Calculating the probability of a continuous random variable – Normal Distribution. Week 9 (1) презентация
Содержание
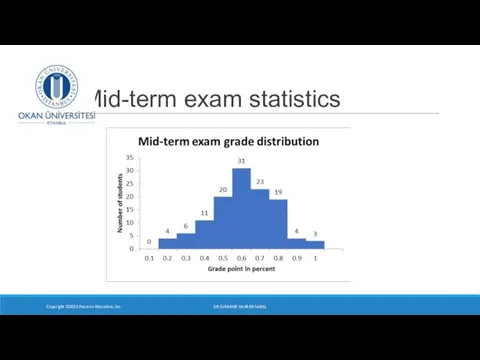
- 2. Mid-term exam statistics Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc. DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL
- 3. Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc. DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL Mid-term exam statistics
- 4. Continuous random variable A continuous random variable can assume any value in an interval on the
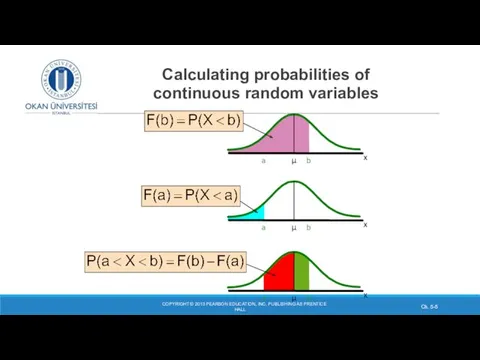
- 5. Calculating probabilities of continuous random variables COPYRIGHT © 2013 PEARSON EDUCATION, INC. PUBLISHING AS PRENTICE HALL
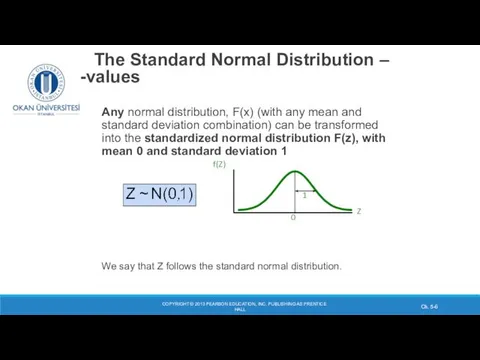
- 6. COPYRIGHT © 2013 PEARSON EDUCATION, INC. PUBLISHING AS PRENTICE HALL Ch. 5- The Standard Normal Distribution
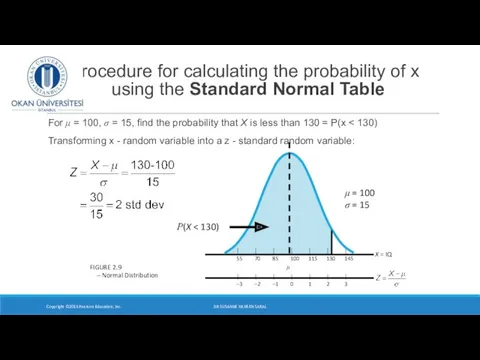
- 7. Procedure for calculating the probability of x using the Standard Normal Table For μ = 100,
- 8. Procedure for calculating the probability of x using the Standard Normal Table (continued) Step 2 Look
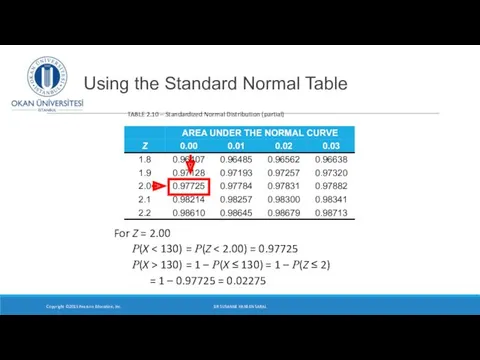
- 9. Using the Standard Normal Table Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc. TABLE 2.10 – Standardized Normal Distribution
- 10. P(z -2) = .9772 In probability terms, a z-score of -2.0 and +2.0 has the same
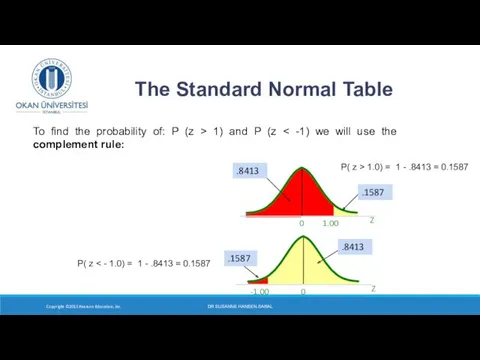
- 11. DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL Z 0 -1.00 Z 0 1.00 .8413 .1587 .8413 .1587 The Standard
- 12. Finding the probability of z-scores with two decimals and graph the probability P ( z P
