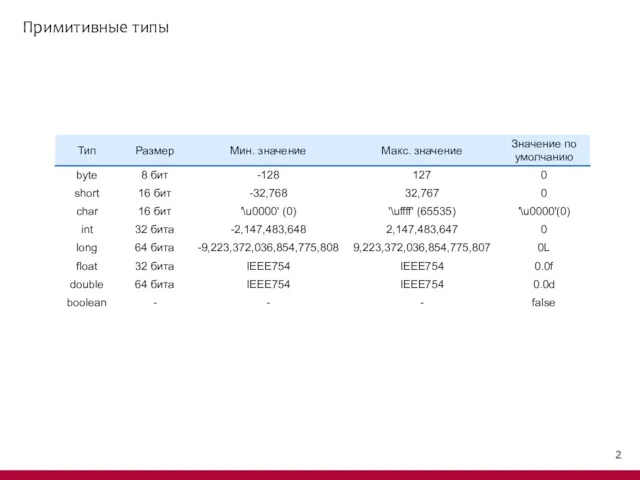
Содержание
- 3. Примитивные типы
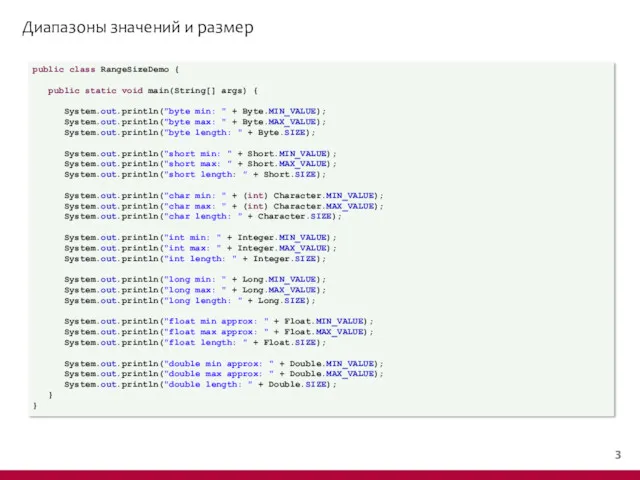
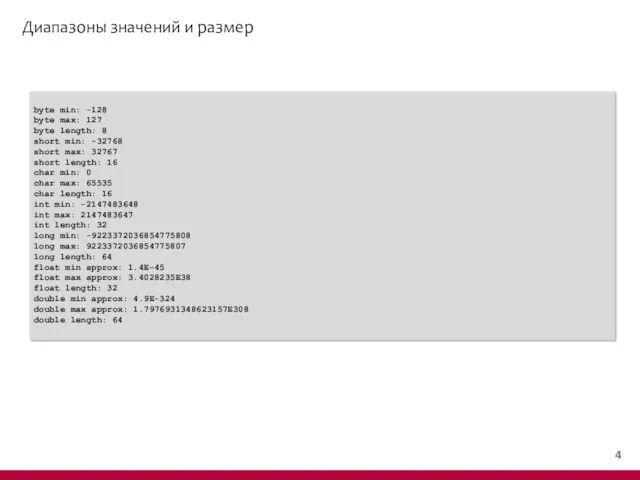
- 4. Диапазоны значений и размер public class RangeSizeDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("byte min:
- 5. Диапазоны значений и размер byte min: -128 byte max: 127 byte length: 8 short min: -32768
- 6. Примитивные переменные [byte|short|char|int|long|float|double|boolean] variable [ = literal | = expression ];
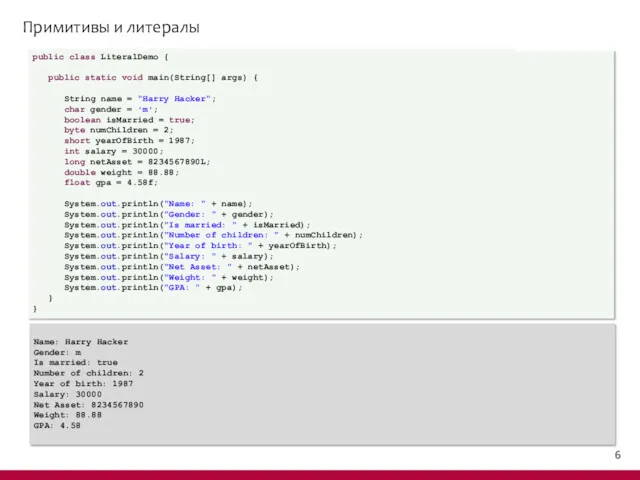
- 7. Примитивы и литералы public class LiteralDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { String name =
- 8. Булевский тип
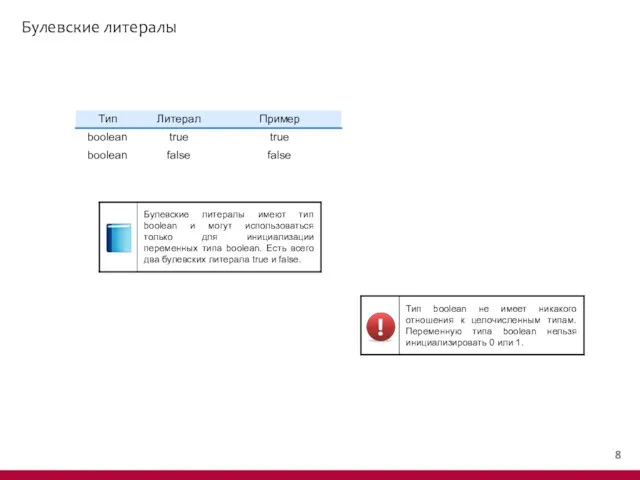
- 9. Булевские литералы
- 10. Булевы логические операторы
