Содержание
- 2. Agenda Test Approaches Test Types by Test Levels Test Types by Test Objectives Testing Order
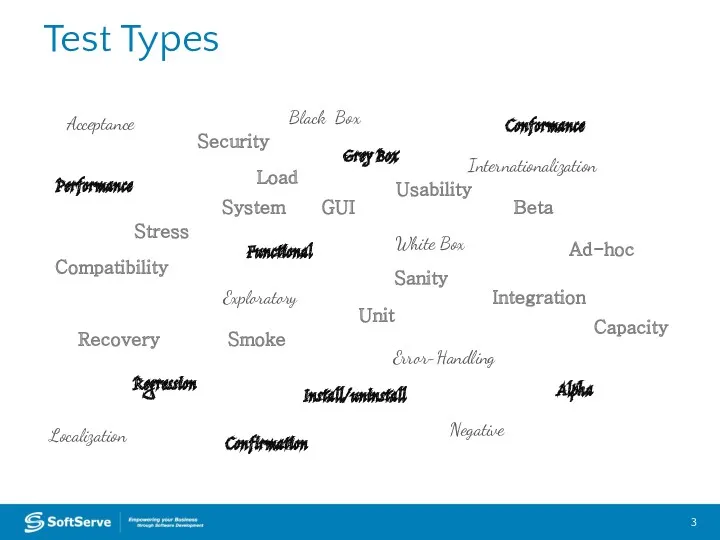
- 3. Test Types Acceptance Load Compatibility Functional Black Box Conformance Integration Performance Regression Smoke Stress System Unit
- 4. Test Type Definition Test Type it’s a group of test activities aimed at testing a component
- 5. Test Approaches
- 6. Test Approaches Proactive and Reactive Manual and Automated Verification and Validation Black-box, White-box and Grey-box Scripted
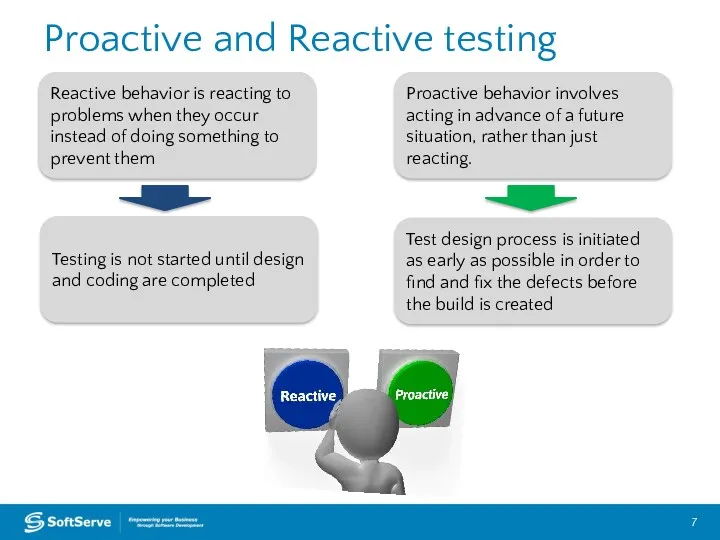
- 7. Reactive behavior is reacting to problems when they occur instead of doing something to prevent them
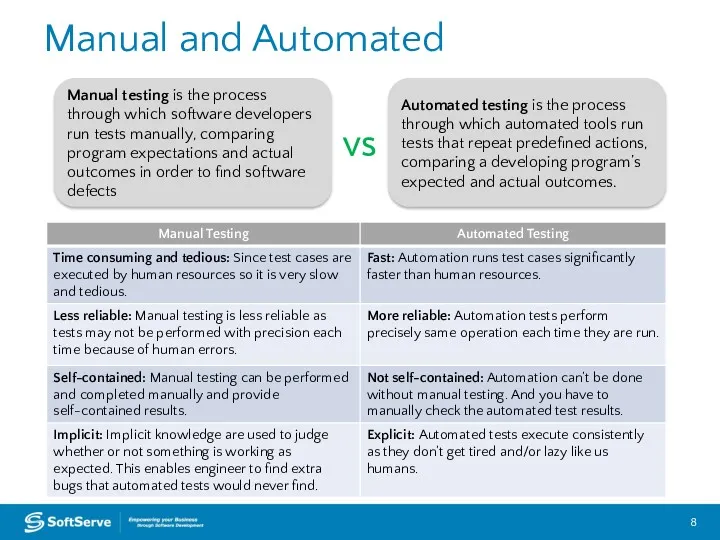
- 8. Manual and Automated Manual testing is the process through which software developers run tests manually, comparing
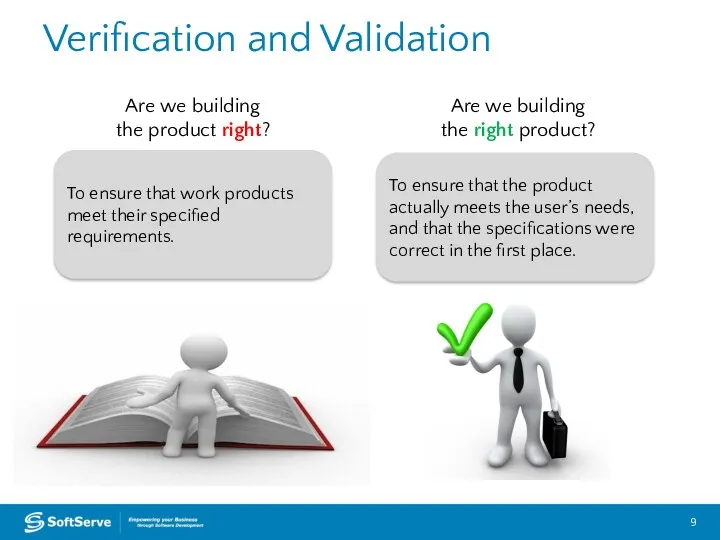
- 9. Verification and Validation To ensure that work products meet their specified requirements. To ensure that the
- 10. Positive and Negative In positive testing our intention is In negative testing our intention is to
