Содержание
- 3. MATH & ALGEBRA
- 4. VECTOR
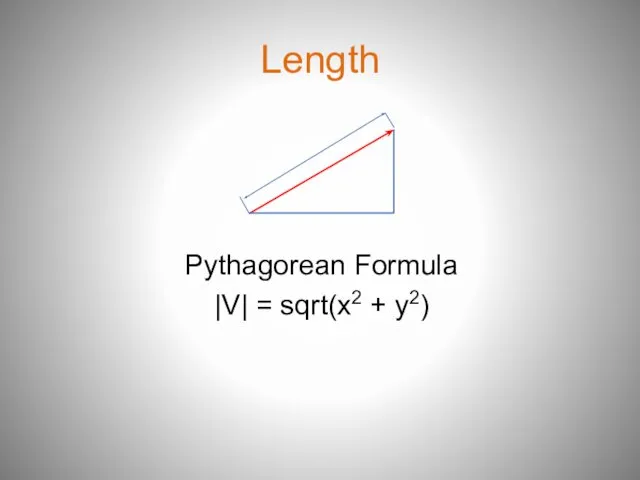
- 5. Length Pythagorean Formula |V| = sqrt(x2 + y2)
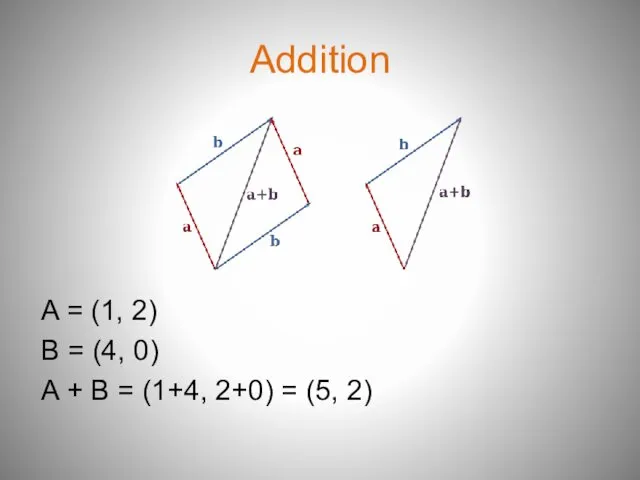
- 6. Addition A = (1, 2) B = (4, 0) A + B = (1+4, 2+0) =
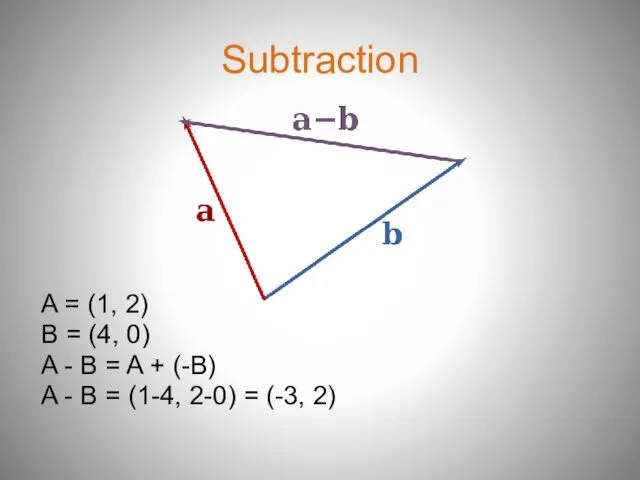
- 7. Subtraction A = (1, 2) B = (4, 0) A - B = A + (-B)
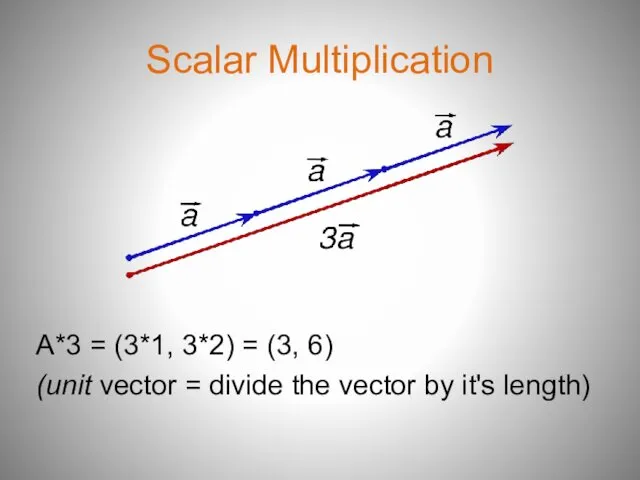
- 8. Scalar Multiplication A*3 = (3*1, 3*2) = (3, 6) (unit vector = divide the vector by
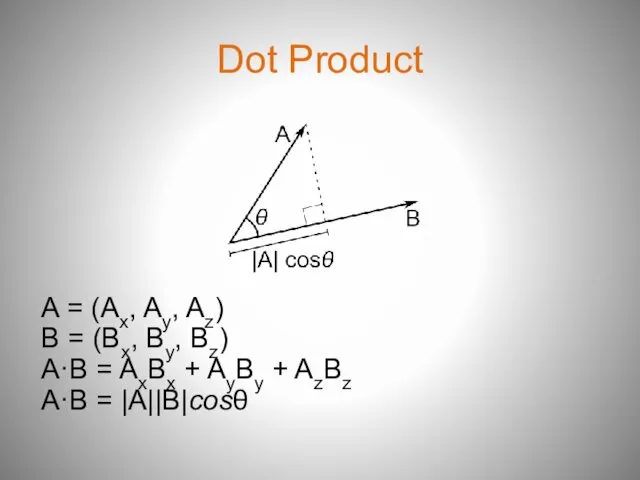
- 9. Dot Product A = (Ax, Ay, Az) B = (Bx, By, Bz) A·B = AxBx +
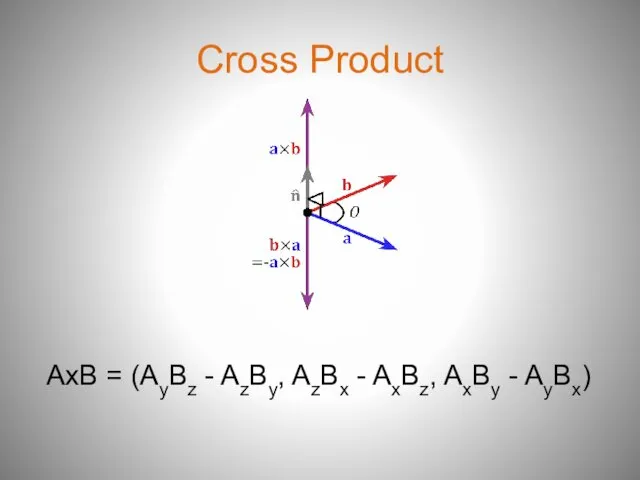
- 10. Cross Product AxB = (AyBz - AzBy, AzBx - AxBz, AxBy - AyBx)
- 11. Real world examples In which direction should the missile be fired to hit the target? Is
- 12. Solutions Solutions have been done by many before. Know the basics to find them quicker. Use
