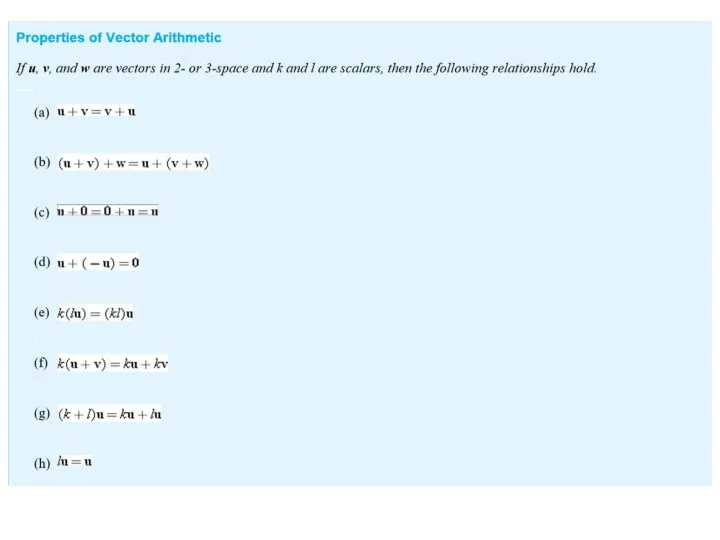
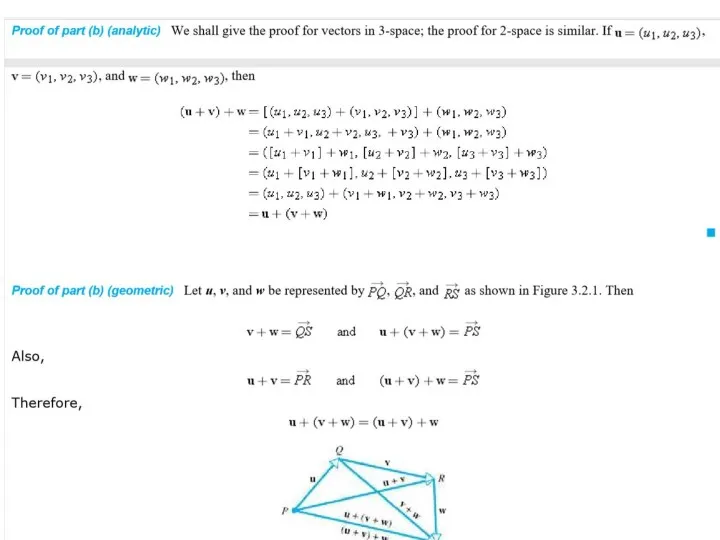
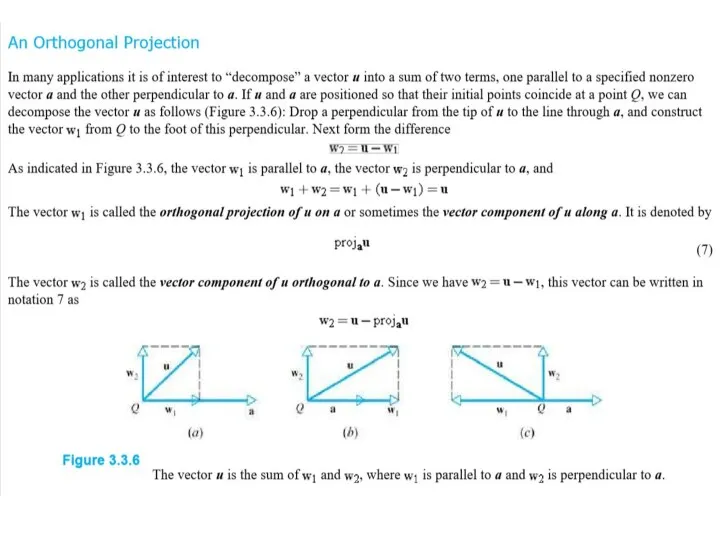
Содержание
- 2. What are Vectors? Vectors are pairs of a direction and a magnitude. We usually represent a
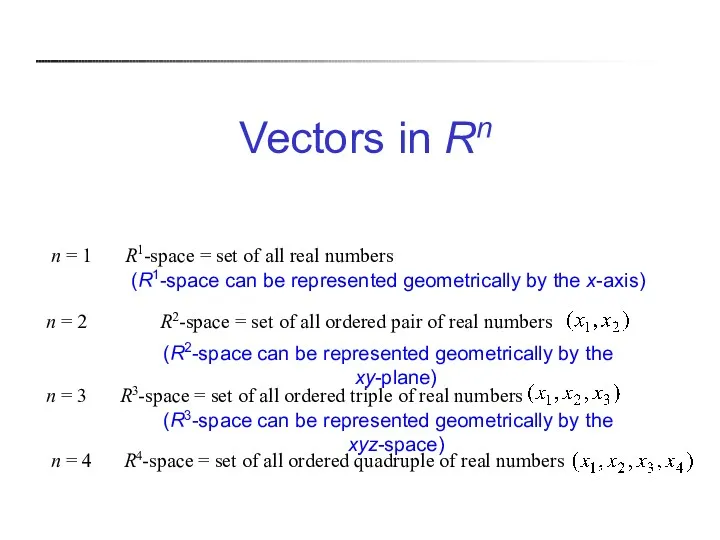
- 3. Vectors in Rn (R1-space can be represented geometrically by the x-axis) (R2-space can be represented geometrically
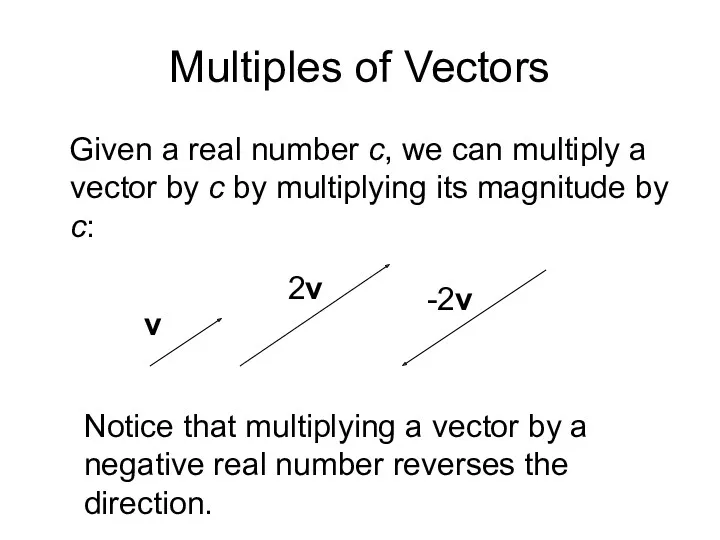
- 4. Multiples of Vectors Given a real number c, we can multiply a vector by c by
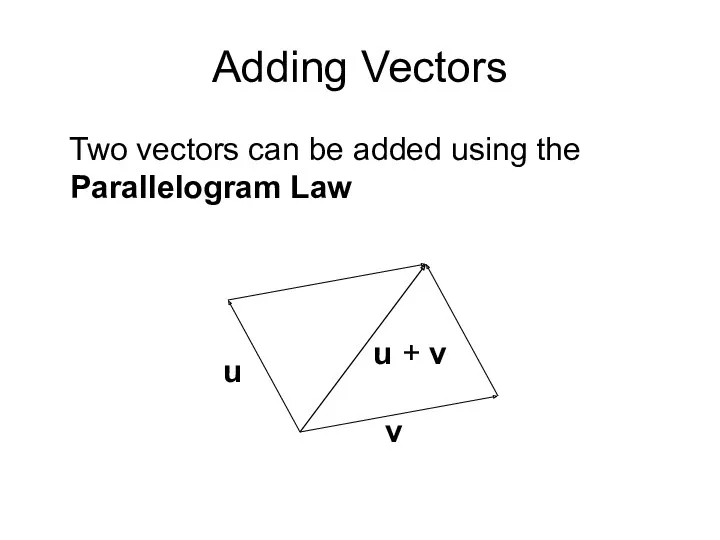
- 5. Adding Vectors Two vectors can be added using the Parallelogram Law u v u + v
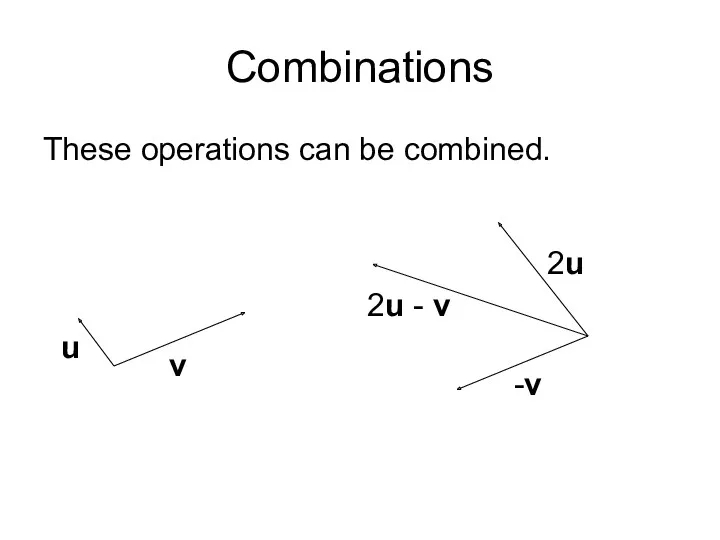
