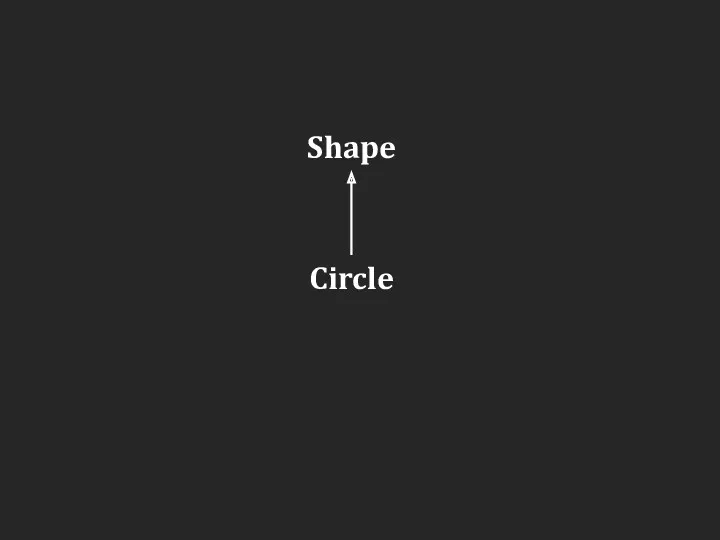
Слайд 2
![class : [, ] { ... };](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293491/slide-1.jpg)
class <имя производного класса> :
<спецификатор доступа> <имя базового класса>
[,
<спецификатор доступа> <имя базового класса> ]
{ ... };
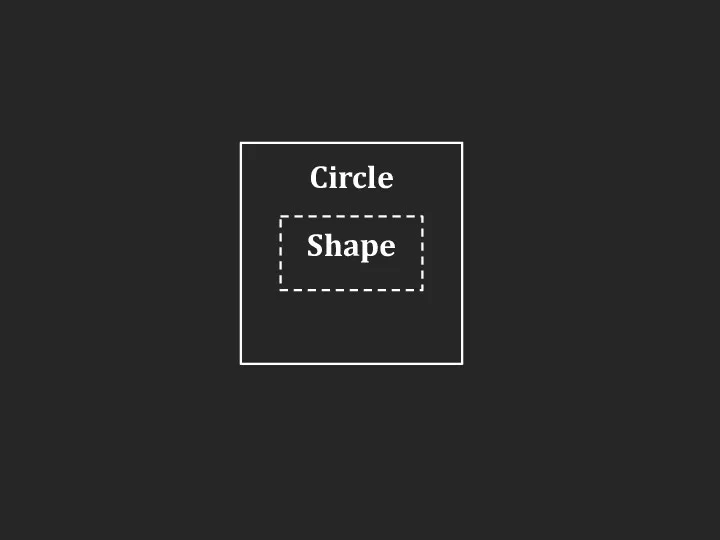
Слайд 3
Слайд 4
Слайд 5
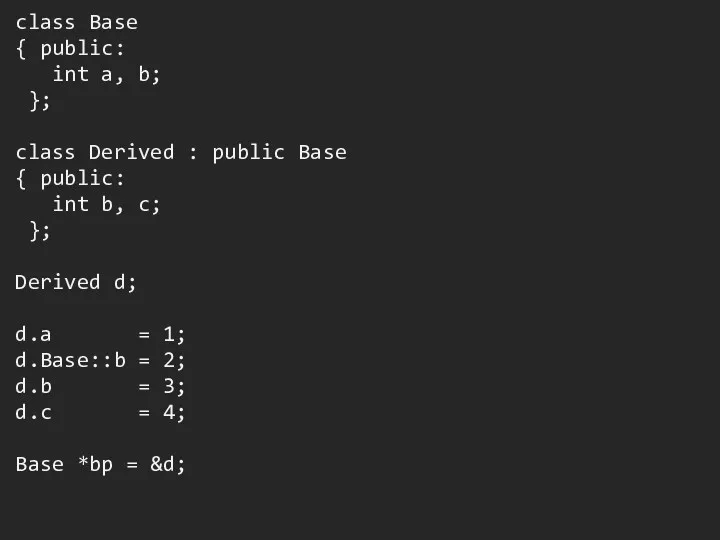
class Base
{ public:
int a, b;
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
int b, c;
};
Derived d;
d.a = 1;
d.Base::b = 2;
d.b = 3;
d.c = 4;
Base *bp = &d;
Слайд 6

class A { public: void f(); };
class B : public A
{ };
class C : public B
{ public:
void f(); void ff();
};
void C::ff()
{ f(); // C::f
A::f(); // A::f
B::f(); // A::f
}
Слайд 7

Спецификатор доступа может быть:
public – в этом случае публичные члены базового
класса становятся публичными членами производного класса, а защищённые члены базового класса становятся защищёнными членами производного класса;
protected – в этом случае публичные и защищённые члены базового класса становятся защищёнными членами производного класса;
private – в этом случае публичные и защищённые члены базового класса становятся приватными членами производного класса.