- 13. SPACES
- 14. Spaces Euclidean space using Cartesian coordinates. (X, Y and Z) Local/Model Space World Space View/Camera Space
- 15. Left- and right-handed systems
- 16. MATRICES AND SPACES ENTER THE MATRIX
- 17. Matrices Matrix = Transformation placeholder So again: Local/Model matrix World matrix View/Camera matrix WVP = world
- 18. Classes/Utils Matrix3D Matrix3DUtils Matrix4x4
- 19. TRANSFORMATIONS
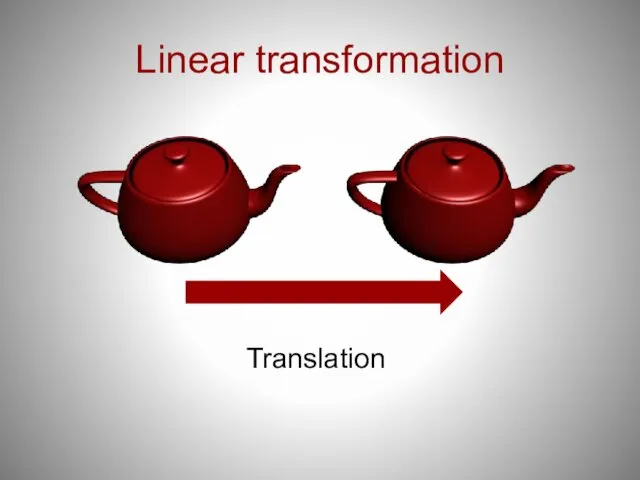
- 20. Linear transformation Translation
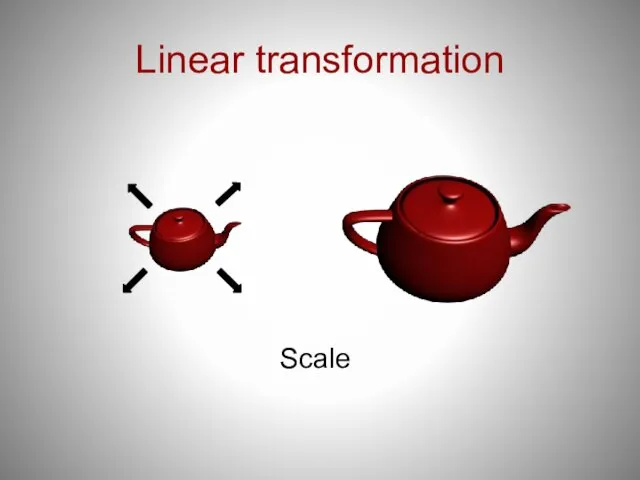
- 21. Linear transformation Scale
- 22. Linear transformation Skew
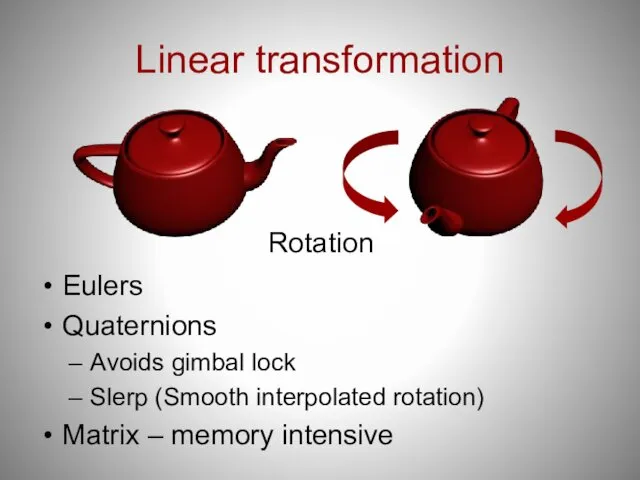
- 23. Linear transformation Eulers Quaternions Avoids gimbal lock Slerp (Smooth interpolated rotation) Matrix – memory intensive Rotation
- 24. Multi linear transformation Stack of matrices Apply all at once to an object The order is
