Содержание
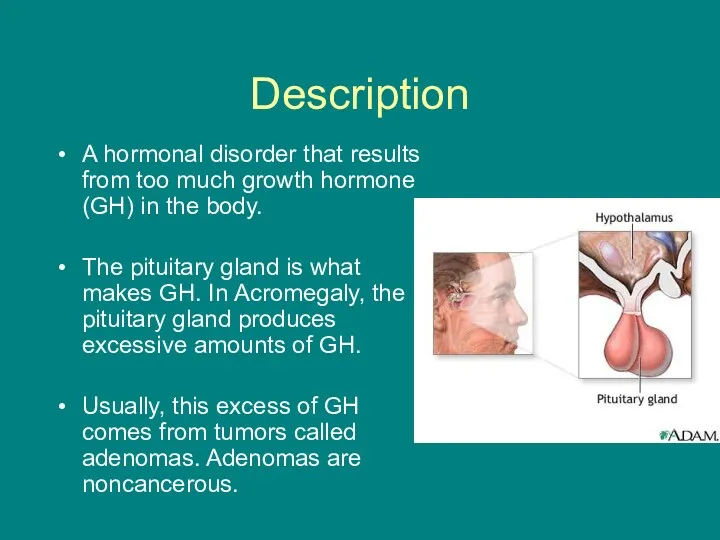
- 2. Description A hormonal disorder that results from too much growth hormone (GH) in the body. The
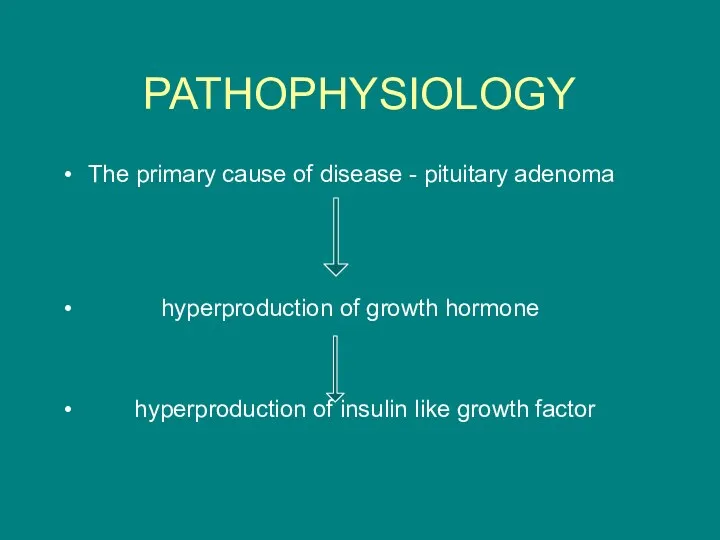
- 3. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY The primary cause of disease - pituitary adenoma hyperproduction of growth hormone hyperproduction of insulin
- 4. Hormonal effects three key hormone Growth hormone (somatotropin) - produced and secreted from the anterior pituitary;
- 5. Signs and symptoms Most common clinical features are : acral enlargement = 86% maxillofacial changes =
- 6. Signs and Symptoms Acromegaly: Greek- “extremities” and “enlargement” = growth of the hands and feet Bones
- 7. Clinical manifestations: 1.Mass effects of the tumor - Headache -Visual field defects -Hyperprolactinemia -Pituitary stalk section
- 8. Clinical manifestations: 4.Metabolic features -Impaired glucose tolerance -Diabetes mellitus -Insulin resistance 5.Respiratory manifestations -Macroglossia -Jaw malocclusion
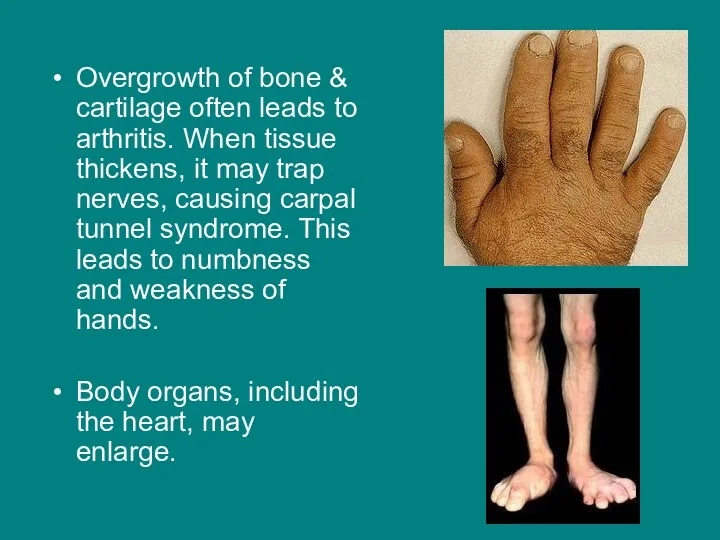
- 9. Overgrowth of bone & cartilage often leads to arthritis. When tissue thickens, it may trap nerves,
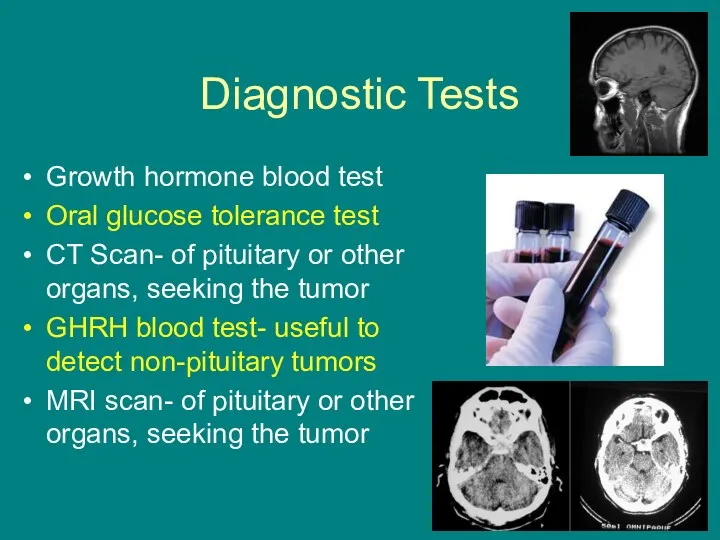
- 10. Diagnostic Tests Growth hormone blood test Oral glucose tolerance test CT Scan- of pituitary or other
- 11. screening test Growth hormone: the criterion of normal levels of GH is the value of G
- 12. Oral test glucose tolerance After oral intake of 75g of glucose glucose level and STG level
