Содержание
- 2. Literature: [1], v. І, p. 174-180, [2], part І, p. 40-57, [3], p. 174-181. Theme: The
- 3. 1.The main definitions 2.The different ways of representing of the functions 3. The main characteristics of
- 4. Given two sets X and Y Definition. A function is a rule which assigns to each
- 5. Examples. D(y) - ? 1) f(x)=x3-4x+2 (polynomial of the third power) 2) 3) . 4) .
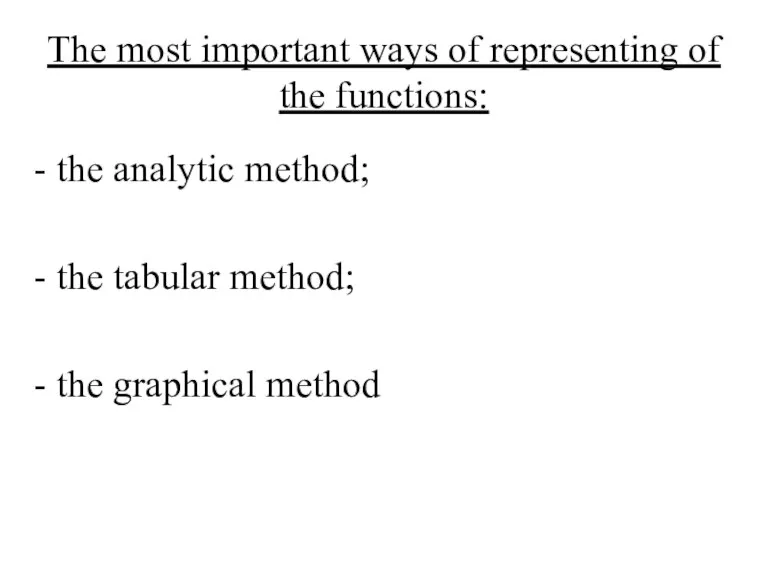
- 6. The most important ways of representing of the functions: - the analytic method; - the tabular
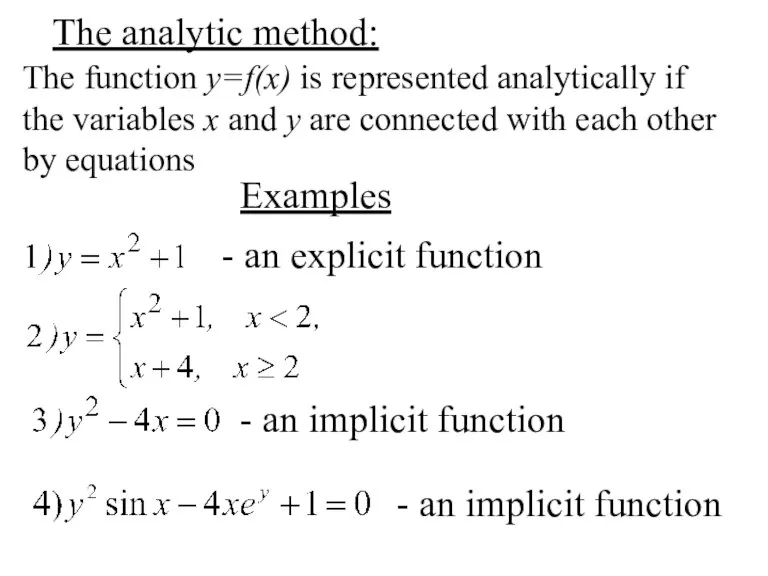
