Содержание
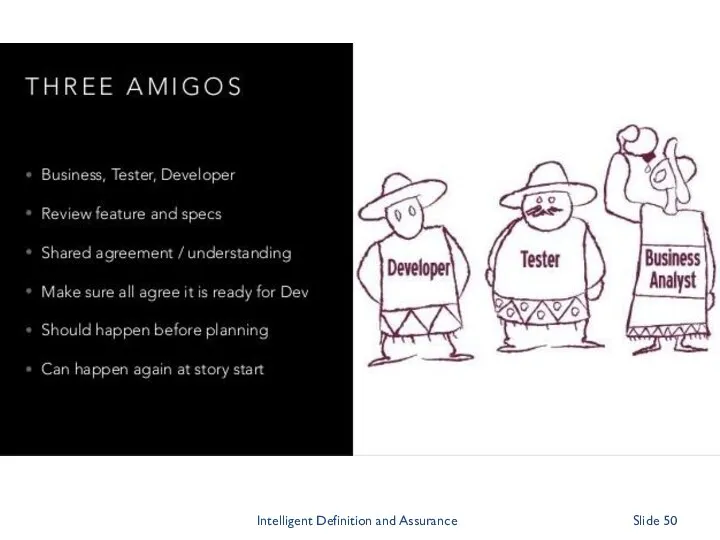
- 2. Helping clients transform their testing through INNOVATION, COACHING and LEADERSHIP Our CLIENTS Want to be agile
- 3. Agenda Digital Transformation Digital is a Business Initiative New Model Testing Shift-Left Collaborative Requirements Continuous Delivery
- 4. Introductions Say hello to your team Give your team a name (nameyourapp) Please try to login
- 5. This class is about thinking for yourself Pressure on testers – greater than ever The IT
- 6. Digital Transformation
- 7. Revolution! Lots of hype around “Digital” bombarding business and IT Digital Transformation programmes are affecting business
- 8. Scope Digital includes traditional IT but includes: Mobile anything The Internet of Things Autonomous vehicles Our
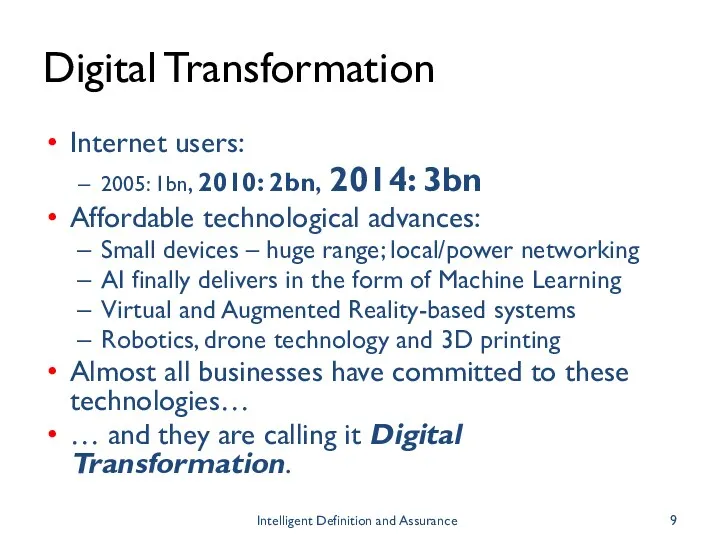
- 9. Digital Transformation Internet users: 2005: 1bn, 2010: 2bn, 2014: 3bn Affordable technological advances: Small devices –
- 10. Unprecedented project ambition Digital visionaries are promise a lot: No human intervention in your systems (Autonomous
- 11. The most complex systems ever? Space Shuttle (2.5m parts) used to be the most complex machine
- 12. A Smart City is… “… an urban development vision to integrate multiple information and communication technology
- 13. Smart Cities: the largest systems ever built? Nodes and endpoints: from a million to billions Bigger,
- 14. Systems of Systems and Ecosystems Unlike ships, smart cities are very vulnerable to attack Every human
- 15. Systems of Every Scale Scale of Digital ranges from the trivial to the largest systems ever
- 16. Systems with Social Impact Digital systems will have a social impact on all citizens who encounter
- 17. Law enforcement E.g. CCTV monitors traffic, people and asset movement and our behaviours too Goal: Prevent
- 18. Ecosystems of Ecosystems The span of Digital covers commerce, agriculture, health, government, the media in its
- 19. Digital is a Business Initiative Agile (an IT initiative) has taken 15 years to get half
- 20. Digital and Marketing Digital is the buzz-phrase of the moment Social, Mobile, Analytics, Cloud (SMAC) Consumerization
- 21. Frequent/regular s/w delivery is critical Mobile users expect apps to change almost daily New features, offers,
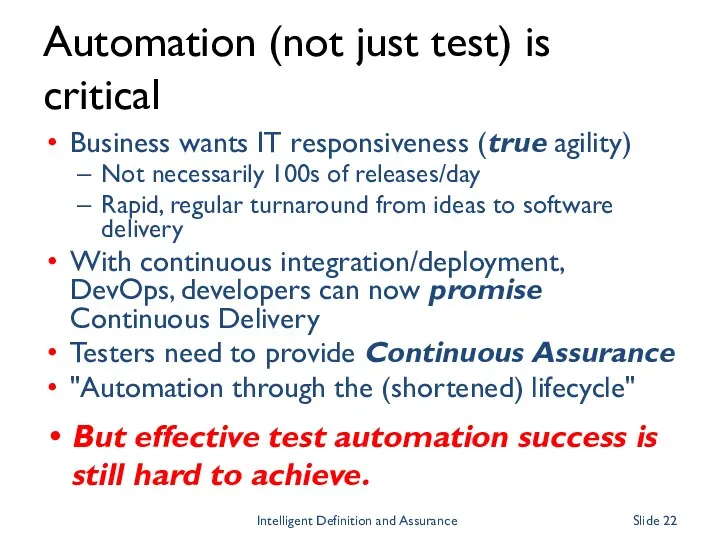
- 22. Automation (not just test) is critical Business wants IT responsiveness (true agility) Not necessarily 100s of
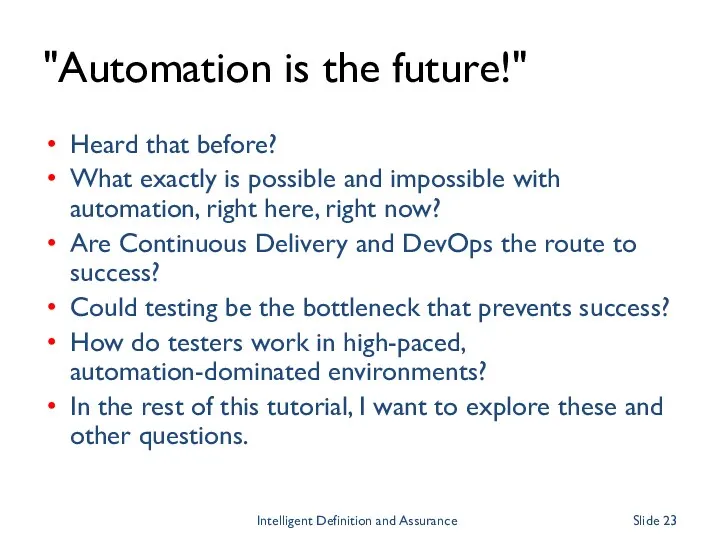
- 23. "Automation is the future!" Heard that before? What exactly is possible and impossible with automation, right
- 24. The old ways won't work in the future We need a New Model of Testing (free
- 25. Forget Logistics (for the time being) Document or not? Automated or manual? Agile v waterfall? This
- 26. ALL Testing is Exploratory We explore sources of knowledge ... ... to build test models ...