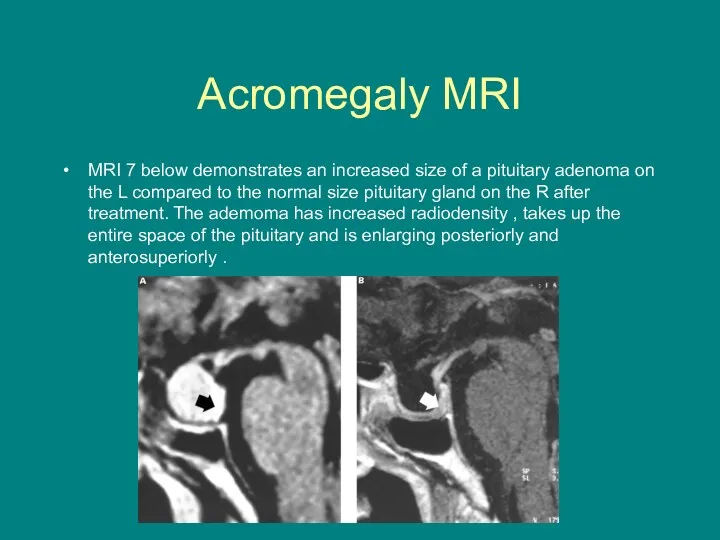
- 13. Acromegaly MRI MRI 7 below demonstrates an increased size of a pituitary adenoma on the L
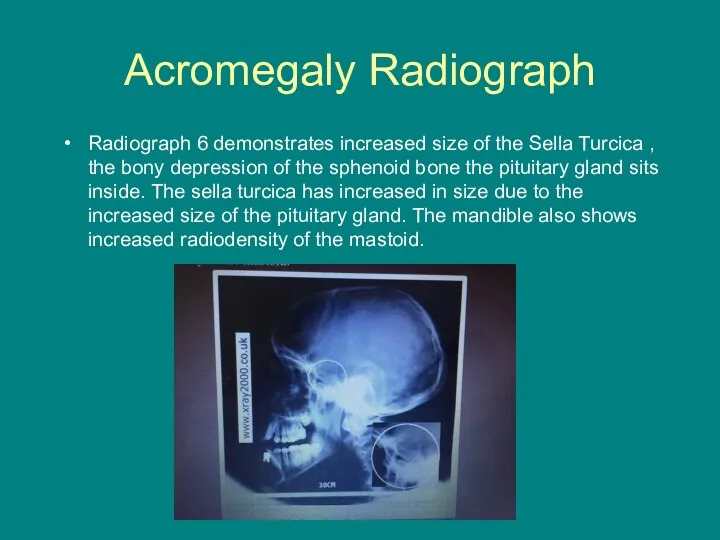
- 14. Acromegaly Radiograph Radiograph 6 demonstrates increased size of the Sella Turcica , the bony depression of
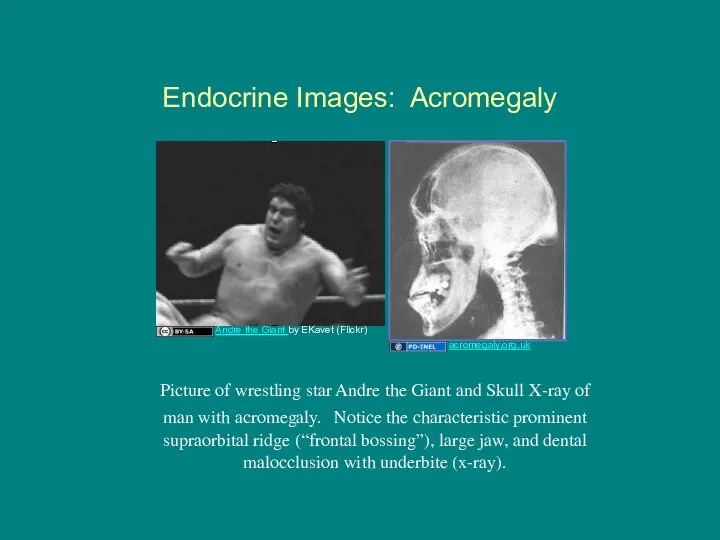
- 15. Endocrine Images: Acromegaly Picture of wrestling star Andre the Giant and Skull X-ray of man with
- 16. Endocrine Images: Acromegaly Individual with acromegaly photographed over a 37-year span. Ages in years are in
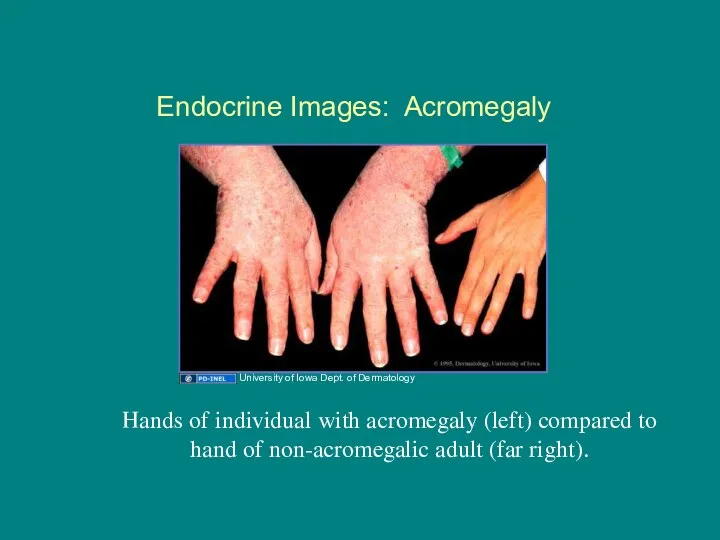
- 17. Endocrine Images: Acromegaly Hands of individual with acromegaly (left) compared to hand of non-acromegalic adult (far
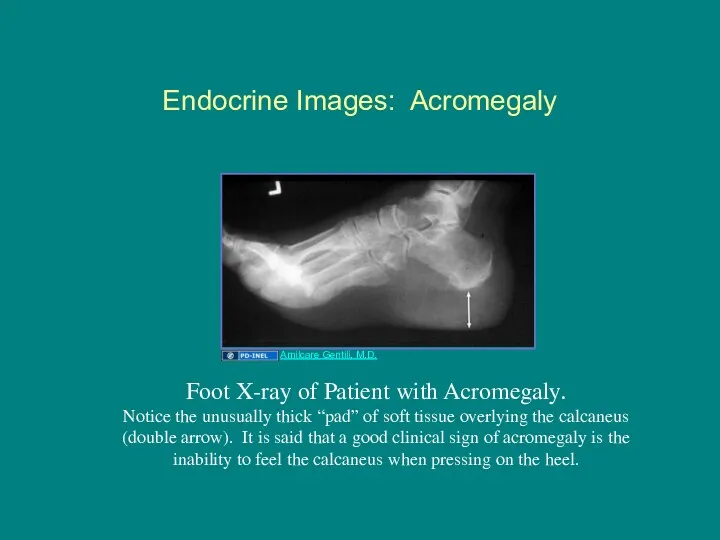
- 18. Endocrine Images: Acromegaly Foot X-ray of Patient with Acromegaly. Notice the unusually thick “pad” of soft
- 19. Treatment Treat the pituitary gland with: Surgery - transsphenoidal adenomectomy Medical therapy - somatostatin analogues -
- 20. Stereotactic radiosurgery octreotide, lanreotide an independent method, after surgery or RADIOTHERAPY inhibit the secretion of GH,
- 21. Dopamine agonists bromocriptine, quinagolide, cabergoline used for a long time, reduce the secretion of GH less
- 22. Antagonists of growth hormone receptors pegvisomant no effect on the tumor need to monitor the level
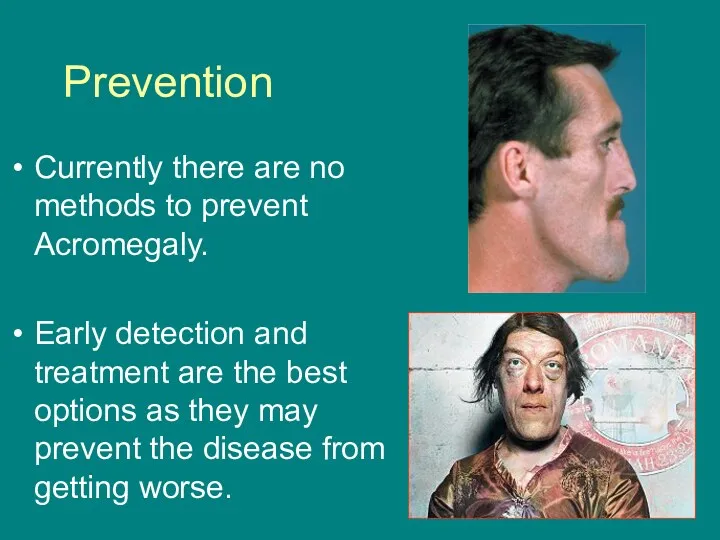