- 7. The analytic method: The function y=f(x) is represented analytically if the variables x and y are
- 8. 5) The demand function: q - price, p – demand 6) Cost function V(x), income function
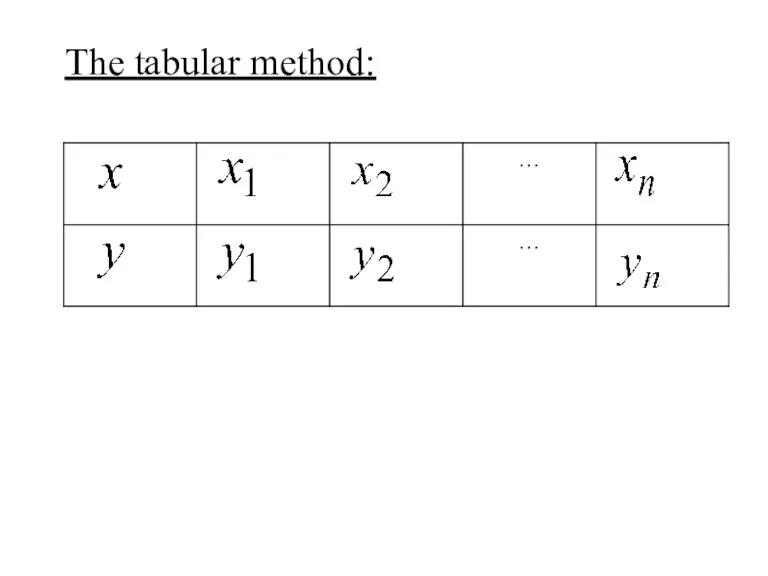
- 9. The tabular method:
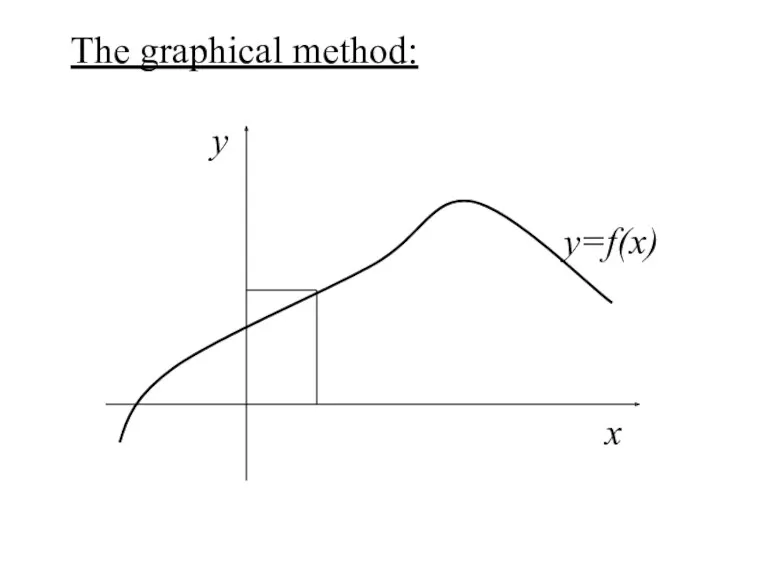
- 10. The graphical method:
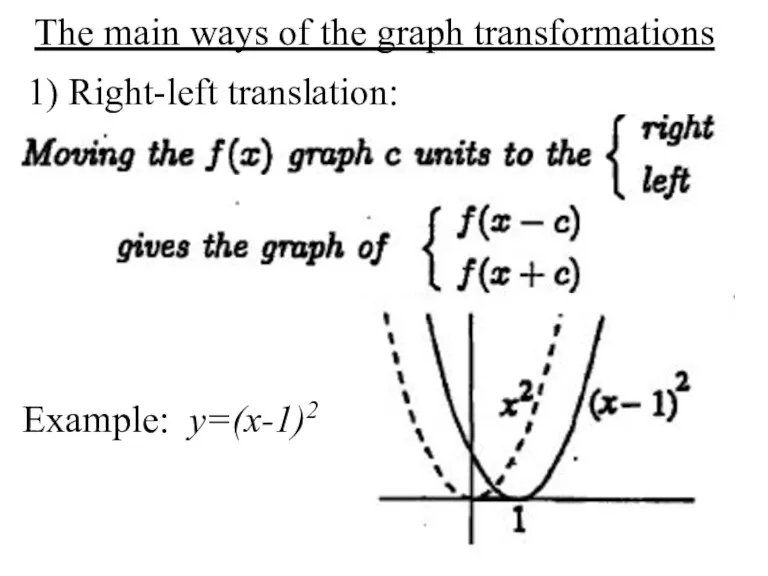
- 11. The main ways of the graph transformations 1) Right-left translation: Example: y=(x-1)2
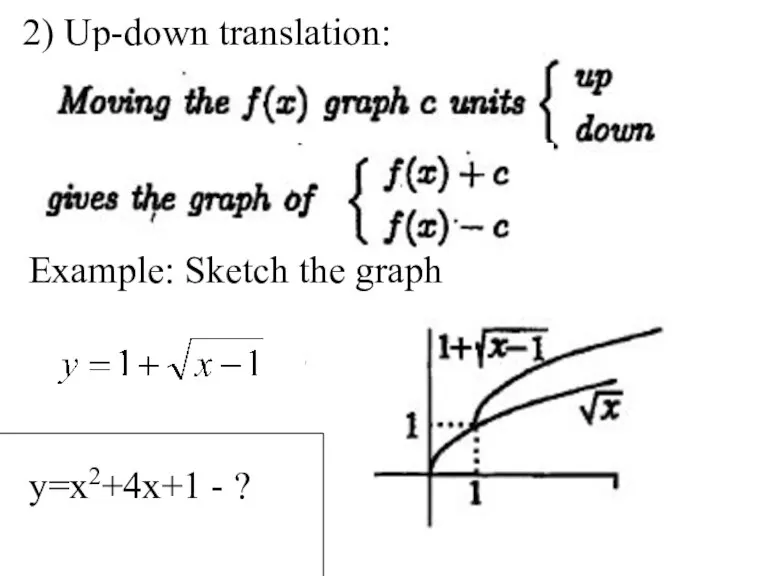
- 12. 2) Up-down translation: Example: Sketch the graph y=x2+4x+1 - ?