Слайд 8
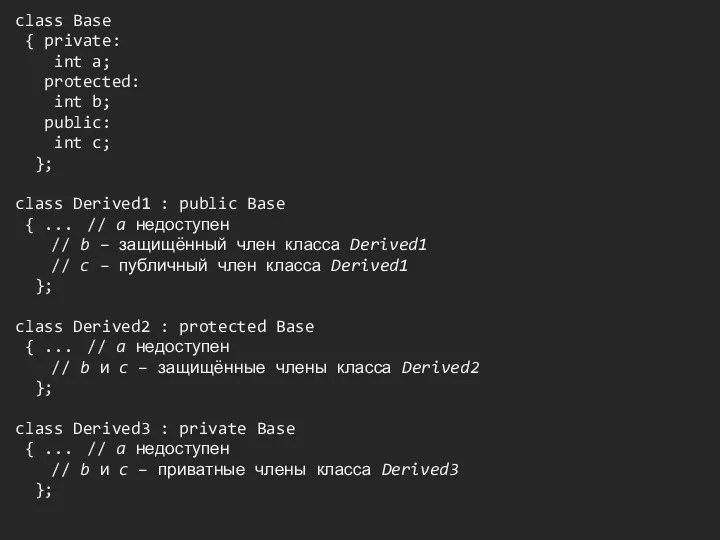
class Base
{ private:
int a;
protected:
int b;
public:
int
c;
};
class Derived1 : public Base
{ ... // a недоступен
// b – защищённый член класса Derived1
// c – публичный член класса Derived1
};
class Derived2 : protected Base
{ ... // a недоступен
// b и c – защищённые члены класса Derived2
};
class Derived3 : private Base
{ ... // a недоступен
// b и c – приватные члены класса Derived3
};
Слайд 9
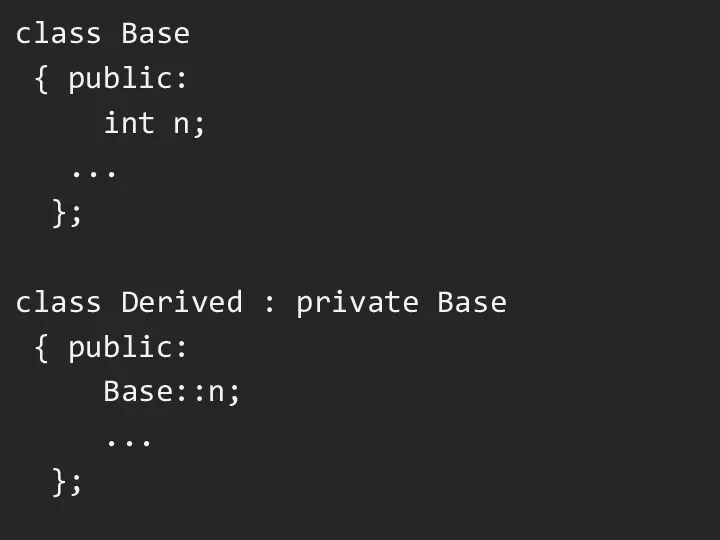
class Base
{ public:
int n;
...
};
class Derived : private
Base
{ public:
Base::n;
...
