Содержание
- 2. Introduction The need to share information and resources among different computers has led to linked computer
- 3. Network Fundamentals Network Classifications Scope Local area network (LAN) Metropolitan area (MAN) Wide area network (WAN)
- 4. Network Classifications LAN: Normally consists of a collection of computers in a single building. Example: computers
- 5. Network Classifications Open network: open network design for a public domain are freely circulated and often
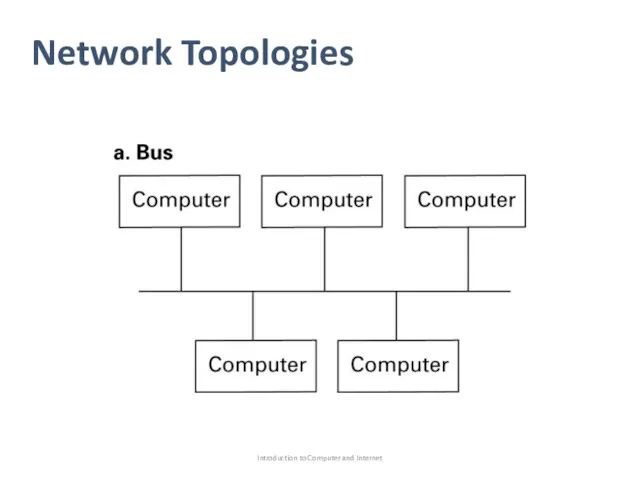
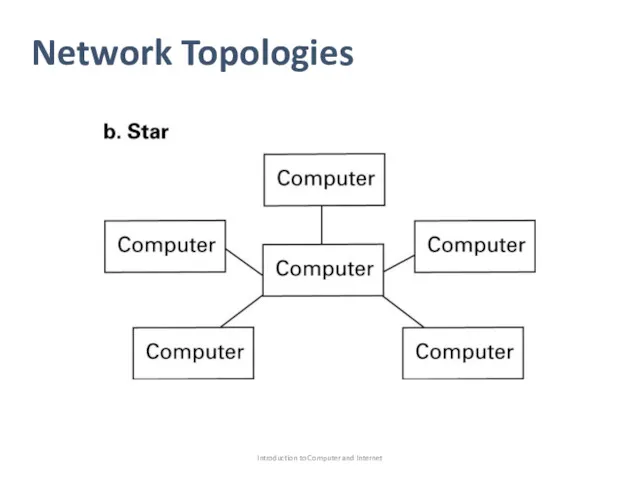
- 6. Network Topologies Network topology refer to the pattern in which the machines are connected. Bus: all
- 7. Network Topologies Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 8. Network Topologies Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 9. Network Classifications Bus topology was popularized in the 1990s under set of standards known as Ethernet.
- 10. Network Classifications Sometimes a bus network is created by running links from each computer to a
- 11. Protocols For network to function reliably, it is important to establish rules by which activities are
- 12. Protocols In a bus network, transmitting messages is controlled by the protocol known as Carrier Sense,
- 13. Protocols If another machine also begins transmitting, both machines detect the clash and pause for a
- 14. Protocols Wireless networks adopts policy that trying to avoid collisions rather than trying to detect it
- 15. Protocols This protocol (CSMA/CA) to a void collision, when a collision occur, messages must be retransmitted.
- 16. Protocols Each individual station must be able to hear all the others, to solve this problem,
- 17. Combining Networks Sometimes it is necessary to connect existing networks to make an extended communication system.