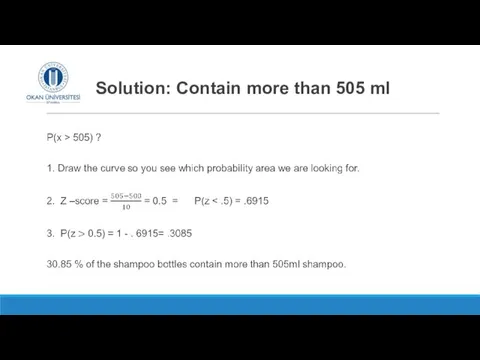
- 13. Determine for shampoo filling machine 1 the proportion of bottles that:
- 15. Solution: Contain more than 505 ml
- 16. P ( z P (z > -1.05 ) = P (z P (z > - 3.34)
- 17. P ( z P (z > -1.05 ) = 0.8531 or 85.31 % P (z P
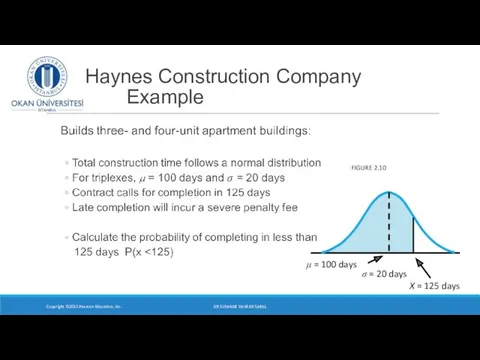
- 18. Haynes Construction Company Example Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc. FIGURE 2.10 DR SUSANNE HANSEN SARAL
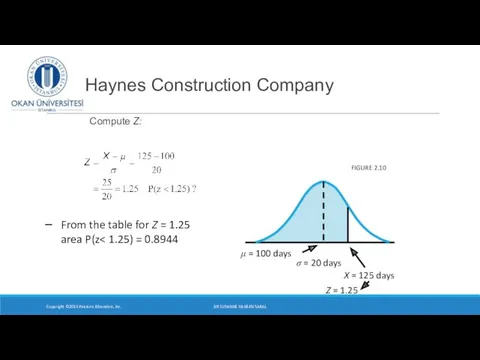
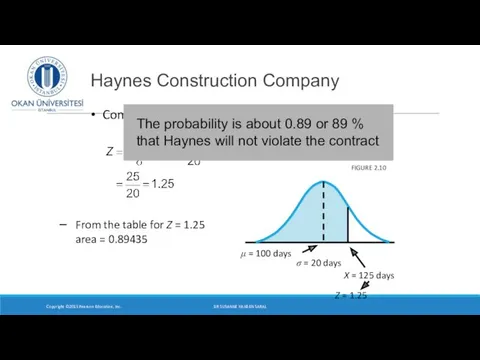
- 19. Haynes Construction Company Compute Z: Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc. FIGURE 2.10 From the table for
- 20. Compute Z Haynes Construction Company Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc. FIGURE 2.10 From the table for
- 21. Haynes Construction Company Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc. FIGURE 2.10 P(z > 1.25) DR SUSANNE HANSEN
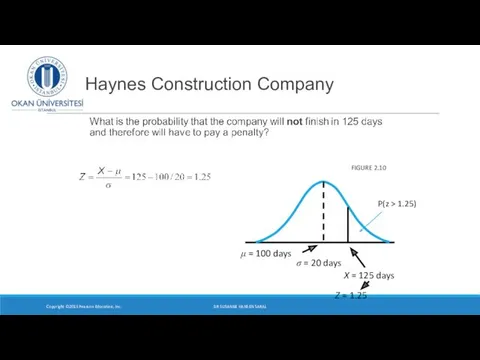
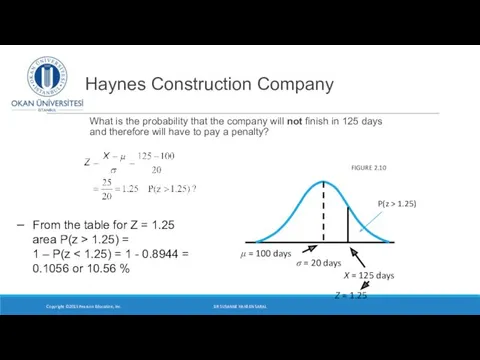
- 22. Haynes Construction Company What is the probability that the company will not finish in 125 days
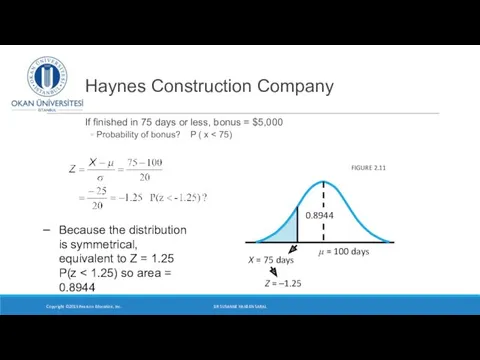
- 23. Haynes Construction Company If finished in 75 days or less, Haynes will get a bonus of
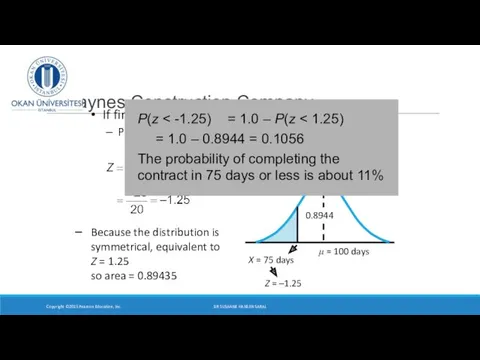
- 24. Haynes Construction Company If finished in 75 days or less, bonus = $5,000 Probability of bonus?
- 25. If finished in 75 days or less, bonus = $5,000 Probability of bonus? Haynes Construction Company
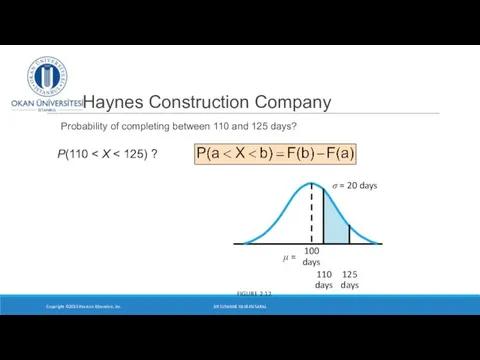
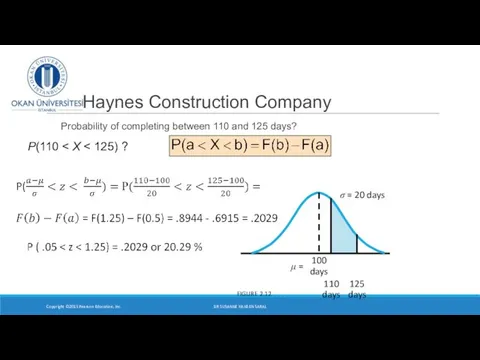