};
Слайд 10

class Base
{ public:
void f();
void f(int n);
};
class Derived
: private Base
{ public:
Base::f;
};
Слайд 11

class Base
{ public:
void f();
};
class Derived : private Base
{ public:
void f(int n);
Base::f;
};
Слайд 12
class Base
{ private:
int a;
protected:
int b;
public:
Base(int
a, int b) : a(a), b(b) { }
// …
};
class Derived : public Base
{ private:
int c;
public:
Derived(int a, int b, int c) :
Base(a, b),
c(c)
{ }
};
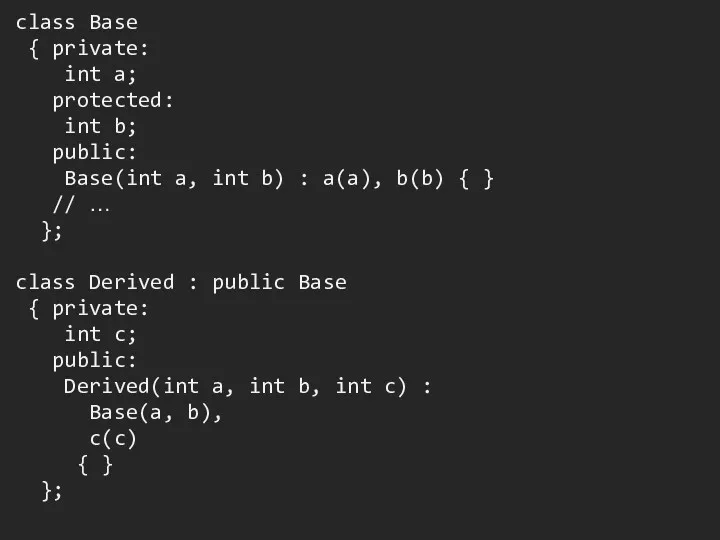
Слайд 13
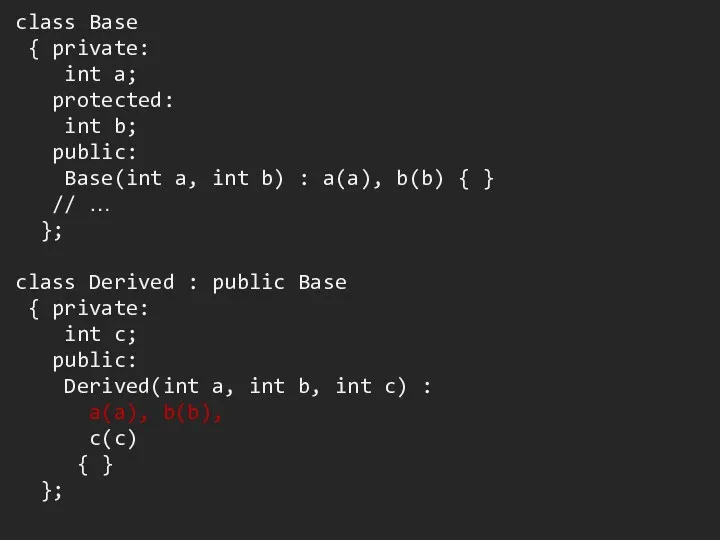
class Base
{ private:
int a;
protected:
int b;
public:
Base(int
a, int b) : a(a), b(b) { }
// …
};
class Derived : public Base
{ private:
int c;
public:
Derived(int a, int b, int c) :
a(a), b(b),
c(c)
{ }
};
Слайд 14
class Base
{ protected:
int n;
};
class Derived1 : public Base
{ ... };
class Derived2 : public Base
{ void member_function(Base *pb, Derived1 *p1);
friend void friend_function(Base *pb, Derived1 *p1,
Derived2 *p2);
};
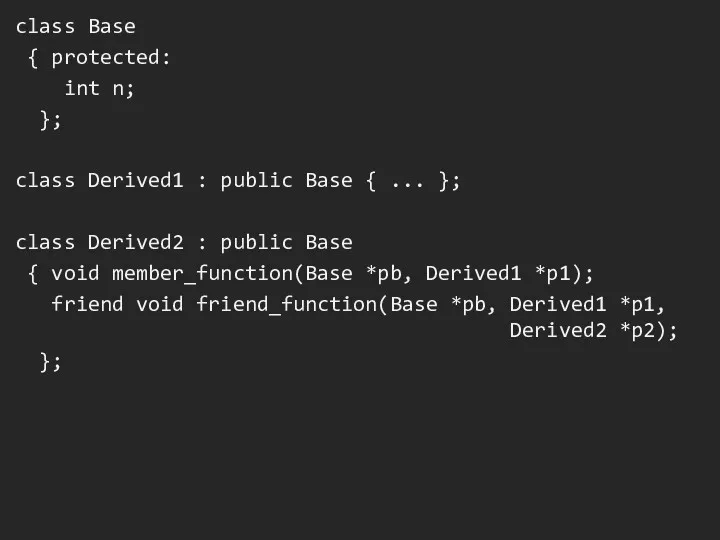
Слайд 15
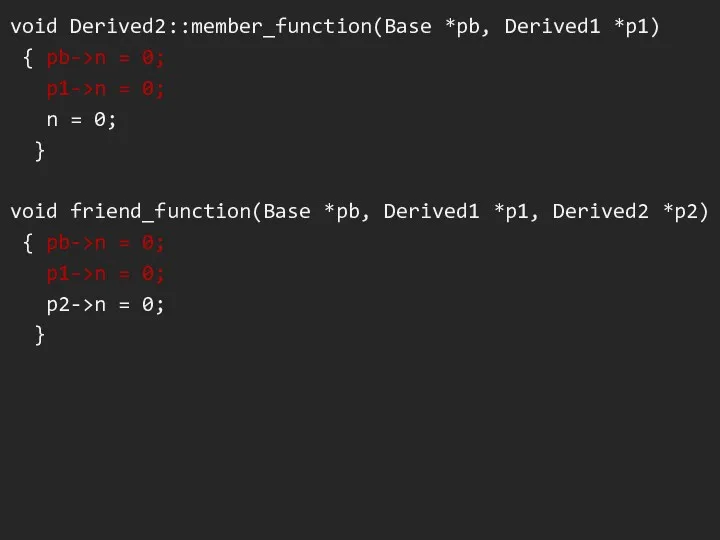
void Derived2::member_function(Base *pb, Derived1 *p1)
{ pb->n = 0;
p1->n =
0;
n = 0;
}
void friend_function(Base *pb, Derived1 *p1, Derived2 *p2)
{ pb->n = 0;
p1->n = 0;
p2->n = 0;
}
Слайд 16
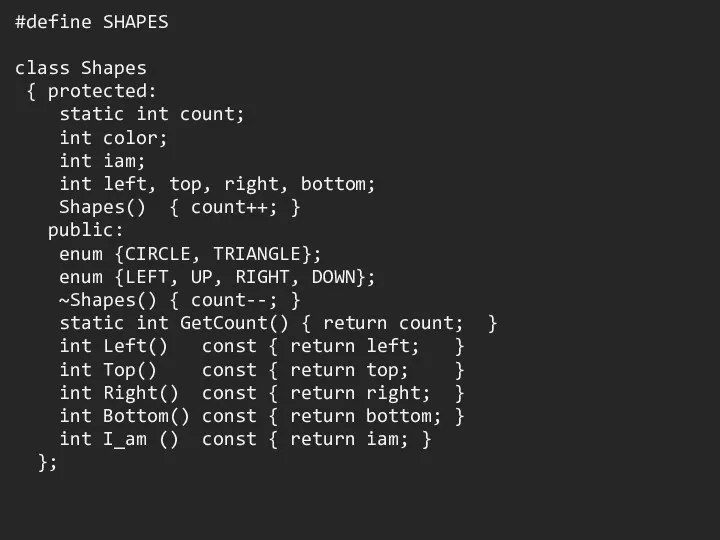
#define SHAPES
class Shapes
{ protected:
static int count;
int color;
int
iam;
int left, top, right, bottom;
