Содержание
- 2. Aims & Objectives Define Ports & Connectors (Serial, Parallel & USB) State reasons for Backing Storage
- 3. Introduction Printers produce paper copies of electronic files. Hard copies of computer documents remain important today.
- 4. Printers As a computer technician, you may be required to purchase, repair, or maintain a printer.
- 5. Printer to Computer Interfaces To access a printer, a computer must have an interface with it.
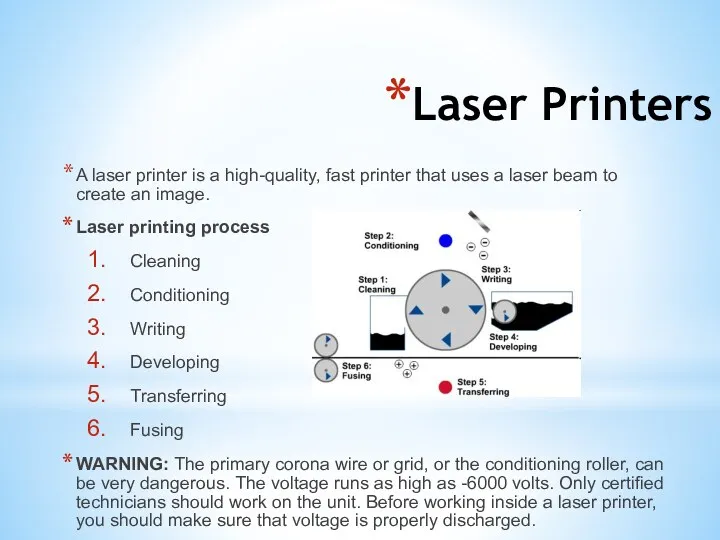
- 6. Laser Printers A laser printer is a high-quality, fast printer that uses a laser beam to
- 7. Impact Printers Impact printers use a print head impacts a printer tape or inked ribbon to
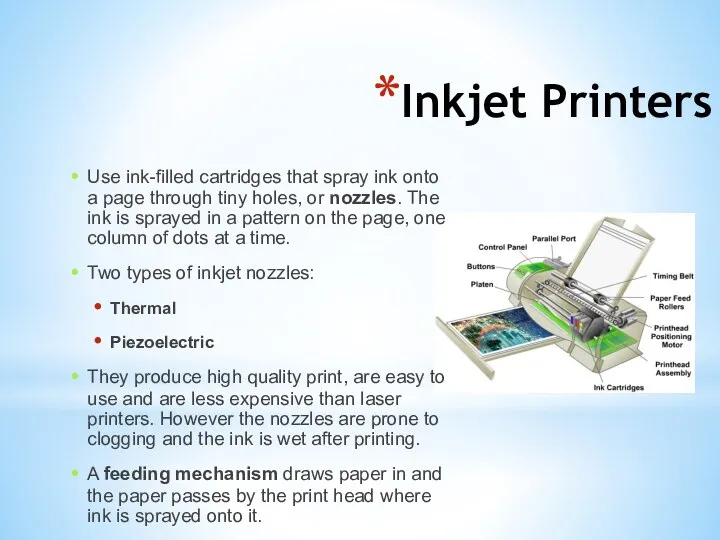
- 8. Inkjet Printers Use ink-filled cartridges that spray ink onto a page through tiny holes, or nozzles.
