Содержание
- 2. LECTURE 2 MEASURES OF LOCATION Temur Makhkamov Indira Khadjieva QM Module Leaders tmakhkamov@wiut.uz i.khadjieva@wiut.uz Office hours:
- 3. Learning Outcomes Upon successful completion of session, students are able to Identify and calculate various measures
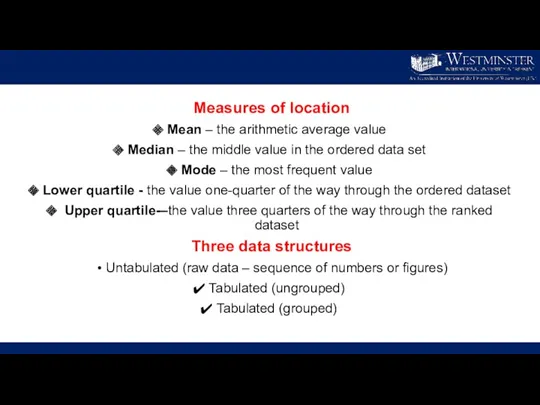
- 4. Measures of location Mean – the arithmetic average value Median – the middle value in the
- 5. Untabulated Data Def: Untabulated data – data given as a sequence of numbers or figures Example
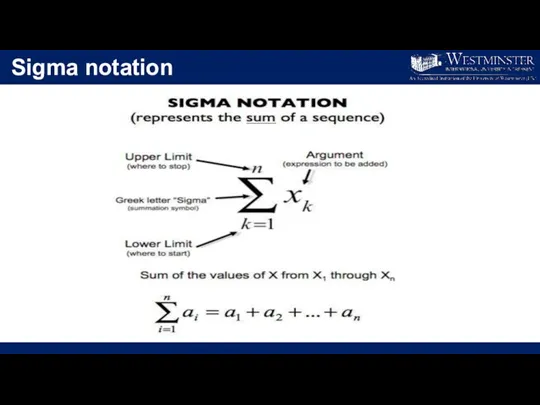
- 6. Sigma notation
- 7. Mean
- 8. Median 7, 13, 13, 15, 20, 24, 27
- 9. Median Note: Odd case: If there are an odd number of items in the data set,
- 10. Mode 20, 15, 13, 13, 27, 24, 7 Mode = 13, because there are two 13s
- 11. Lower quartile
- 12. Upper quartile
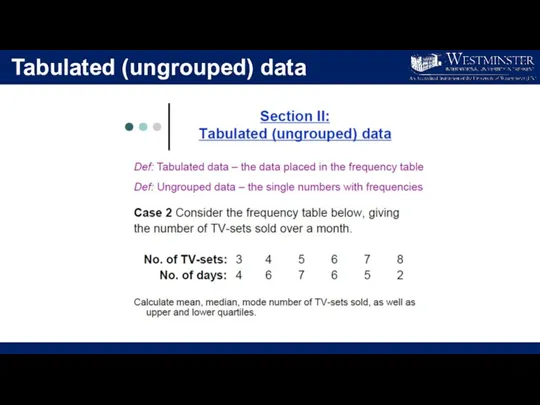
- 13. Tabulated (ungrouped) data