- 27. Models Pub Quiz How many models can YOU name? Twitter: @paul_gerrard Paul Gerrard paul@gerrardconsulting.com gerrardconsulting.com Intelligent
- 28. Models are innate, essential, human Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
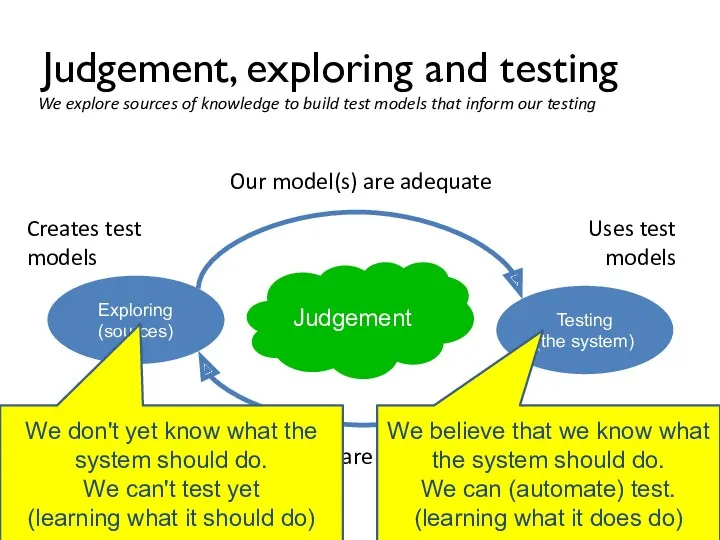
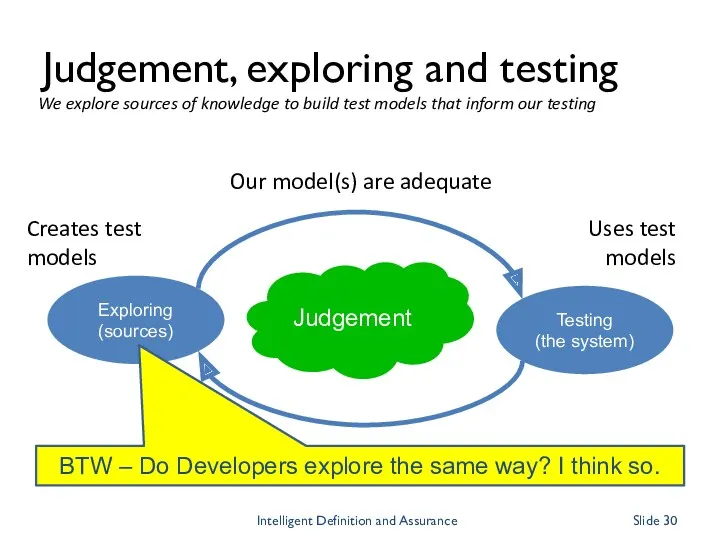
- 29. Judgement, exploring and testing Testing (the system) Our model(s) are adequate Our model(s) are not adequate
- 30. Judgement, exploring and testing Testing (the system) Our model(s) are adequate Our model(s) are not adequate
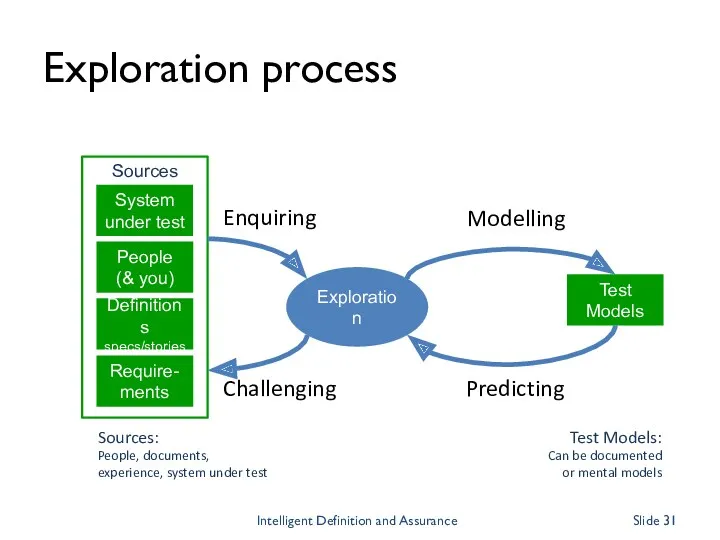
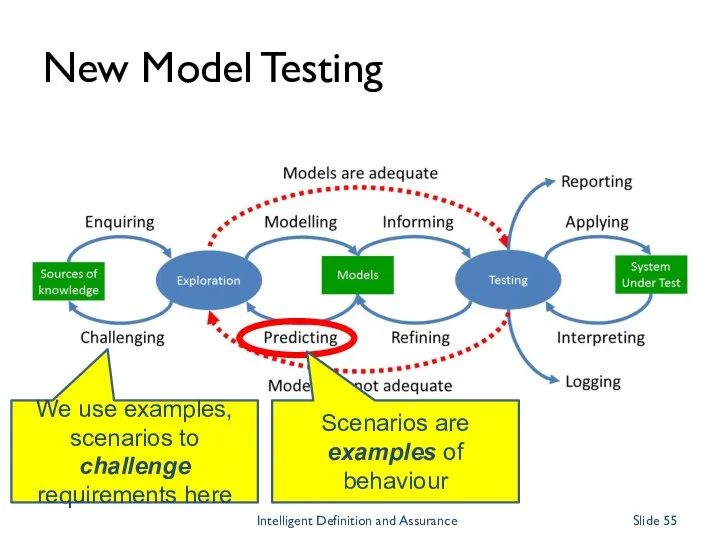
- 31. Exploration process Exploration Test Models Enquiring Challenging Sources: People, documents, experience, system under test Modelling Test
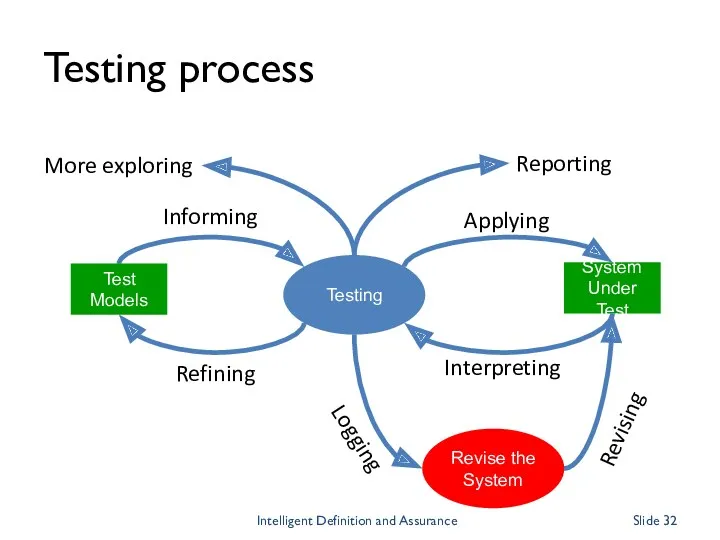
- 32. Testing process Testing System Under Test Refining Informing Applying Interpreting Test Models Revise the System Logging
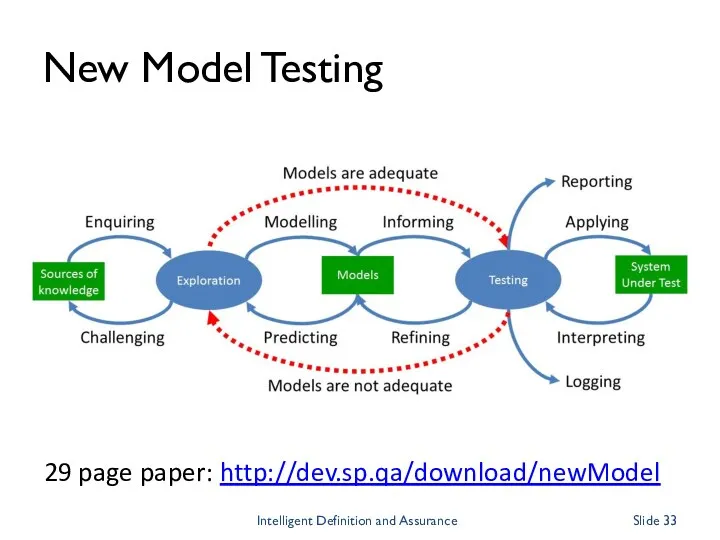
- 33. New Model Testing 29 page paper: http://dev.sp.qa/download/newModel Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 34. Some Consequences There are others
- 35. Relation to TDD and BDD? TDD is not really testing BDD is modelling using stories
- 36. Test automation from a different perspective Automation efforts fail too often Automation uses different test models
- 37. Capabilities Enquiring, Modelling, Predicting, Challenging Informing, Applying, Interpreting, Refining Reporting and Logging
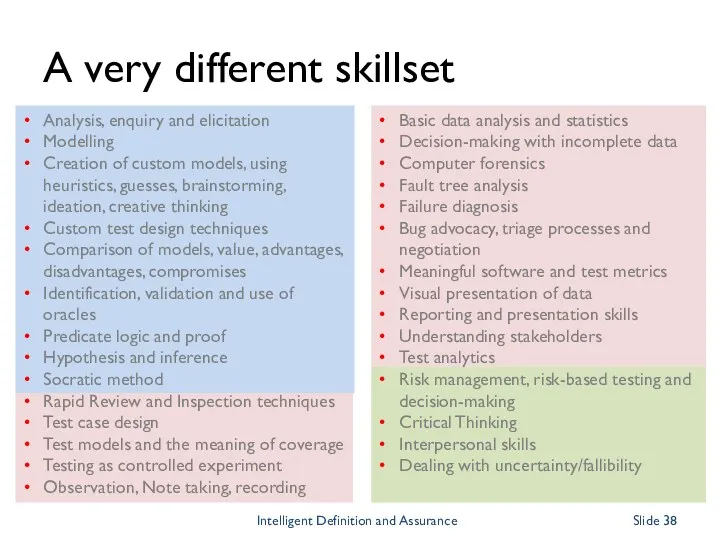
- 38. Analysis, enquiry and elicitation Modelling Creation of custom models, using heuristics, guesses, brainstorming, ideation, creative thinking
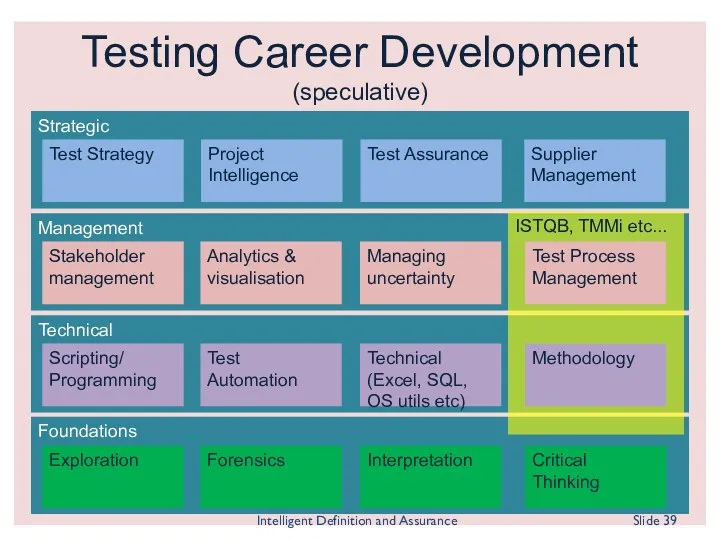
- 39. Testing Career Development (speculative) Foundations Technical Management Strategic Test Strategy Project Intelligence Test Assurance Exploration Forensics
- 40. Shift-Left
- 41. Shift-left Teams redistribute responsibility for testing and collaborate more Shift-Left can mean: Developers take ownership for
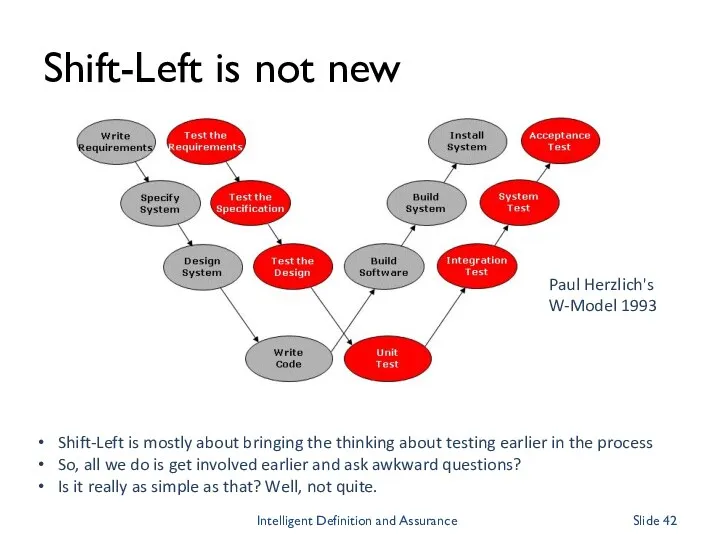
- 42. Shift-Left is not new Shift-Left is mostly about bringing the thinking about testing earlier in the