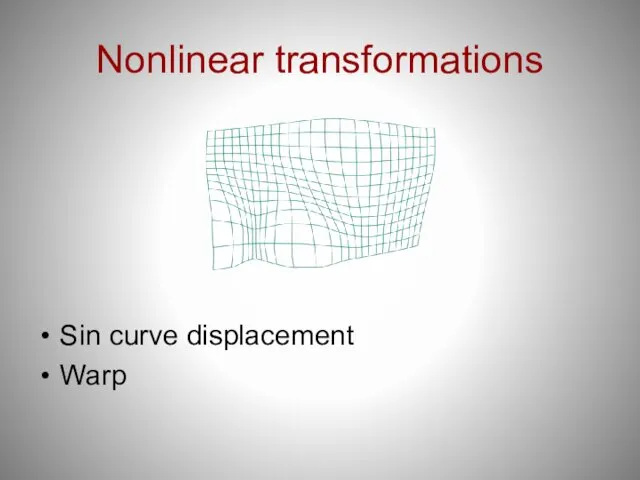
- 25. Nonlinear transformations Sin curve displacement Warp
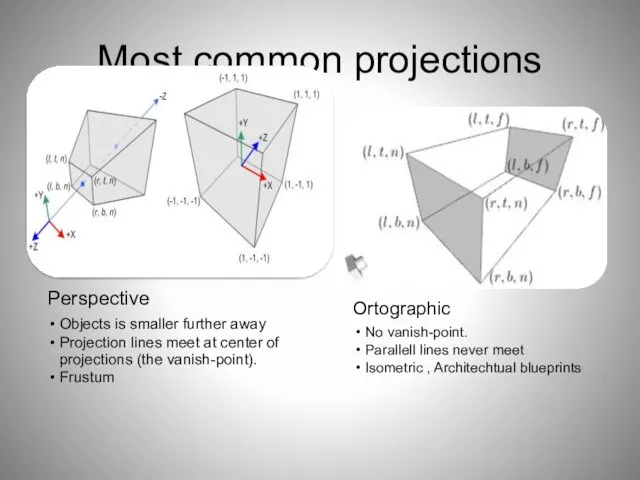
- 26. PROJECTIONS Converting a three-dimensional graphics object or scene into two dimensions
- 27. Most common projections
- 28. GRAPHICS PIPELINE
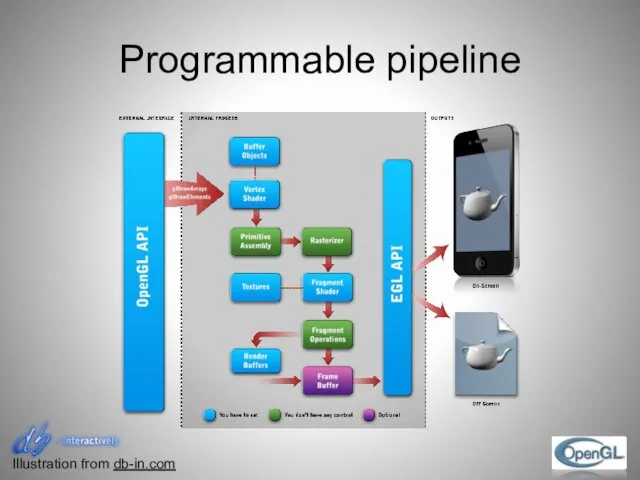
- 29. Programmable pipeline Illustration from db-in.com
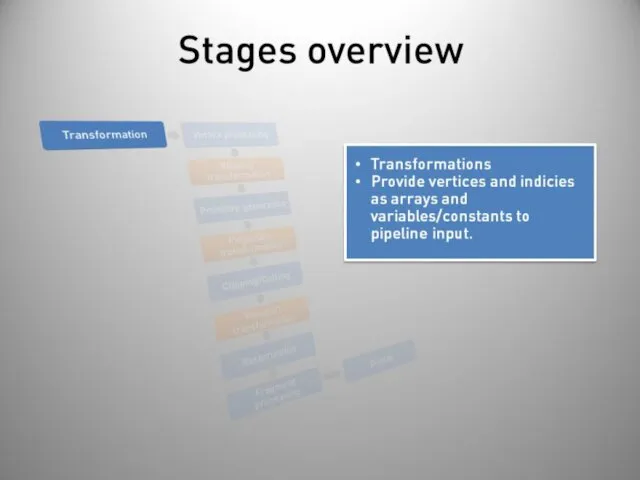
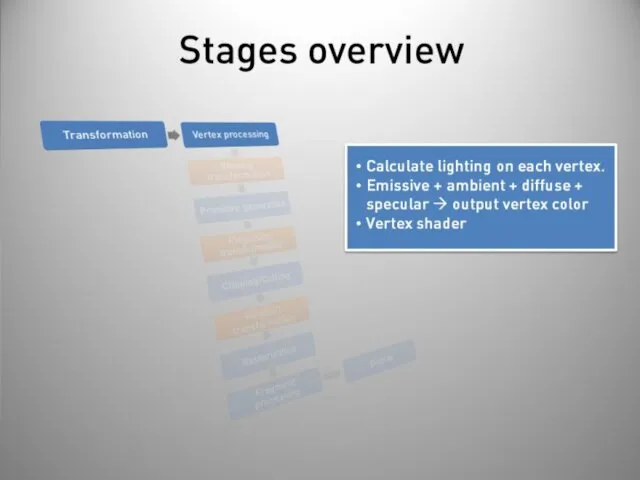
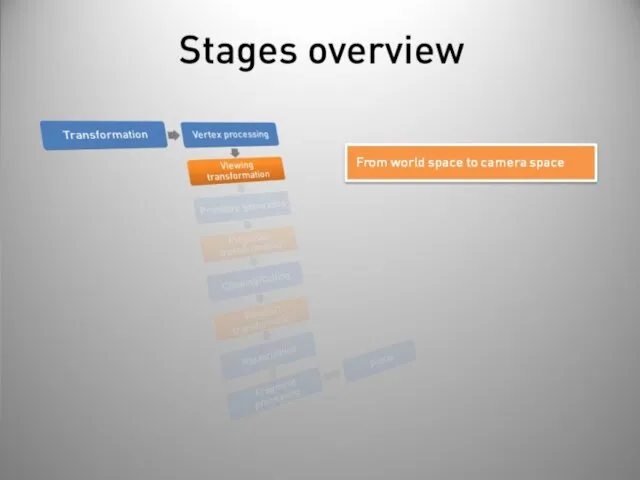
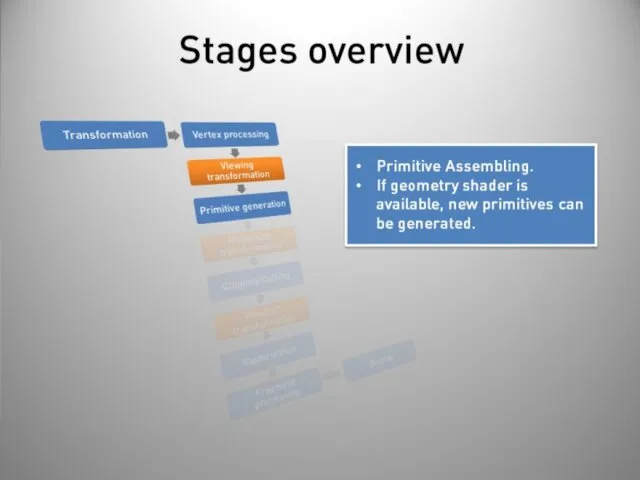
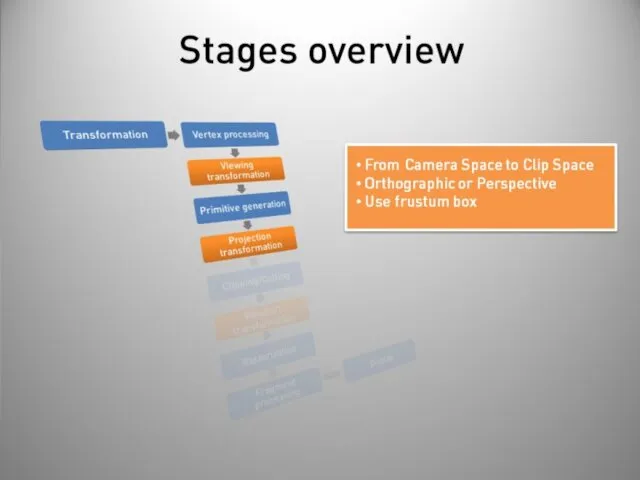
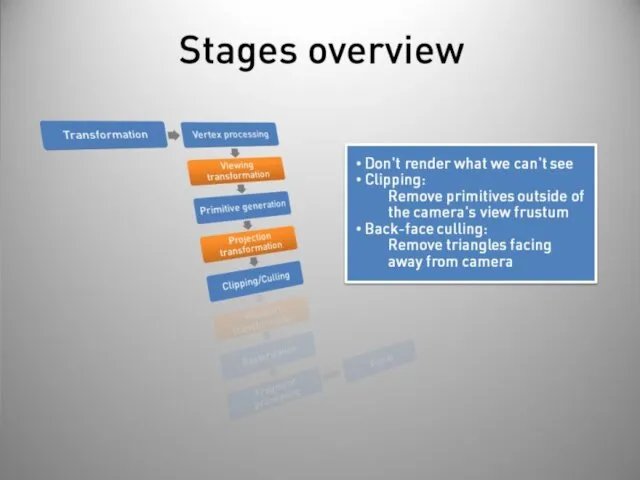
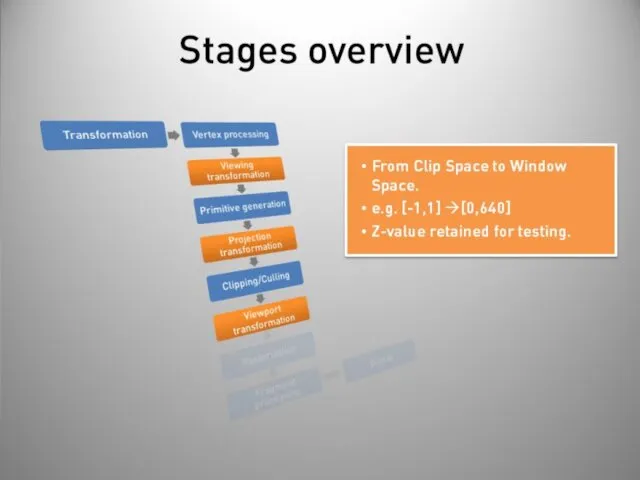
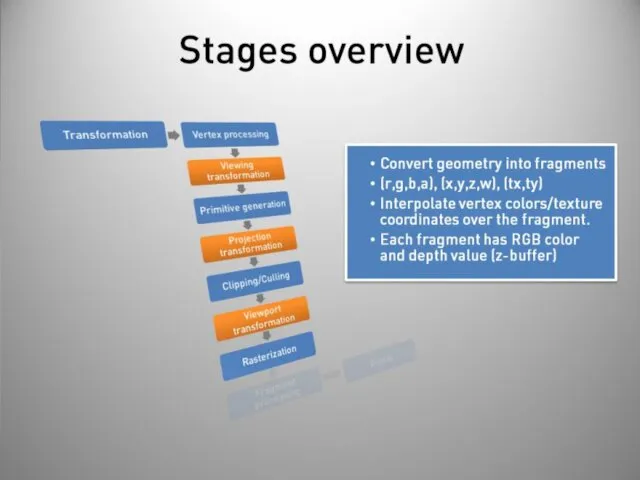
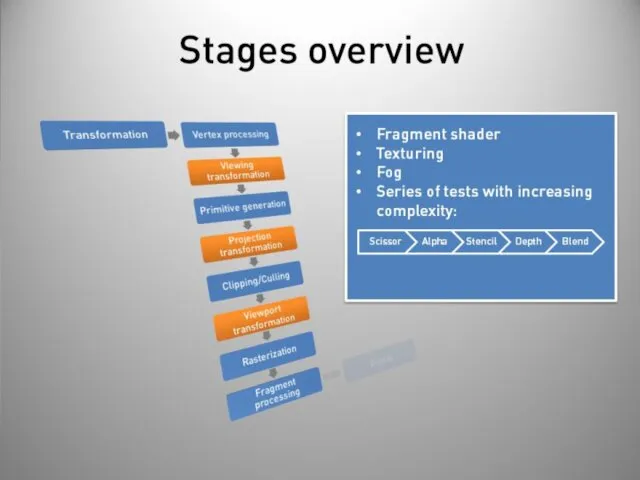
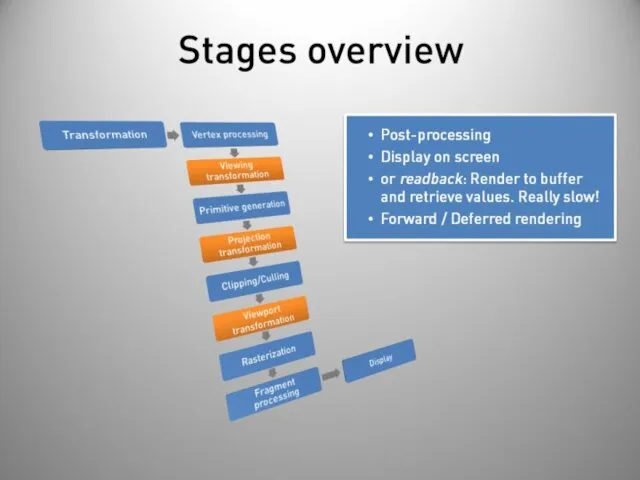
