Содержание
- 2. Decision problems. Multi-criteria problems Basic definitions of decision-making theory Decision Support System (DSS) Lecture 1: Basics
- 3. Course Basics of decision-making theory/ Informatics of DM
- 4. 2 semester
- 7. 1. Decision problems. Multi-criteria problems
- 8. Systems analysis is a problem solving method that decomposes a system into its component pieces for
- 9. Analysis of complex problems – alternatives, subsystems, goal.. Definition of criteria Decomposition of a complex problem
- 10. 1. Additive aggregation Methods of Aggregation of subsystems into one system - decision multi-criteria problems 2.
- 11. Example: Definitions and estimation of the sources of the projects financing Where to take 100 000
- 12. Example 1 Definitions and estimation of the sources of the projects financing (decomposition and aggregation) Example
- 13. 2. Basic definitions of decision-making theory Decision-making - a goal-oriented choice of the one alternative from
- 14. Maine properties of systems: Emergence - the appearance of the property not previously observed as a
- 15. Decision-making theory answers questions: where decisions are made - man-machine systems (pilot – aircraft, air traffic
- 16. Decision-making stages: perception of information identification of information decision-making action
- 17. OODA Model
- 18. Decision Support System (DSS) is a computerized system designed to help a user make decisions Database
- 19. James Reason model - mistakes Human Factors (HF) problem. Evolution of HFs Models. SHELL model Socio-technical
- 20. Evolution of HFs Models. Socio-technical systems - “Large-scale, high-technology systems such as nuclear power generation and
- 21. Evolution Human factor's models
- 22. The synergetic effect - LS of aviation technique with using AI capability AI White Paper /
- 23. The synergetic effect: analysis of problem (DM) and synthesis of problem (AI) Analysis (DM) – integrated
- 24. Books about DM of H-O in ANS: DM of ATC; pilot of AC/ UAV; engineer; flight
- 25. Types of system Classification of methods of decision-making Expert Judgment Method (main steps of Method). Matrix
- 26. Research methods - Analysis and synthesis of aviation ergatic system (man-machine system), for example, pilot –
- 27. Using optimization methods we choose from many alternatives to one alternative. Optimization problem must have goal
- 28. APPLICATIONS - systems Ergatic (man-machine system) system Artificial Intelligence АІS Decision support system Expert Systems
- 29. 2. Classification of Decision Making Methods – 3D - Classification It is known a lot of
- 30. Extent of dynamics – Axis y At point O, we have methods for solving one-step decision-making
- 31. According with the variables types, constraints and objective function type there are following main methods: Decision
- 32. 3. Expert Judgment Method The main steps of Expert Judgment Method
- 33. Examples. Matrix of individual preferences Number of expert, m≥30 Example 1: Estimation of the sources of
- 34. Matrix 3. To determine the significance (complexity) of the phases of flight of the aircraft Take-off
- 35. Algorithm of Expert Judgment Method
- 36. Algorithm of Expert Judgment Method Example of Expert Judgment Method. Lecture 3: ”Algorithm of Expert Judgment
- 37. Algorithm of Expert Judgment Method
- 40. 9. Weight coefficients 10. Graph
- 41. 2. Example N1 of using Expert Judgment Method. Definition the difficulty of procedures of ATCO for
- 42. 2.Matrix of group preferences - if variation is less than υ ≤ 33% - opinion of
- 43. 3 Definition of Kendal’s coordination coefficient
- 44. 4 Correlation coefficient of Spirman rs 0 ≤ rs ≤ 1 Our result is 0.934. So,