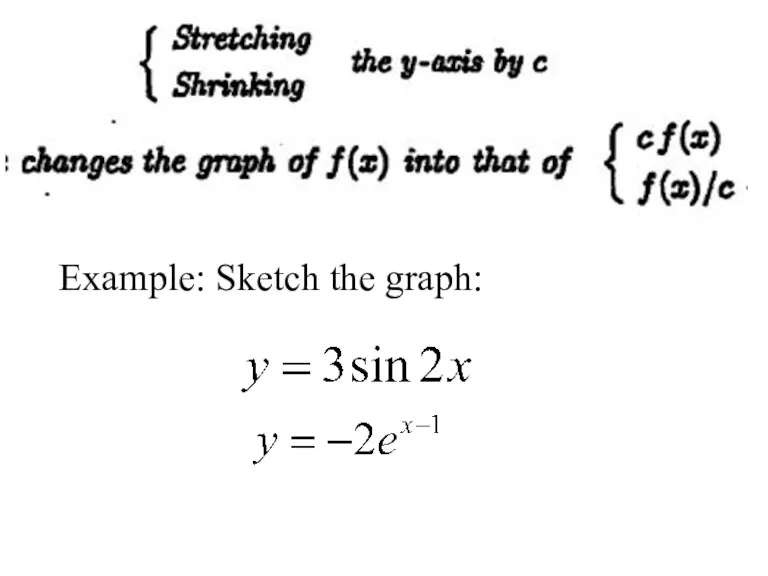
- 13. 3) Changing scale: stretching and shrinking Example: Sketch the graph
- 14. Example: Sketch the graph:
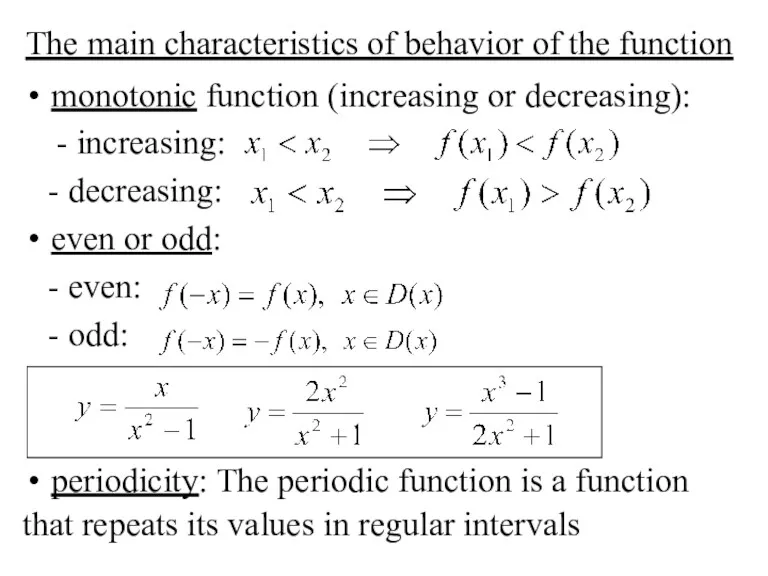
- 15. The main characteristics of behavior of the function monotonic function (increasing or decreasing): - increasing: -
- 16. The basic elementary functions: The power function; The exponential function; The logarithmic function; The trigonometric functions
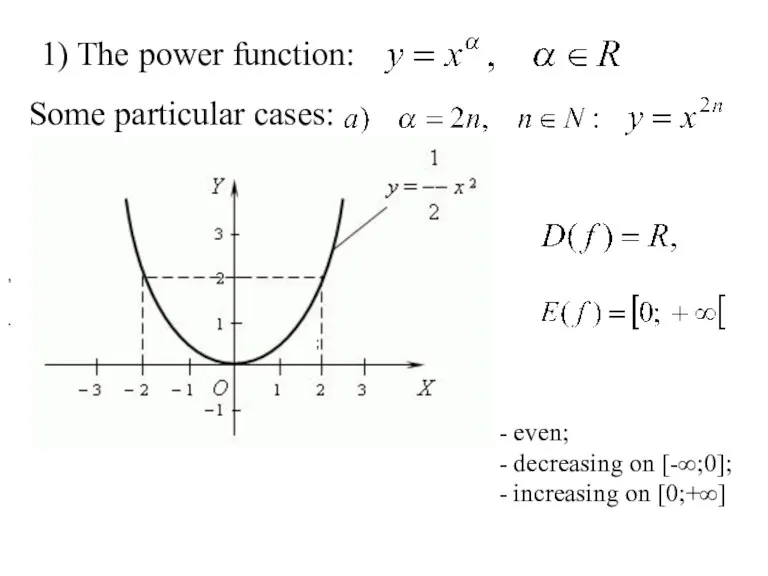
- 17. 1) The power function: Some particular cases: , . - even; - decreasing on [-∞;0]; -