- 11. Таблица истинности public class TruthTableDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("L\tR\tAND\tOR\tXOR\tNOT"); printLine(true, true); printLine(true,
- 12. Целочисленные типы
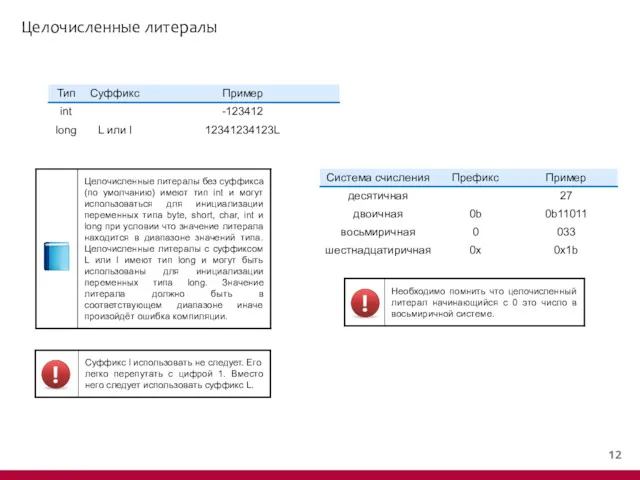
- 13. Целочисленные литералы
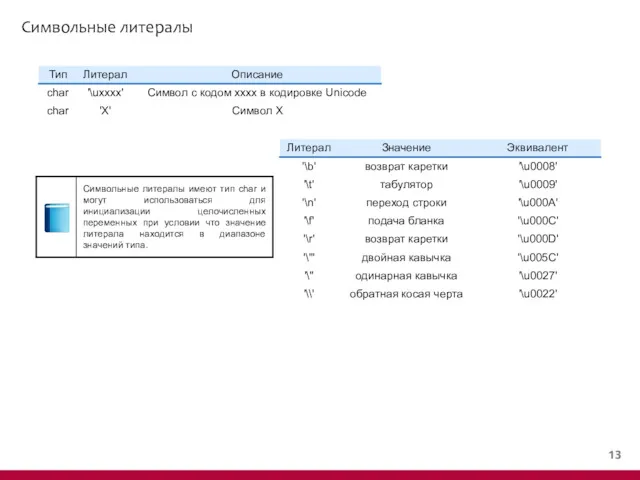
- 14. Символьные литералы
- 15. Преобразования целочисленных типов
- 16. Преобразование типов public class ByteIntConversionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int xInt; byte xByte;
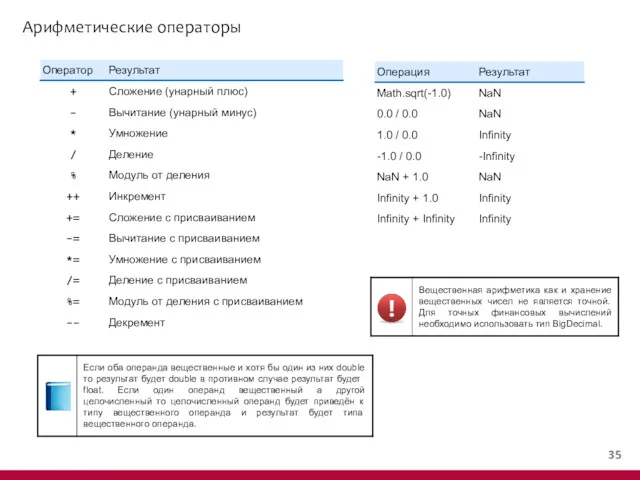
- 17. Арифметические операторы
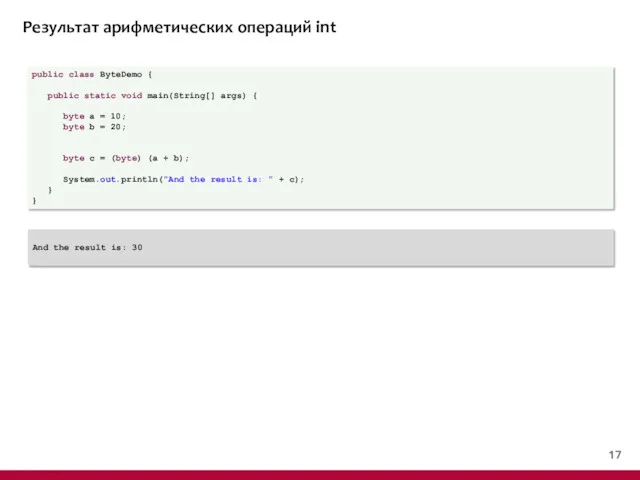
- 18. Результат арифметических операций int public class ByteDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { byte a