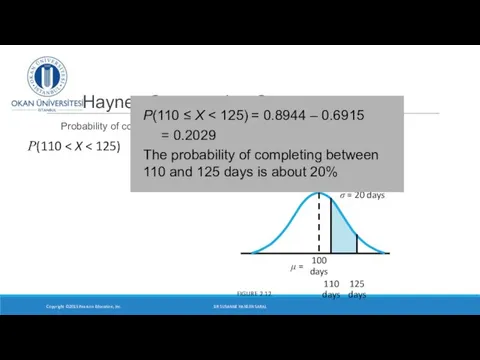
- 26. Haynes Construction Company Probability of completing between 110 and 125 days? Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 27. Haynes Construction Company Probability of completing between 110 and 125 days? Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 28. Haynes Construction Company Probability of completing between 110 and 125 days? Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
- 30. Скачать презентацию










 Действие с многочленами. 7 класс
Действие с многочленами. 7 класс Бесконечно малые, бесконечно большие функции, их свойства. Теоремы о пределе функции, замечательные пределы
Бесконечно малые, бесконечно большие функции, их свойства. Теоремы о пределе функции, замечательные пределы Математическое моделирование автоматических систем регулирования
Математическое моделирование автоматических систем регулирования Задача и алгоритм Прима
Задача и алгоритм Прима Электрорадиоизмерения и метрология. Урок №5. Тема 1.3. Средства измерений
Электрорадиоизмерения и метрология. Урок №5. Тема 1.3. Средства измерений Задача по математике (4 класс)
Задача по математике (4 класс) Задания типа С5
Задания типа С5 Многоугольники. Примеры многоугольников
Многоугольники. Примеры многоугольников Показательная функция, ее свойства и график
Показательная функция, ее свойства и график Графический диктант 6. 5 класс
Графический диктант 6. 5 класс Урок математики во 2 классе Свойства умножения и деления. Площадь прямоугольника
Урок математики во 2 классе Свойства умножения и деления. Площадь прямоугольника Процесс решения задачи, как вид деятельности учащихся