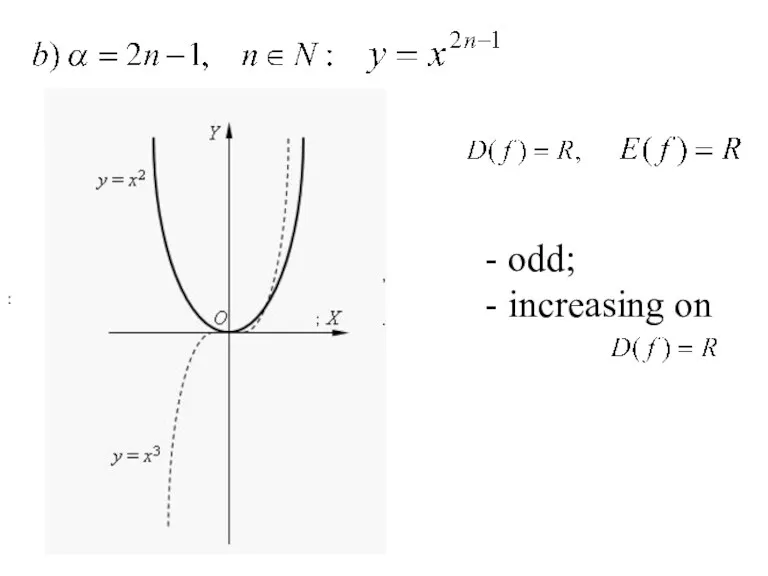
- 18. : , . - odd; - increasing on ;
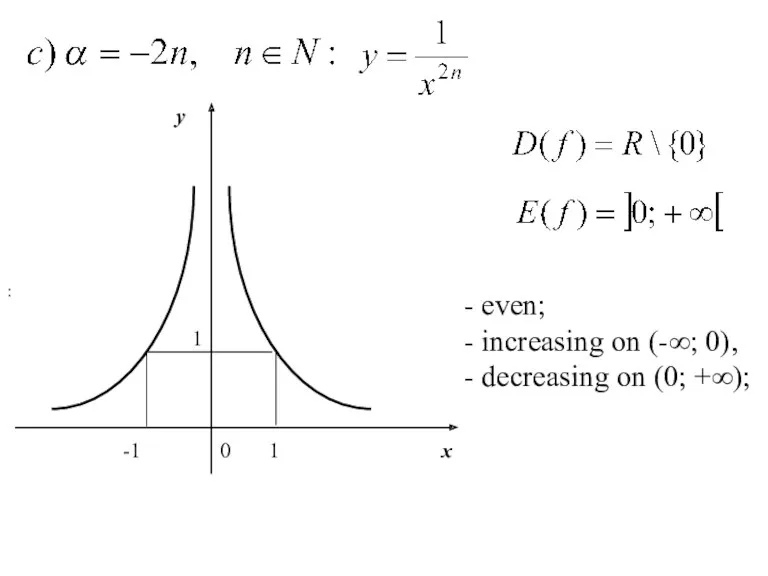
- 19. : - even; - increasing on (-∞; 0), - decreasing on (0; +∞);
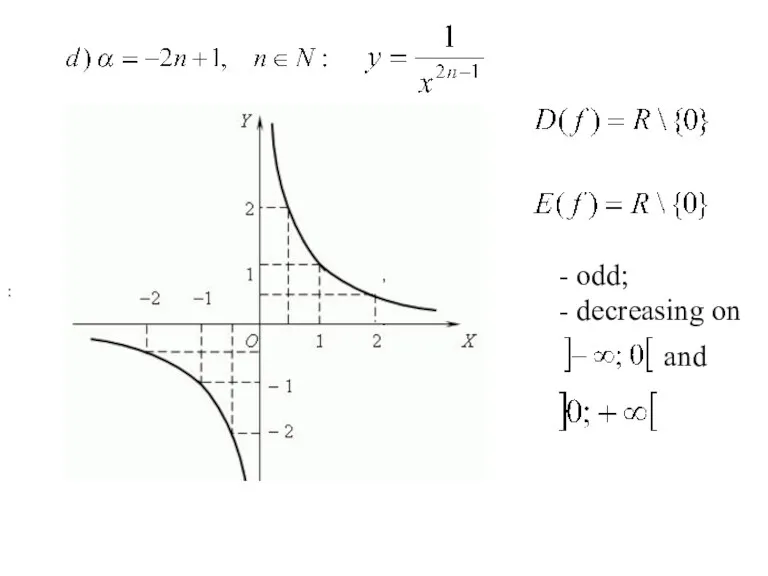
- 20. : , . - odd; - decreasing on and .
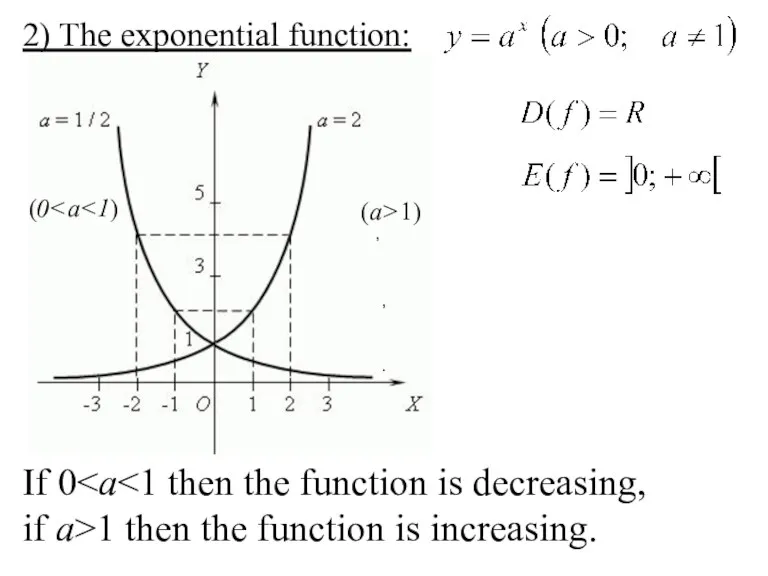
- 21. 2) The exponential function: (a>1) (0 , , . If 0 if a>1 then the function
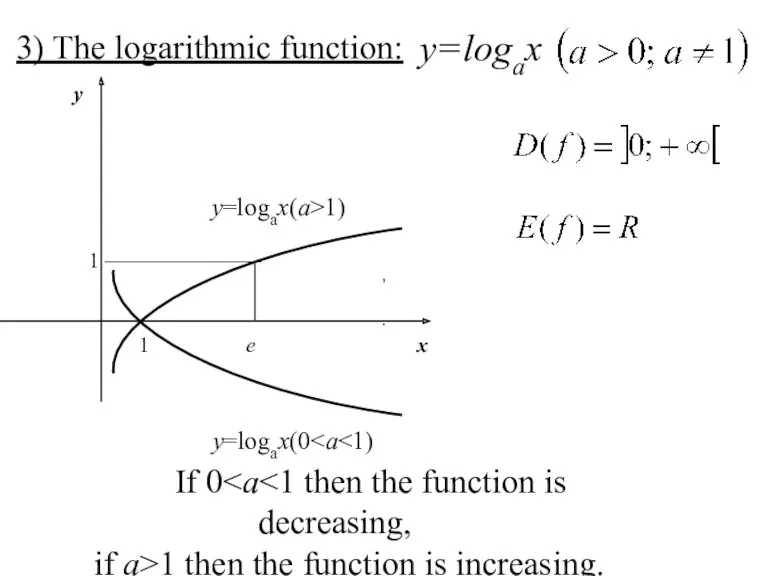
- 22. 3) The logarithmic function: y=logax , . If 0 if a>1 then the function is increasing.