- 18. Combining Networks Repeater: device that simply passes signals back and forth between the two originals buses
- 19. Combining Networks A switch : is a bridge with multiple connections, allowing it to connect several
- 20. Combining Networks In this case, the networks must be connected in manner that build a network
- 21. Combining Networks The connection between these networks is handled by router, which is a special purpose
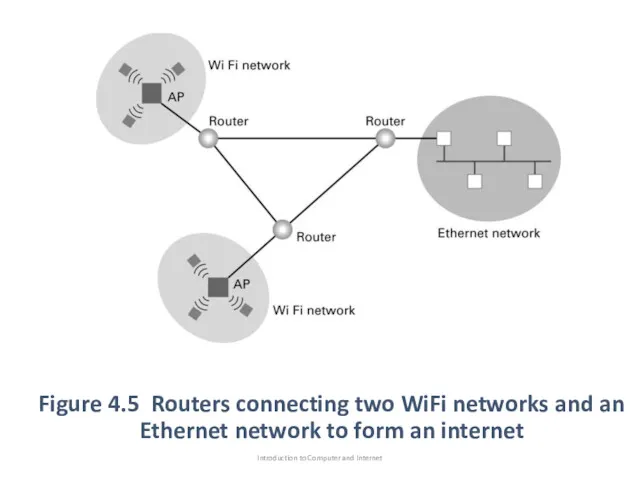
- 22. Figure 4.5 Routers connecting two WiFi networks and an Ethernet network to form an internet Introduction
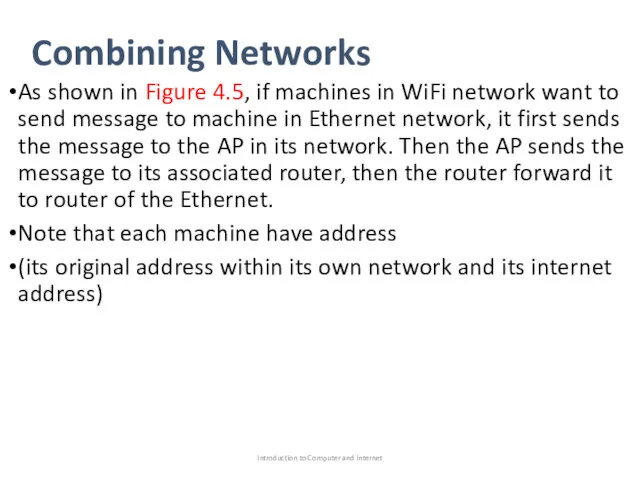
- 23. Combining Networks As shown in Figure 4.5, if machines in WiFi network want to send message
- 24. Combining Networks When the machine want to send a message to a machine, it attaches the
- 25. Combining Networks The point at which one network is linked to an internet is often called
- 26. Methods of Process Communication The activities (process) executing on the different computers within a network must
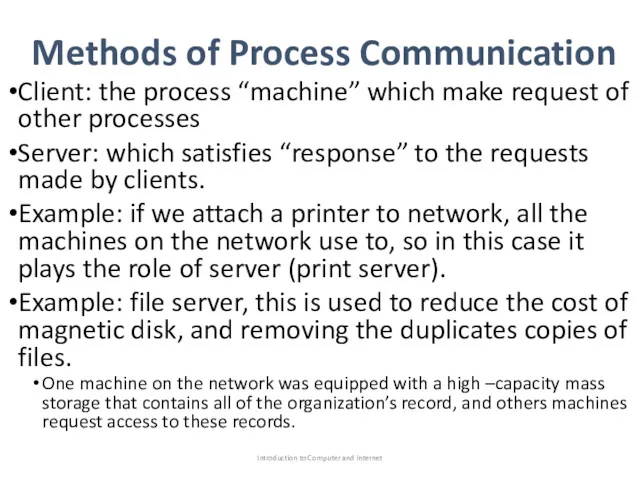
- 27. Methods of Process Communication Client: the process “machine” which make request of other processes Server: which
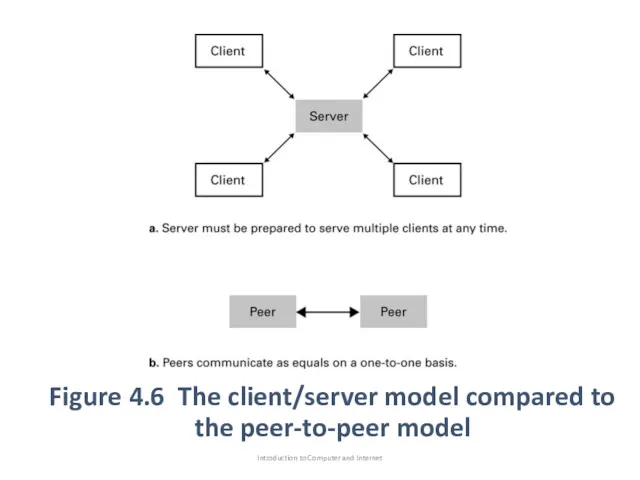
- 28. Methods of Process Communication Another model of process communication is the peer-to-peer (p2p),Figure 4.6 (machine can
- 29. Figure 4.6 The client/server model compared to the peer-to-peer model Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 30. Methods of Process Communication We can see that p2p model replaced the client/server model for file
- 31. Methods of Process Communication Unfortunately, The lack of a central server makes legal efforts to enforce
- 32. Distributed Systems Software units that execute as processes on different computers. Many modern software systems such
- 33. The Internet As we mentioned before the Internet is an example of internet. The Internet was
- 34. Internet Architecture The Internet (networks) are constructed and maintained by organization called Internet Service Provider (ISP).
