Содержание
- 2. Chapter Goals Describe the purpose of files, file systems, and directories Distinguish between text and binary
- 3. Chapter Goals Compare and contrast sequential and direct file access Discuss the issues related to file
- 4. File Systems File A named collection of related data File system The logical view that an
- 5. Text and Binary Files Text file A file in which the bytes of data are organized
- 6. Text and Binary Files The terms text file and binary file are somewhat misleading They seem
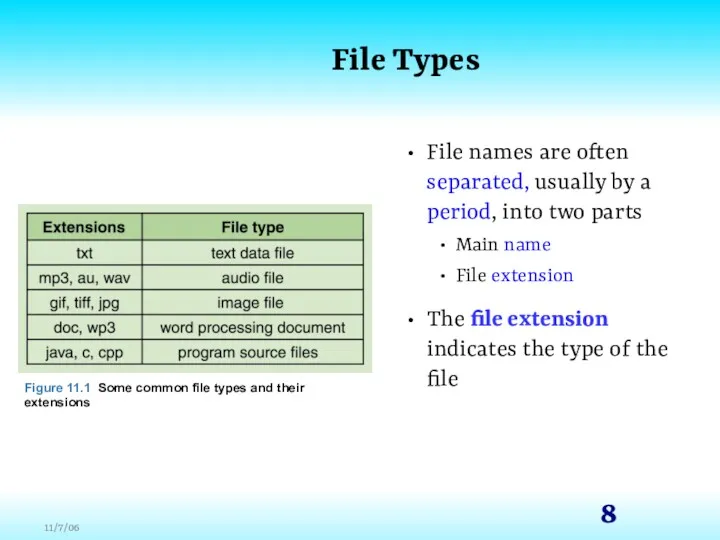
- 7. File Types Most files, whether they are in text or binary format, contain a specific type
- 8. File Types File names are often separated, usually by a period, into two parts Main name
- 9. File Operations Create a file Delete a file Open a file Close a file Read data
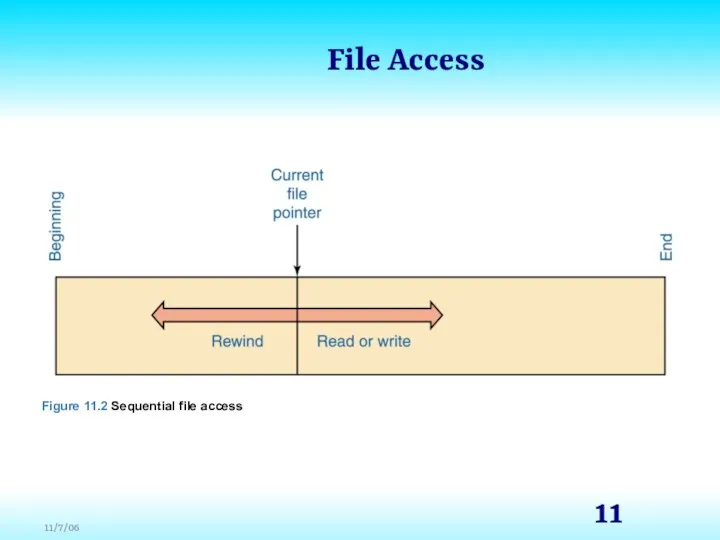
- 10. File Access Sequential access Information in the file is processed in order, and read and write
- 11. File Access Figure 11.2 Sequential file access
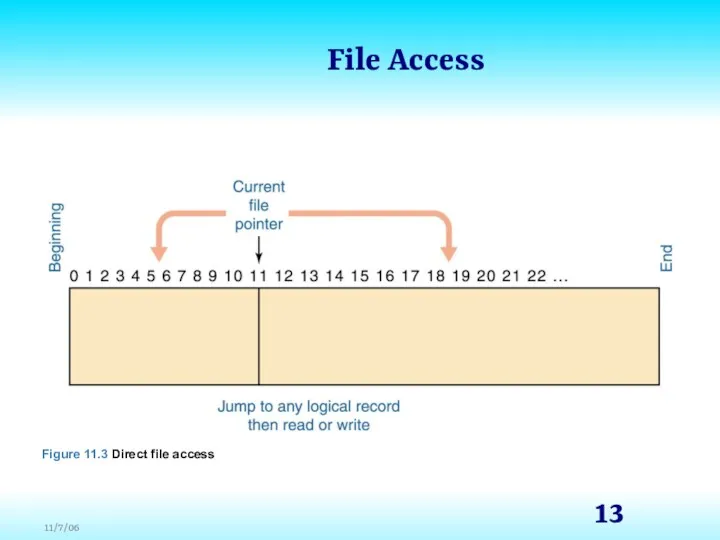
- 12. File Access Direct access Files are conceptually divided into numbered logical records and each logical record
- 13. File Access Figure 11.3 Direct file access
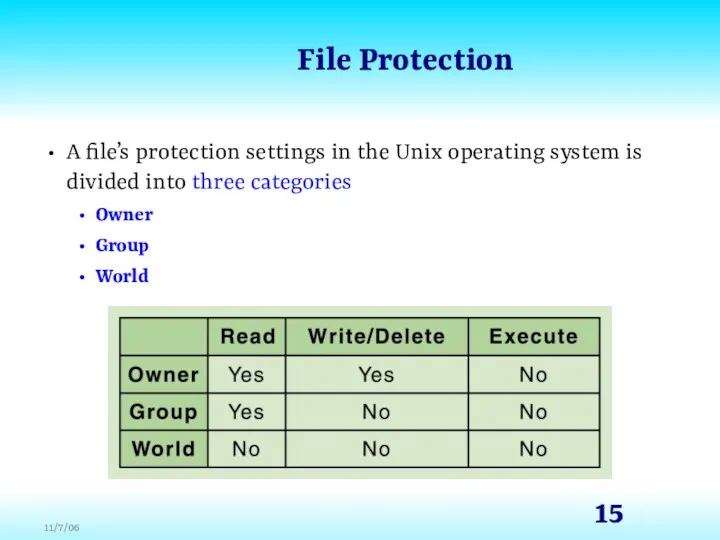
- 14. File Protection In multiuser systems, file protection is of primary importance We don’t want one user