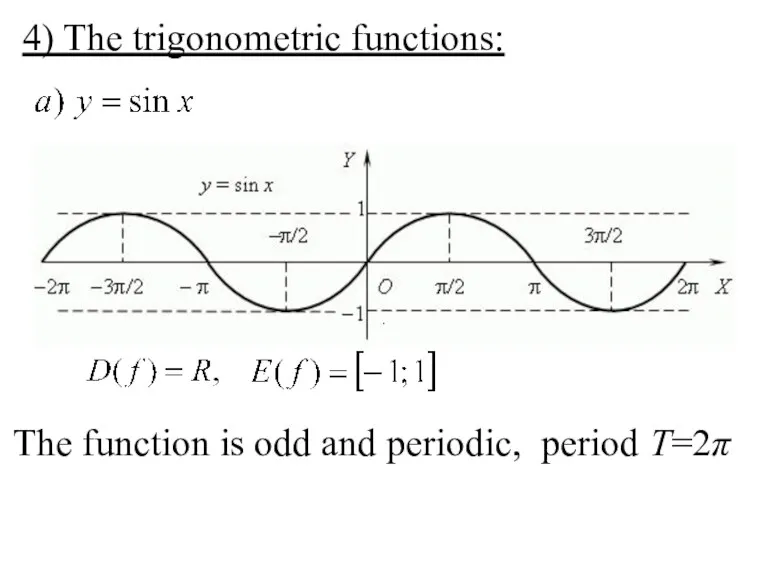
- 23. 4) The trigonometric functions: , . The function is odd and periodic, period T=2π
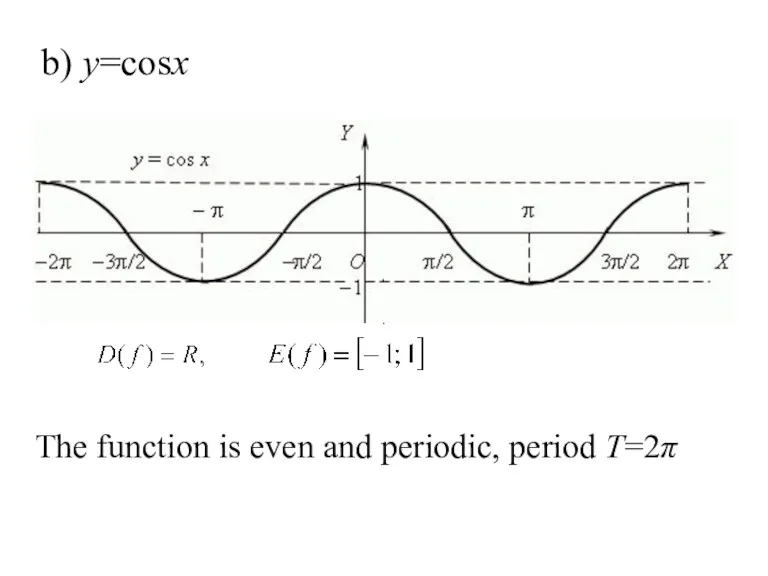
- 24. b) y=cosx , . The function is even and periodic, period T=2π
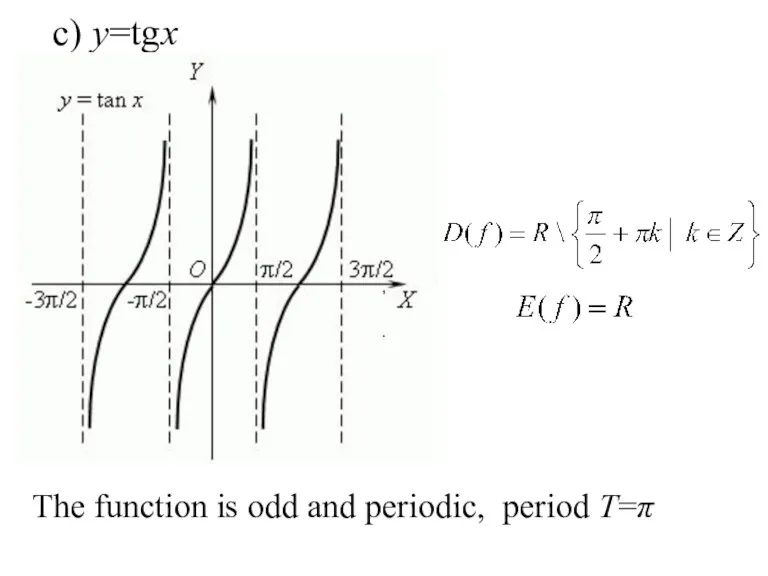
- 25. c) y=tgx , . The function is odd and periodic, period T=π
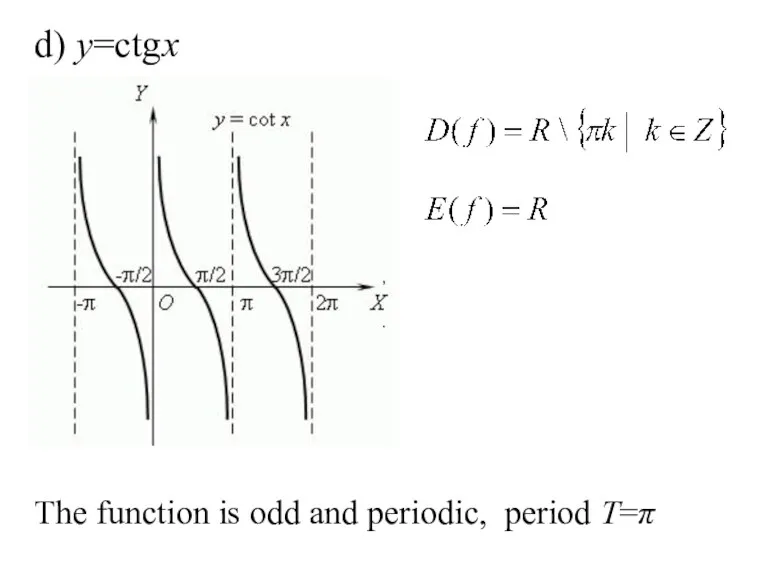
- 26. d) y=сtgx , . The function is odd and periodic, period T=π
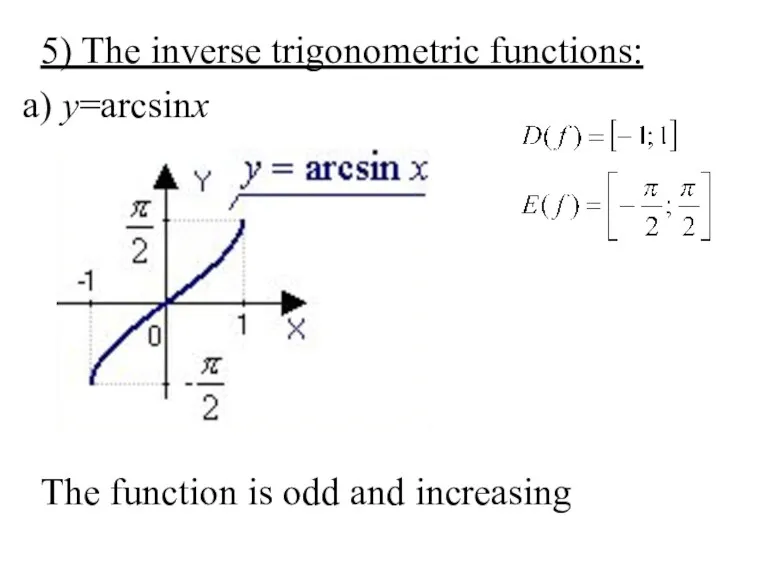
- 27. 5) The inverse trigonometric functions: а) y=arcsinx , . The function is odd and increasing
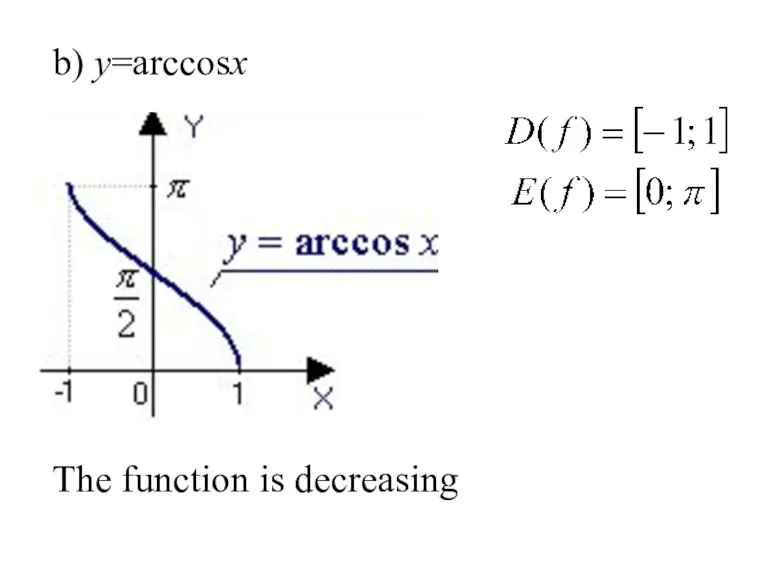
- 28. b) y=arccosx , . The function is decreasing
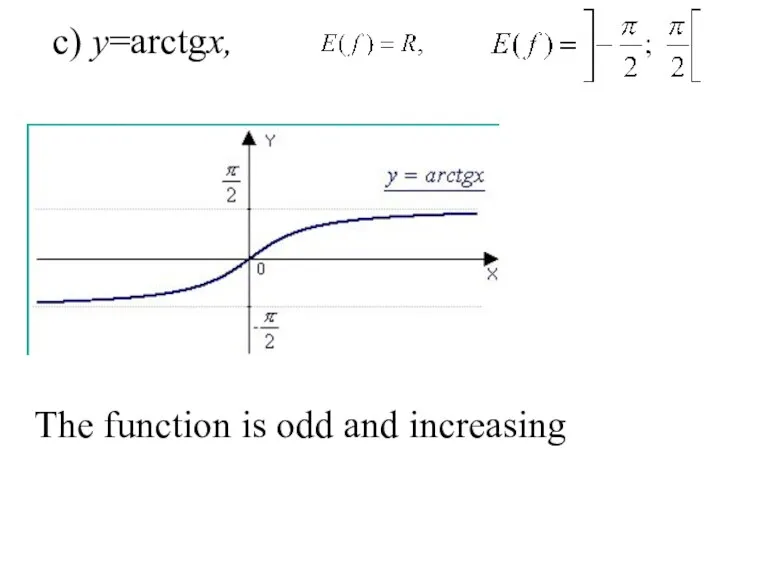
- 29. c) y=arctgx, . The function is odd and increasing
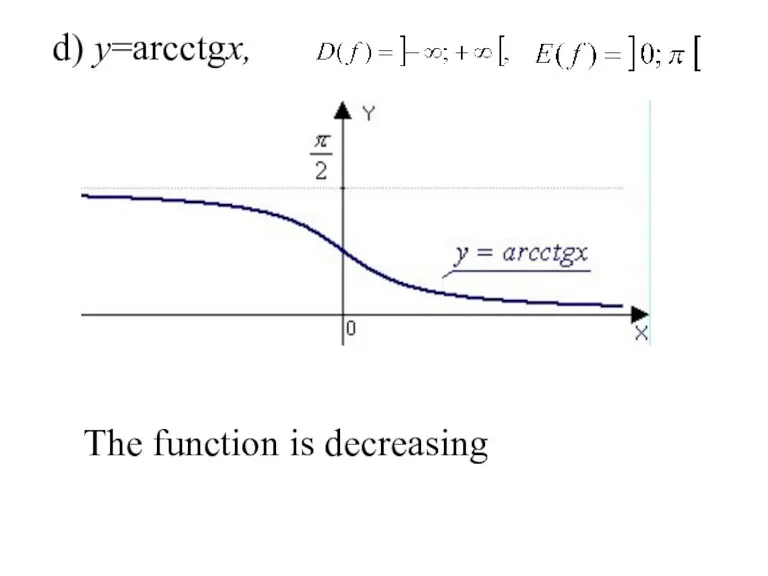
- 30. d) y=arcсtgx, . The function is decreasing
- 31. Examples 3)
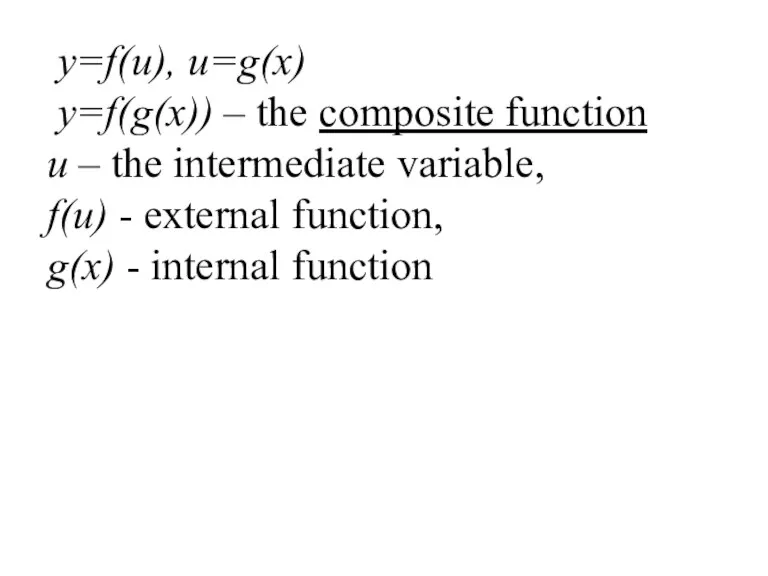