- 23. Prevention Currently there are no methods to prevent Acromegaly. Early detection and treatment are the best
- 24. Prognosis One in 20,000 people experience this abnormality. It is most often diagnosed in middle-aged adults.
- 26. Скачать презентацию












 Здоровое питание – активное долголетие
Здоровое питание – активное долголетие Современные лабораторные маркеры аутоиммунных заболеваний. Аутоимунный гепатит, аутоимунный тиреоидит
Современные лабораторные маркеры аутоиммунных заболеваний. Аутоимунный гепатит, аутоимунный тиреоидит Акушерские кровотечения во время беременности
Акушерские кровотечения во время беременности Анатомо - физиологические особенности сердечно - сосудистой системы детей
Анатомо - физиологические особенности сердечно - сосудистой системы детей Робот Da Vinci
Робот Da Vinci Заключительная лекция по аллергии и иммунопатологии
Заключительная лекция по аллергии и иммунопатологии Эндокринная система
Эндокринная система Принципи будови та функції нервової системи. Безумовні рефлекси. Система довільних рухів
Принципи будови та функції нервової системи. Безумовні рефлекси. Система довільних рухів Беременность и рак молочной железы
Беременность и рак молочной железы Гастриты. Классификация острых гастритов
Гастриты. Классификация острых гастритов БДСҰ ұсынысы бойынша ана сүтімен тамақтануға дайындау,жанұяны жоспарлау,контрацепция,аналық сүт безі обыры
БДСҰ ұсынысы бойынша ана сүтімен тамақтануға дайындау,жанұяны жоспарлау,контрацепция,аналық сүт безі обыры Туберкулез және жүктілік