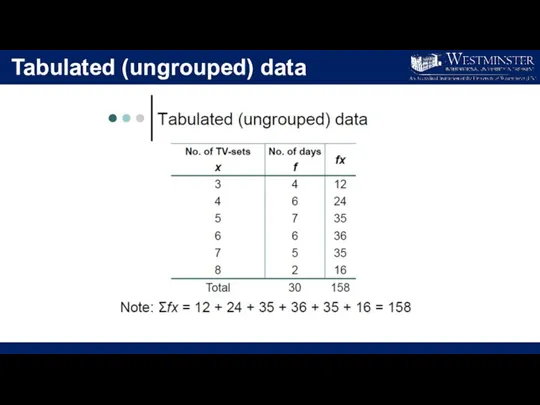
- 14. Tabulated (ungrouped) data
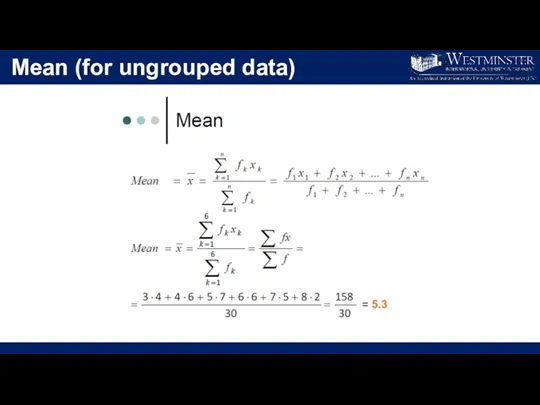
- 15. Mean (for ungrouped data)
- 16. Median (for ungrouped data)
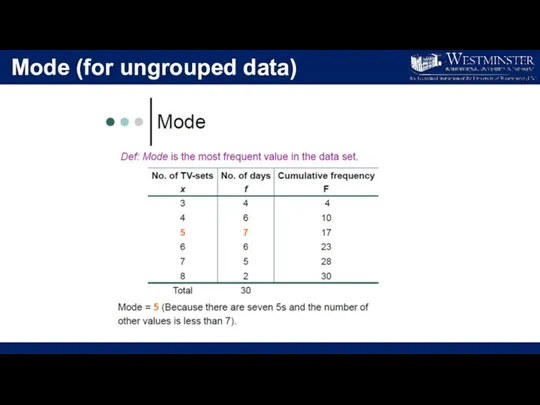
- 17. Mode (for ungrouped data)
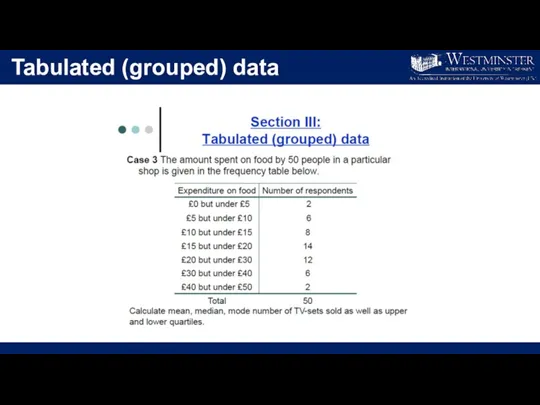
- 18. Tabulated (grouped) data
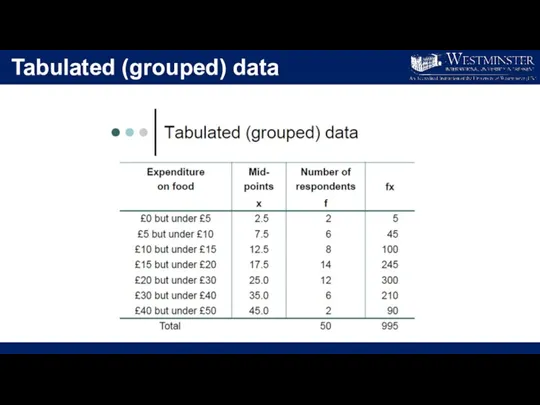
- 19. Tabulated (grouped) data
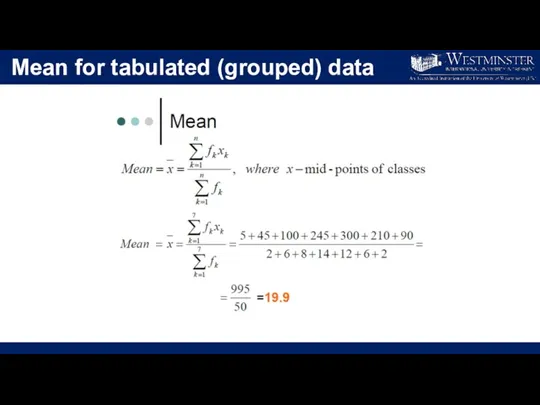
- 20. Mean for tabulated (grouped) data
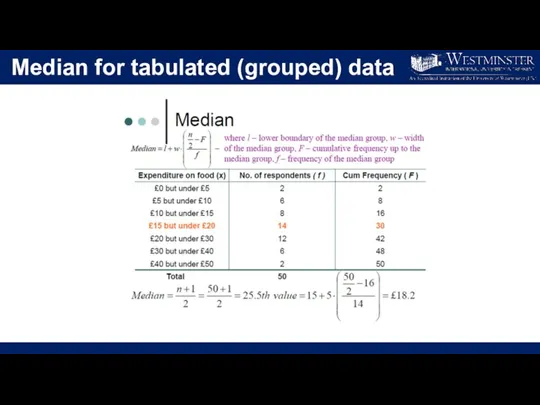
- 21. Median for tabulated (grouped) data
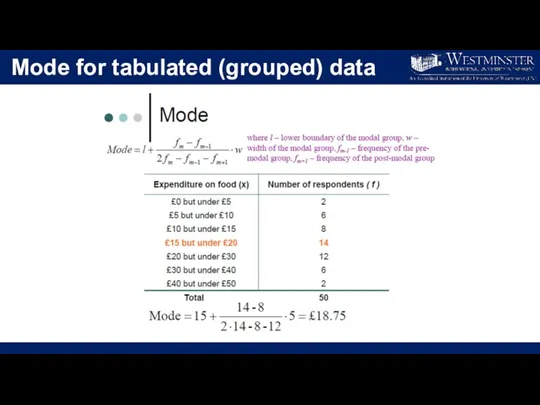
- 22. Mode for tabulated (grouped) data
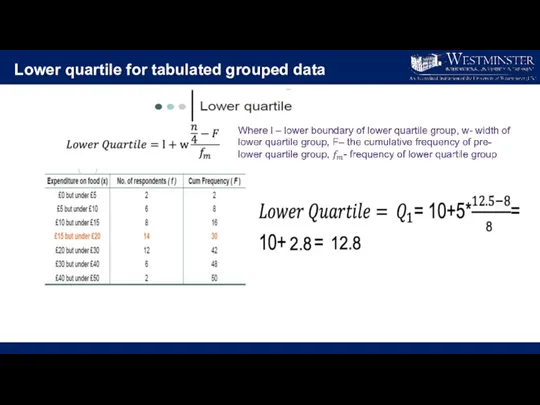
- 23. Lower quartile for tabulated grouped data
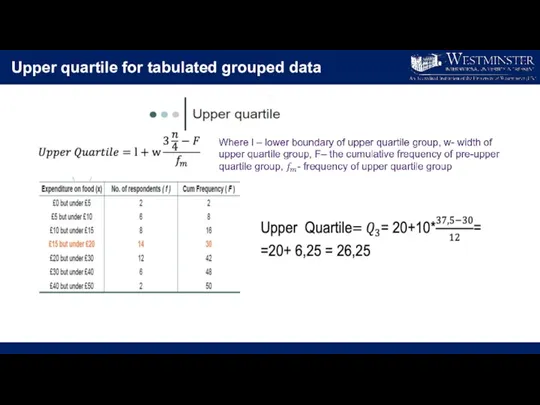
- 24. Upper quartile for tabulated grouped data
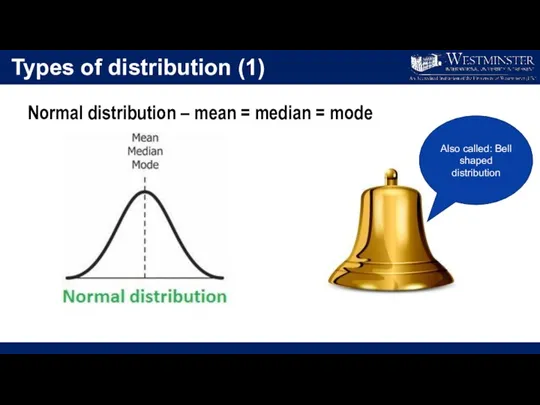
- 25. Types of distribution (1) Normal distribution – mean = median = mode Also called: Bell shaped