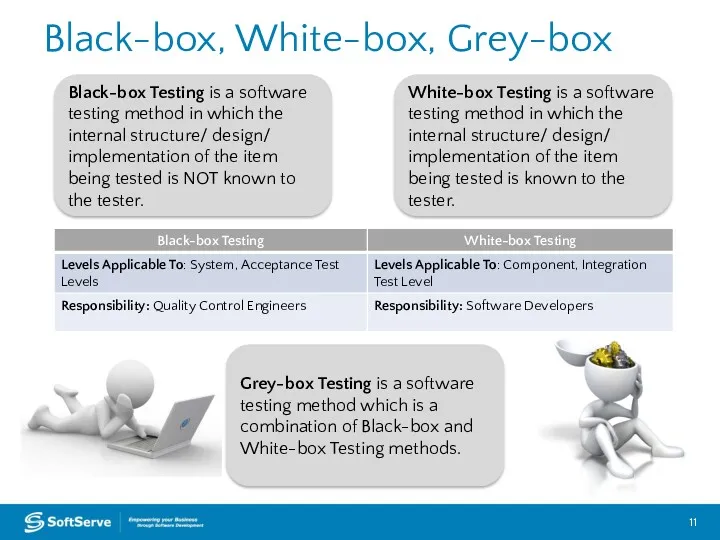
- 11. Black-box, White-box, Grey-box Black-box Testing is a software testing method in which the internal structure/ design/
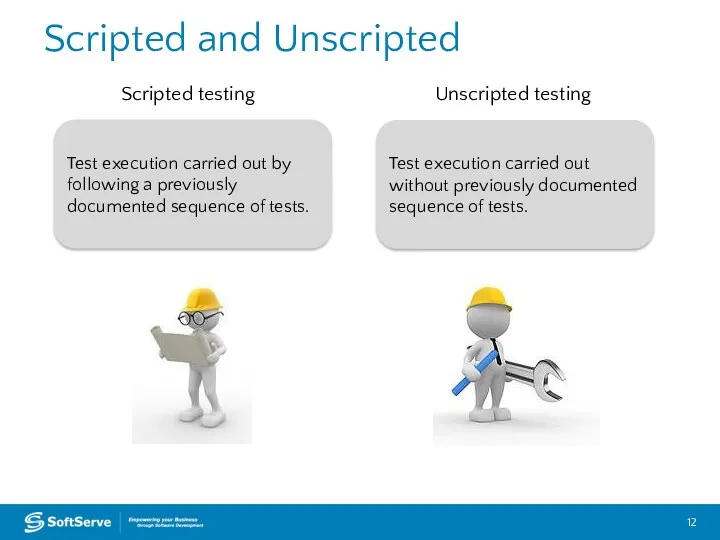
- 12. Scripted and Unscripted Test execution carried out by following a previously documented sequence of tests. Test
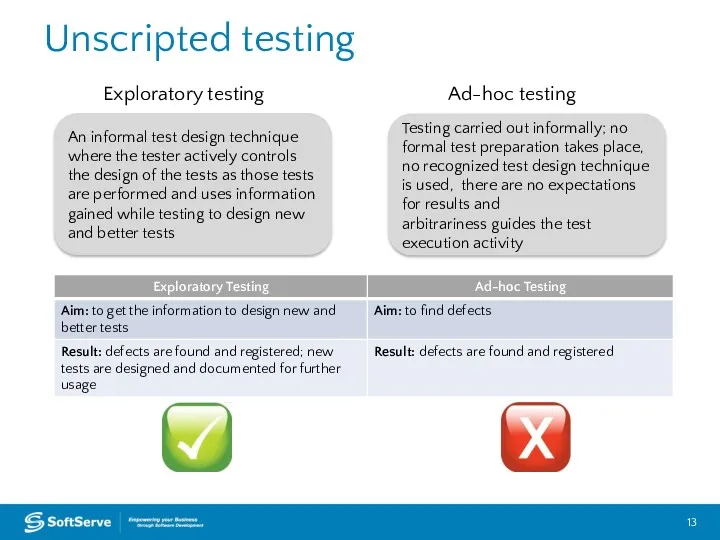
- 13. Unscripted testing An informal test design technique where the tester actively controls the design of the
- 14. Test Types by Test Levels
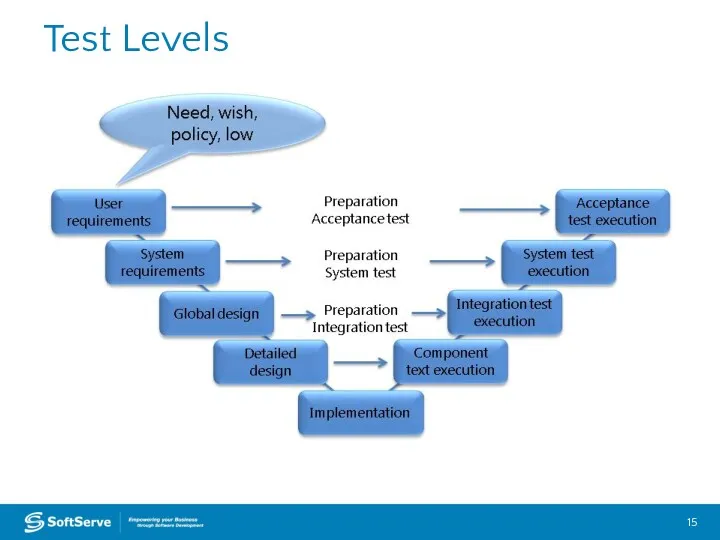
- 15. Test Levels
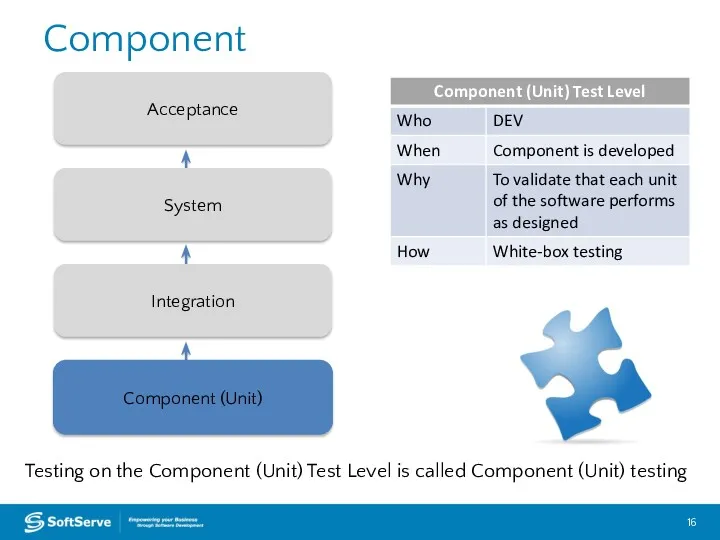
- 16. Component Component (Unit) Integration System Acceptance Testing on the Component (Unit) Test Level is called Component
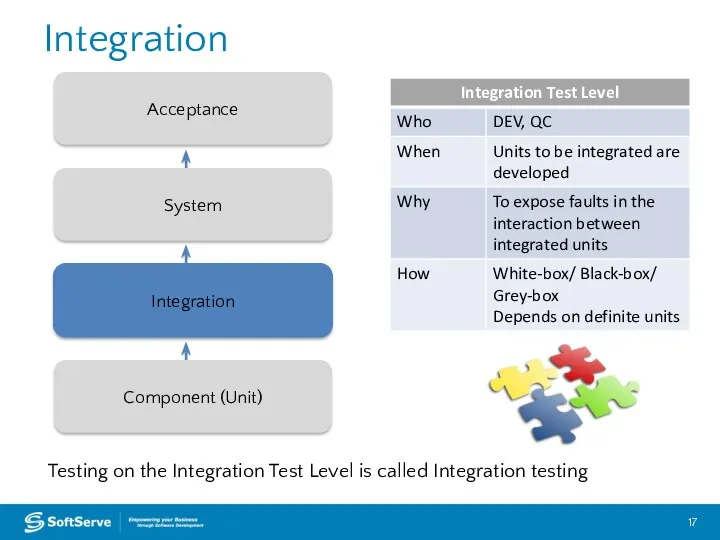
- 17. Integration Integration Component (Unit) System Acceptance Testing on the Integration Test Level is called Integration testing
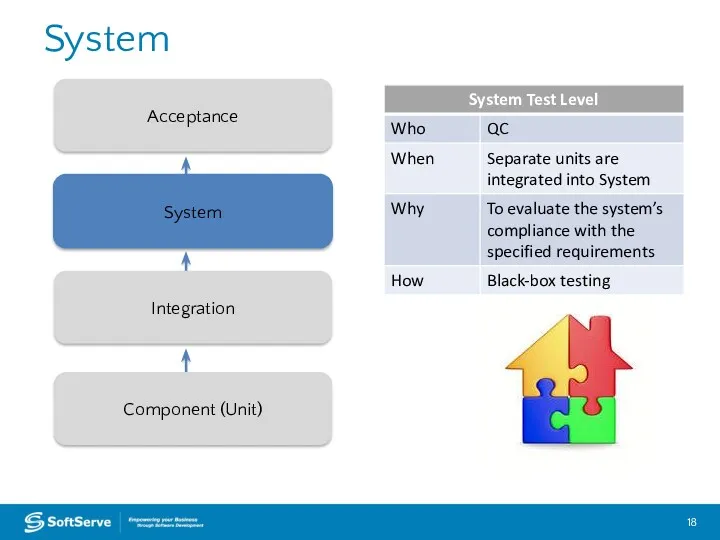
- 18. System System Integration Component (Unit) Acceptance
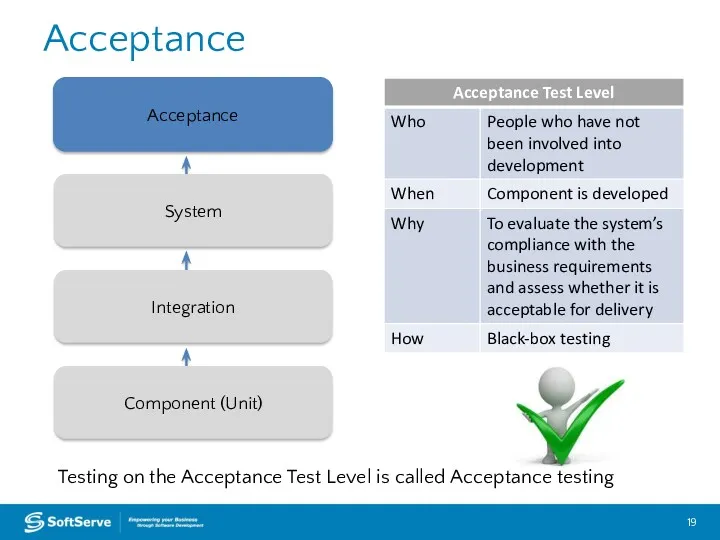
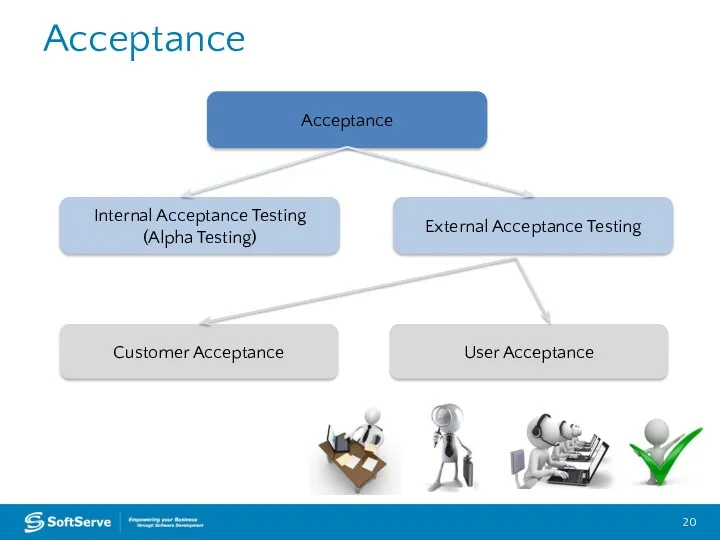