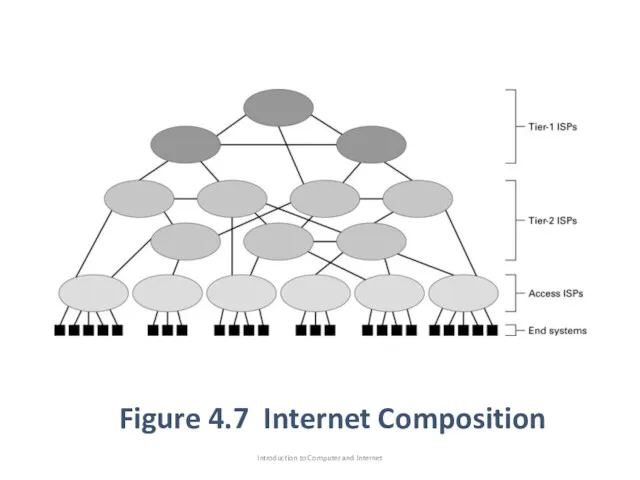
- 35. Figure 4.7 Internet Composition Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 36. Internet Architecture These network are though of as the backbone of the internet, they are typically
- 37. Internet Architecture Tier-1 and tier-2 are essentially networks of routers that collectively provide the Internet’s communications
- 38. Internet Architecture End system or host: the devices that individual users connect to the access ISPs.
- 39. Internet Architecture The fastest growing end systems are wireless connections based WiFi technology. The strategy is
- 40. Internet Architecture Other popular technique for connecting to access ISP’s use telephone lines or cable/satellite systems.
- 41. Internet Addressing As mentioned before that each machine in the network have an address. In the
- 42. Internet Addressing Blocks of numbered of IP address are awarded to ISPs by the internet corporation
- 43. Internet Addressing For example, using dotted decimal notation, the pattern 5.2 would represent the two-byte bit
- 44. Internet Addressing Address in bit-pattern form are rarely conducive to human consumption, so that the internet
- 45. Internet Addressing As an example of domain is aw.com Note that the suffix following the period
- 46. Internet Addressing Each domain must be registered with ICANN- the process handled by companies called registrars.
- 47. Internet Addressing For example: if nowhere university was assigned the domain nowhere.edu, then an individual computer
- 48. Internet Addressing As mentioned before, messages always transferred over the internet by means of IP address.
- 49. Internet Addressing The server used as an Internet-wide directory system known as the domain name system
- 50. Internet Applications Electronic Mail: one of the most popular uses of Internet is email, a system
- 51. Electronic Mail When a user sends email, it is first transferred to the user’s mail server,
- 52. Electronic Mail Two popular protocols used for accessing email that has arrived and accumulated at a
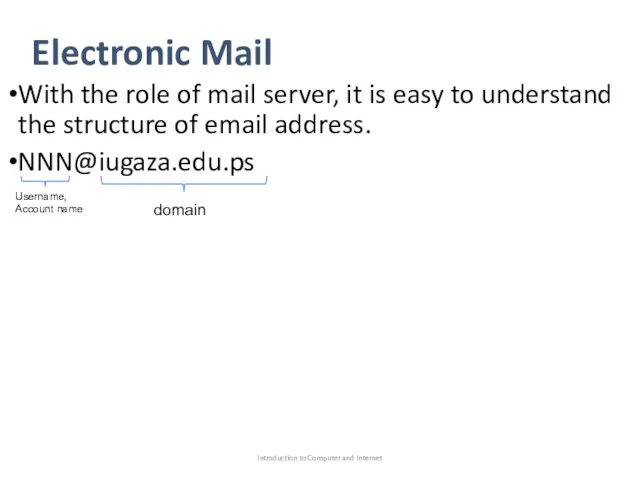
- 53. Electronic Mail With the role of mail server, it is easy to understand the structure of
- 54. File Transfer Protocol (FTP) One means of transferring files is to attach them to email messages.