- 9. Solid-ink Printers Use solid sticks of ink rather than toner or ink cartridges. The printing process:
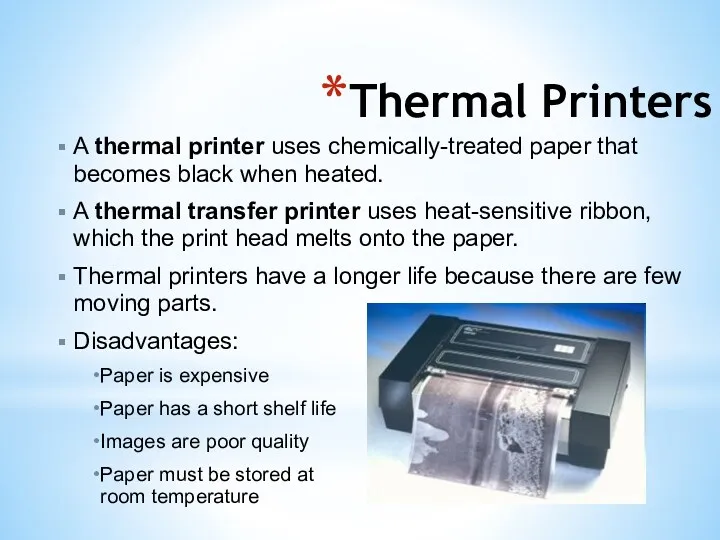
- 10. Thermal Printers A thermal printer uses chemically-treated paper that becomes black when heated. A thermal transfer
- 11. Dye-Sublimation Printers Also called thermal dye printers Usually used in producing photo-quality images for graphic printing
- 12. Installation and Configuration of Printers When purchasing a printer, the installation and configuration information is usually
- 13. Types of Scanners Technicians may be required to purchase, repair, or maintain a scanner. The following
- 14. Scanners Scanners typically create an RGB image that can be converted into image formats such as
- 15. All-in-one Scanners An all-in-one device combines the functionality of multiple into one physical piece of hardware
- 16. Flatbed Scanners Often used to scan books and photographs for archiving. Image is acquired by placing