- 15. File Protection A file’s protection settings in the Unix operating system is divided into three categories
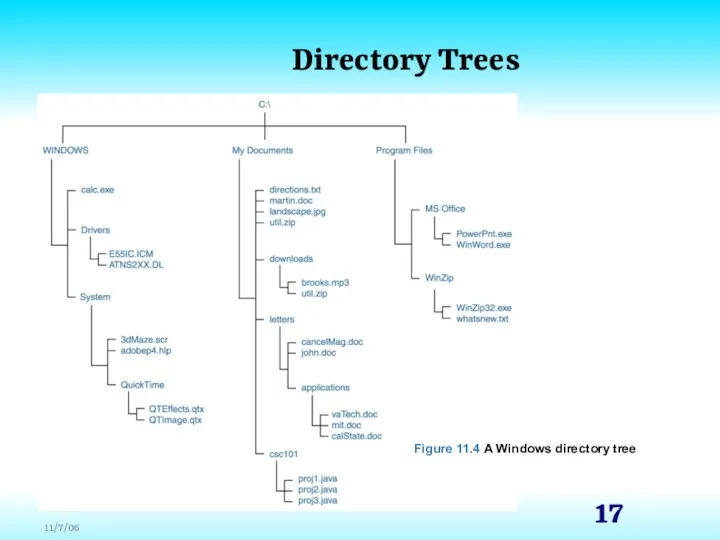
- 16. Directory Trees A directory of files can be contained within another directory The directory containing another
- 17. Directory Trees Figure 11.4 A Windows directory tree
- 18. Directory Trees At any point in time, you can be thought of as working in a
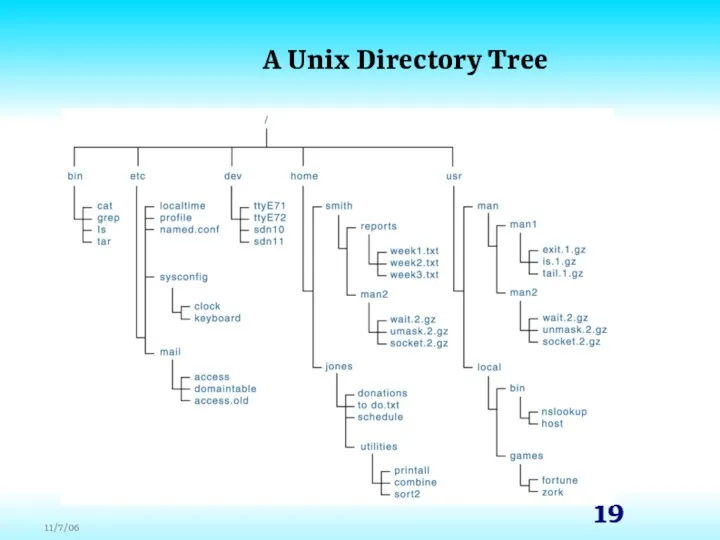
- 19. A Unix Directory Tree
- 20. Path Names Path A text designation of the location of a file or subdirectory in a
- 21. Path Names Examples of absolute path C:\Program Files\MS Office\WinWord.exe C:\My Documents\letters\applications\vaTech.doc C:\Windows\System\QuickTime Suppose the current working
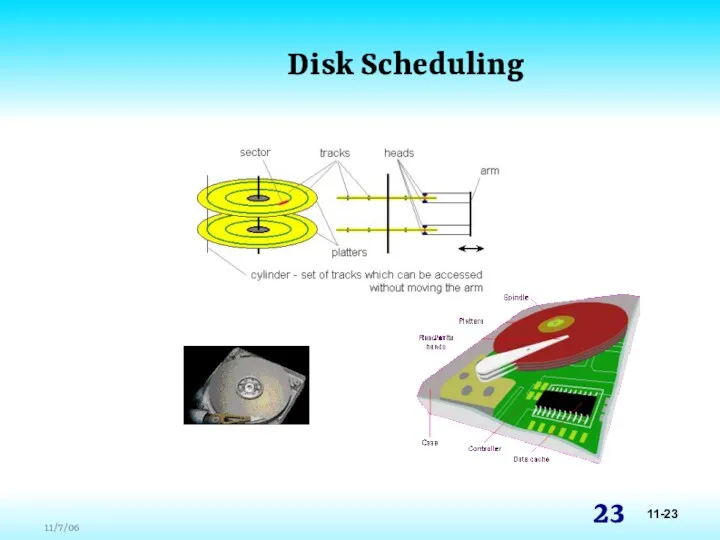
- 22. Disk Scheduling File systems must be accessed in an efficient manner As a computer deals with
- 23. Disk Scheduling 11-23
- 24. Disk Scheduling First-Come, First-Served Requests are serviced in the order they arrive, without regard to the
- 25. Disk Scheduling SCAN Disk Scheduling works like an elevator An elevator is designed to visit floors
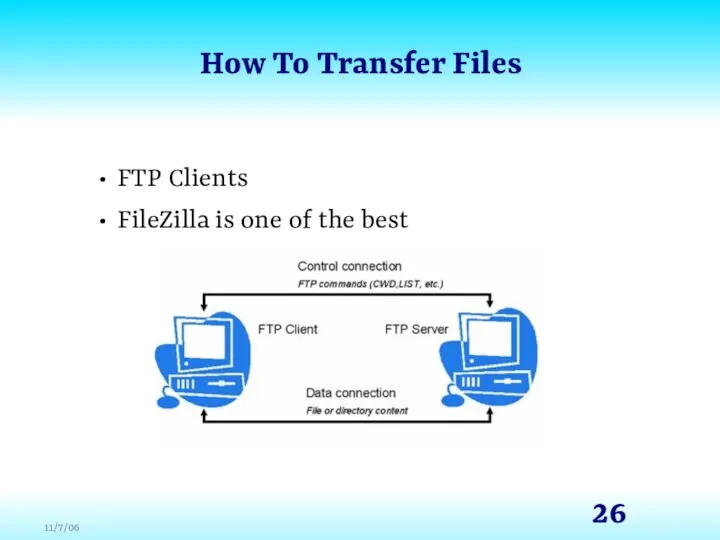
- 26. How To Transfer Files FTP Clients FileZilla is one of the best