- 6. Combinations These operations can be combined. u v 2u -v 2u - v
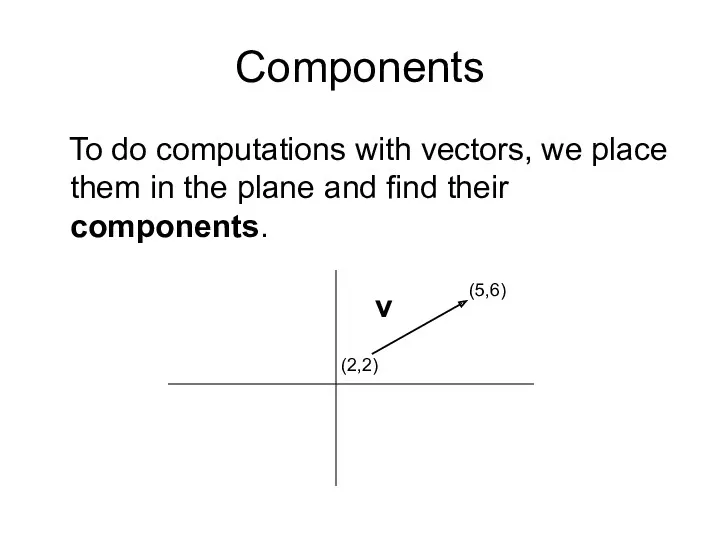
- 7. Components To do computations with vectors, we place them in the plane and find their components.
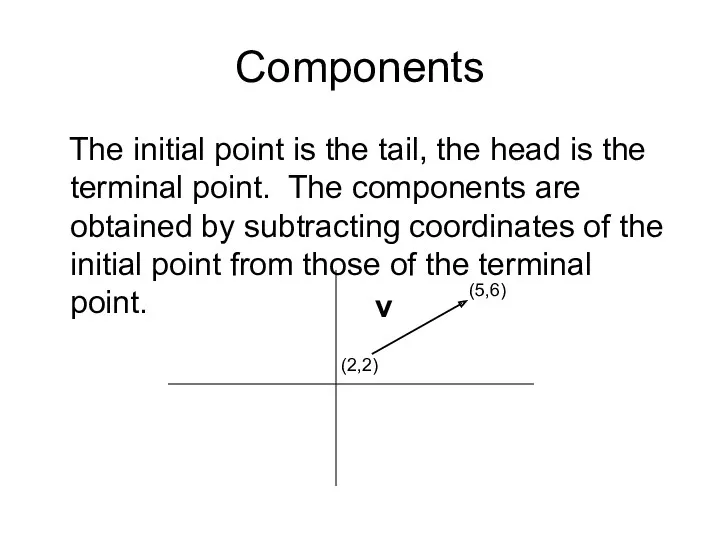
- 8. Components The initial point is the tail, the head is the terminal point. The components are
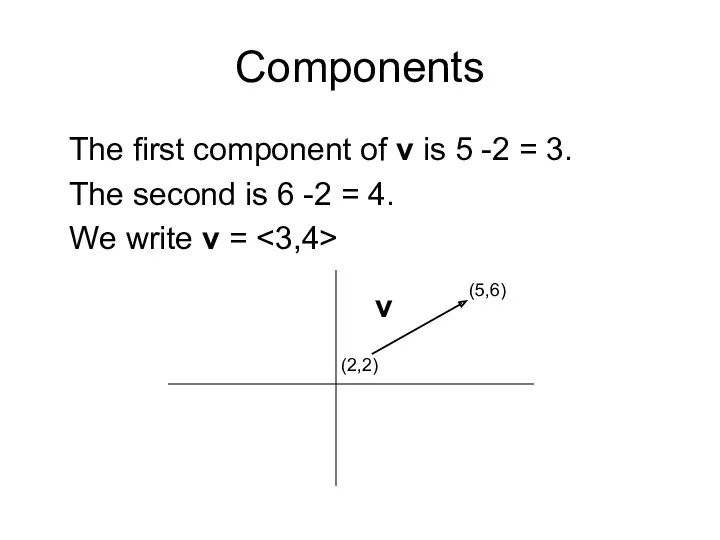
- 9. Components The first component of v is 5 -2 = 3. The second is 6 -2
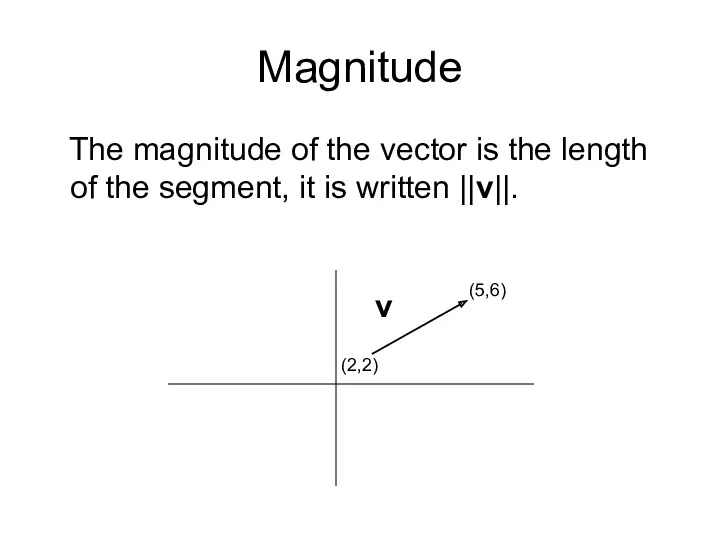
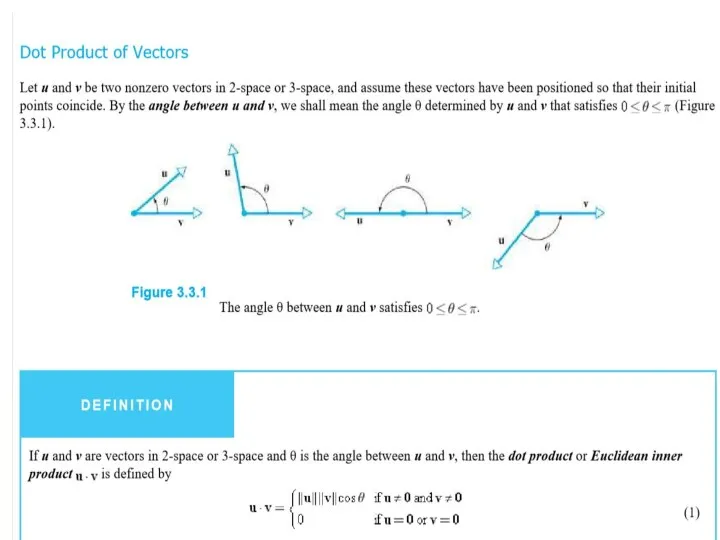
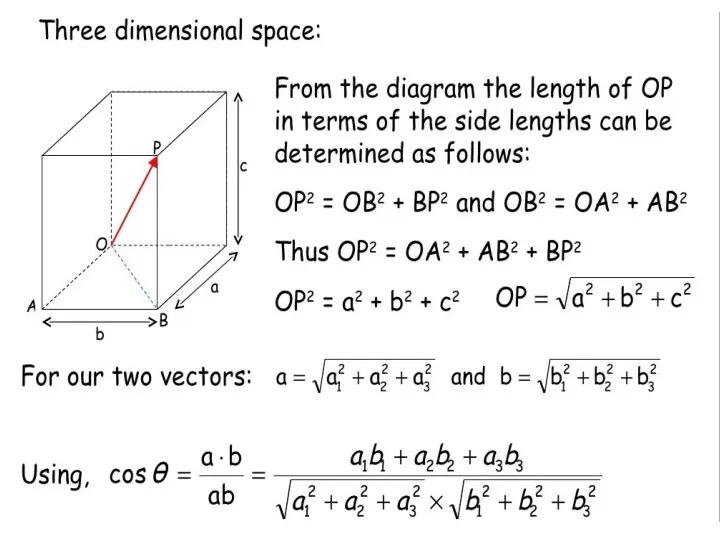
- 10. Magnitude The magnitude of the vector is the length of the segment, it is written ||v||.
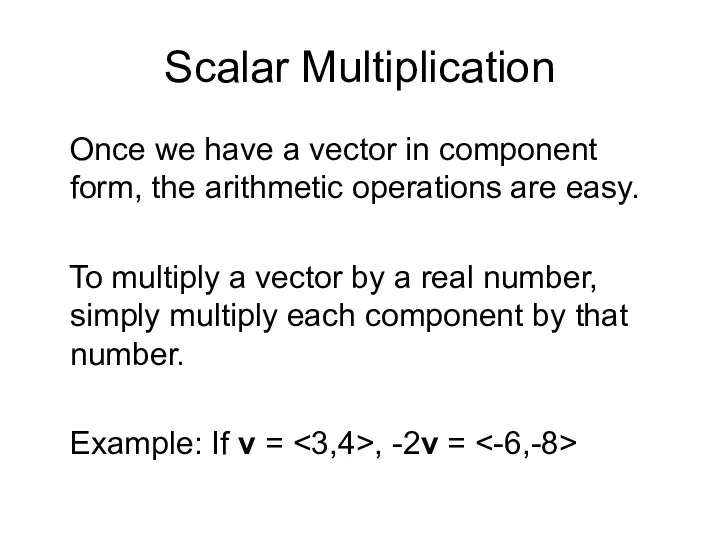