- 17. Handheld Scanners A handheld scanner is small and portable. Pass the scanner head across the surface
- 18. Drum Scanners Drum scanners produce a high-quality scanned image, but they are being replaced by lower
- 19. Installation and Configuration of Scanners An installation media includes drivers, manuals, and diagnostic software will be
- 20. Preventive Maintenance Techniques Printers and scanners have many moving parts that can wear out over time
- 21. Preventive Maintenance Techniques (Continued) Printer Maintenance Printers have many moving parts and require more maintenance than
- 22. Preventive Maintenance Techniques (Continued) Scanner Maintenance The scanner surface should be kept clean. If the glass
- 23. Exercise 1 – Identify Component parts Indentify Component Parts
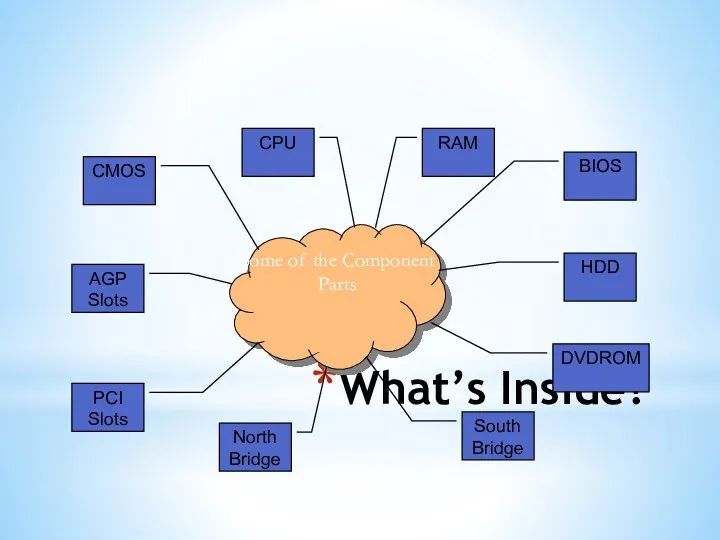
- 24. What’s Inside? Some of the Component Parts RAM HDD DVDROM AGP Slots CMOS BIOS CPU North
- 25. Functional Skills Links English Preparation for Reading Understanding Expressing yourself clearly Maths Reading and expressing numerical