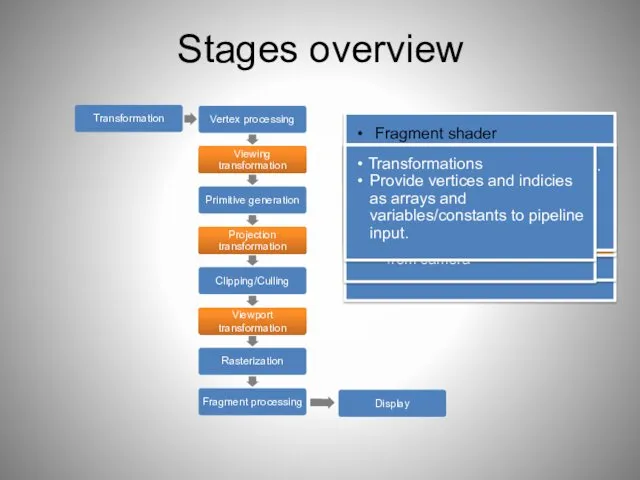
- 40. Stages overview Post-processing Display on screen or readback: Render to buffer and retrieve values. Really slow!
- 41. SHADERS The method to render an object.
- 42. About shaders Small programs that runs on the GPU. Most shader languages are the same. Vertex
- 43. Low level shading language Assembly language ARB (GPU) AGAL (Adobe Graphics Assembly Language) !!ARBfp1.0 TEMP color;
- 44. High level shading languages HLSL – DirectX API Cg – NVIDIA GLSL – OpenGL ShaderLab –
- 45. Vertex shader VS or VSH Executed at each vertex Transform between coordinate systems Lighting Defines the
- 46. Geometry Shader Dynamic creation of geometry on the GPU Only Shader Model 4.0 Direct3D 10, OpenGL
- 47. Fragment Shader FSH Processed at each visible fragment Fragment != Pixel Handles bump effects, shadows and
