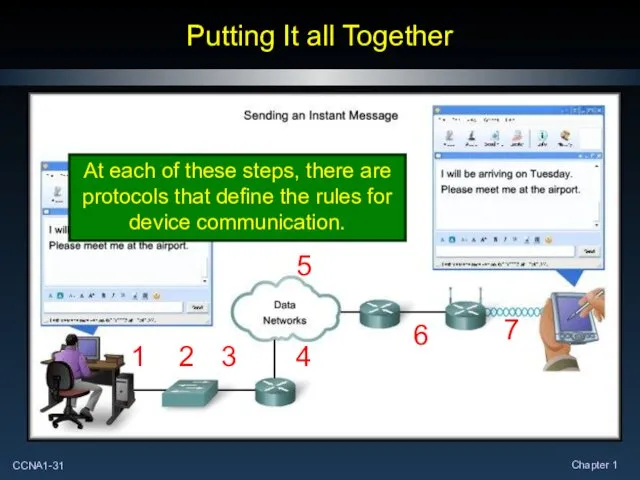
- 31. Putting It all Together 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 At each of these steps,
- 32. Putting It All Together Of course, it always helps to know what you’re doing.
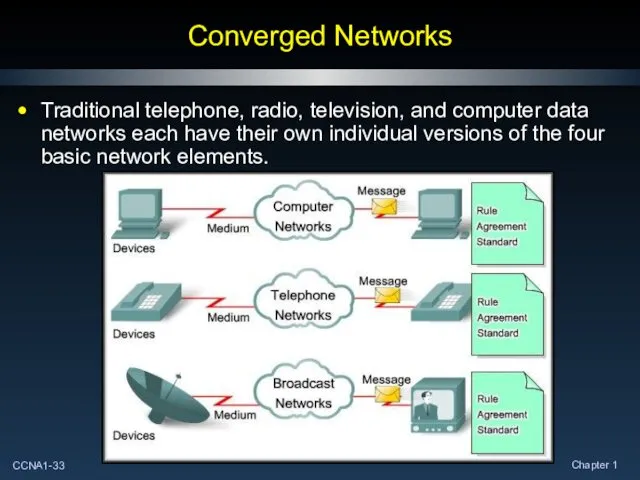
- 33. Converged Networks Traditional telephone, radio, television, and computer data networks each have their own individual versions
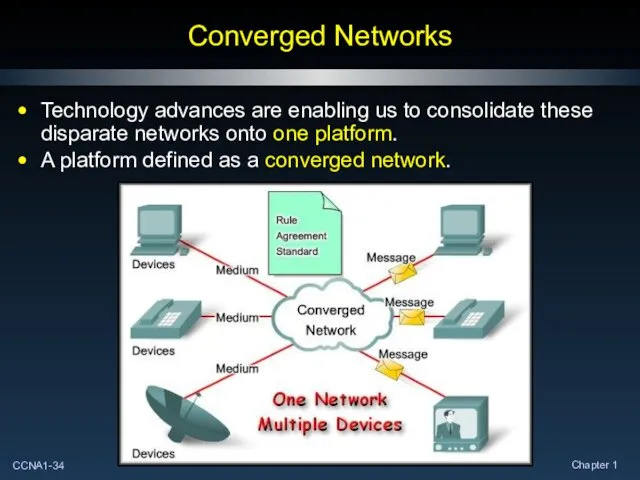
- 34. Converged Networks Technology advances are enabling us to consolidate these disparate networks onto one platform. A
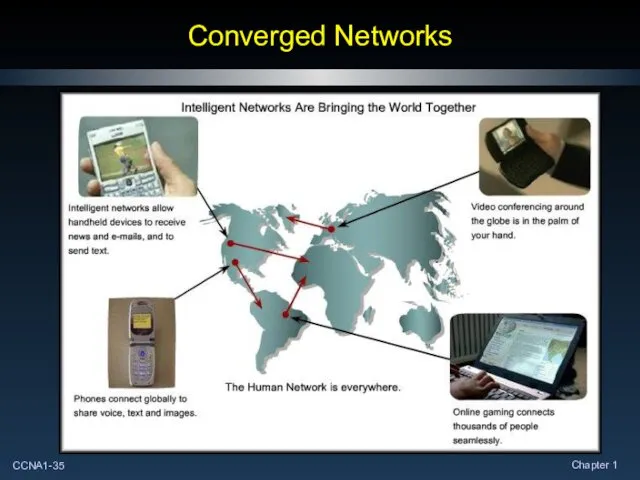
- 35. Converged Networks
- 36. The Architecture of the Internet The term Network Architecture: Technologies that support the infrastructure Programmed services
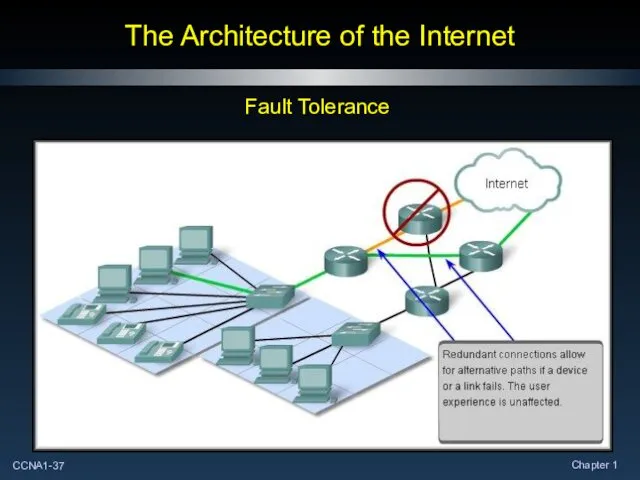
- 37. The Architecture of the Internet Fault Tolerance
- 38. The Architecture of the Internet Fault Tolerance: The Internet, in its early inception, was the result
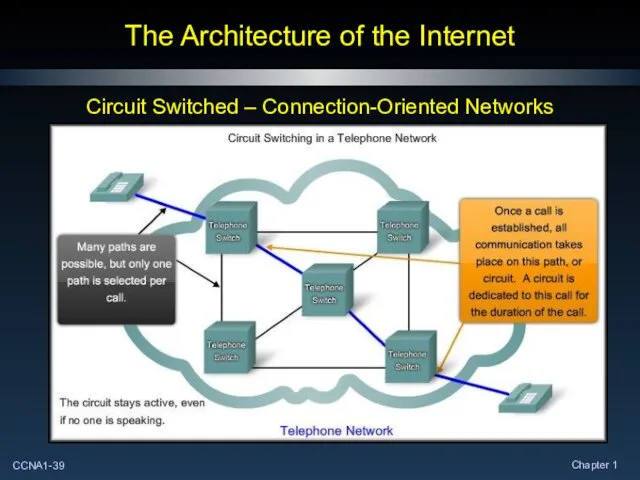