Туберкулез және жүктілік Микола Михайлович Амосов
Микола Михайлович Амосов Проблема бессонницы в структуре соматических заболеваний
Проблема бессонницы в структуре соматических заболеваний Проблемы регулирования цен на лекарственные препараты в Российской Федерации и возможные пути их решения
Проблемы регулирования цен на лекарственные препараты в Российской Федерации и возможные пути их решения Цирроз печени
Цирроз печени Обследование гинекологических больных
Обследование гинекологических больных Косметика. Косметология
Косметика. Косметология Холецистэктомия. Травма печени
Холецистэктомия. Травма печени Анафилактический шок. Неотложная помощь. Интенсивная терапия
Анафилактический шок. Неотложная помощь. Интенсивная терапия Здоровый образ жизни
Здоровый образ жизни Развитие в онтогенезе. Младенческий возраст
Развитие в онтогенезе. Младенческий возраст Косметический массаж. (Тема 4.5)
Косметический массаж. (Тема 4.5) Синдром дефицита внимания и гиперактивности
Синдром дефицита внимания и гиперактивности Лабораторная диагностика заболеваний спинномозговой жидкости
Лабораторная диагностика заболеваний спинномозговой жидкости Ерте босану немесе мерзімінен бұрын босану
Ерте босану немесе мерзімінен бұрын босану Гиподинамия. Причины гиподинамии
Гиподинамия. Причины гиподинамии Использование УЗИ при катетеризации центральных вен
Использование УЗИ при катетеризации центральных вен