- 48. Texture objects Texels Power of Two (POT) 2, 4,…512, 1024 pixels Flipped pixel order (OpenGL) Integer/Floating-point
- 49. Texture Filtering Fixing artifacts Texture magnification/minification Mipmapping Different techniques:
- 50. Let’s have a look at the WegGL implementation (click on image) three.js
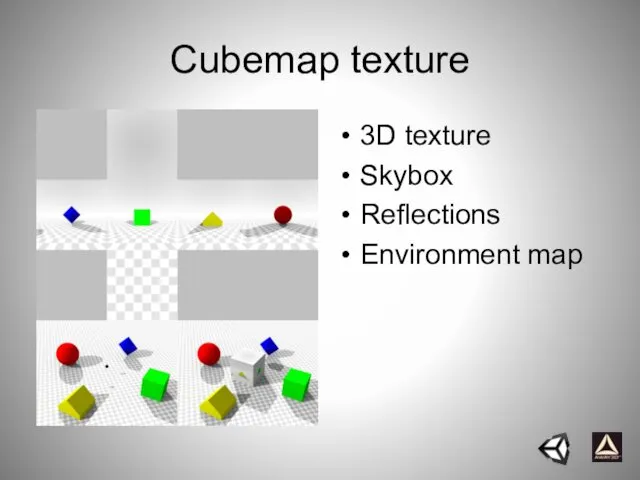
- 51. Cubemap texture 3D texture Skybox Reflections Environment map
- 52. Shader tool examples Shader Toy – WebGL MeShade – WebGL PixelBender3D – Molehill Node Based Shader
- 53. Interior mapping
- 54. Animations, Skin and Bones Tweens Animation controllers Blending Mixing/Additive Vertex animations in shader Procedurally animating
- 55. Animations in Away3D Broomstick
- 56. Materials Material is the collection of properties applied to an object. Shaders is the implemention. ”The