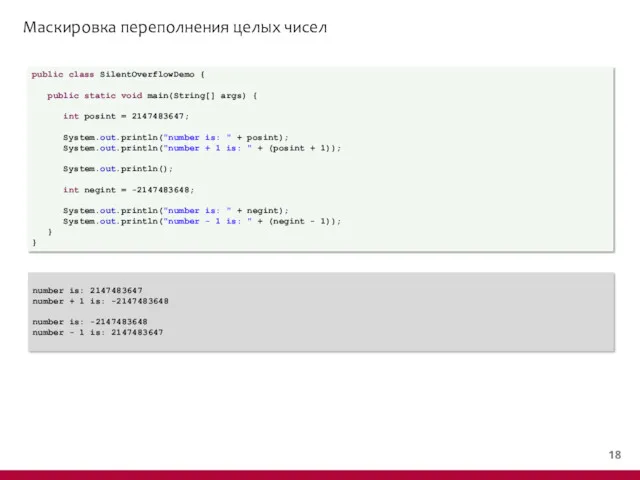
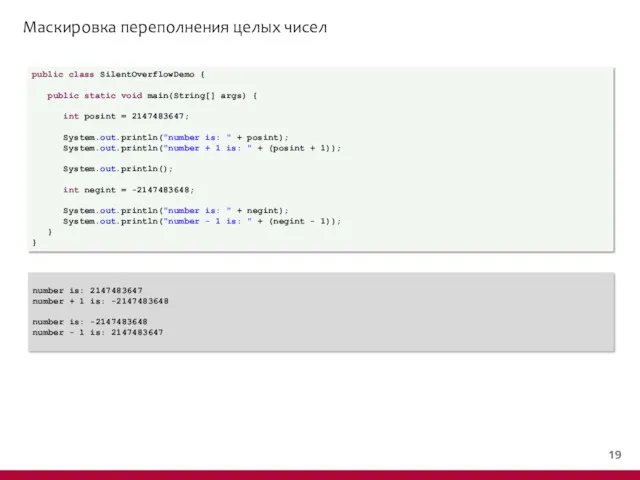
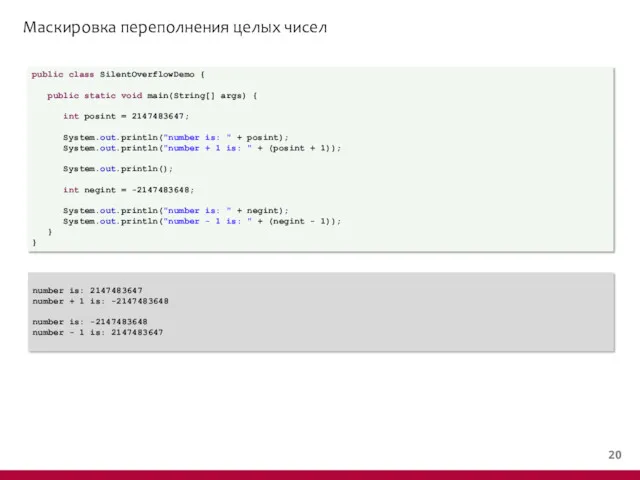
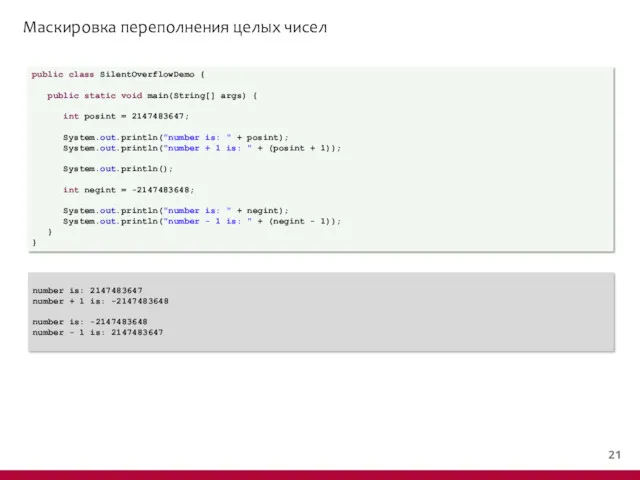
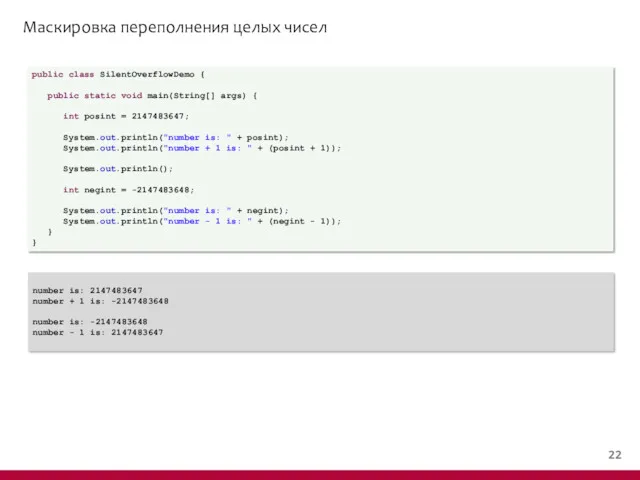
- 19. Маскировка переполнения целых чисел public class SilentOverflowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int posint
- 20. Маскировка переполнения целых чисел public class SilentOverflowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int posint
- 21. Маскировка переполнения целых чисел public class SilentOverflowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int posint
- 22. Маскировка переполнения целых чисел public class SilentOverflowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int posint