- 55. File Transfer Protocol (FTP) FTP has become a popular way of providing limited access to data
- 56. Telnet and Secure Shell One of the early uses of the Internet was to allow computer
- 57. Telnet and Secure Shell Secure shell (SSH) is an alternative to telnet that offers a solution
- 58. VOIP An example of a more recent Internet applications Consider it as in which, the Internet
- 59. VOIP One drawback to Skype is that it is proprietary systems, and thus much of its
- 60. Internet Radio Transmission of radio station programming- a process called webcasting as apposed to broadcasting, because
- 61. Some Concepts, Internet Radio Unicast: refer to one sender sending message to one receiver N-unicast: single
- 62. Some Concepts, Internet Radio Another alternative, multicast, transfers the distribution problem to the Internet routers. Server
- 63. World Wide Web The information is disseminated over the Internet based on the concept of hypertext.
- 64. World Wide Web By using a hypertext, documents can explore related documents or follow a train
- 65. Web Implementation Software package that allows to access hypertext on the Internet Two categories: Package that
- 66. Web Implementation The server package (web-server): resides on a computer containing hypertext documents to be accessed.
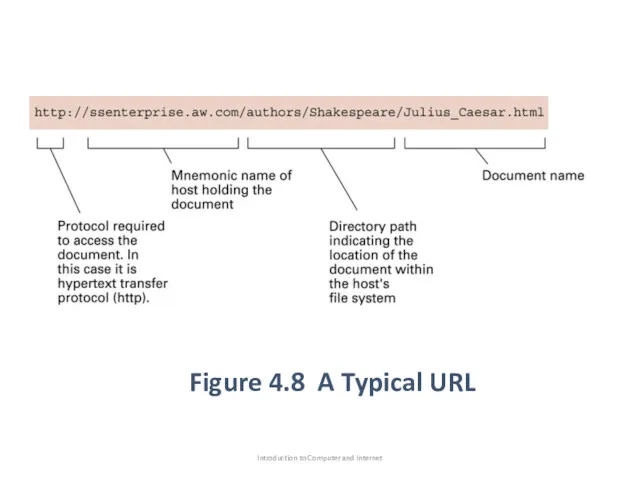
- 67. Figure 4.8 A Typical URL Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 68. Web Implementation Some times a URL might not explicitly contain all the segments. Some times a
- 69. HTML A traditional hypertext documents is similar to a text file. The different is that a
- 70. HTML The html encoded version “source version” is shown in figure 4.9a Note that the tag
- 71. Figure 4.9 A simple Web page Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 72. Introduction to Computer and Internet Figure 4.9 A simple Web page
- 73. Figure 4.10 An enhanced simple Web page Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 74. HTML is an anchor tag, Links to other documents and content to start a new paragraph
- 75. Client-side and server-side activities Consider the steps that would be required to retrieve the web page
- 76. What if we want web page that allow the customers to fill out an order form
- 77. There are some programs that control the client side activities: Java script within the HTML code
- 78. Security Attacks: computer system and its contents can be attacked via network connections. Many of attacks
- 79. Attacks(Virus) Virus: is software( piece of code) that infects a computer by inserting itself into programs
- 80. Attacks(Worms) worm: is an autonomous(مستقل) program that transfers itself through a network, taking up residence(الذي يقيم)
- 81. Attacks(Trojan horses) Trojan horse: is a program that enters a computer system disguised as a desirable
- 82. Attacks(Spyware) Spyware: (sometimes called sniffing soft- ware), which is software that collects information about activities at
- 83. Attacks(Phishing) Phishing: is a technique of obtaining(الحصول على) information explicitly by simply asking for it. مرتكب
- 84. Attacks(Denial of service) Denial of service : is the process of overloading a computer with requests
- 85. Protection Firewalls: A primary prevention(الوقاية) technique is to filter traffic passing through a point in the
- 86. Firewall spam filter: which are firewalls designed to block unwanted email proxy server: is a software