- 43. Shift-Left is Not New “Test early, test often”: a mantra for 25 years The underlying principle:
- 44. What is Driving Shift-Left? Several changes in the market are at play It started around some
- 45. Shift-Left – it’s all about feedback Testers provide feedback – whenever possible Get involved early –
- 46. Discussion: How often do apps change? How often are these apps released? Facebook LinkedIn eBay Amazon
- 47. Collaborative Requirements
- 48. Collaborative requirements Testers can make a huge contribution to the requirements phase In most contexts, user
- 49. Using Stories to Articulate/Validate Requirements Chapter 4 of the Business Story Pocketbook Download here: https://tkbase.com/resources/viewResource/19
- 50. Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
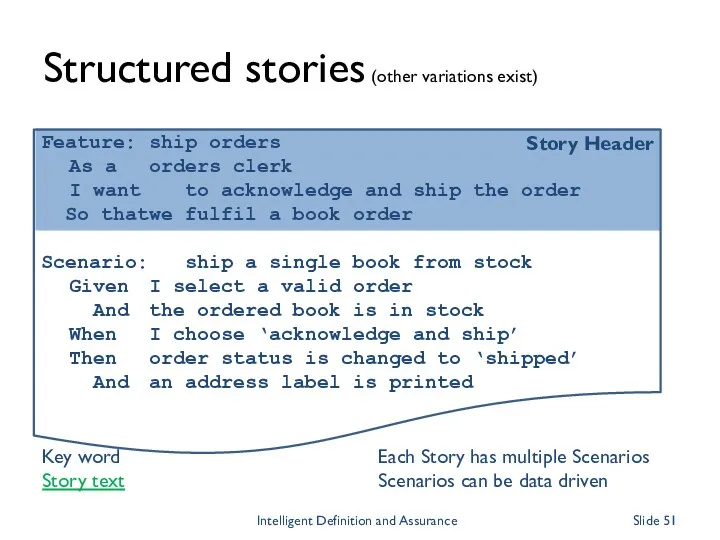
- 51. Story Header Feature: ship orders As a orders clerk I want to acknowledge and ship the
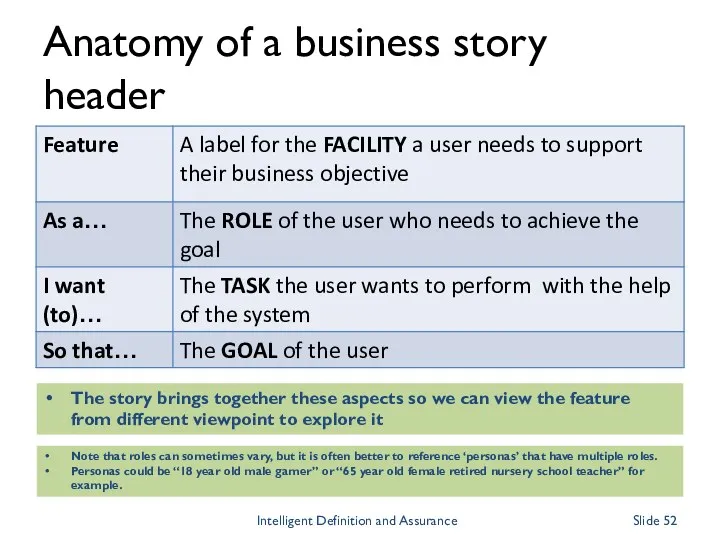
- 52. Anatomy of a business story header Note that roles can sometimes vary, but it is often
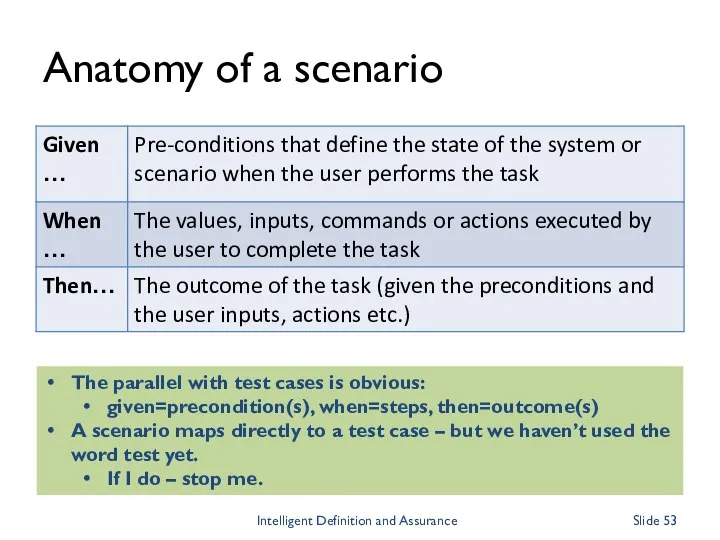
- 53. Anatomy of a scenario The parallel with test cases is obvious: given=precondition(s), when=steps, then=outcome(s) A scenario
- 54. Stories may have many scenarios Feature: Ship an Order In order to fulfil a book order
- 55. We use examples, scenarios to challenge requirements here New Model Testing Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 56. Exercise: what needs definition? Jot down the terms to define A customer order will have a
- 57. Exercise: what needs definition? A customer order will have a unique order reference a customer identifier,
- 58. What other questions might you ask? 'customer order will have…' means what? unique order reference’ unique
- 59. Typical questions to ask of a requirement What do the nouns and verbs actually mean? What
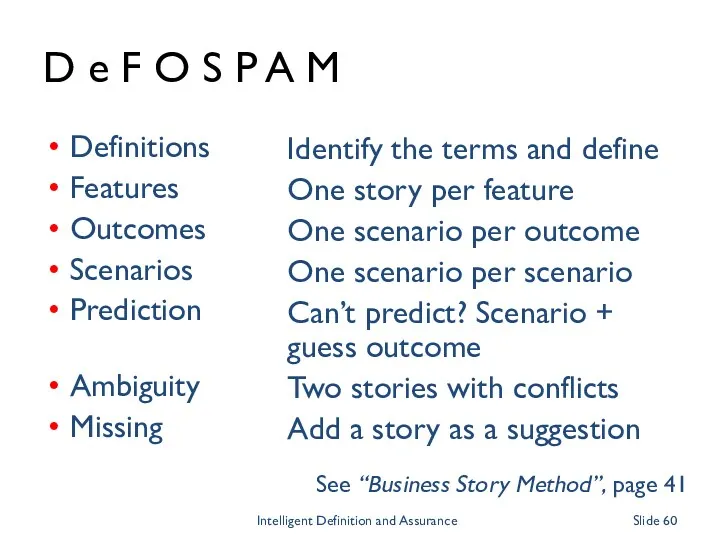
- 60. D e F O S P A M Definitions Features Outcomes Scenarios Prediction Ambiguity Missing Identify
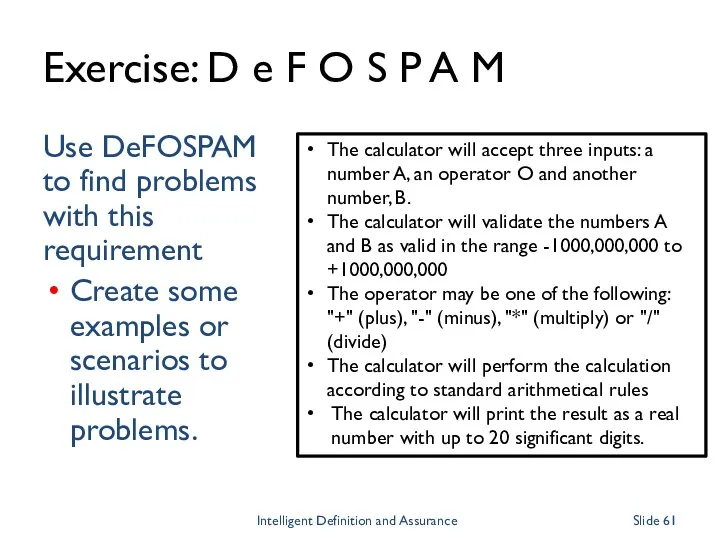
- 61. Exercise: D e F O S P A M Use DeFOSPAM to find problems with this
- 62. Did you find any anomalies? Do you want to share them?