Shapes() { count++; }
public:
enum {CIRCLE, TRIANGLE};
enum {LEFT, UP, RIGHT, DOWN};
~Shapes() { count--; }
static int GetCount() { return count; }
int Left() const { return left; }
int Top() const { return top; }
int Right() const { return right; }
int Bottom() const { return bottom; }
int I_am () const { return iam; }
};
Слайд 17
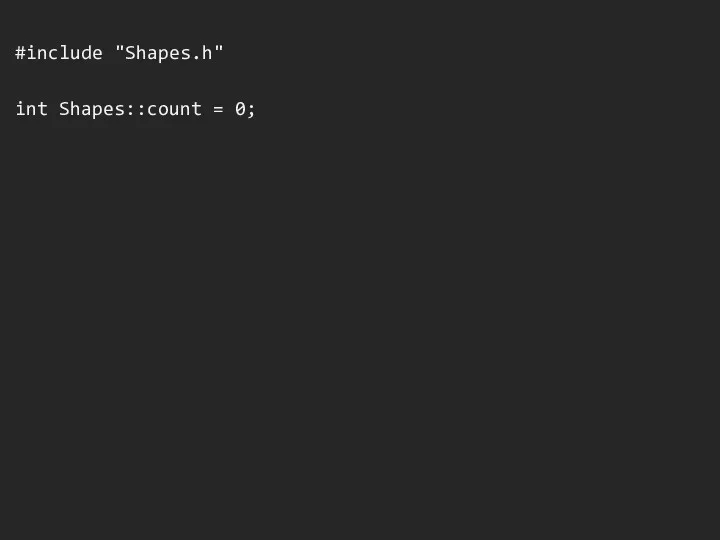
#include "Shapes.h"
int Shapes::count = 0;
Слайд 18
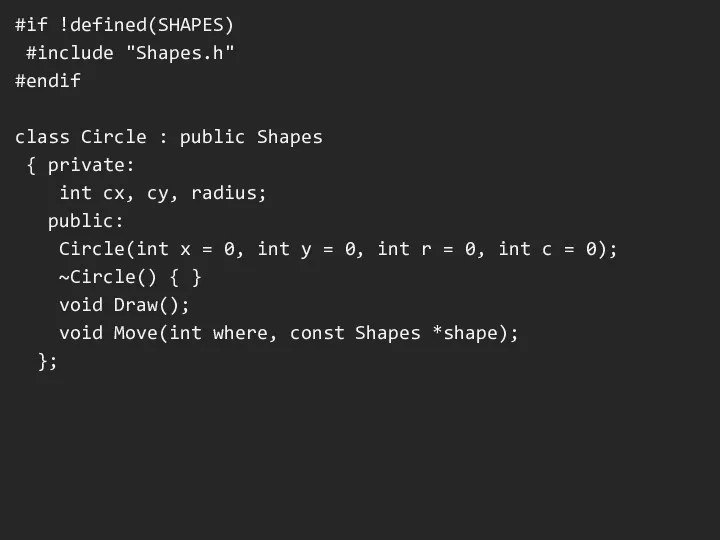
#if !defined(SHAPES)
#include "Shapes.h"
#endif
class Circle : public Shapes
{ private:
int
cx, cy, radius;
public:
Circle(int x = 0, int y = 0, int r = 0, int c = 0);
~Circle() { }
void Draw();
void Move(int where, const Shapes *shape);
};
Слайд 19
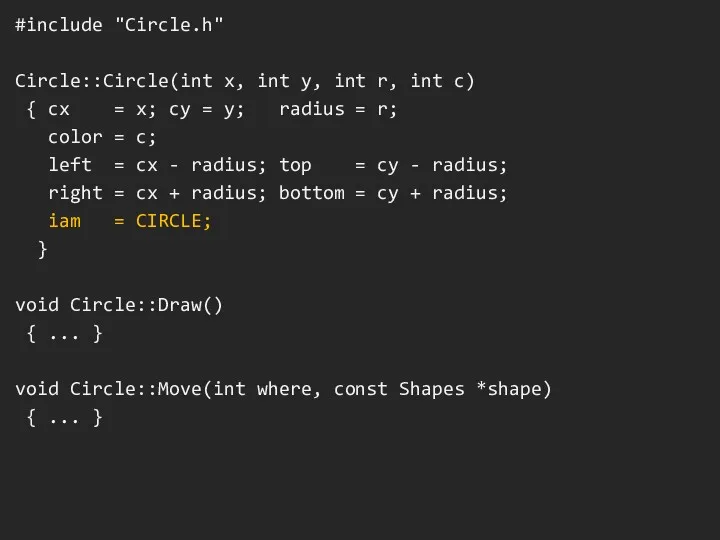
#include "Circle.h"
Circle::Circle(int x, int y, int r, int c)
{ cx
= x; cy = y; radius = r;
color = c;
left = cx - radius; top = cy - radius;
right = cx + radius; bottom = cy + radius;
iam = CIRCLE;
}
void Circle::Draw()
{ ... }
void Circle::Move(int where, const Shapes *shape)
{ ... }
Слайд 20
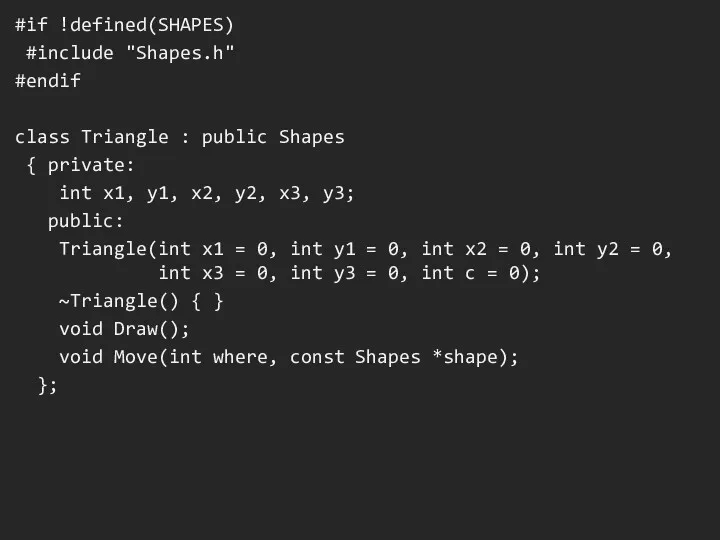
#if !defined(SHAPES)
#include "Shapes.h"
#endif
class Triangle : public Shapes
{ private:
int
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3;
public:
Triangle(int x1 = 0, int y1 = 0, int x2 = 0, int y2 = 0,
int x3 = 0, int y3 = 0, int c = 0);
~Triangle() { }
void Draw();