- 19. Acceptance Acceptance Integration System Component (Unit) Testing on the Acceptance Test Level is called Acceptance testing
- 20. Acceptance Acceptance Internal Acceptance Testing (Alpha Testing) External Acceptance Testing Customer Acceptance User Acceptance
- 21. Test Types by Test Objectives
- 22. What it does? Test Types Depending on its objectives, testing will be organized differently: Testing of
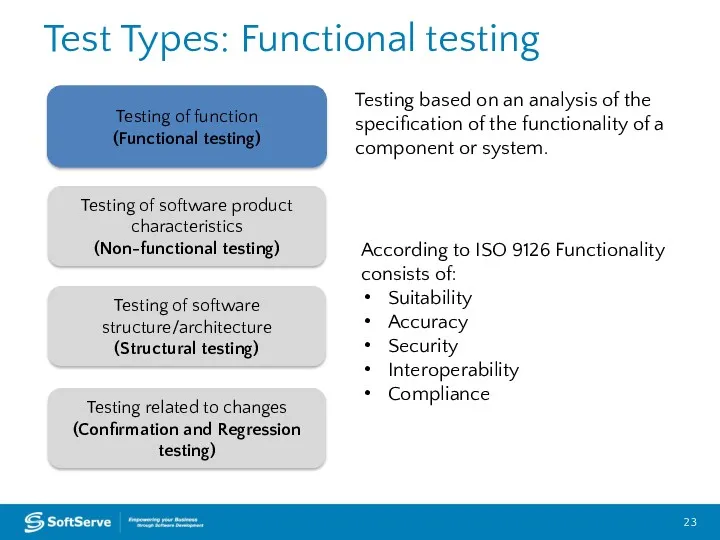
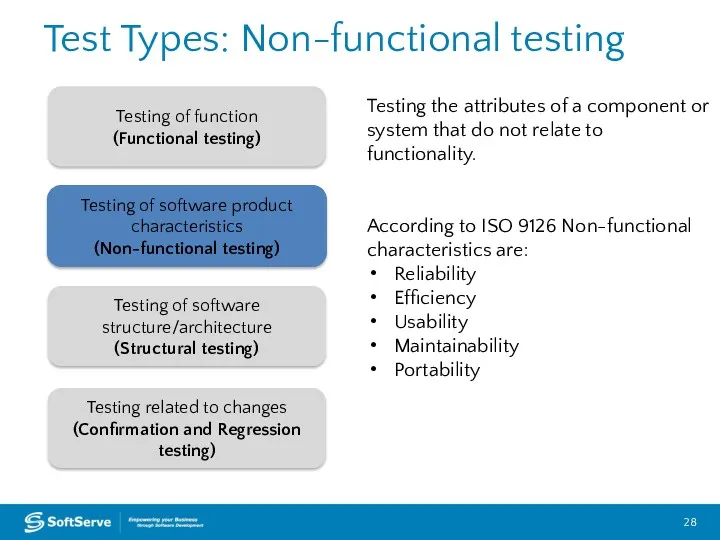
- 23. Test Types: Functional testing Testing of function (Functional testing) Testing of software product characteristics (Non-functional testing)
- 24. Functional testing Suitability: the capability to provide an appropriate set of functions for specified tasks and
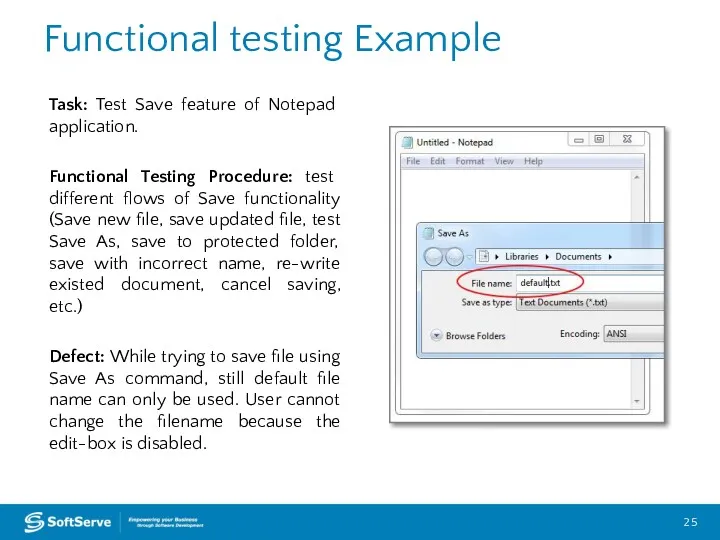
- 25. Functional testing Example Task: Test Save feature of Notepad application. Functional Testing Procedure: test different flows
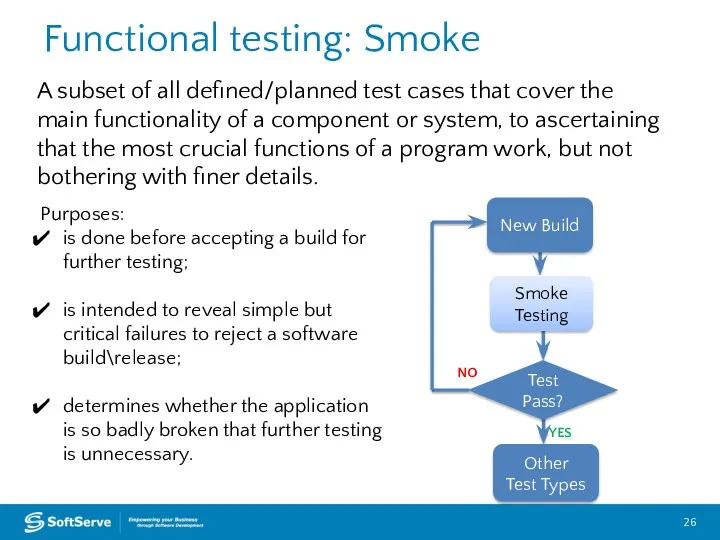
- 26. Functional testing: Smoke A subset of all defined/planned test cases that cover the main functionality of