- 63. Continuous Delivery
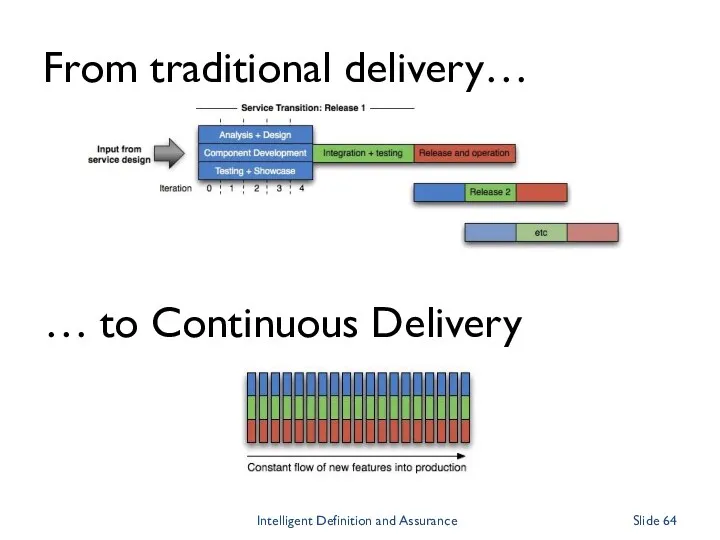
- 64. From traditional delivery… … to Continuous Delivery Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
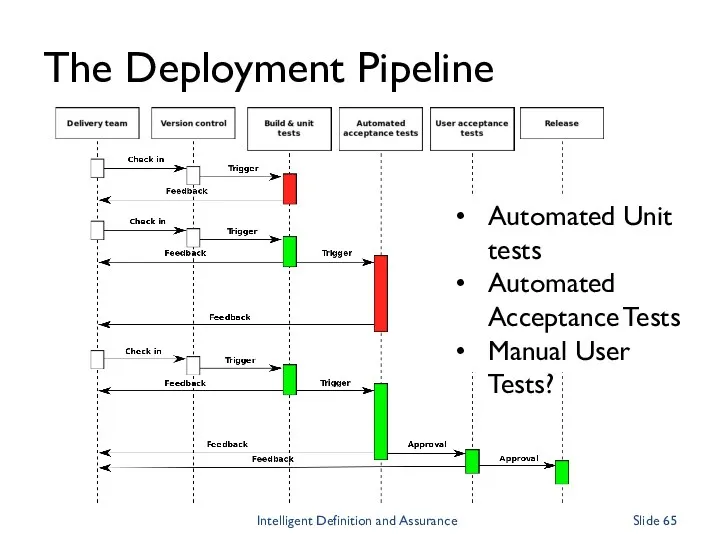
- 65. The Deployment Pipeline Automated Unit tests Automated Acceptance Tests Manual User Tests? Intelligent Definition and Assurance
- 66. Introducing Continuous Delivery Rigorously scoped features If a feature can't be squeezed into the next release,
- 67. Introducing Continuous Delivery 2 Test-Driven Development – all tests pass Commits must work – broken builds
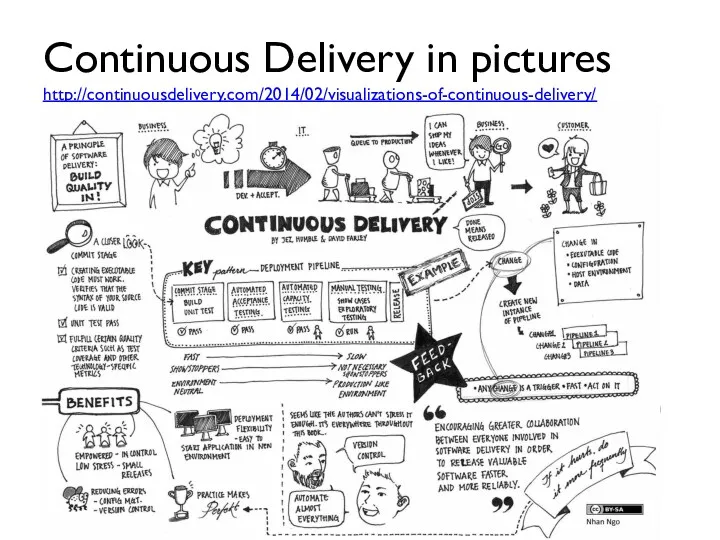
- 68. Continuous Delivery in pictures http://continuousdelivery.com/2014/02/visualizations-of-continuous-delivery/
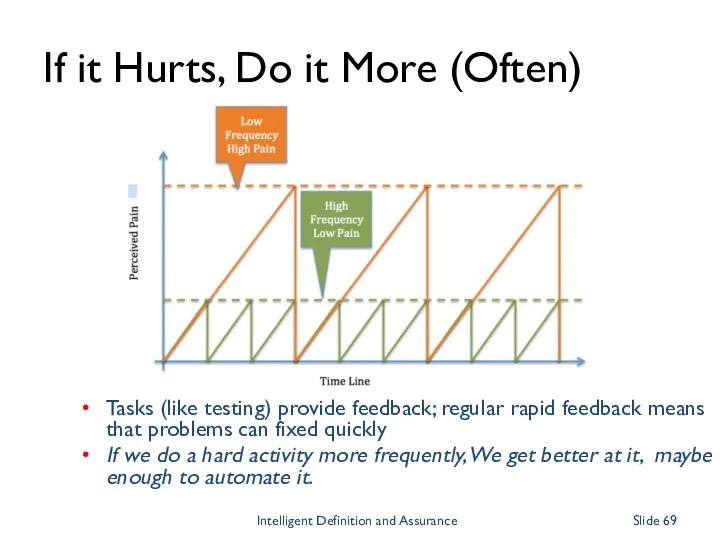
- 69. If it Hurts, Do it More (Often) Tasks (like testing) provide feedback; regular rapid feedback means
- 70. OK, we’re going to implement CD Boss: “We’re want to automate EVERYTHING!” Break down the test
- 71. Exercise: what test activities can be automated and what cannot? What can be automated? What can’t
- 72. It’s not about automation, it’s about trust A Deployment Pipeline depends on a Trusted Requirements Pipeline
- 73. If a requirement drives today’s delivery it must be trusted Continuous delivery is a hungry beast
- 74. Tests, Automation and Trust There is debate around: The meaning of checking and testing The reliance
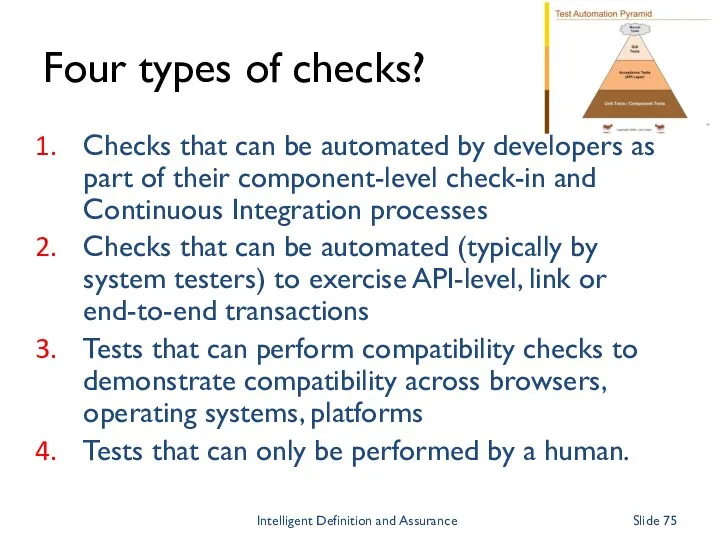
- 75. Four types of checks? Checks that can be automated by developers as part of their component-level
- 76. Typical questions and objections When do we create the test automation? There are too many system
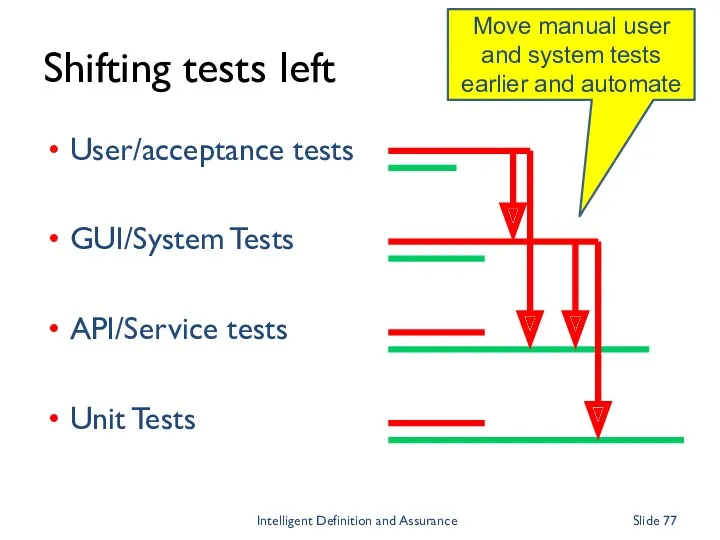
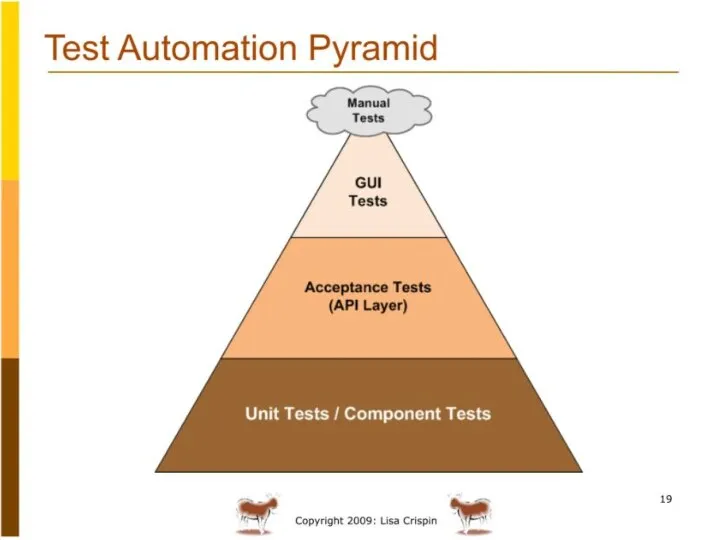
- 77. Shifting tests left User/acceptance tests GUI/System Tests API/Service tests Unit Tests Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
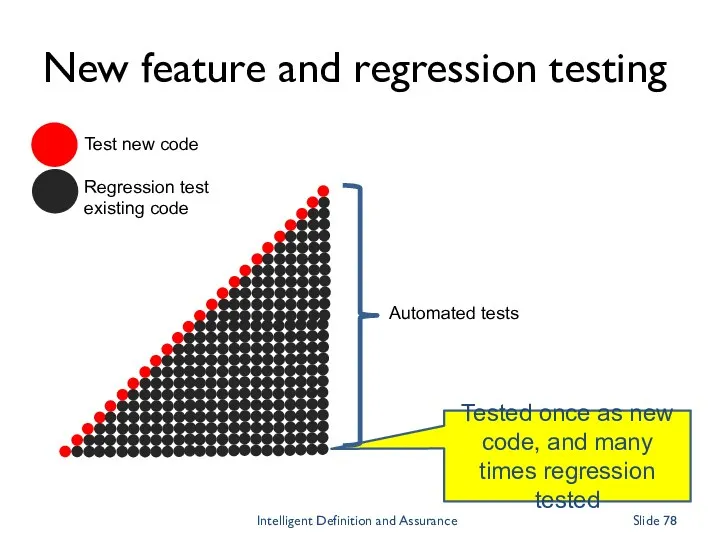
- 78. New feature and regression testing Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide Test new code Regression test existing
- 79. Development Patterns
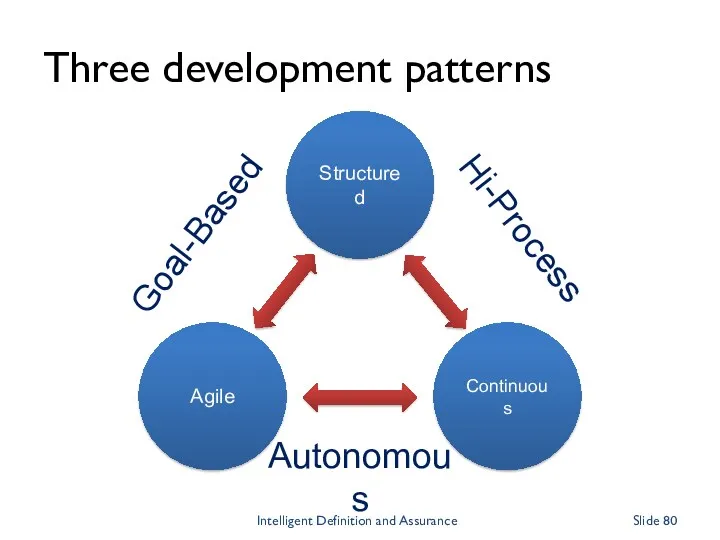
- 80. Three development patterns Structured Agile Continuous Goal-Based Hi-Process Autonomous Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 81. Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
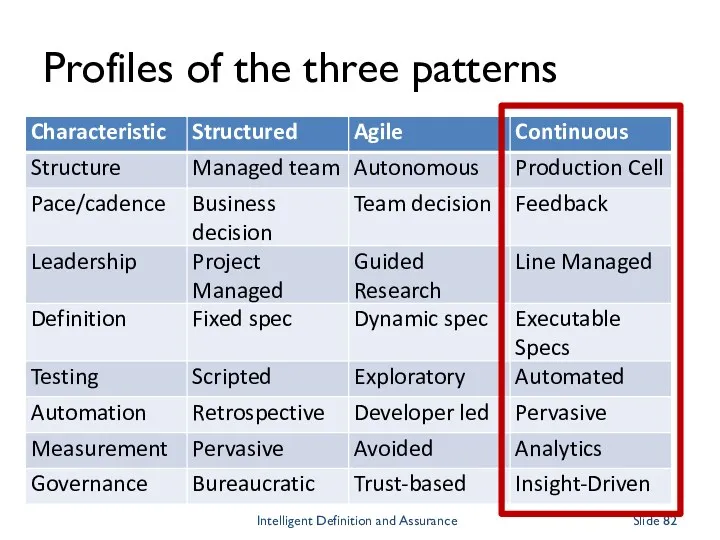
- 82. Profiles of the three patterns Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 83. Not three patterns; There are many You have to work out your own hybrid approach that
- 84. DevOps an overview
- 85. Exercise: How long does it take? Stages between dev-done and Go Live e.g: Integration Installing Testing