void Move(int where, const Shapes *shape);
};
Слайд 21
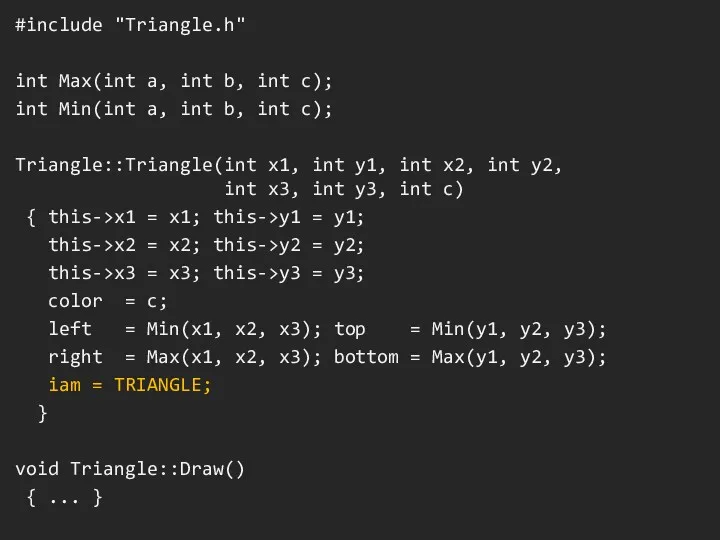
#include "Triangle.h"
int Max(int a, int b, int c);
int Min(int a, int
b, int c);
Triangle::Triangle(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2,
int x3, int y3, int c)
{ this->x1 = x1; this->y1 = y1;
this->x2 = x2; this->y2 = y2;
this->x3 = x3; this->y3 = y3;
color = c;
left = Min(x1, x2, x3); top = Min(y1, y2, y3);
right = Max(x1, x2, x3); bottom = Max(y1, y2, y3);
iam = TRIANGLE;
}
void Triangle::Draw()
{ ... }
Слайд 22
![#include "Circle.h" #include "Triangle.h" void main() { Shapes* shapes[10]; shapes[0]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293491/slide-21.jpg)
#include "Circle.h"
#include "Triangle.h"
void main()
{ Shapes* shapes[10];
shapes[0] = new Circle(100,
100, 30, 50);
shapes[1] = new Triangle(0, 0, 20, 0, 0, 20, 90);
shapes[2] = new Circle(200, 200, 50, 20);
for(int i = 0; i < Shapes::GetCount(); i++)
if (shapes[i]->I_am() == Shapes::CIRCLE)
static_cast(shapes[i])->Draw();
else
static_cast(shapes[i])->Draw();
Слайд 23
![for(int i = 1; i if (shapes[i]->I_am() == Shapes::CIRCLE) static_cast](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293491/slide-22.jpg)
for(int i = 1; i < Shapes::GetCount(); i++)
if (shapes[i]->I_am()
== Shapes::CIRCLE)
static_cast(shapes[i])->Move(Shapes::LEFT,
shapes[i - 1]);
else
static_cast(shapes[i])->Move(Shapes::LEFT,