- 32. y=f(u), u=g(x) y=f(g(x)) – the composite function u – the intermediate variable, f(u) - external function,
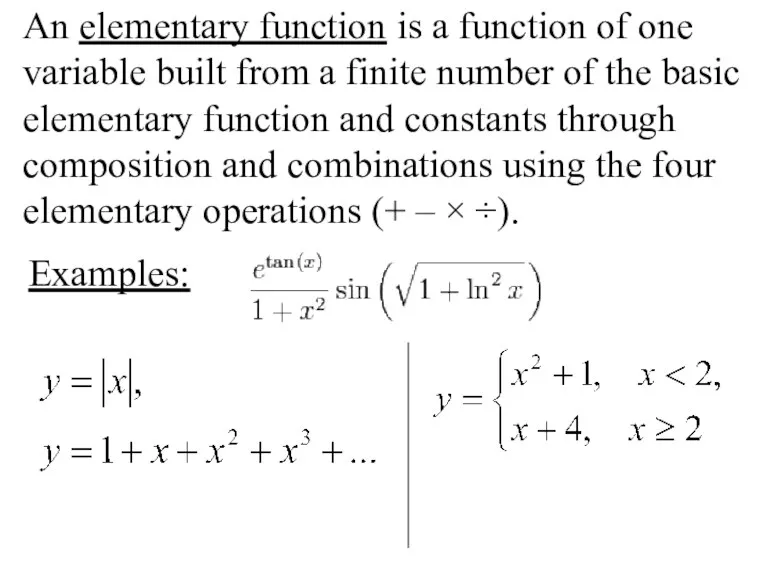
- 33. An elementary function is a function of one variable built from a finite number of the
- 35. Скачать презентацию
![Literature: [1], v. І, p. 174-180, [2], part І, p.](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/439364/slide-1.jpg)






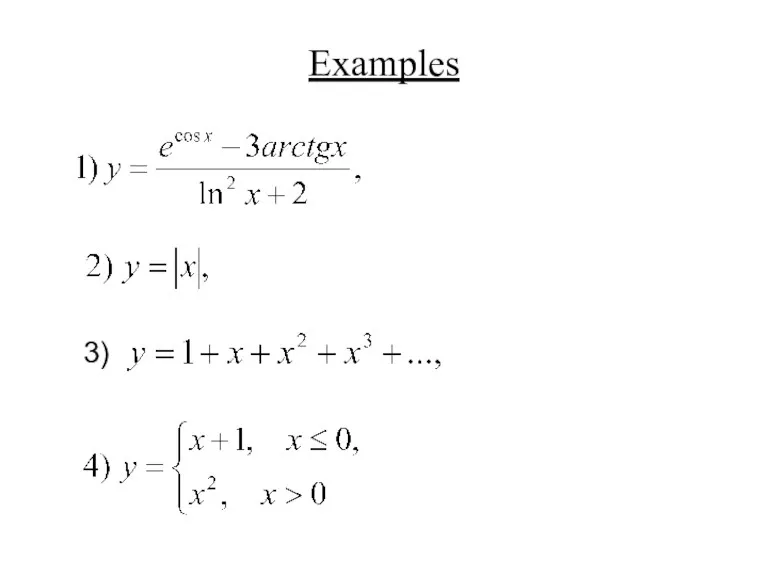
 Описательная статистика
Описательная статистика Интегрированный урок: математика + биология. Простые и сложные листья
Интегрированный урок: математика + биология. Простые и сложные листья Математика и музыка. Реалити-шоу
Математика и музыка. Реалити-шоу Цена. Количество. Стоимость
Цена. Количество. Стоимость Длина окружности (6 класс)
Длина окружности (6 класс) Презентация к уроку математики по теме Задачи на движение
Презентация к уроку математики по теме Задачи на движение Непрерывная случайная величина. Равномерное, показательное и нормальное распределение