- 57. Some ingredients: Color Diffuse: base color Ambient: color of ambient light (shadowed parts). Mostly the same
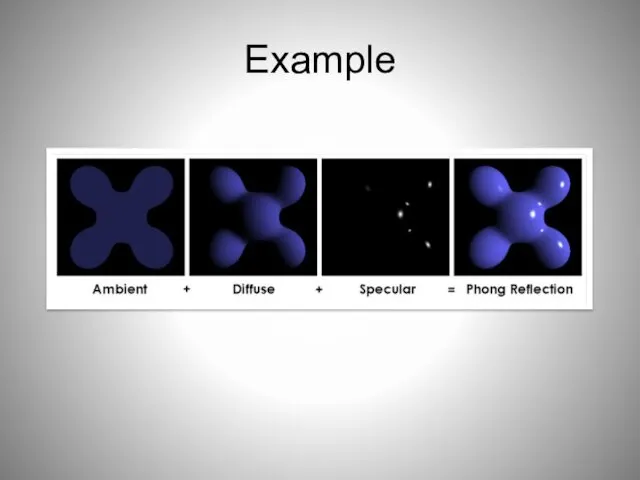
- 58. Example
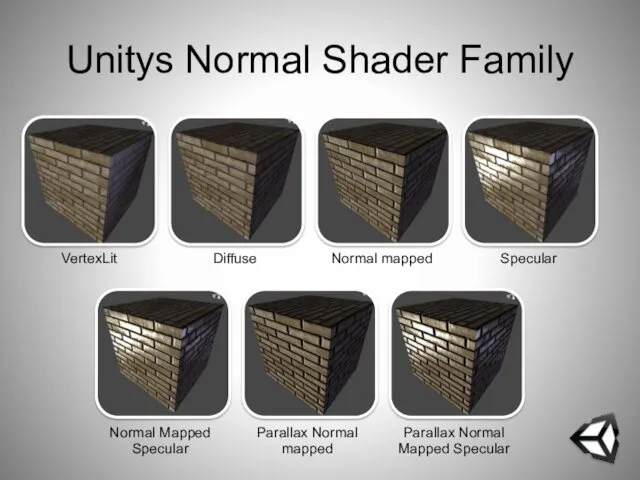
- 59. Unitys Normal Shader Family
- 60. Lighting Uses normals Directional/point-lights Material settings to decide final color. Lighting is computed at each vertex.
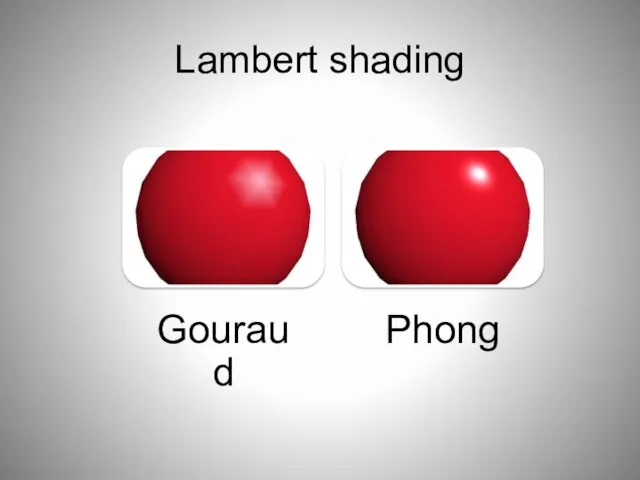
- 61. Lambert shading
- 62. Real-time shadows
- 63. Quality and performance Non realtime-shadows fastest! Shadow map resolution Number of lights
- 64. Example in Unity
- 65. Special effects Effects Color correction Postprocessing stage / GPU LDR/HDR, Tone mapping
- 67. Physics
- 68. Very simple physics demo
- 69. Frameworks Goal: Games, experimental, Vizualisation? Reach: Plugin? Multiple platforms/screens? Cost: Open source? Licenced? Support: Large community?