- 86. Slow Release, Deployment and Infrastructure Change We're interested in Continuous Delivery We've shifted left Testers get
- 87. Deployment process 1 Does this sound familiar? Integration – "nothing works"! First time developers code is
- 88. Deployment process 2 Testing – "it could be so much better!" Some functionality is available; but
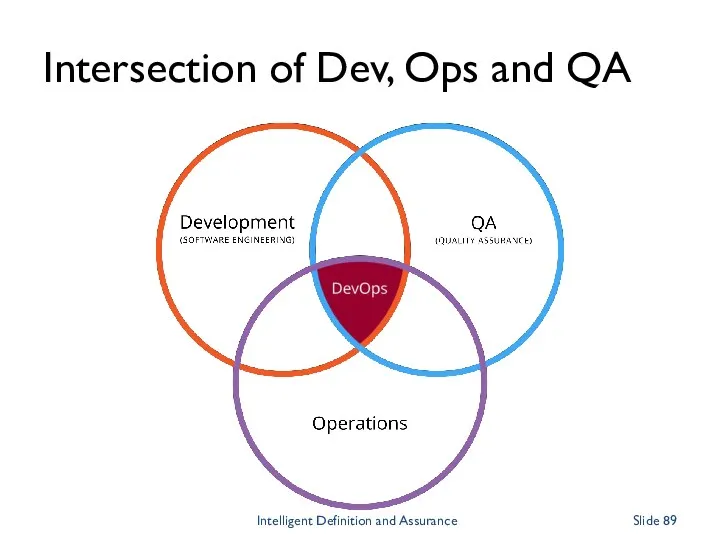
- 89. Intersection of Dev, Ops and QA Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 90. Definition "DevOps is a development methodology with a set of practices aimed at bridging the gap
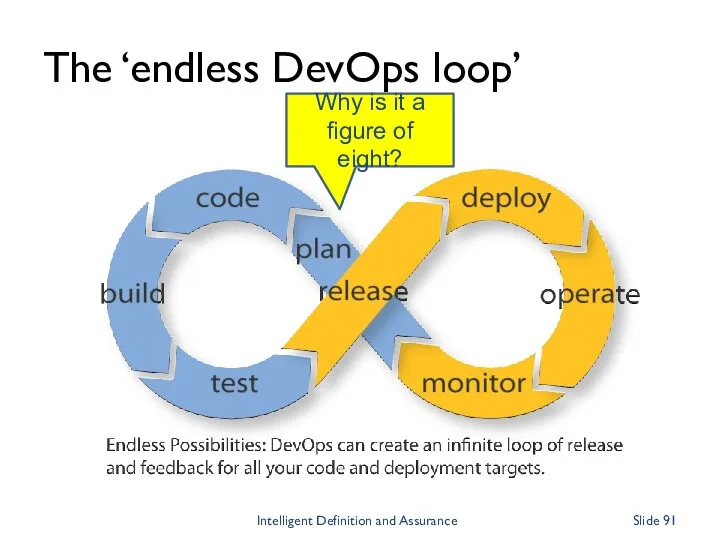
- 91. The ‘endless DevOps loop’ Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide Why is it a figure of eight?
- 92. What is DevOps? The DevOps ‘movement’ (for want of a better label) is progressing rapidly Like
- 93. Is DevOps about tools or people? At one level, the goal of DevOps is to speed
- 94. So DevOps is just Dev and Ops working more closely? No, it's not that either The
- 95. DevOps - CAMS Culture Develop Dev-Ops relationship, communications, collaboration, bring Dev closer to the customer Automation
- 96. The Tools Landscape
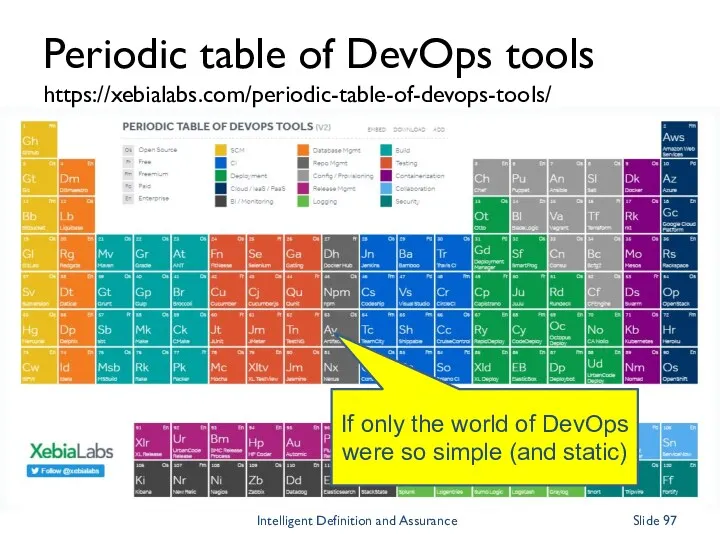
- 97. Periodic table of DevOps tools https://xebialabs.com/periodic-table-of-devops-tools/ If only the world of DevOps were so simple (and
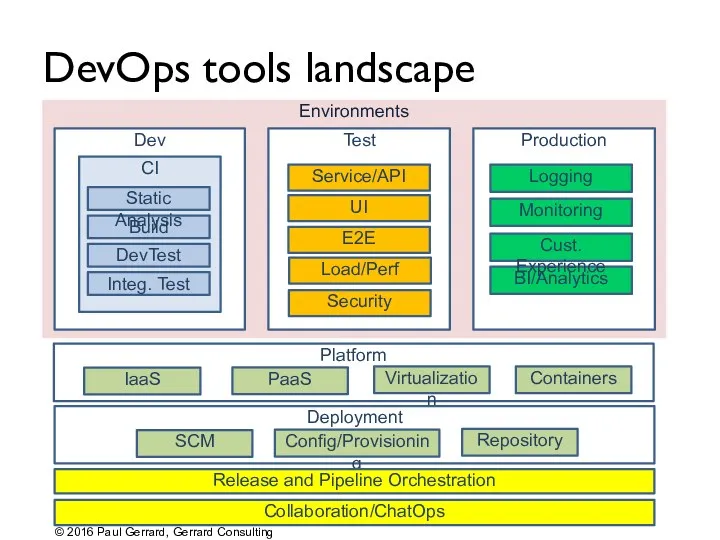
- 98. Environments DevOps tools landscape Dev Test CI Production Deployment Config/Provisioning Release and Pipeline Orchestration Build DevTest
- 99. How many tools do you use? NewRelic - Application monitoring - gives us the eyes on
- 100. The Tools Knowledge Base https://tkbase.com
- 101. Some Ancient History
- 102. CAST Report 4th edition (1999) Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 103. Remember WinRunner? This is a sample tools page from the CAST Report WinRunner had a two
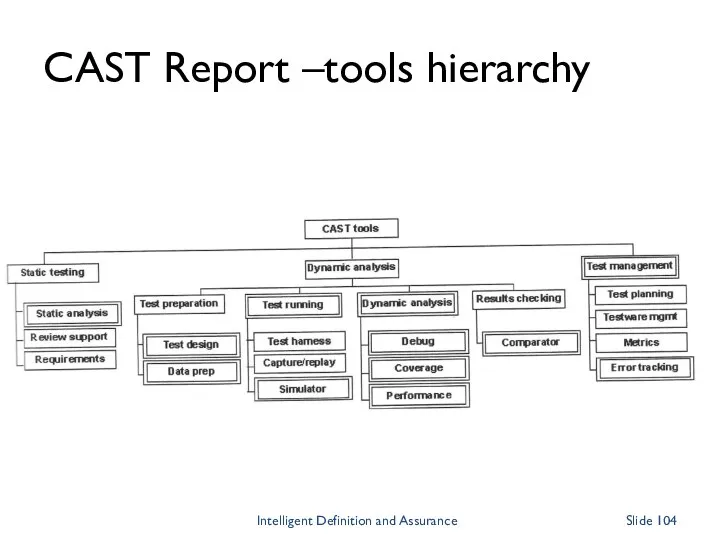
- 104. CAST Report –tools hierarchy Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
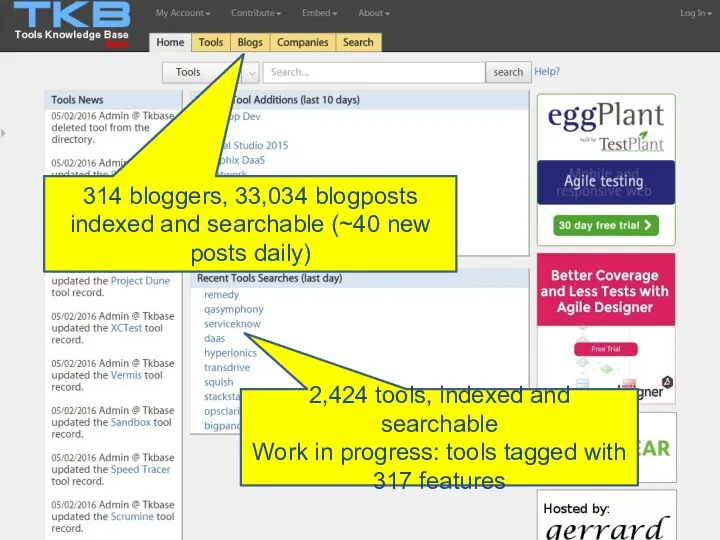
- 105. How many tools are there anyway? I'm researching tools for tkbase.com 2424 of which 686 are
- 106. Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide 314 bloggers, 33,034 blogposts indexed and searchable (~40 new posts daily)
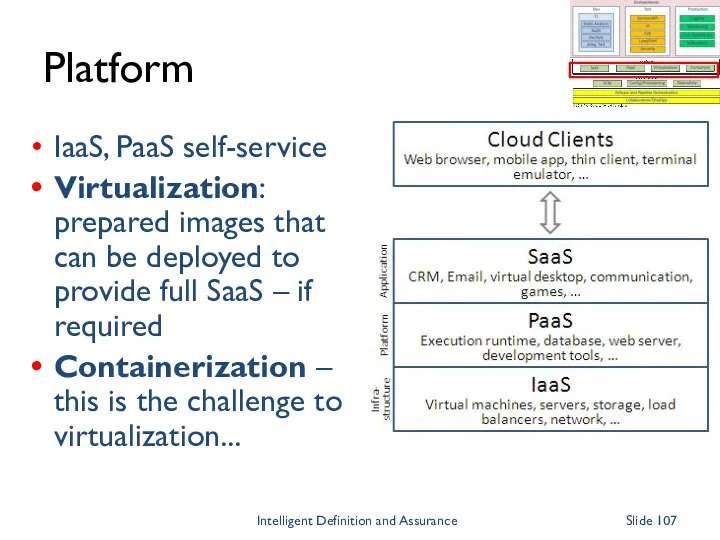
- 107. Platform IaaS, PaaS self-service Virtualization: prepared images that can be deployed to provide full SaaS –
- 108. Containerization Hottest topic in the DataCentre right now Virtual machines replicate much of the host machine
- 109. Configuration/Provisioning "Infrastructure as code" is an emerging concept Define your environments as code in text files