- 87. Protection(Antivirus software) is used to detect and to remove the presenceوجود of known viruses and other
- 88. Encryption Encryption use to maintain data confidentially many traditional Internet applications have been altered to incorporate
- 89. Encryption FTPS which is a secure version of FTP, and SSH which is the replacement for
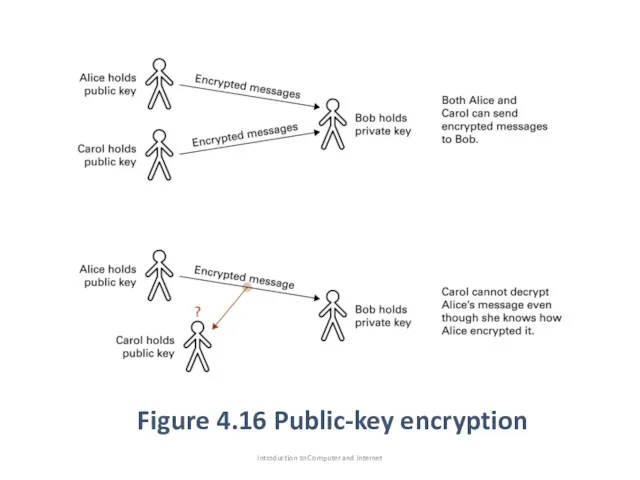
- 90. Encryption(Public-Key Encryption) public-key encryption : is an encryption system in which knowing how to encrypt messages
- 91. Figure 4.16 Public-key encryption Introduction to Computer and Internet
- 93. Скачать презентацию

















































 Массивы
Массивы Қазақстан мен сыртқы әлем арасындағы байланыс құралдары
Қазақстан мен сыртқы әлем арасындағы байланыс құралдары Принципы представления данных и команд в компьютере
Принципы представления данных и команд в компьютере Переферійні пристрої
Переферійні пристрої Таргетированная реклама Вконтакте. Вводный курс
Таргетированная реклама Вконтакте. Вводный курс Анонс новой редакции 1С:Университет ПРОФ
Анонс новой редакции 1С:Университет ПРОФ Особенности восприятия графики посетителями сайтов
Особенности восприятия графики посетителями сайтов Автоматизированное тестирование
Автоматизированное тестирование Таблиці. Електронні таблиці. Формати даних та форматування таблиць
Таблиці. Електронні таблиці. Формати даних та форматування таблиць Внедрение в практику преподавания учителей-предметников технологии Web 2.0. с целью повышения эффективности урока
Внедрение в практику преподавания учителей-предметников технологии Web 2.0. с целью повышения эффективности урока Word мәтінідік құжатына графикалық кескіндерді кірістіру
Word мәтінідік құжатына графикалық кескіндерді кірістіру Проектирование баз данных и работа с ними веб-приложений. (Лекция 8)
Проектирование баз данных и работа с ними веб-приложений. (Лекция 8) JavaScript Basics
JavaScript Basics СУБД MS Access
СУБД MS Access Множества. Массивы (Delphi)
Множества. Массивы (Delphi) Система CRM - твой верный помощник
Система CRM - твой верный помощник Система сбора и анализа сведений о преподавателях
Система сбора и анализа сведений о преподавателях Створення розкладу
Створення розкладу Методи equals та hashcode
Методи equals та hashcode Ерекшеліктерді өңдеу. Java
Ерекшеліктерді өңдеу. Java Презентация по теме Табличные вычисления на компьютере к учебнику Семакина. 9 класс.
Презентация по теме Табличные вычисления на компьютере к учебнику Семакина. 9 класс. Отчет о прохождении учебной практики по модулю Эксплуатация и модификация информационных систем
Отчет о прохождении учебной практики по модулю Эксплуатация и модификация информационных систем Локальные компьютерные сети
Локальные компьютерные сети Module 28: Digital Forensics and Incident Analysis and Response
Module 28: Digital Forensics and Incident Analysis and Response Компьютерная грамотность и информационная культура
Компьютерная грамотность и информационная культура Презентация к уроку информатики в 9 классе по теме Информационное общество
Презентация к уроку информатики в 9 классе по теме Информационное общество викторина по информатике для 5-6 классов Информашка
викторина по информатике для 5-6 классов Информашка Антивирусные программы. Антивирусная защита информации
Антивирусные программы. Антивирусная защита информации