- 27. Other Types Of File Transfers & Systems Secure FTP (SSH, SFTP, FTPS) Network File System (NFS)
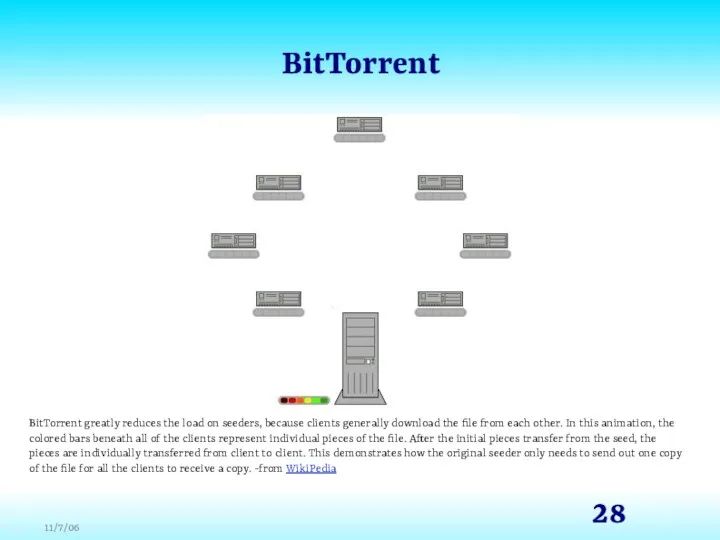
- 28. BitTorrent BitTorrent greatly reduces the load on seeders, because clients generally download the file from each
- 30. Скачать презентацию

















 Дискретный анализ. Лекция 1
Дискретный анализ. Лекция 1 Комьюнити— менеджмент. Как работать с клиентом
Комьюнити— менеджмент. Как работать с клиентом Удаленное администрирование
Удаленное администрирование Tuning SQL query performance
Tuning SQL query performance Методы визуального анализа и проектировангия систем. Диаграммы UML
Методы визуального анализа и проектировангия систем. Диаграммы UML Цифровизация в Казахстане
Цифровизация в Казахстане Виртуальный мир – окно в параллельную реальность
Виртуальный мир – окно в параллельную реальность PRO пожарики. Познавательная игра
PRO пожарики. Познавательная игра Функции пользователя
Функции пользователя How to install Java
How to install Java Цифрові моделі місцевості
Цифрові моделі місцевості Объектно- ориентированное программирование. Агрегация и композиция
Объектно- ориентированное программирование. Агрегация и композиция Технология WMI
Технология WMI Коммерческое предложение по рекламе медицинских препаратов Артериум
Коммерческое предложение по рекламе медицинских препаратов Артериум Набор и редактирование текста