- 27. Smoke testing Example Task: Test new version of a Notepad application. Smoke Testing Procedure: quickly check
- 28. Test Types: Non-functional testing Testing of function (Functional testing) Testing of software product characteristics (Non-functional testing)
- 29. Non-functional testing • Reliability: maturity (robustness), fault-tolerance, recoverability and compliance. • Usability: understandability, learnability, operability, attractiveness
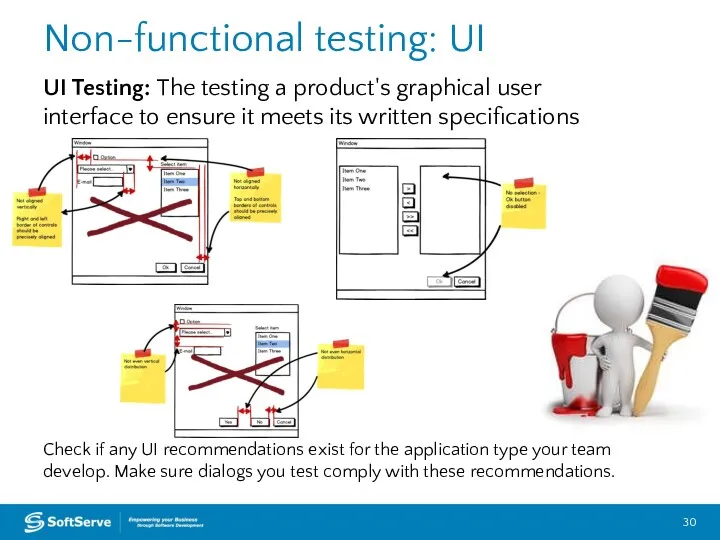
- 30. Non-functional testing: UI UI Testing: The testing a product's graphical user interface to ensure it meets
- 31. Non-functional testing: Performance Performance Testing: Testing with the intent of determining how efficiently a product handles
- 32. Performance testing Example Task: Server should respond in less than 2 sec when up to 100
- 33. Non-functional testing: Load Load testing is a type of performance testing conducted to evaluate the behavior
- 34. Load testing Example Task: Server should allow up to 500 concurrent connections. Load Testing Procedure: emulate