Процесс решения задачи, как вид деятельности учащихся Теория вероятностей
Теория вероятностей Преобразование графиков функций
Преобразование графиков функций Параллельность в пространстве. (Графическая работа 2)
Параллельность в пространстве. (Графическая работа 2) Таралым параметрлерінің физикалық мағынасы
Таралым параметрлерінің физикалық мағынасы Эконометрика. Эконометрическое моделирование
Эконометрика. Эконометрическое моделирование Преобразования. Оконное преобразование Фурье. Области применения и ограничения оконного преобразования Фурье
Преобразования. Оконное преобразование Фурье. Области применения и ограничения оконного преобразования Фурье Тест по теме Сложение и вычитание с поддержкой макроса
Тест по теме Сложение и вычитание с поддержкой макроса Задачи на смекалку
Задачи на смекалку Решение уравнений. 2 класс
Решение уравнений. 2 класс Площадь прямоугольника. Площадь параллелограмма и ромба
Площадь прямоугольника. Площадь параллелограмма и ромба Симметрия. Урок математики для учащихся 4 класса
Симметрия. Урок математики для учащихся 4 класса Правила построения рядов динамики
Правила построения рядов динамики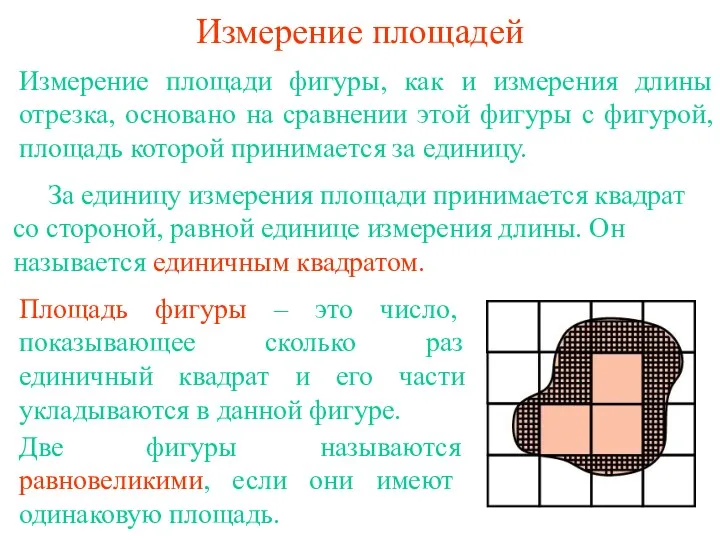 Измерение площадей
Измерение площадей Урок математики в 1 классе по системе Л. В. Занкова Верные и неверные равенства и неравенства
Урок математики в 1 классе по системе Л. В. Занкова Верные и неверные равенства и неравенства Конспект занятия по ФЭМП (+ презентация)
Конспект занятия по ФЭМП (+ презентация) Решение систем уравнений второй степени
Решение систем уравнений второй степени