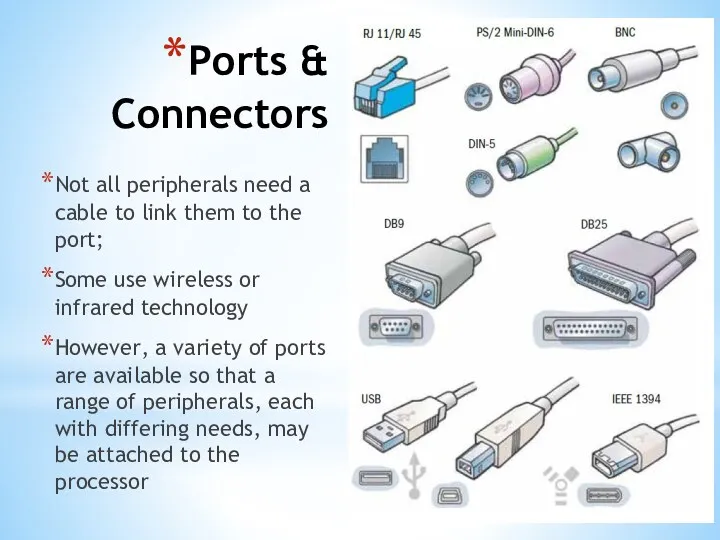
- 26. Ports & Connectors Not all peripherals need a cable to link them to the port; Some
- 27. Ports & Connectors Cont. If cabling is used, the transfer of data to and from the
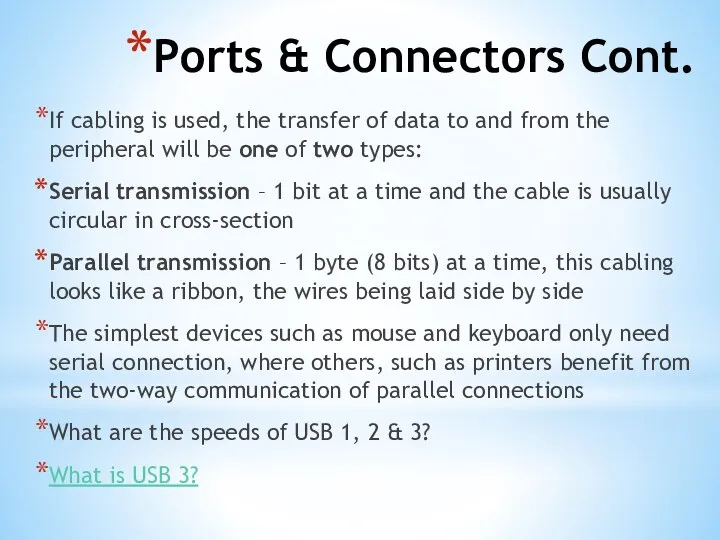
- 28. Serial & Parallel Port The serial and parallel ports on the PC are very different, as
- 29. Serial/Parallel Dictionary Activity Using two Dictionaries…
- 30. Serial & Parallel Connectors
- 31. Parallel & USB USB was designed to make the installation of slow peripherals, such as the
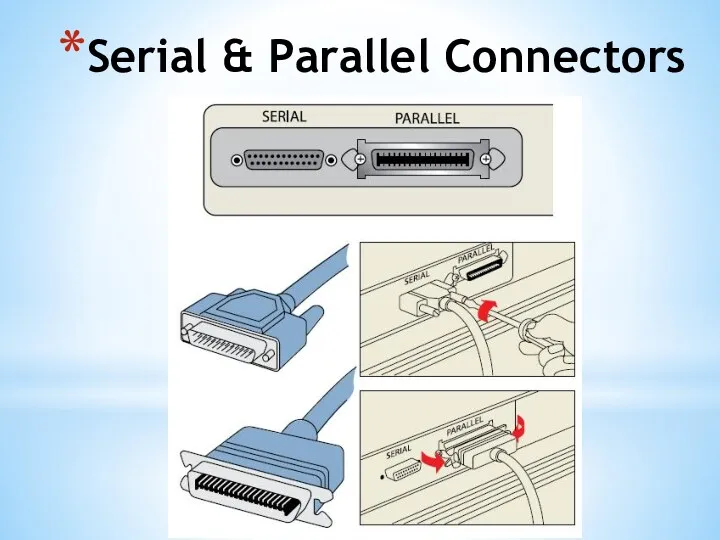
- 32. USB Connections
- 33. USB (Cont.) It is also possible to link the devices in a ‘daisy chain’ so that
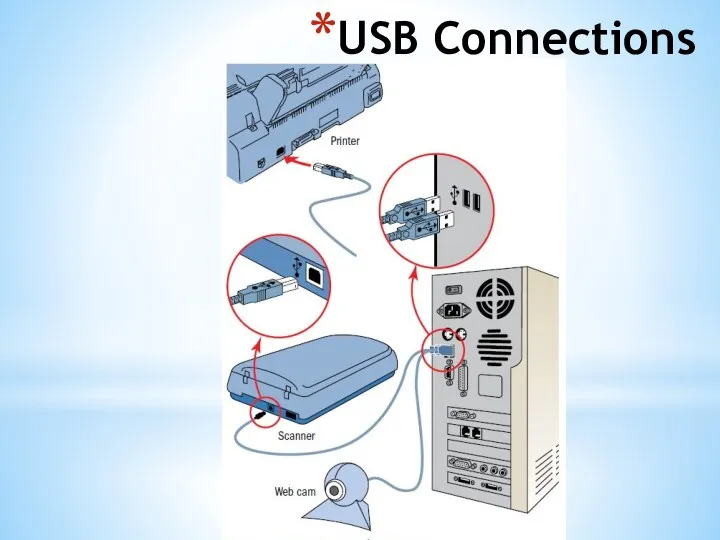
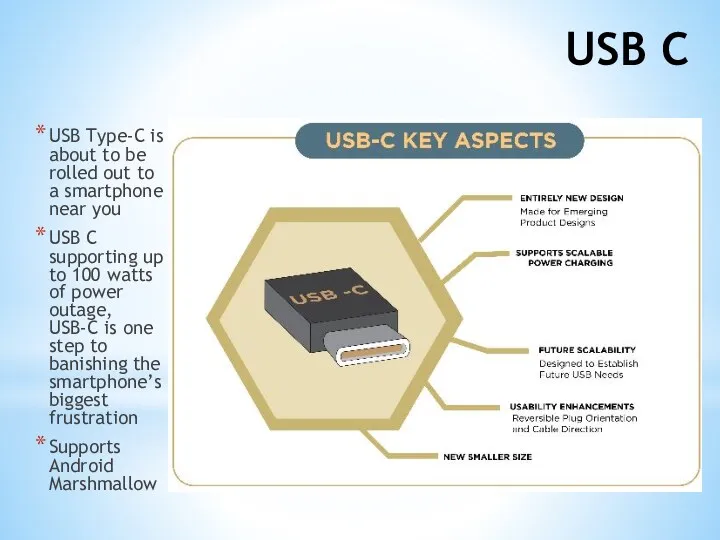
- 34. USB C USB Type-C is about to be rolled out to a smartphone near you USB
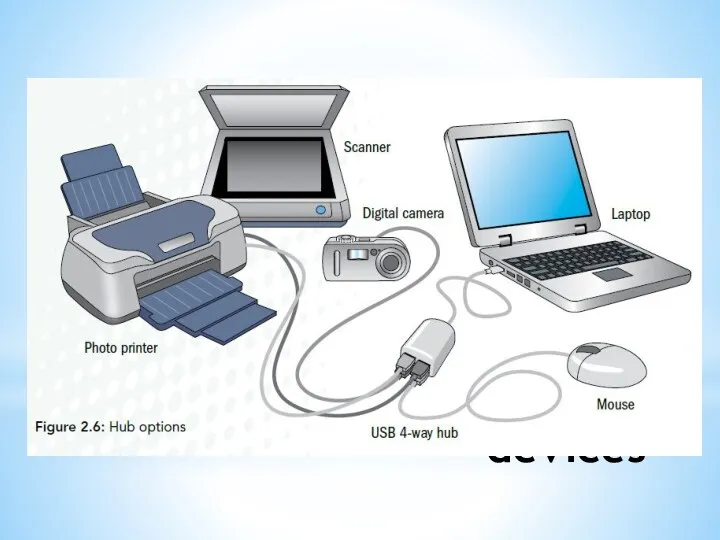
- 35. Daisy chaining devices
- 36. SERIOUS QUESTION!!!?! Why has SATA and USB been adopted over Parallel communications devices such as IDE?