- 35. Non-functional testing: Stress Stress testing: A type of performance testing conducted to evaluate a system or
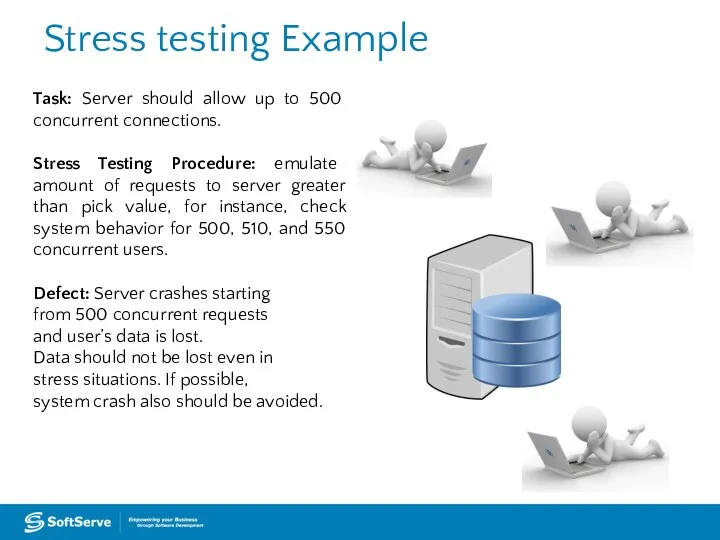
- 36. Stress testing Example Task: Server should allow up to 500 concurrent connections. Stress Testing Procedure: emulate
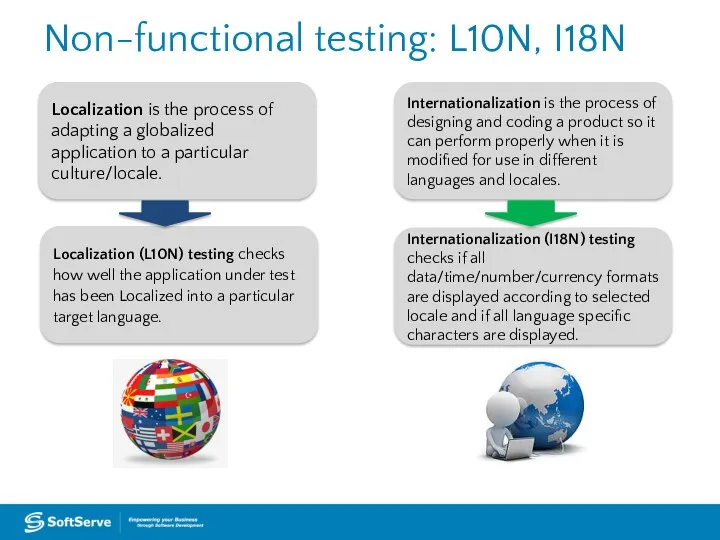
- 37. Non-functional testing: L10N, I18N Localization is the process of adapting a globalized application to a particular
- 38. Localization testing Example Task: Verify that ‘Login’ page is translated to German Localization Testing Procedure: Test
- 39. Internationalization testing Example Task: Verify that list of users with German special characters (e.g.: “ü”, “ß”
- 40. Test Types: Structural testing Testing of function (Functional testing) Testing of software product characteristics (Non-functional testing)
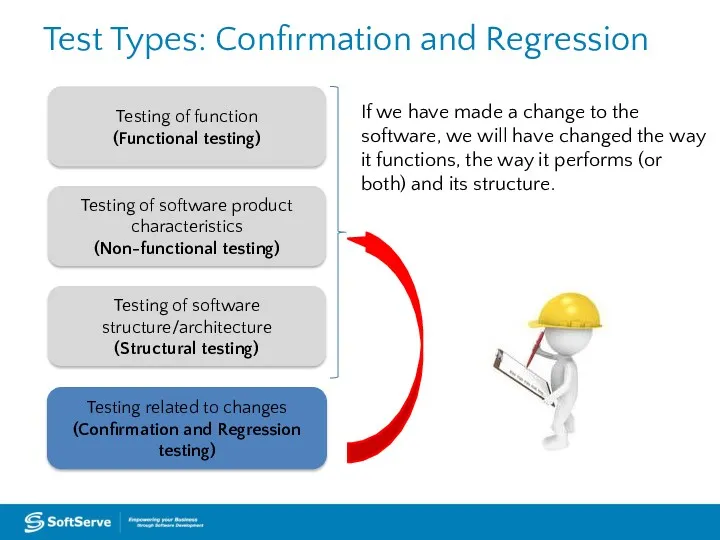
- 41. Testing of function (Functional testing) Testing of software product characteristics (Non-functional testing) Testing related to changes
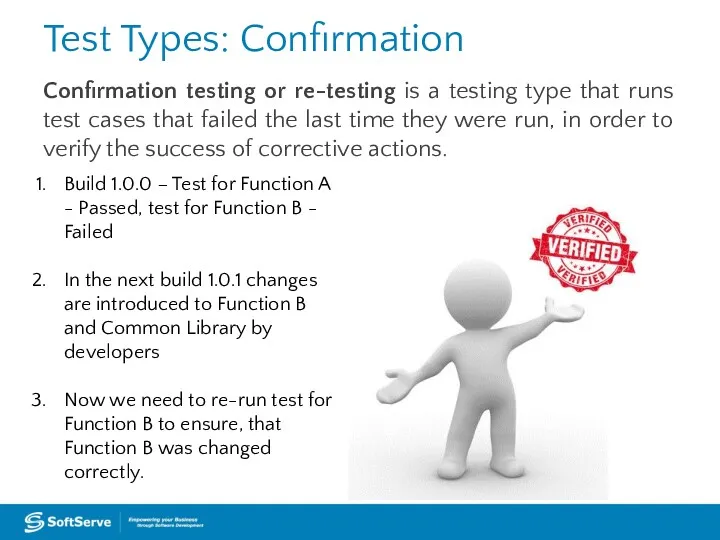
- 42. Test Types: Confirmation Confirmation testing or re-testing is a testing type that runs test cases that