- 39. The Architecture of the Internet Circuit Switched – Connection-Oriented Networks
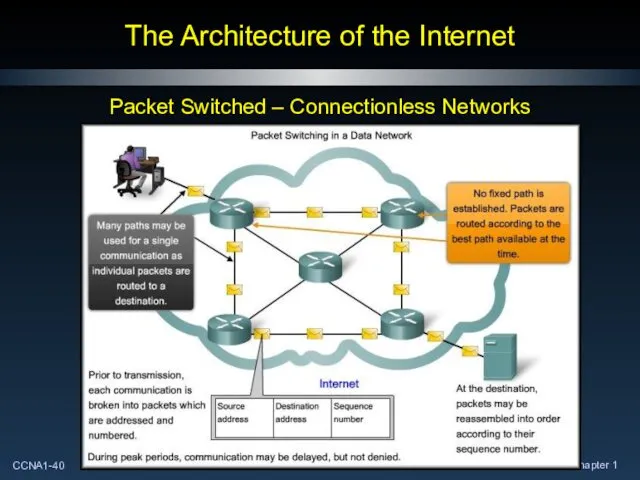
- 40. The Architecture of the Internet Packet Switched – Connectionless Networks
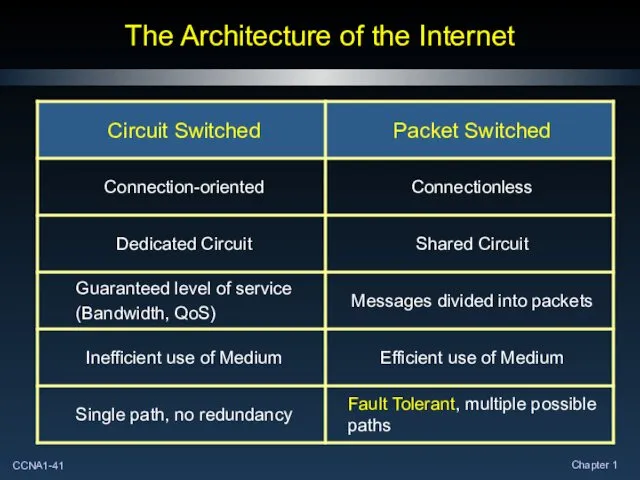
- 41. The Architecture of the Internet
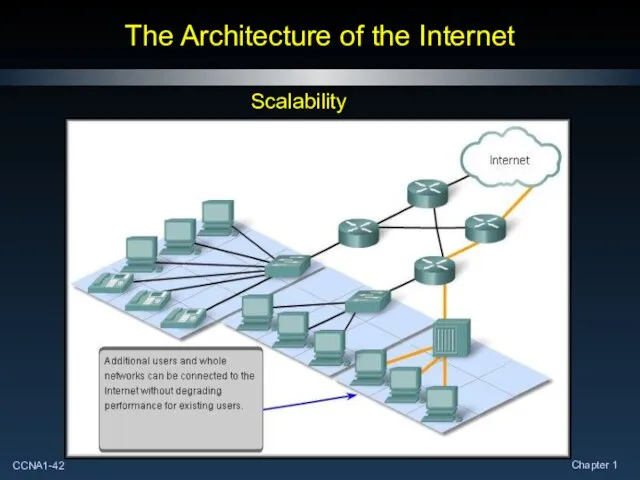
- 42. The Architecture of the Internet Scalability
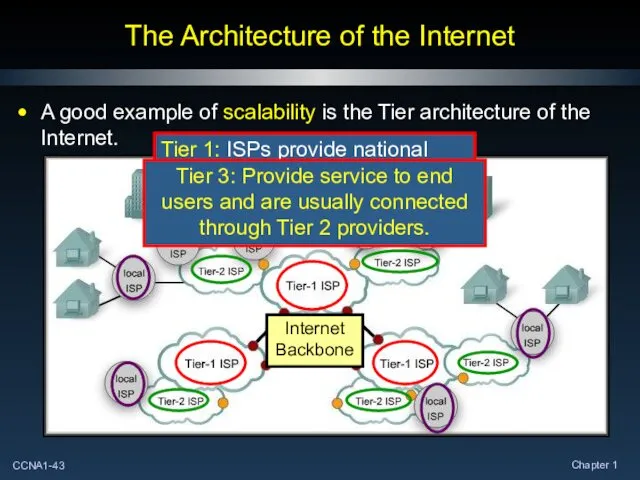
- 43. The Architecture of the Internet A good example of scalability is the Tier architecture of the
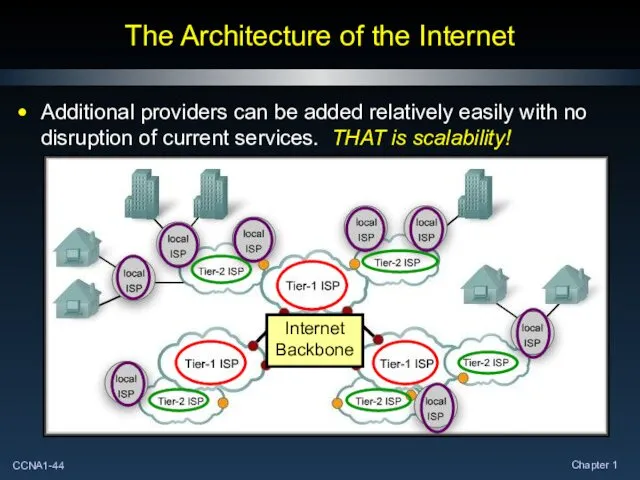
- 44. The Architecture of the Internet Additional providers can be added relatively easily with no disruption of
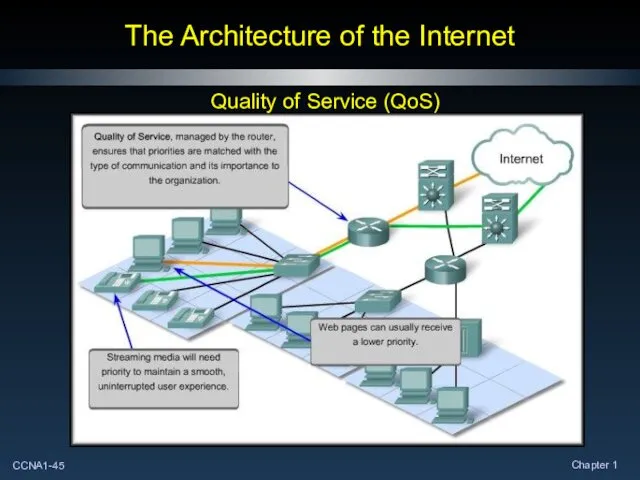
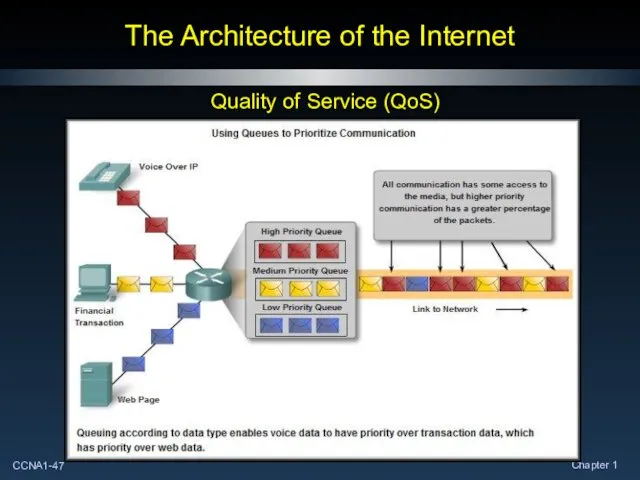
- 45. The Architecture of the Internet Quality of Service (QoS)
- 46. The Architecture of the Internet Quality of Service (QoS)
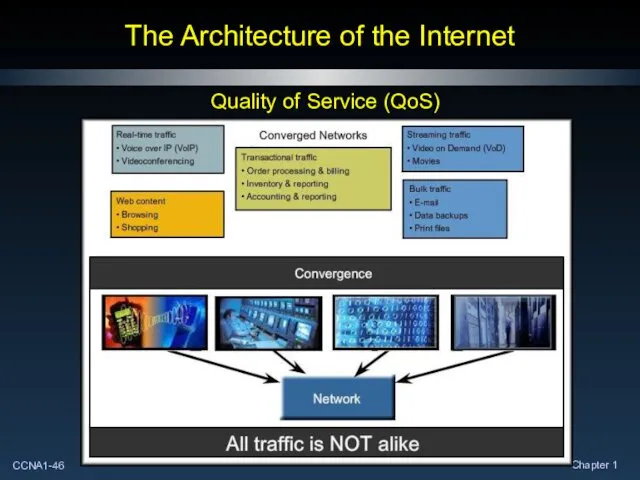
- 47. The Architecture of the Internet Quality of Service (QoS)