- 11. Scalar Multiplication Once we have a vector in component form, the arithmetic operations are easy. To
- 12. Addition To add vectors, simply add their components. For example, if v = and w =
- 13. Unit Vectors A unit vector is a vector with magnitude 1. Given a vector v, we
- 14. Special Unit Vectors A vector such as can be written as 3 + 4 . For
- 24. Скачать презентацию






 Умножение целых чисел
Умножение целых чисел Разность квадратов
Разность квадратов Прямоугольный параллелепипед
Прямоугольный параллелепипед Фигуры вращения
Фигуры вращения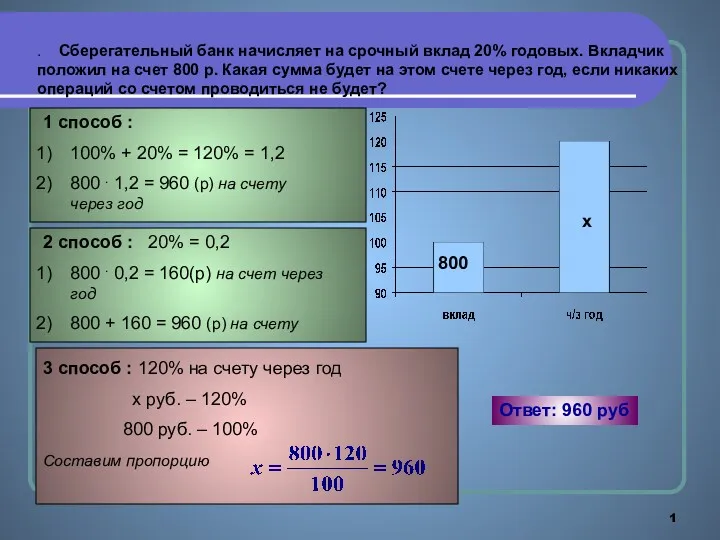 Задачи на проценты
Задачи на проценты Умножение положительных и отрицательных чисел. 6 класс