- 45. The significance of the calculations: Significance W , for using criterion - χ2
- 46. Significance Rs , for using Student's t – criterion
- 47. Algorithm of Definition the weight coefficients Definition of ATCO’s loads for using weight coefficients Lecture 4:
- 48. 1. Definition the weight coefficients / Multi-criteria decision problems
- 49. Task. Definition of importance coefficient workloads for a controller’s on Tower ω1 - Take-off; ω2 Landing;
- 51. 2 method Estimates Cj are determining by helping experts, from 1 to 0, descending importance rank
- 52. References John Boyd. Organic Design for Command and Control, 2003 Юзеф Козелецкий Психологическая теория принятия решений,
- 53. Books about DM of H-O in ANS: DM of ATC; pilot of AC/ UAV; engineer; flight
- 54. Homework: Choose a multi-criteria problems: Remark: Choosing a telecommunication system Choosing a product marketing strategy Choosing
- 55. Individual research work (RW) for course IDM. Application EJM for building “Expert system”
- 56. Examples (results – weights coefficients of subsystems):
- 58. INDIVIDUAL WORK by Rodrigo Pillajo
- 60. Скачать презентацию
 Решение уравнений. Алгоритм решения уравнений
Решение уравнений. Алгоритм решения уравнений Векторы. Модуль вектора. Равенство векторов. Сложение векторов
Векторы. Модуль вектора. Равенство векторов. Сложение векторов Математический конкурс-викторина
Математический конкурс-викторина Приёмы письменного вычитания в пределах 1000
Приёмы письменного вычитания в пределах 1000 Площади простых фигур. Автор учебника: Атанасян Л.С. 8 класс
Площади простых фигур. Автор учебника: Атанасян Л.С. 8 класс Компланарные векторы
Компланарные векторы Геометрия части В
Геометрия части В Закрепление пройденного материала
Закрепление пройденного материала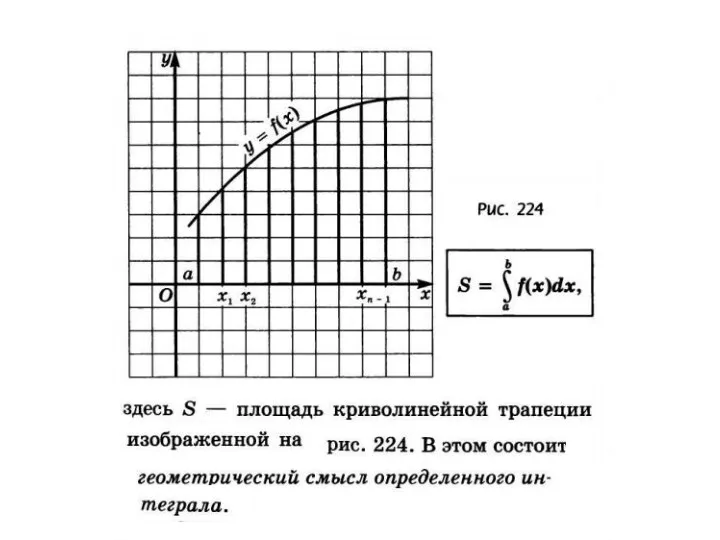 Применение интеграла
Применение интеграла Соотношение единиц площади.
Соотношение единиц площади. Деление трехзначного числа на однозначное. 4 класс
Деление трехзначного числа на однозначное. 4 класс Объемы прямой призмы и цилиндра
Объемы прямой призмы и цилиндра Множества. Эквивалентные множества
Множества. Эквивалентные множества Сложение и вычитание дробей с разными знаменателями
Сложение и вычитание дробей с разными знаменателями How many ways are there to tile a rectangle with polyominoes?
How many ways are there to tile a rectangle with polyominoes? Математичне моделювання. Епідермальне загоєння ран
Математичне моделювання. Епідермальне загоєння ран Аксиомы стереометрии, следствия из аксиом. Урок № 1
Аксиомы стереометрии, следствия из аксиом. Урок № 1 Интерактивный тест по математике Задачи на приведениее к единице, 3 класс. Диск
Интерактивный тест по математике Задачи на приведениее к единице, 3 класс. Диск Розв’язання систем лінійних алгебраїчних рівнянь
Розв’язання систем лінійних алгебраїчних рівнянь Архимедовы тела
Архимедовы тела Единая система обозначений для маркировки автомобильных шин
Единая система обозначений для маркировки автомобильных шин Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей. 5 класс
Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей. 5 класс Призма. Виды призм
Призма. Виды призм Ikkinchi, uchinchi tartibli determinantlar va ularning xossalari. Laplas teoremasi. Teskari Matrisa
Ikkinchi, uchinchi tartibli determinantlar va ularning xossalari. Laplas teoremasi. Teskari Matrisa Случаи вычитания 12 -
Случаи вычитания 12 - Изучение многозначных чисел в начальной школе
Изучение многозначных чисел в начальной школе Математика, русский язык
Математика, русский язык Понятие обратной функции. Определение обратных тригонометрических функций
Понятие обратной функции. Определение обратных тригонометрических функций