Набор и редактирование текста Представление опыта работы директора МАОУ Енгорбойская СОШ Очировой Аюны Владимировны
Представление опыта работы директора МАОУ Енгорбойская СОШ Очировой Аюны Владимировны Модульное программирование. Глава 4
Модульное программирование. Глава 4 История вычислительной техники
История вычислительной техники Использование методов типа ветвей и границ для решения экстремальных задач на графах
Использование методов типа ветвей и границ для решения экстремальных задач на графах История развития вычислительной техники. Поколения ЭВМ
История развития вычислительной техники. Поколения ЭВМ 2015 год глазами Facebook Community
2015 год глазами Facebook Community Хочу писать красивые тексты: что делать?
Хочу писать красивые тексты: что делать? Об универсальном анализе кода или Зачем нам ещё один анализатор, как его можно сделать и куда применять
Об универсальном анализе кода или Зачем нам ещё один анализатор, как его можно сделать и куда применять HTML5-формы
HTML5-формы ColorGate Final. Полезные функции ColorGate
ColorGate Final. Полезные функции ColorGate Презентация к практическому занятию Геоинформационные системы.
Презентация к практическому занятию Геоинформационные системы. Что такое компьютерная программа?
Что такое компьютерная программа? Топ 10 сайтов, посещаемых мной
Топ 10 сайтов, посещаемых мной