- 37. Output Devices There are many different Output devices but the most commonly used are: Monitors Printers
- 38. Monitors Monitors display the information on a screen. You can get 2 main types of monitors:
- 39. Which Monitor do I need? For anyone who owns a desktop PC, you’re going to need
- 40. Size Let’s begin with size. Depending on exactly what you’ll be using your new monitor for
- 41. Size Cont. Ultimately, you need to consider what you’ll be using your monitor for Perhaps you’re
- 42. Resolution One careful consideration to make, and one which is closely linked to screen size, is
- 43. Refresh Rate Another feature gamers should pay particular attention to is a monitor’s refresh rate which
- 44. Response Time Response time concerns the amount of time (measure in milliseconds) it takes the pixels
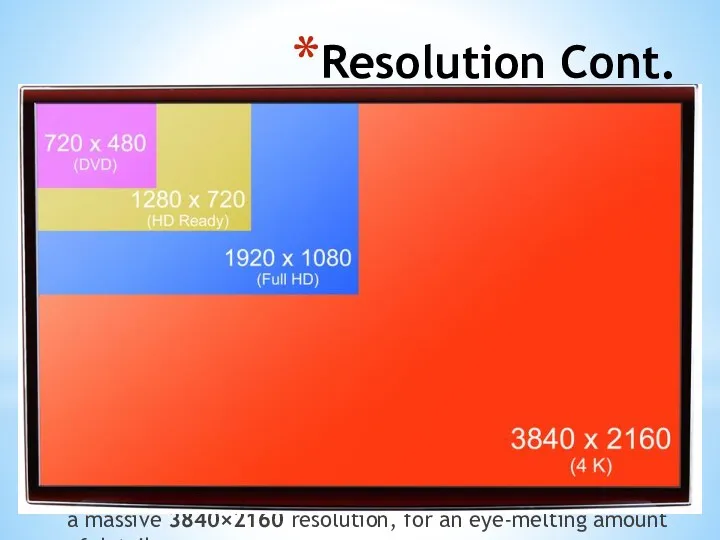
- 45. Resolution Cont. As you rise up the ladder of monitor sizes, resolutions will inevitably rise alongside
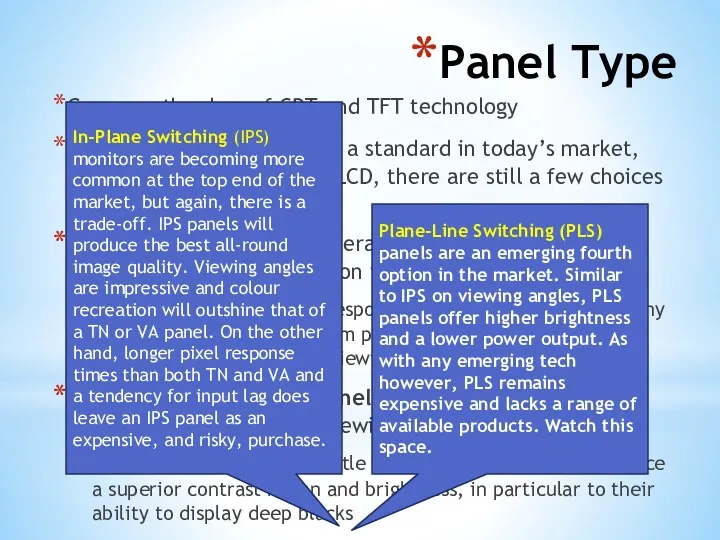
- 46. Panel Type Gone are the days of CRT and TFT technology LCD panels are pretty much
- 47. Gaming Monitors You many have noticed a lot of talk of response times and refresh rates
- 48. Gaming Monitors For a gamer then, it’s vital to enhancing their gameplay As such, a response
- 49. Connections Your final major consideration revolves around connections and ports HDMI has grown into the most
- 50. Connections DisplayPort connections are becoming increasingly popular, but are generally limited to a computer connection Capable
- 51. Connections Some newer monitors are opting for DVI connection, often alongside HDMI. Again, if this is
- 52. Price As computing technology moves ever forward, components such as monitors will continue to fall in
- 53. Printers There are 3 types of Printers: Dot Matrix : This printer is the oldest of
- 54. Plotters These devices produce high quality lines diagrams on paper. (Architects, Engineers and Scientist often use
- 55. Speakers / Headphones There is usually a small speaker within the computer however to increase the
- 56. Backing storage Primary storage, located within the computer, is relatively small and the majority of it
- 57. Backing Storage
- 58. Portable and fixed drives In the design of early computers, the drives (i.e. The readers) were
- 59. Key terms Primary storage – the memory of the computer Secondary storage – a backing store
- 61. Скачать презентацию











































 Создание своего мини-бота в python
Создание своего мини-бота в python Подання графічних даних. Адитивні та субтрактивні кольори в комп'ютерній графіці