shapes[i - 1]);
for(int i = 0; i < Shapes::GetCount(); i++)
if (shapes[i]->I_am() == Shapes::CIRCLE)
static_cast(shapes[i])->Draw();
else
static_cast(shapes[i])->Draw();
![class : [, ] { ... };](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293491/slide-1.jpg)



















![#include "Circle.h" #include "Triangle.h" void main() { Shapes* shapes[10]; shapes[0]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293491/slide-21.jpg)
![for(int i = 1; i if (shapes[i]->I_am() == Shapes::CIRCLE) static_cast](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/293491/slide-22.jpg)
 Управление доступом к базе данных. (Лекция 3)
Управление доступом к базе данных. (Лекция 3) Решение Schneider Electric для построения инженерной инфраструктуры ЦОД
Решение Schneider Electric для построения инженерной инфраструктуры ЦОД Визуализация. Лекция 1
Визуализация. Лекция 1 Пример оформления ссылок
Пример оформления ссылок Кодирование. Оптимальный код Хаффмана. Лекция 14
Кодирование. Оптимальный код Хаффмана. Лекция 14 Циклы. Основные понятия
Циклы. Основные понятия Методы разработки алгоритмов
Методы разработки алгоритмов Шаблон презентаций для сейлзкитов
Шаблон презентаций для сейлзкитов Локальна мережа. Гра Допуск
Локальна мережа. Гра Допуск Проектирование информационных систем
Проектирование информационных систем Возможности CCleaner