Умножение положительных и отрицательных чисел. 6 класс Арифметическая прогрессия. 9 класс
Арифметическая прогрессия. 9 класс Подготовка к ЕГЭ (решение заданий С2,С4)
Подготовка к ЕГЭ (решение заданий С2,С4) Презентация по теме: Многоугольники 2 класс.( Программа Начальная школа XXI века)
Презентация по теме: Многоугольники 2 класс.( Программа Начальная школа XXI века) Спортивная метрология, как учебная дисциплина. Основы теории спортивных измерений
Спортивная метрология, как учебная дисциплина. Основы теории спортивных измерений Вектор ұғымы
Вектор ұғымы Законы распределения случайных величин. (Лекция 5)
Законы распределения случайных величин. (Лекция 5) Единица длины - дициметр
Единица длины - дициметр Нахождение дроби от числа
Нахождение дроби от числа Умножение и деление. Задачи на движение
Умножение и деление. Задачи на движение Решение дробно-рациональных неравенств методом интервалов
Решение дробно-рациональных неравенств методом интервалов Дискретная математика. Теория множеств
Дискретная математика. Теория множеств Закрепление по теме Прибавить и вычесть 2
Закрепление по теме Прибавить и вычесть 2 Равнобедренный треугольник и его свойства
Равнобедренный треугольник и его свойства Измерительные работы на местности. Творческое название: Геометрия на свежем воздухе
Измерительные работы на местности. Творческое название: Геометрия на свежем воздухе Презентация по математике Квадратные уравнения