- 23. Маскировка переполнения целых чисел public class SilentOverflowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int posint
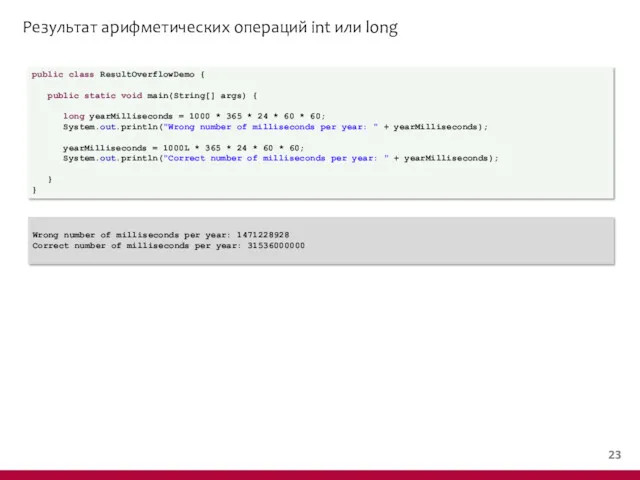
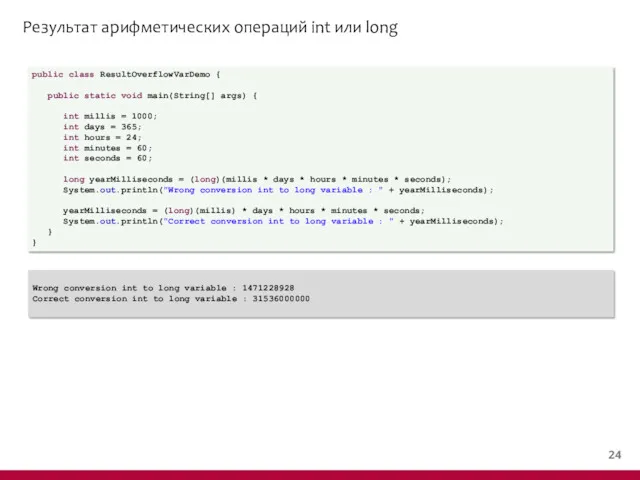
- 24. Результат арифметических операций int или long public class ResultOverflowDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {
- 25. Результат арифметических операций int или long public class ResultOverflowVarDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {
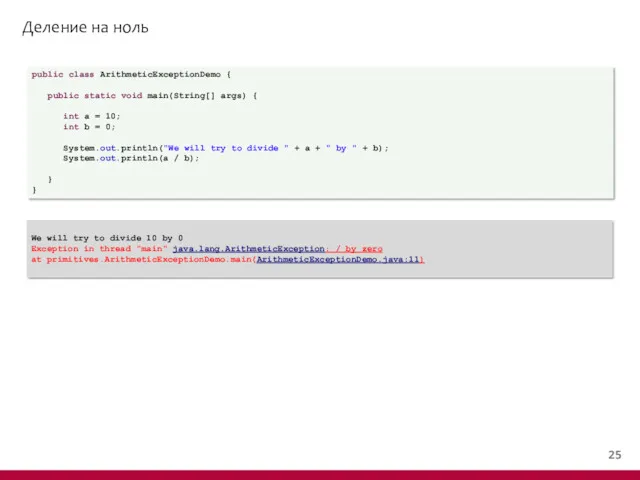
- 26. Деление на ноль public class ArithmeticExceptionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int a =
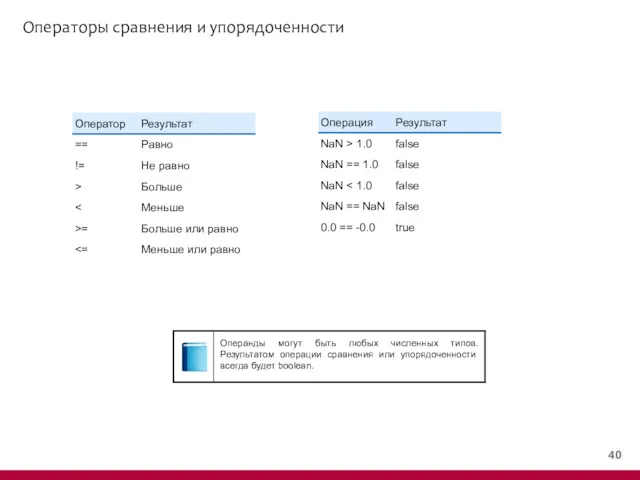
- 27. Операторы сравнения и упорядоченности
- 28. Битовые целочисленные операторы
- 29. Вещественные типы