- 71. Unity3D Boo, C# and JavaScript Plugin Great and simple IDE Competent and mature framework Pro version
- 73. Flash/Molehill Actionscript Plugin 3D content always under the DisplayList All the other stuff in the flash
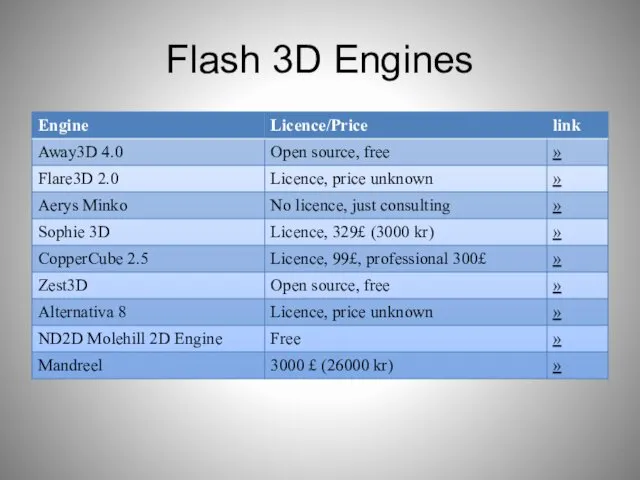
- 74. Flash 3D Engines
- 75. Optimizing Profiling memory usage, cleanup/destroy Object Pooling! polygonal lab Take control of rendering pipeline Compression/Model to
- 77. WebGL Javascript No plugin Open / Royalty-free Not available in all browsers yet Frameworks in early
- 78. WebGL Frameworks
- 79. Jellyfish Aleksandar Rodic
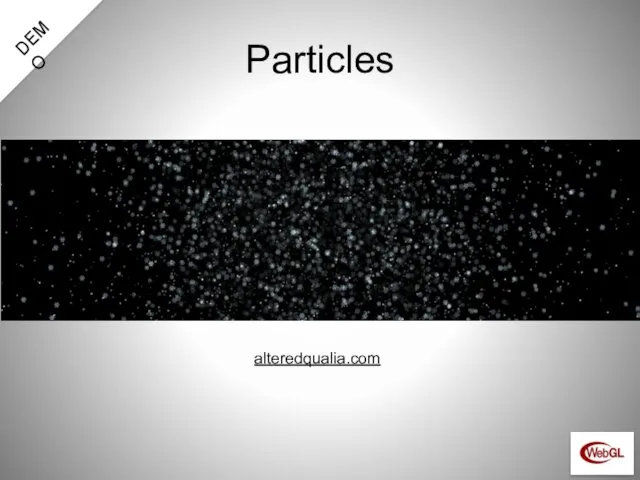
- 80. Particles alteredqualia.com
- 81. Hello Racer HelloEnjoy™
- 82. Clouds Mr Doob
- 83. WebGL vs. Molehill APIs HTML5 vs. Plugin. WebGL will probably run in iOS browser. Easy to
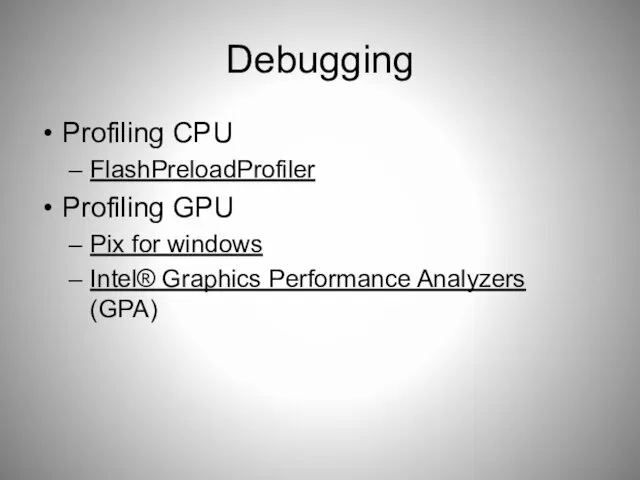
- 84. Debugging Profiling CPU FlashPreloadProfiler Profiling GPU Pix for windows Intel® Graphics Performance Analyzers (GPA)
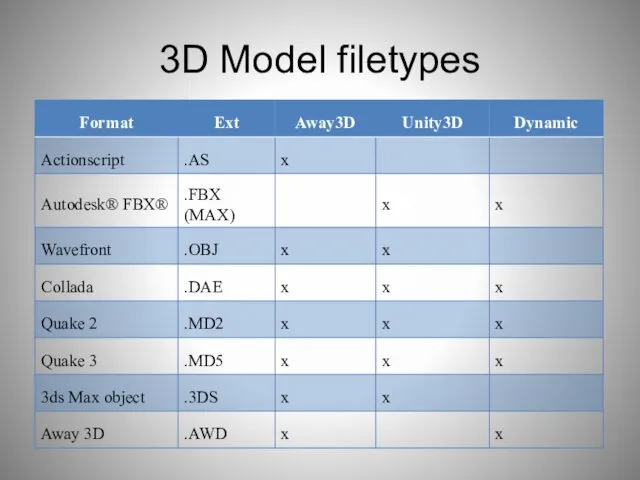
- 85. 3D Model filetypes
- 86. Learning tips
- 87. Random interesting topics
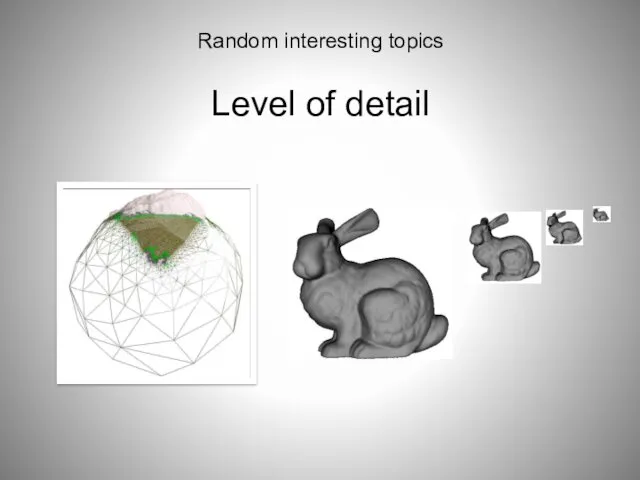
- 88. Random interesting topics Level of detail
- 89. Octree, BSP Tree, Portals and Sectors Random interesting topics
- 90. Global illumination / Ambient occlusion Random interesting topics
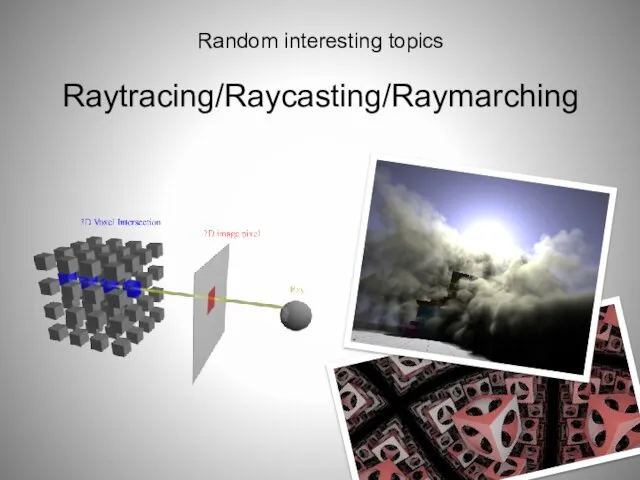
- 91. Raytracing/Raycasting/Raymarching Random interesting topics
- 92. Some useful resources
- 93. Books and papers Away3D 3.6 essentials Mathematics for Game Developer by Christopher Tremblay Mathematics for 3D
- 95. Скачать презентацию























































 Текстовые задачи. Решение
Текстовые задачи. Решение Показникова функція
Показникова функція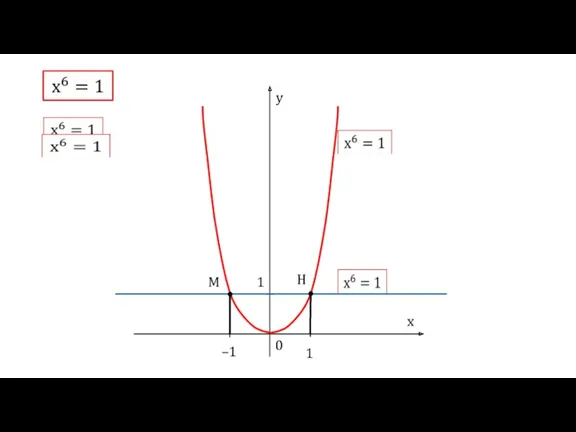 Понятие корня n-й степени из действительного числа
Понятие корня n-й степени из действительного числа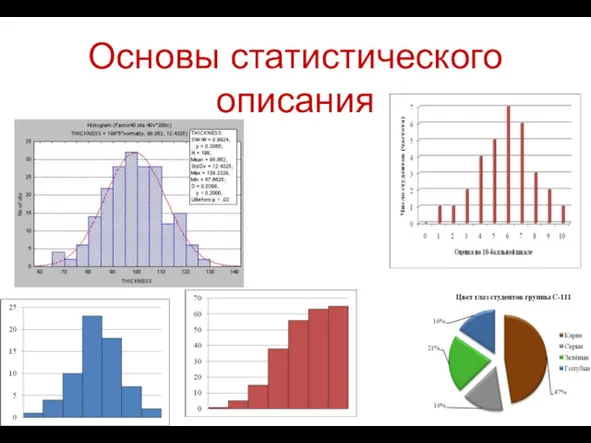 Основы статистического описания
Основы статистического описания Симметрия