Непрерывная случайная величина. Равномерное, показательное и нормальное распределение решение неравенств второй степени с помощью графика квадратичной функции
решение неравенств второй степени с помощью графика квадратичной функции Презентация к уроку русского языка в 4 классе Неопределённая форма глагола
Презентация к уроку русского языка в 4 классе Неопределённая форма глагола Математические предложения
Математические предложения Вычитание вида 12 -
Вычитание вида 12 - Транспортные сети. Поиск максимального потока в сети. (Лекция 10)
Транспортные сети. Поиск максимального потока в сети. (Лекция 10) компьютерная математическая игра Космическое путешествие (1-2 классы)
компьютерная математическая игра Космическое путешествие (1-2 классы) Определение модуля числа
Определение модуля числа Дециметр. Урок математики 1 класс
Дециметр. Урок математики 1 класс Эконометрика. Гетероскедастичность случайной составляющей
Эконометрика. Гетероскедастичность случайной составляющей Графический диктант. Верно или не верно
Графический диктант. Верно или не верно Крестики-нолики
Крестики-нолики Функция у=х 3. График функции
Функция у=х 3. График функции Комбинация призмы и цилиндра
Комбинация призмы и цилиндра Приемы письменного умножения в пределах 1000
Приемы письменного умножения в пределах 1000 Загадка числа Пи
Загадка числа Пи Жазық фигураның жазықтыққа ортогональ проекциясы және оның ауданы
Жазық фигураның жазықтыққа ортогональ проекциясы және оның ауданы Умножение и деление десятичных дробей. Контрольная работа
Умножение и деление десятичных дробей. Контрольная работа урок математики в 3 классе по теме Закрепление таблицы умножения и деления на 2 и 3
урок математики в 3 классе по теме Закрепление таблицы умножения и деления на 2 и 3 Решение неравенств с одной переменной. 8 класс
Решение неравенств с одной переменной. 8 класс Отклонение. Дисперсия
Отклонение. Дисперсия Площадь прямоугольника
Площадь прямоугольника