- 30. Вещественные литералы
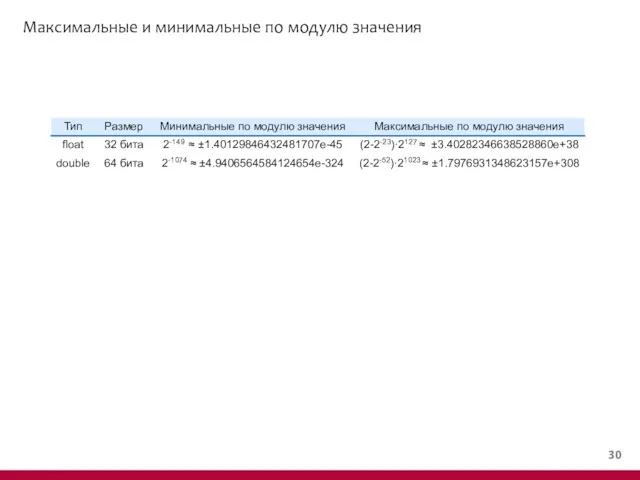
- 31. Максимальные и минимальные по модулю значения
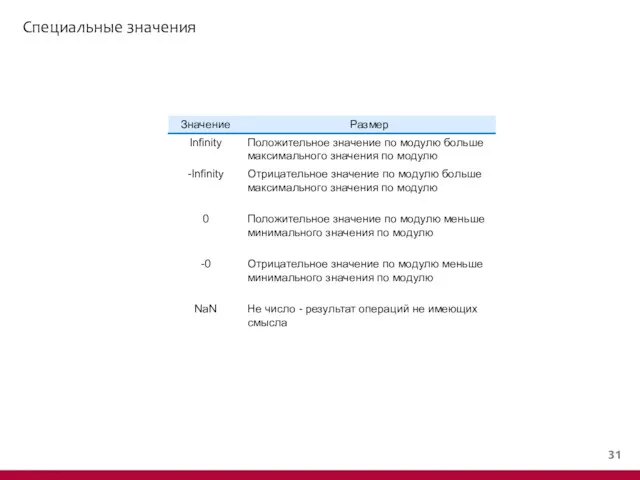
- 32. Специальные значения
- 33. Специальные значения public class SpecialValuesDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { double max = Double.MAX_VALUE;
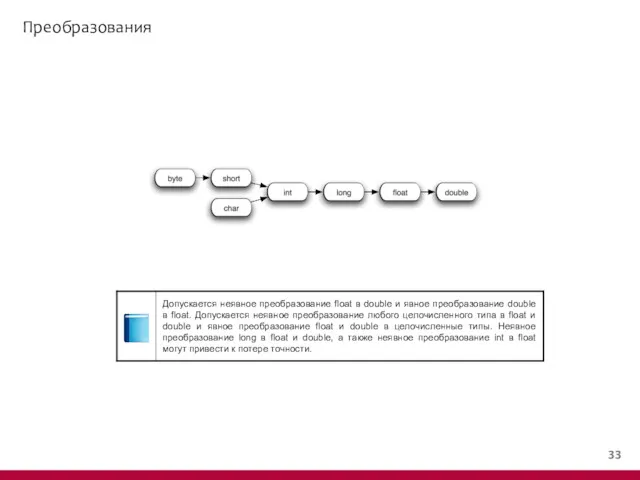
- 34. Преобразования
- 35. Преобразование типов public class IntDoubleConversionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { int xInt; double xDouble;
- 36. Арифметические операторы
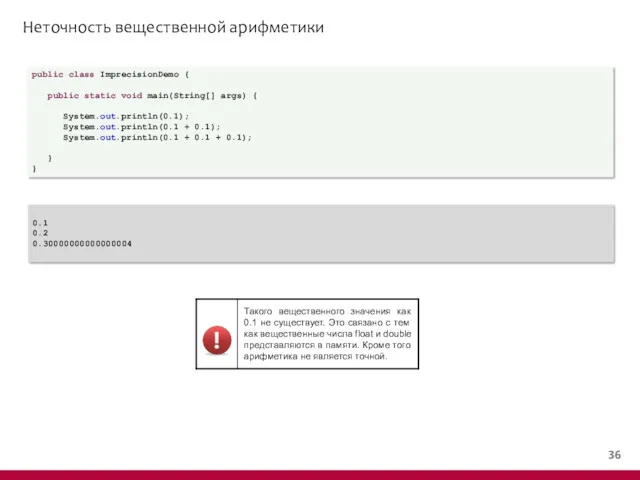
- 37. Неточность вещественной арифметики public class ImprecisionDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(0.1); System.out.println(0.1 +