Симметрия Маршрутизация перевозок грузов. Модель транспортной сети
Маршрутизация перевозок грузов. Модель транспортной сети Уравнения, приводимые к квадратным. Cпицион Ферро [1465-1526] и его ученик Фиоре
Уравнения, приводимые к квадратным. Cпицион Ферро [1465-1526] и его ученик Фиоре Куля та сфера. (11 клас)
Куля та сфера. (11 клас) Вид треугольника. Геометрия. 7 класс
Вид треугольника. Геометрия. 7 класс Арифметический корень n-ой степени
Арифметический корень n-ой степени Математическая модель
Математическая модель Тренажер. Значения коэффициентов квадратичной функции
Тренажер. Значения коэффициентов квадратичной функции Подготовка к контрольной работе Умножение и деление дробей
Подготовка к контрольной работе Умножение и деление дробей Задание В7, открытого банка ЕГЭ по математике
Задание В7, открытого банка ЕГЭ по математике Статистикалық болжамдарды тексеру теориясының негіздері
Статистикалық болжамдарды тексеру теориясының негіздері Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей. 5 класс
Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей. 5 класс Презентация к уроку математики по теме: Доли и дроби
Презентация к уроку математики по теме: Доли и дроби Координатный угол. 4 класс
Координатный угол. 4 класс Вероятность равновозможных событий. 9 класс
Вероятность равновозможных событий. 9 класс Метод главных компонент
Метод главных компонент Интерполяции сплайнами
Интерполяции сплайнами Числа от 1 до 100 с использованием игровых технологий
Числа от 1 до 100 с использованием игровых технологий Системы двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными, как математические модели реальных ситуаций
Системы двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными, как математические модели реальных ситуаций Пропорции. 6 класс
Пропорции. 6 класс “Математика озаты” интеллектуалдық олимпиада
“Математика озаты” интеллектуалдық олимпиада урок математики по теме число и цифра 3
урок математики по теме число и цифра 3 Центральные проблемы эконометрики
Центральные проблемы эконометрики Пропорции
Пропорции