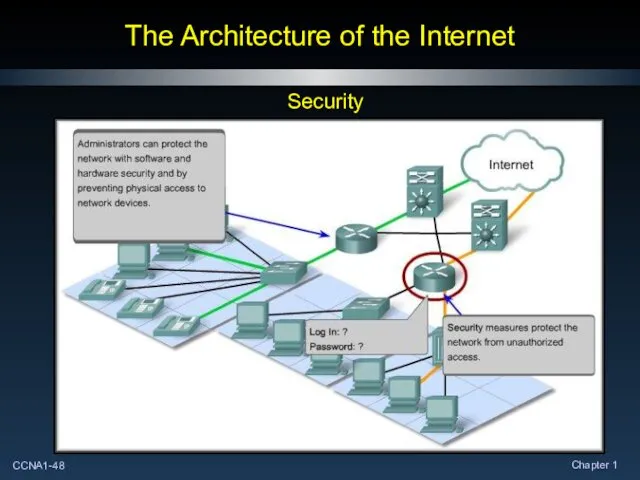
- 48. The Architecture of the Internet Security
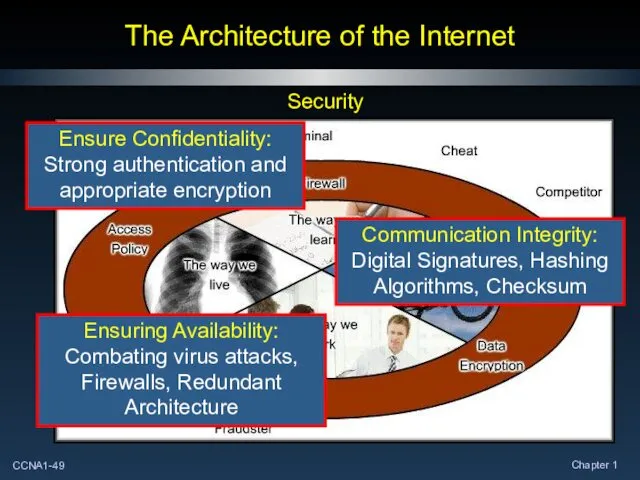
- 49. The Architecture of the Internet Security Ensure Confidentiality: Strong authentication and appropriate encryption Communication Integrity: Digital
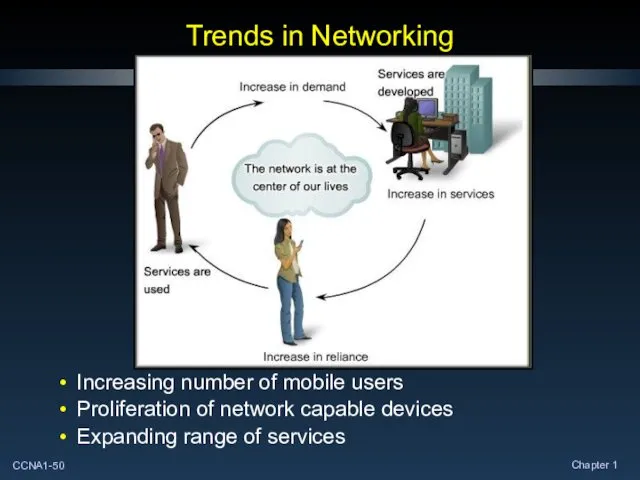
- 50. Trends in Networking Increasing number of mobile users Proliferation of network capable devices Expanding range of
- 51. Careers Information Technology and networking careers are growing and evolving as fast as the underlying technologies
- 52. “IT” is not the Network – it IS the users. The IT (Information Technology) department is
- 53. A Shift in Attitude Old school IT doesn’t work any more. We don’t support MACs. We
- 55. Скачать презентацию




















 Единицы измерения информации
Единицы измерения информации Освещение и камеры в Blender
Освещение и камеры в Blender Информационная безопасность предприятия