- 110. Repository management Infrastructure as code means... Environments created accurately and reliably But these still take time
- 111. Development Static analysis tools scan code and look for problems and provide code metrics that indicate
- 112. Test Service/API tests call web services/APIs directly GUI tools are the traditional user-oriented tests that simulate
- 113. Production Logging tools can be configured to Record execution statistics at virtually any level Trigger alarms
- 114. Release and pipeline orchestration These tools define the deployment and release pipeline, tasks and dependencies They
- 115. Collaboration/ChatOps Tools so far enable technical folk to define and implement environments, build, deploy and test
- 116. ChatOps example > bot: twitter says "we are down" > bot: twitter silenced for 15 min,
- 117. ChatOps
- 118. Exercise: Create a Delivery Pipeline from these activities (env/activity) Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 119. Exercise: ChatOps Let's look at a simulation of a Deployment Pipeline and use ChatOps to manage
- 120. Test Automation - Ambition and Reality
- 121. "Automation is the future!" Heard that before? What exactly is possible and impossible with automation, right
- 122. What Goes Wrong with Test Execution Automation?
- 123. Tools are sensitive instruments You don't need tools and tools won't help, if your software is
- 124. The anti-regression goal What are you trying to do with automation? Anti-regression is the primary goal
- 125. Testing and automation – a modelling problem not a tools problem Need to shift testing thinking
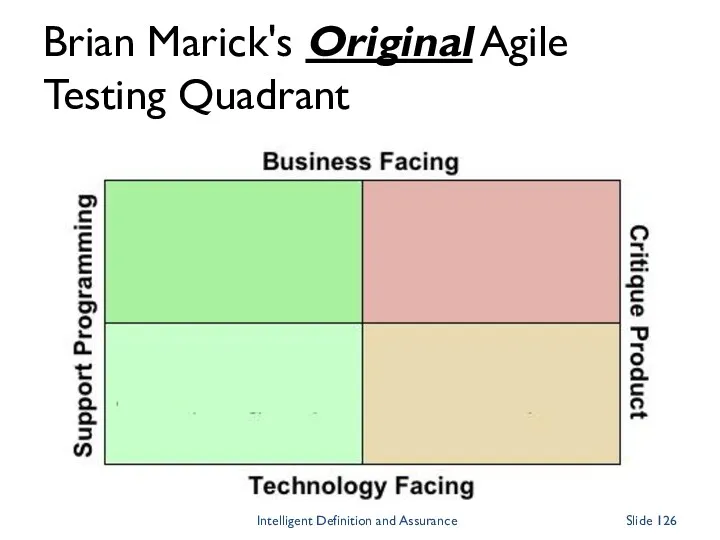
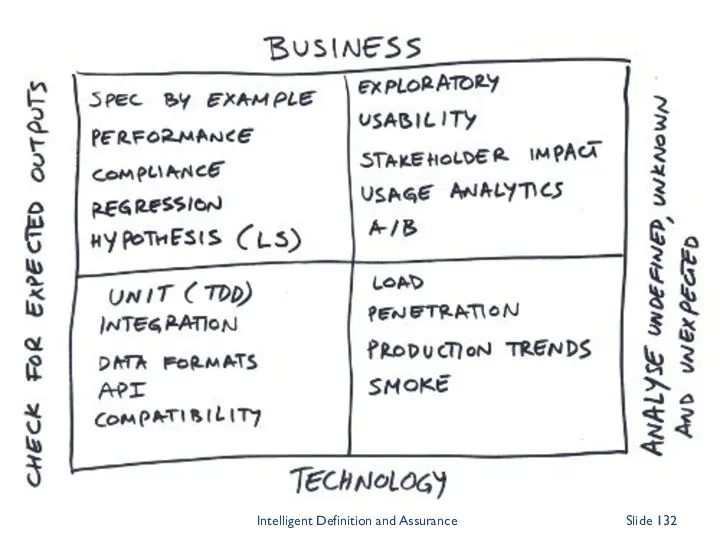
- 126. Brian Marick's Original Agile Testing Quadrant Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 127. Crispin & Gregory (Agile Testing version) Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 128. Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 129. Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 130. What does this tell you?
- 131. Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 132. Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
- 133. How do we get better at test automation?
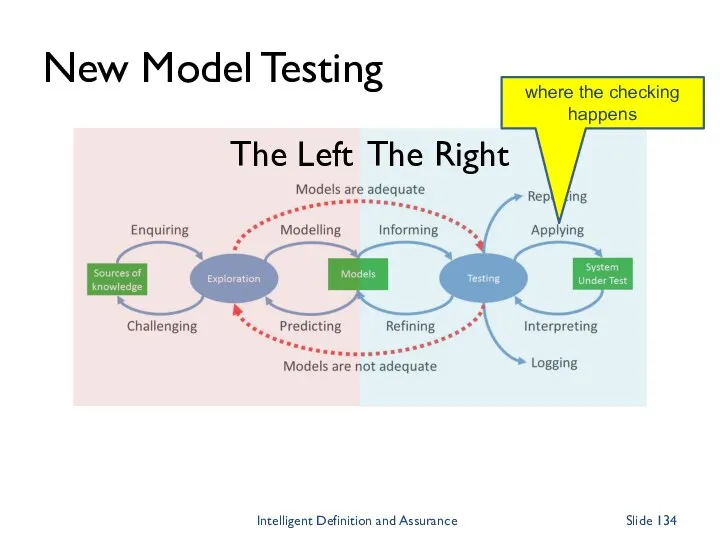
- 134. New Model Testing The Left The Right where the checking happens Intelligent Definition and Assurance Slide
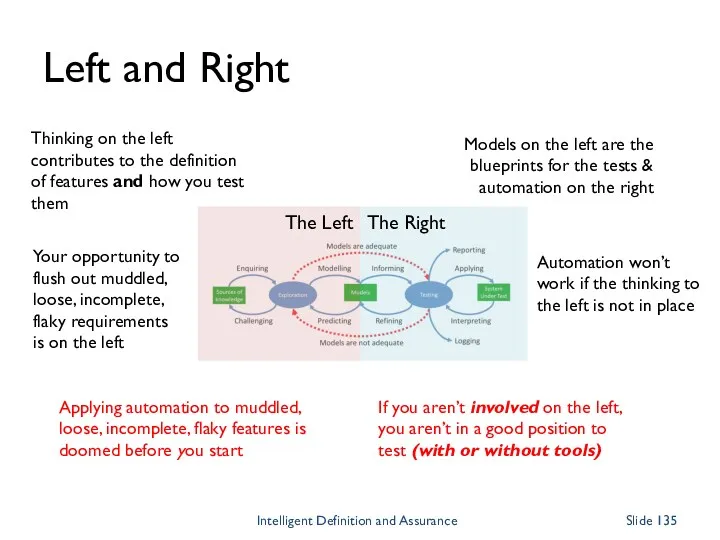
- 135. Left and Right Automation won’t work if the thinking to the left is not in place
- 136. Shift-Left (thinking, not people) If you are not contributing on the left, you are doomed to
- 137. Your homework for today Are tools just drones that can only execute regression testing? Could tools
- 138. Digital Testing Strategy Agile Test Strategy – an Oxymoron?