- 38. Как хранятся числа с плавающей точкой
- 39. Пример хранения float 0.8125 = 0.5+0.25+0.0625 (-1)s × (1+m) × 2(e - 127) 0.8125 = (-1)0
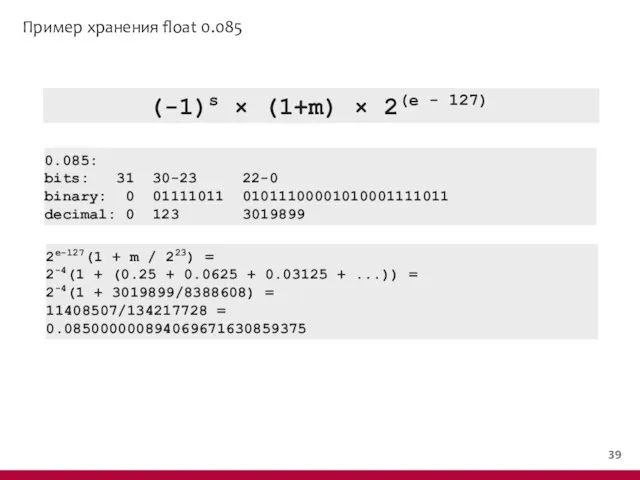
- 40. Пример хранения float 0.085 (-1)s × (1+m) × 2(e - 127) 0.085: bits: 31 30-23 22-0
- 41. Операторы сравнения и упорядоченности
- 43. Скачать презентацию

![Примитивные переменные [byte|short|char|int|long|float|double|boolean] variable [ = literal | = expression ];](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/148690/slide-5.jpg)


![Таблица истинности public class TruthTableDemo { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/148690/slide-10.jpg)


![Преобразование типов public class ByteIntConversionDemo { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/148690/slide-15.jpg)





![Специальные значения public class SpecialValuesDemo { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/148690/slide-32.jpg)
![Преобразование типов public class IntDoubleConversionDemo { public static void main(String[]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/148690/slide-34.jpg)


 1С и Telegram
1С и Telegram Множества и логика в задачах ЕГЭ по информатике
Множества и логика в задачах ЕГЭ по информатике Средства коммуникационной техники. Средства и системы телефонной связи
Средства коммуникационной техники. Средства и системы телефонной связи Корпусная лингвистика
Корпусная лингвистика Сайти
Сайти Web - сайты и web-страницы
Web - сайты и web-страницы QR-кодирование. Что такое QR-код?