Презентация по математике Квадратные уравнения Элементы математической статистики
Элементы математической статистики Методики выполнения измерений, как основа метрологического обеспечения
Методики выполнения измерений, как основа метрологического обеспечения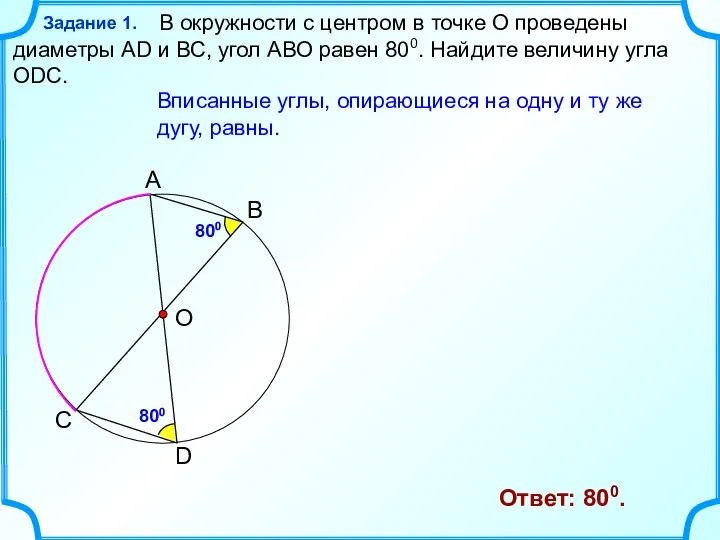 Дуги. Хорды. Углы
Дуги. Хорды. Углы Закрепление знаний, умений и навыков решения задач на проценты
Закрепление знаний, умений и навыков решения задач на проценты Упрощение выражений (5 класс)
Упрощение выражений (5 класс) Конспект урока по математике по теме: Таблица умножения. Закрепление
Конспект урока по математике по теме: Таблица умножения. Закрепление Системы линейных уравнений. Основные понятия
Системы линейных уравнений. Основные понятия