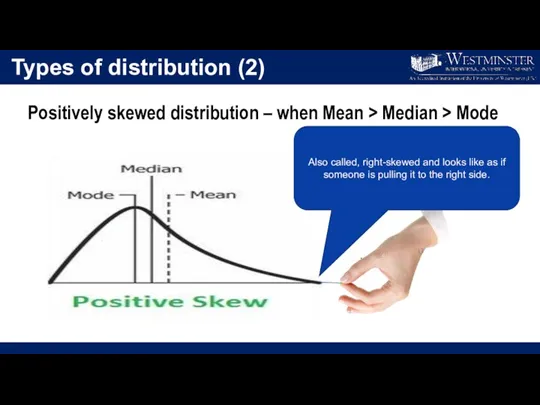
- 26. Types of distribution (2) Positively skewed distribution – when Mean > Median > Mode Also called,
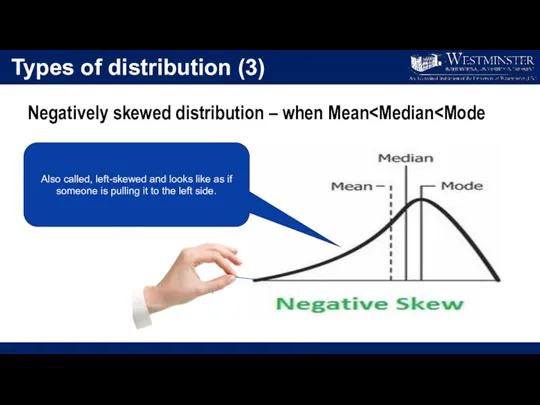
- 27. Types of distribution (3) Negatively skewed distribution – when Mean Also called, left-skewed and looks like
- 28. Concluding remarks: Today, You learnt: the analysis of tabulated and untabulated, grouped and ungrouped data; the
- 30. Скачать презентацию











 урок по математике Письменное сложение трехзначных чисел
урок по математике Письменное сложение трехзначных чисел Додавання і віднімання чисел у межах 20. Задачі на різницеве порівняння. Урок 3
Додавання і віднімання чисел у межах 20. Задачі на різницеве порівняння. Урок 3 Квадратні рівняння. Розв’язування неповних квадратних рівнянь
Квадратні рівняння. Розв’язування неповних квадратних рівнянь Цыфра 7. Число 7.