Возможности CCleaner Понятие модели. Моделирование
Понятие модели. Моделирование Дорожные знаки. Знаки сервиса
Дорожные знаки. Знаки сервиса Макет сайта
Макет сайта Создание макета Современные символы России при помощи интерактивного голосования
Создание макета Современные символы России при помощи интерактивного голосования Информация и её виды
Информация и её виды Способы представления информации. Виды информации
Способы представления информации. Виды информации Проектирование реляционной базы данных. Лекция №6
Проектирование реляционной базы данных. Лекция №6 Git (гит) - распределенная система управления версиями Think Results
Git (гит) - распределенная система управления версиями Think Results Кодирование и обработка текстовой информации. Урок – зачет
Кодирование и обработка текстовой информации. Урок – зачет Своя игра по информатике
Своя игра по информатике Git: установка
Git: установка Логические основы компьютеров
Логические основы компьютеров Фон для презентации о мультфильмах. Диск
Фон для презентации о мультфильмах. Диск Архитектура персонального компьютера
Архитектура персонального компьютера Урок-дискуссия.Операционные системы. Windows или Linux.
Урок-дискуссия.Операционные системы. Windows или Linux. Как не нужно делать презентации
Как не нужно делать презентации Тест: Программа подготовки презентаций Microsoft PowerPoint
Тест: Программа подготовки презентаций Microsoft PowerPoint