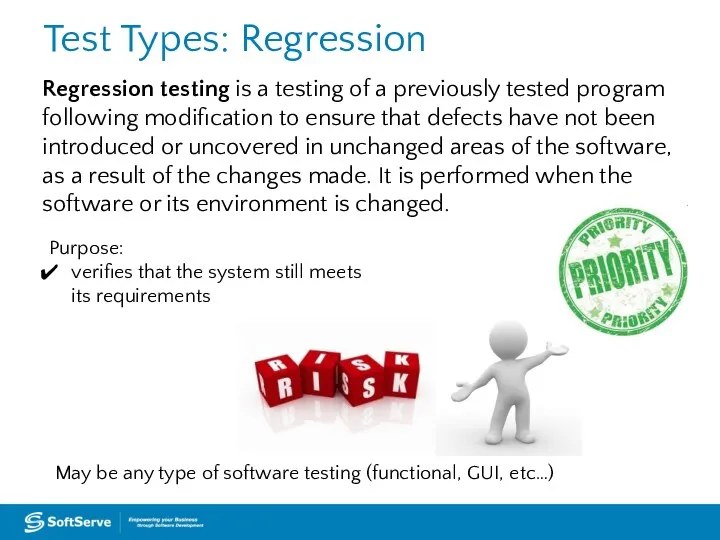
- 43. Test Types: Regression Regression testing is a testing of a previously tested program following modification to
- 44. Testing Order
- 45. Testing Order
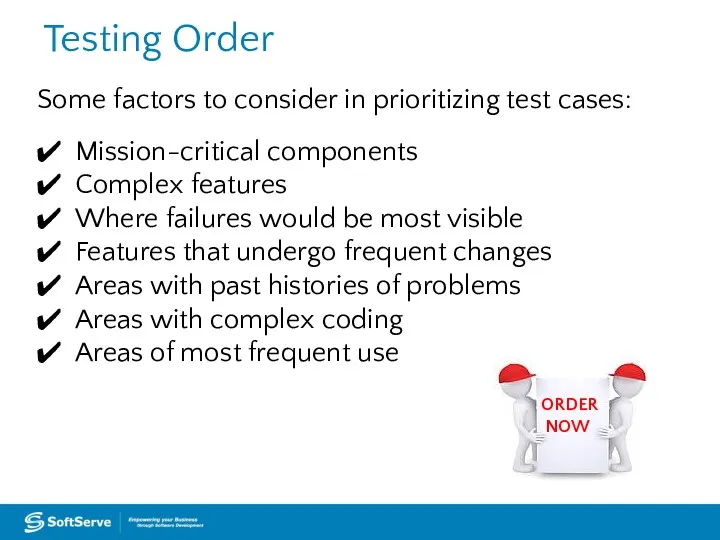
- 46. Testing Order Some factors to consider in prioritizing test cases: Mission-critical components Complex features Where failures
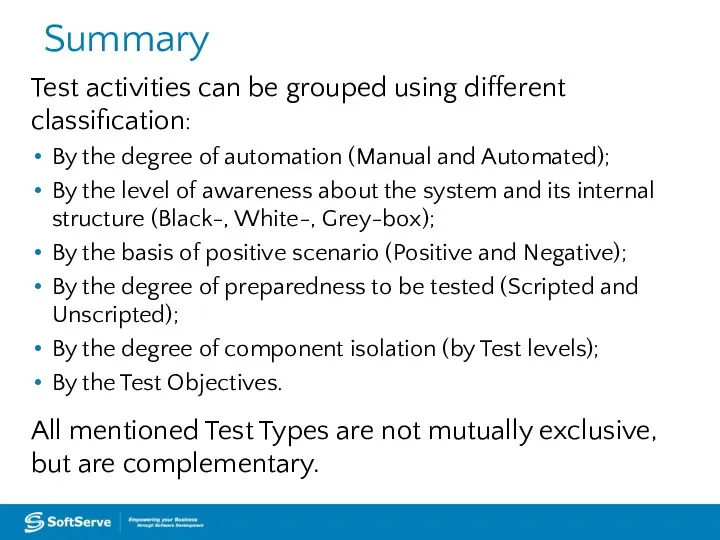
- 47. Summary Test activities can be grouped using different classification: By the degree of automation (Manual and
- 49. Скачать презентацию













 Презентация и разработка урока информатики во 2 классе Техника безопасности в компьютерном классе
Презентация и разработка урока информатики во 2 классе Техника безопасности в компьютерном классе C++. Основные достоинства языка
C++. Основные достоинства языка Информационные технологии
Информационные технологии Представление о программных средах компьютерной графики. Лекция 18
Представление о программных средах компьютерной графики. Лекция 18 МБУ Молодежный центр отдел социально-психологической помощи молодежи