QR-кодирование. Что такое QR-код? Инструкция по работе с веб-сайтом программного обеспечения Corel
Инструкция по работе с веб-сайтом программного обеспечения Corel Информационные системы и технологии с элементами искусственного интеллекта. Лекция 8
Информационные системы и технологии с элементами искусственного интеллекта. Лекция 8 Упрощенный прием РПО
Упрощенный прием РПО Действия с информацией
Действия с информацией Диалоговые окна
Диалоговые окна Цифровая платформа Российский Фермер
Цифровая платформа Российский Фермер 16-сабақ. Ғаламтормен дұрыс жұмыс жасау -мәдениет
16-сабақ. Ғаламтормен дұрыс жұмыс жасау -мәдениет Web-страницы. Язык HTML и др. Тема 1
Web-страницы. Язык HTML и др. Тема 1 Компьютерная этика
Компьютерная этика Вспомогательные режимы построения объектов
Вспомогательные режимы построения объектов Единый портал государственных и муниципальных услуг
Единый портал государственных и муниципальных услуг Архитектурная схема ЭВМ. Состав ПК
Архитектурная схема ЭВМ. Состав ПК Разработка мобильных приложений в THUNKABLE. Начало
Разработка мобильных приложений в THUNKABLE. Начало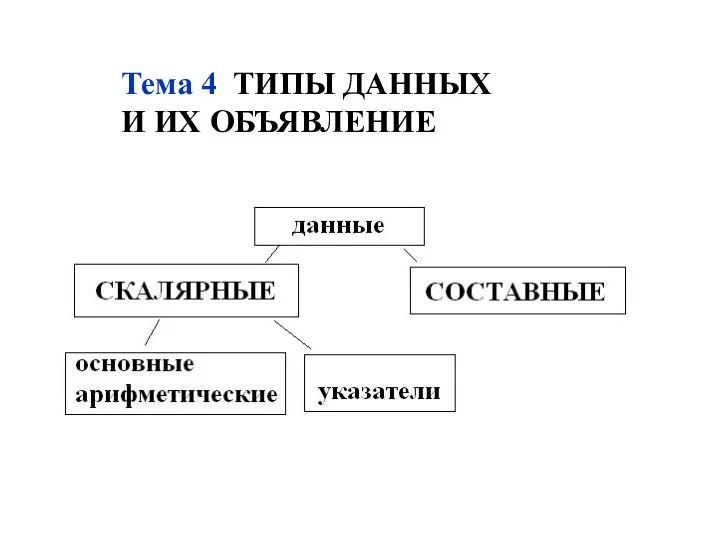 Типы данных и их объявление
Типы данных и их объявление Мошенничество в сети Интернет
Мошенничество в сети Интернет Право в интернете
Право в интернете Информатика и информатизация общества
Информатика и информатизация общества Қазақ мерзімді баспасөзінің пайда болуы және қазақ тіліндегі алғашқы газеттер
Қазақ мерзімді баспасөзінің пайда болуы және қазақ тіліндегі алғашқы газеттер Лекция 7. Моделирование технологических процессов. Травление, литография, проявление
Лекция 7. Моделирование технологических процессов. Травление, литография, проявление Java Массивы
Java Массивы Понятие объекта
Понятие объекта