Цыфра 7. Число 7. Деятельностный подход в обучении математике
Деятельностный подход в обучении математике Paradigme de proiectare a algoritmilor
Paradigme de proiectare a algoritmilor Основы математического анализа
Основы математического анализа Здоровьесберегающие технологии. Задачи о фруктах.
Здоровьесберегающие технологии. Задачи о фруктах. Решение треугольников. 9 класс
Решение треугольников. 9 класс Китайская система счисления
Китайская система счисления Движение. Симметрия. Поворот. Параллельный перенос. Осевая симметрия. Центральная симметрия
Движение. Симметрия. Поворот. Параллельный перенос. Осевая симметрия. Центральная симметрия Презентация Считалочка
Презентация Считалочка Свойства сторон прямоугольника 2 класс
Свойства сторон прямоугольника 2 класс Системи лінійних рівнянь, умови їх сумісності і визначенності. Метод Гаусса
Системи лінійних рівнянь, умови їх сумісності і визначенності. Метод Гаусса Методическая разработка - технологическая карта урока математики в 3 классе по теме Проверка умножения. ФГОС
Методическая разработка - технологическая карта урока математики в 3 классе по теме Проверка умножения. ФГОС Квадратные уравнения и способы их решения
Квадратные уравнения и способы их решения Сложение и вычитание обыкновенных дробей
Сложение и вычитание обыкновенных дробей Дидактические игры по математике
Дидактические игры по математике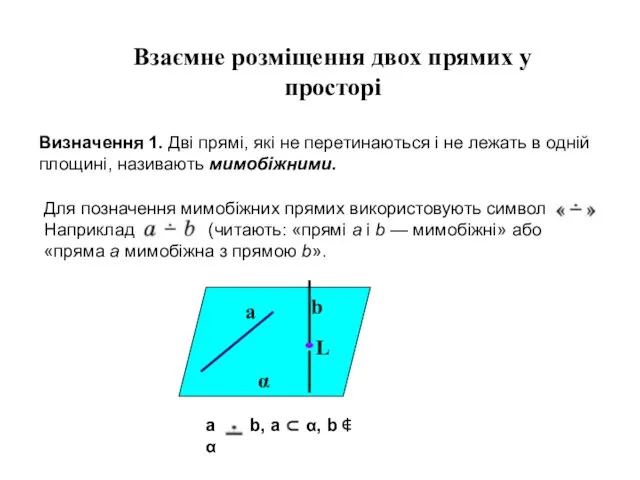 Взаємне розміщення двох прямих у просторі
Взаємне розміщення двох прямих у просторі Алгоритм отыскания наибольшего и наименьшего значения функции
Алгоритм отыскания наибольшего и наименьшего значения функции Презентация к фрагменту урока в 1 классе. Тема Число и цифра 3
Презентация к фрагменту урока в 1 классе. Тема Число и цифра 3 Земная кора. Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей
Земная кора. Сложение и вычитание десятичных дробей Уменьшаемое. Вычитаемое. Разность
Уменьшаемое. Вычитаемое. Разность Урок математики 1 класс
Урок математики 1 класс Теорема о площади треугольника
Теорема о площади треугольника Прямая и плоскость в пространстве
Прямая и плоскость в пространстве Образование чисел из одного десятка
Образование чисел из одного десятка Дифференциальное исчисление функции нескольких переменных. Основные понятия функции нескольких переменных
Дифференциальное исчисление функции нескольких переменных. Основные понятия функции нескольких переменных