МБУ Молодежный центр отдел социально-психологической помощи молодежи Объектно-ориентированное программирование в Java. Лекция 2
Объектно-ориентированное программирование в Java. Лекция 2 Массовые коммуникации и Интернет
Массовые коммуникации и Интернет Иерархия в SQL. Способы представления иерархических данных
Иерархия в SQL. Способы представления иерархических данных Использование информационных технологий в образовательном процессе
Использование информационных технологий в образовательном процессе Представление звуковой информации в компьютере
Представление звуковой информации в компьютере Стандарты и методология разработки корпоративных инфокоммуникационых систем
Стандарты и методология разработки корпоративных инфокоммуникационых систем Создание единого информационно-образовательного пространства
Создание единого информационно-образовательного пространства Инструкция участия в вебинаре в системе веб-коммуникаций на базе IVA R
Инструкция участия в вебинаре в системе веб-коммуникаций на базе IVA R Работа с формами в HTML
Работа с формами в HTML Разработка урока Знакомство с Visual Basic
Разработка урока Знакомство с Visual Basic Операционные системы и их интерфейсы
Операционные системы и их интерфейсы КВН Веселая информатика
КВН Веселая информатика Эволюция компьютерных систем
Эволюция компьютерных систем Сетевое оборудование
Сетевое оборудование Проектирование и разработка автоматизированной информационной системы складского учета в 1С
Проектирование и разработка автоматизированной информационной системы складского учета в 1С открытый урок по теме Архивация данных. 10 класс. профиль
открытый урок по теме Архивация данных. 10 класс. профиль Службы сети интернет
Службы сети интернет Программирование на Java (2022 - 2023)
Программирование на Java (2022 - 2023) Как работает современный поиск
Как работает современный поиск Законы распределения и их применение для расчетов и анализа
Законы распределения и их применение для расчетов и анализа Виды информационно-поисковых тезаурусов
Виды информационно-поисковых тезаурусов Что может SMM и что можем мы. Инстаграм и Вконтакте
Что может SMM и что можем мы. Инстаграм и Вконтакте Компьютерные презентации
Компьютерные презентации