Подання графічних даних. Адитивні та субтрактивні кольори в комп'ютерній графіці Программы и программное обеспечение
Программы и программное обеспечение Информационное общество
Информационное общество Сегменты информационного бизнеса
Сегменты информационного бизнеса Основные понятия и задачи моделирования процессов и систем
Основные понятия и задачи моделирования процессов и систем Екологія програмного забезпечення
Екологія програмного забезпечення Топологический анализ защищенности
Топологический анализ защищенности Компьютерная безопасность
Компьютерная безопасность Основы операционных систем
Основы операционных систем Основы алгоритмизации и программирования. Лекция 15. Динамические структуры данных
Основы алгоритмизации и программирования. Лекция 15. Динамические структуры данных Вещественные числа. Стандарт IEEE 754. Команды и регистры математического сопроцессора [MASM]
Вещественные числа. Стандарт IEEE 754. Команды и регистры математического сопроцессора [MASM] История создания электронной почты
История создания электронной почты Условная функция со сложными условиями в EXCEL. 9 класс
Условная функция со сложными условиями в EXCEL. 9 класс История мемов
История мемов Работа со слоями эффектов. (Лекция 2)
Работа со слоями эффектов. (Лекция 2) Защищенные мультисервисные телекоммуникационные системы (полное наименование дисциплины без сокращений)
Защищенные мультисервисные телекоммуникационные системы (полное наименование дисциплины без сокращений) Текстовый процессор Microsoft Word
Текстовый процессор Microsoft Word Системы автоматизированного проектирования и производства
Системы автоматизированного проектирования и производства Робота з файлами. Текстові файли. Лекция 17
Робота з файлами. Текстові файли. Лекция 17 Информационное покрытие НПАО Светогорский ЦБК в СМИ и медиа
Информационное покрытие НПАО Светогорский ЦБК в СМИ и медиа Разработка АРМ менеджера оконного комбината на примере ООО Светоч в среде Delphi 6.0
Разработка АРМ менеджера оконного комбината на примере ООО Светоч в среде Delphi 6.0 Проектирование многотабличной базы данных
Проектирование многотабличной базы данных Автоматизация аптек
Автоматизация аптек Структура и основные виды обеспечения САПР
Структура и основные виды обеспечения САПР Сымcыз интернет: оның ерекшелыіктері
Сымcыз интернет: оның ерекшелыіктері Организация документооборота. Информационно-поисковые справочники
Организация документооборота. Информационно-поисковые справочники История медиа. Теоретические основы исследований медиа
История медиа. Теоретические основы исследований медиа