- 139. (Test Strategy as) Agile Interventions I’m using Scrum/Sprint terminology, but you don’t have to of course
- 140. Interventions (government client example) On the following slides, we highlight 8 interventions Some are test phases,
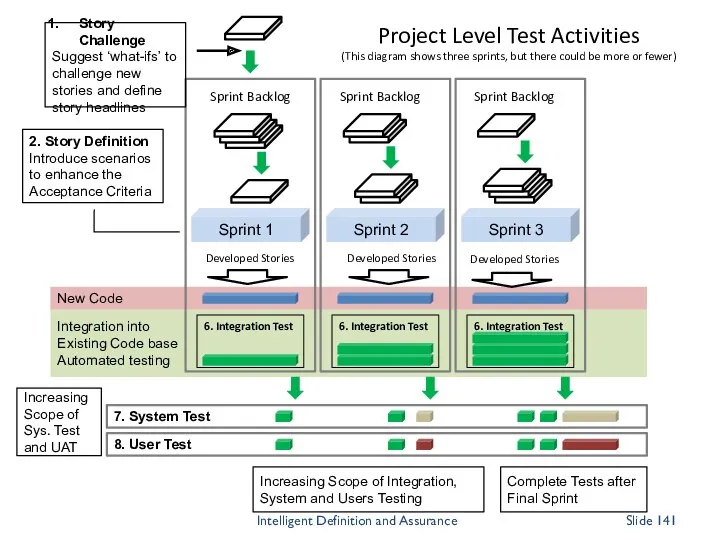
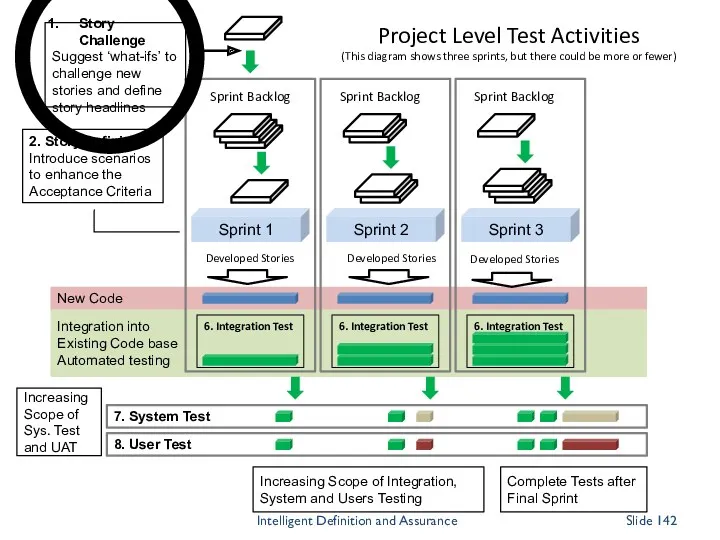
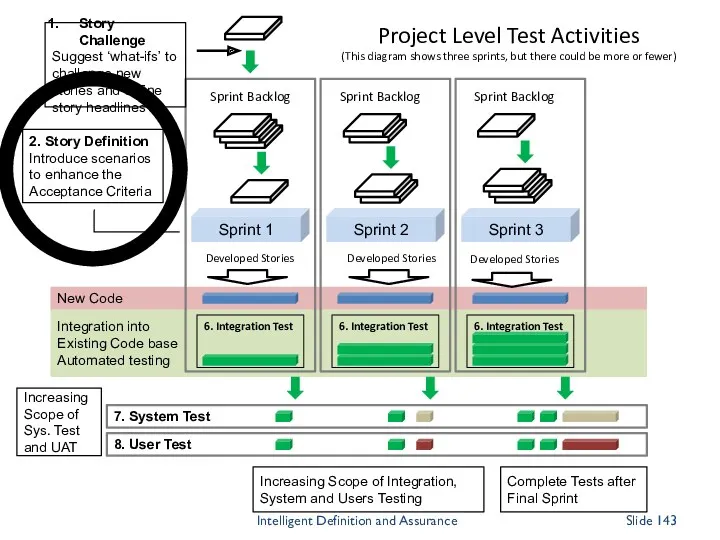
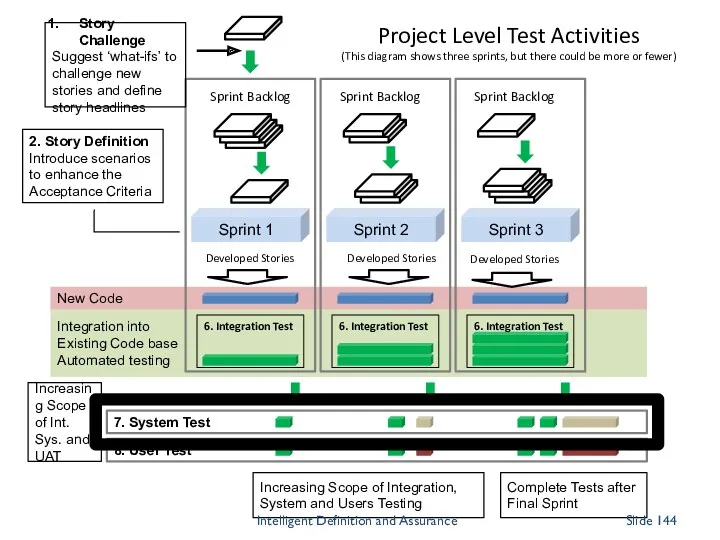
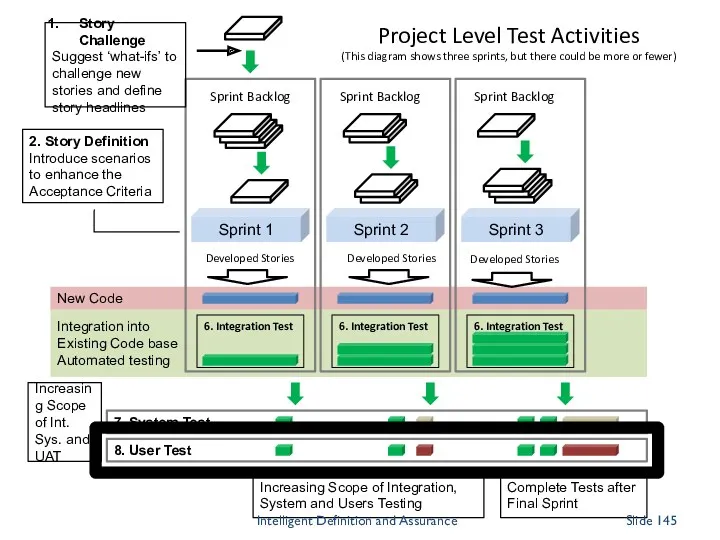
- 141. Integration into Existing Code base Automated testing New Code 8. User Test 7. System Test Sprint
- 142. Integration into Existing Code base Automated testing New Code 8. User Test 7. System Test Sprint
- 143. Integration into Existing Code base Automated testing New Code 8. User Test 7. System Test Sprint
- 144. Integration into Existing Code base Automated testing New Code 8. User Test 7. System Test Sprint
- 145. Integration into Existing Code base Automated testing New Code 8. User Test 7. System Test Sprint
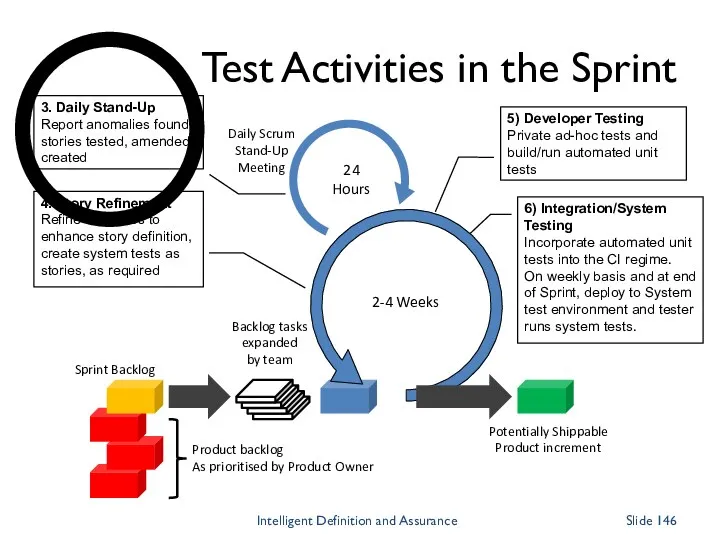
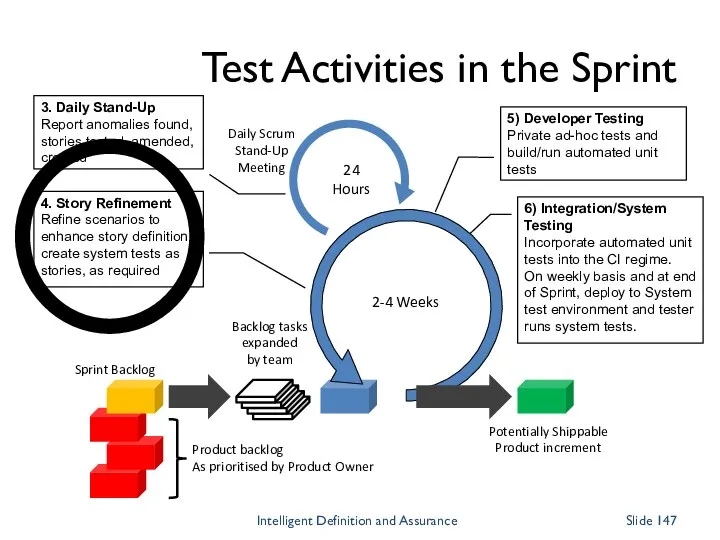
- 146. Daily Scrum Stand-Up Meeting 24 Hours 2-4 Weeks Backlog tasks expanded by team Potentially Shippable Product
- 147. Daily Scrum Stand-Up Meeting 24 Hours 2-4 Weeks Backlog tasks expanded by team Potentially Shippable Product
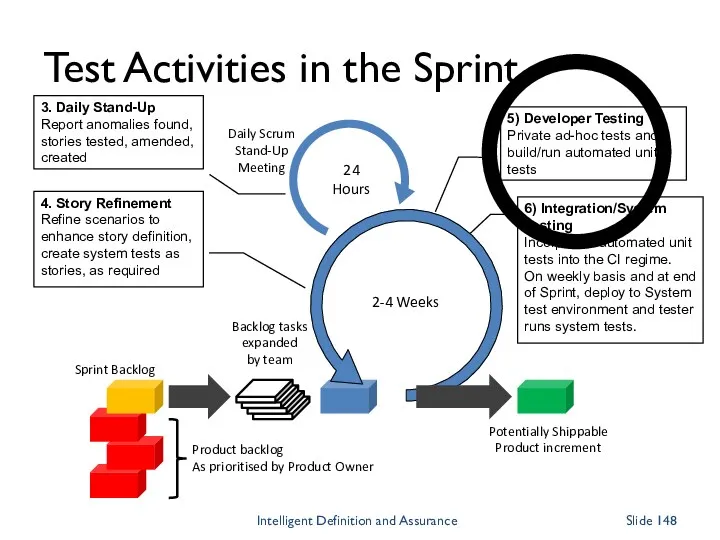
- 148. Daily Scrum Stand-Up Meeting 24 Hours 2-4 Weeks Backlog tasks expanded by team Potentially Shippable Product
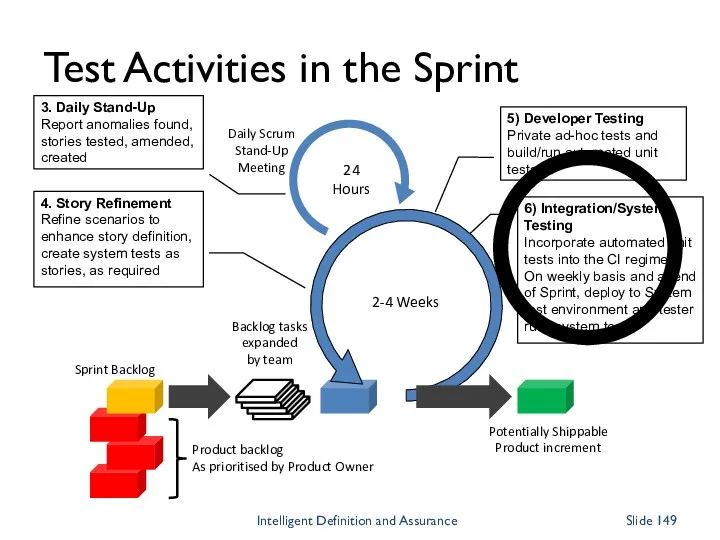
- 149. Daily Scrum Stand-Up Meeting 24 Hours 2-4 Weeks Backlog tasks expanded by team Potentially Shippable Product
- 150. The tester’s contribution Think of testing as interventions, not stages The testing role is redistributed and
- 151. Surviving Continuous Delivery and DevOps How do Testers fit into a DevOps regime?