Информационная безопасность предприятия Анимации в презентации
Анимации в презентации 3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный)
3Д окно, механизмы отображения (Open GL и векторный) Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома)
Исследование возможностей применения BIM-технологии в компьютерном дизайне (на примере интерьера загородного дома) Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики
Презентация к сценарию внеклассного мероприятия Путешествие в страну Информатики Распределенные вычисления в Интернет
Распределенные вычисления в Интернет HTML/ CSS Base
HTML/ CSS Base Разработка и эксплуатация АИС
Разработка и эксплуатация АИС Getting more physical in Call of Duty
Getting more physical in Call of Duty Коллекции Python
Коллекции Python Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей
Архитектура вычислительных систем и сетей Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии
Лекция 1. Основы программной инженерии. Понятие программной инженерии. Стандарты программной инженерии 9 класс. Алгоритмизация.
9 класс. Алгоритмизация. История развития Интернета
История развития Интернета Service Tool
Service Tool Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия
Протокол межсетевого взаимодействия Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2)
Основы делопроизводства. (Лекция 2) Искусственный интеллект
Искусственный интеллект Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных
Программное обеспечение. Правовая охрана программ и данных Теория нейронных сетей
Теория нейронных сетей Интернет в работе переводчика
Интернет в работе переводчика Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа
Электронные таблицы Excel. Самостоятельная работа Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word
Форматирование текста в текстовом редакторе MS Word MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы
MS Word - мәтіндік редакторы Поняття про мультимедіа
Поняття про мультимедіа Independent Component Analysis
Independent Component Analysis