- 152. Tests, Automation and Trust Can we trust automation to do all our testing? Consider four areas:
- 153. It's easier to trust if you're a visionary Is your concern that you can't trust the
- 154. The Deployment Pipeline Consider your test and release processes as a linked chain of processes (very
- 155. Test automation The manual interventions between automated activities in DevOps are the pain points: bottlenecks, delays,
- 156. Monitoring and Improvement A key discipline of DevOps is a deeper level of monitoring in production
- 157. As a Tester, What Should You Do? There are 'critical moments' in all projects where you
- 158. I'm a Test Lead/Manager. What Should I Do? It might be harder to justify your role
- 159. When should DevOps not be attempted? A good question but the answer is a simple challenge:
- 160. The phase after development is Re-Work
- 161. Thank-You! @paul_gerrard Paul Gerrard email: paul@gerrardconsulting.com Twitter: @paul_gerrard LinkedIn: http://linkedin.com/in/paulgerrard tkbase.com | testopera.com
- 162. Testing, Analytics and Decision-Making (Shift-Right)
- 163. Introduction The purpose of testing is to gather information for someone to make a decision Testing
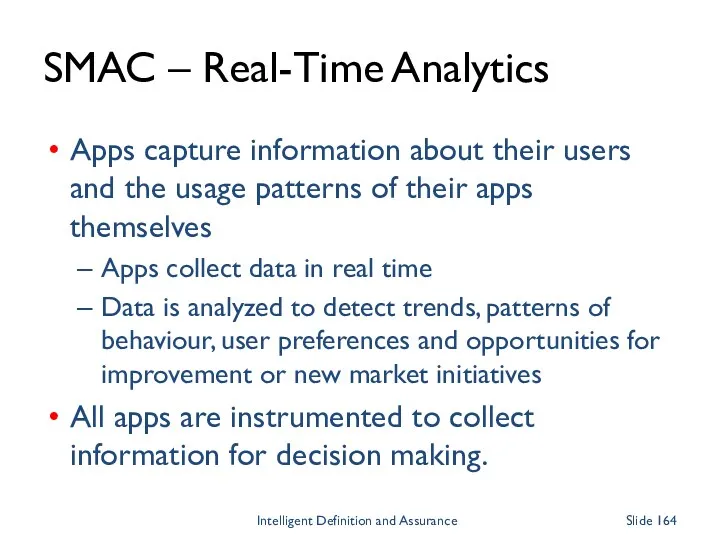
- 164. SMAC – Real-Time Analytics Apps capture information about their users and the usage patterns of their
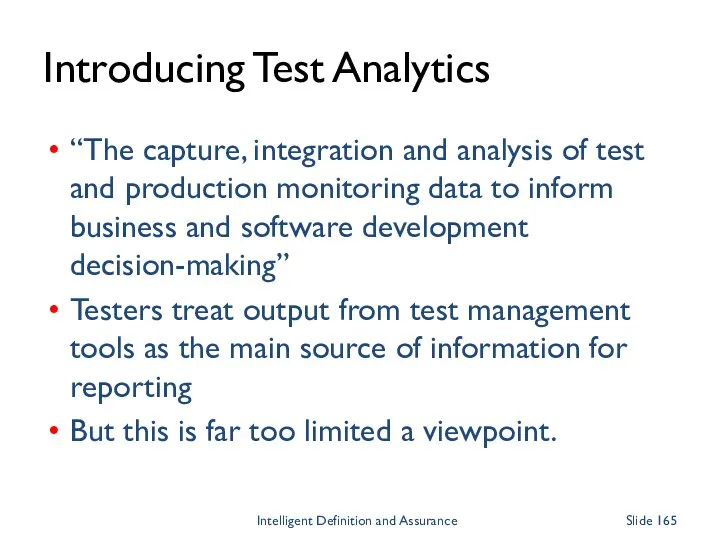
- 165. Introducing Test Analytics “The capture, integration and analysis of test and production monitoring data to inform
- 166. Modern Practices – Opportunities for Testing Shift-Left aims to reduce, if not eliminate, misunderstandings in requirements
- 167. Testing and Decision-Making Testing supports decision making at all levels Testing Stakeholders can have many roles
- 168. The challenge of test prediction and planning The Testing Uncertainty Principle: We can predict test status,
- 169. The Testing Theory of Relativity 1 The value of a test is affected by many things
- 170. The Testing Theory of Relativity 2 Most of the challenge of test planning is scope We
- 171. Quantum Theory of Testing When we perform a test, pass or fail - the test incrementally
- 173. Скачать презентацию














































































































 Электронные таблицы. Диаграмма
Электронные таблицы. Диаграмма Exceptions and testing
Exceptions and testing Програмне забезпечення ЕОМ. Основні функції операційних систем, файлова система
Програмне забезпечення ЕОМ. Основні функції операційних систем, файлова система Справочно-библиографическое обслуживание в современной общедоступной библиотеке: технологии и ресурсы
Справочно-библиографическое обслуживание в современной общедоступной библиотеке: технологии и ресурсы информационные процессы
информационные процессы Компьютерный вирус. Антивирус
Компьютерный вирус. Антивирус Керування кольорами. Розміщення малюнків на веб-сторінці
Керування кольорами. Розміщення малюнків на веб-сторінці Понятие информационной системы, БД и СУБД. Лекция №2
Понятие информационной системы, БД и СУБД. Лекция №2 Влияние социальных сетей на современных школьников
Влияние социальных сетей на современных школьников Spiritsofts is provides SAP HANA Online Training
Spiritsofts is provides SAP HANA Online Training Арифметические операции в позиционных системах счисления
Арифметические операции в позиционных системах счисления История развития компьютерной техники
История развития компьютерной техники Понятие процесса в ОС. Раздел 5
Понятие процесса в ОС. Раздел 5 Методы и технологии поиска информации в научной и образовательной деятельности
Методы и технологии поиска информации в научной и образовательной деятельности Актуалізація опорних знань. (інформатика 7 класс)
Актуалізація опорних знань. (інформатика 7 класс) Пользовательский интерфейс
Пользовательский интерфейс Отчет о прохождении учебной практики. Специальность 09.02.07 Информационные системы и программирование
Отчет о прохождении учебной практики. Специальность 09.02.07 Информационные системы и программирование Управление ключами. Лекция по дисциплине Основы защиты информации
Управление ключами. Лекция по дисциплине Основы защиты информации Как зарабатывать в Интернете
Как зарабатывать в Интернете Spatial data development for SDI
Spatial data development for SDI Извлечение данных из таблиц. Семинар 2
Извлечение данных из таблиц. Семинар 2 Мультимедиялық технология
Мультимедиялық технология Презентация к уроку Файлы
Презентация к уроку Файлы Монтаж абонентских линий (инсталлятор)
Монтаж абонентских линий (инсталлятор) База данных Oracle
База данных Oracle Основы инстаграм
Основы инстаграм Таѕдау операторы
Таѕдау операторы Технические средства телекоммуникационных технологий
Технические средства телекоммуникационных технологий