Содержание
- 2. Outline Gestational trophoblastic disease. Molar pregnancy. Classification. Pathogenesis. Risk factors. Presentation. Treatment . Follow up.
- 3. GTD Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a diverse group of interrelated diseases resulting in the abnormal
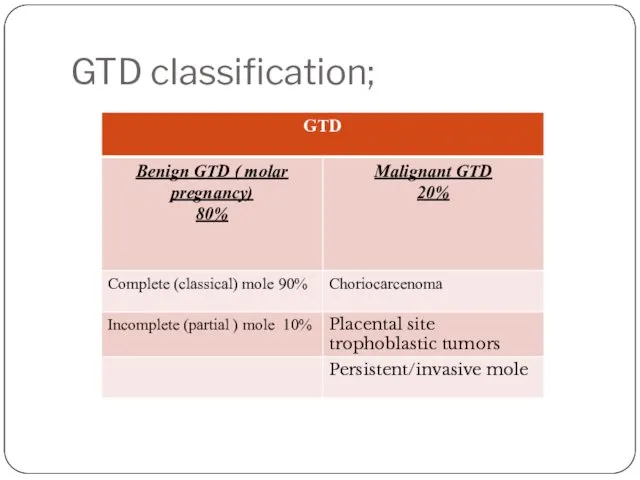
- 4. GTD classification;
- 5. Molar pregnancy The incidence of molar pregnancy is about 1 in 1,000 pregnancies highest among Asian
- 6. Molar Pregnancy Complete mole - Fertilization an empty egg by one sperm. -All placental villa swollen.
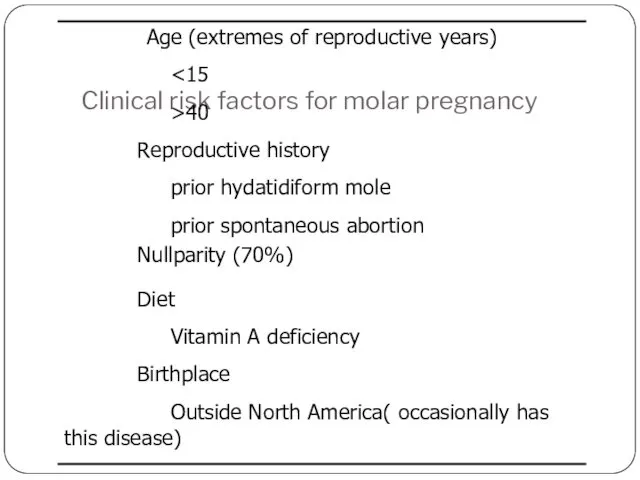
- 9. Clinical risk factors for molar pregnancy
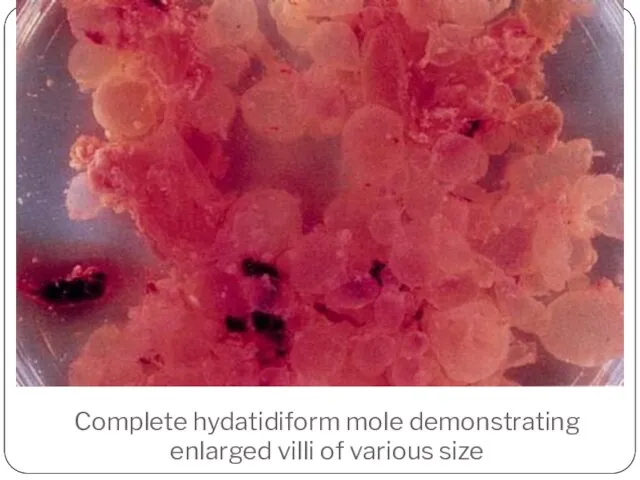
- 10. Complete hydatidiform mole demonstrating enlarged villi of various size
- 11. A large amount of villi in the uterus.
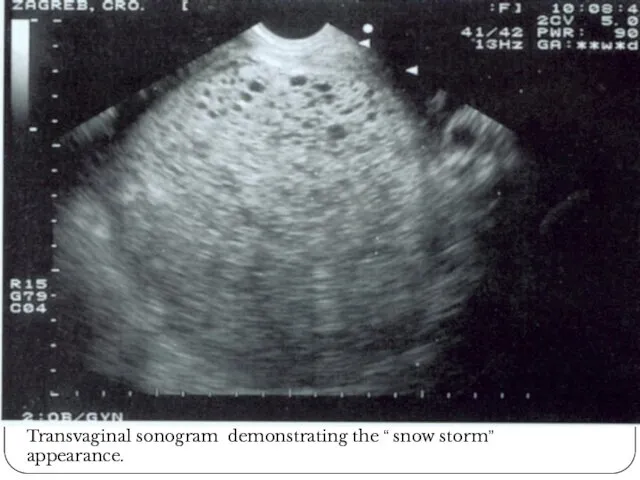
- 12. Transvaginal sonogram demonstrating the “ snow storm” appearance.
- 13. Molar Pregnancy
- 14. Molar Pregnancy Diagnosis: -Ultrasound shows snowstorm-like appearance, no fetus, theca lutein cyst -Beta hCG in normal
- 15. Management Baseline hCG level. Rh(D) status. Suction curettage (D&C). (RhoGAM) should be given to all Rhnegative
- 16. Follow up 95% to 100% cure rates after suction curettage Persistent disease will develop in 15%
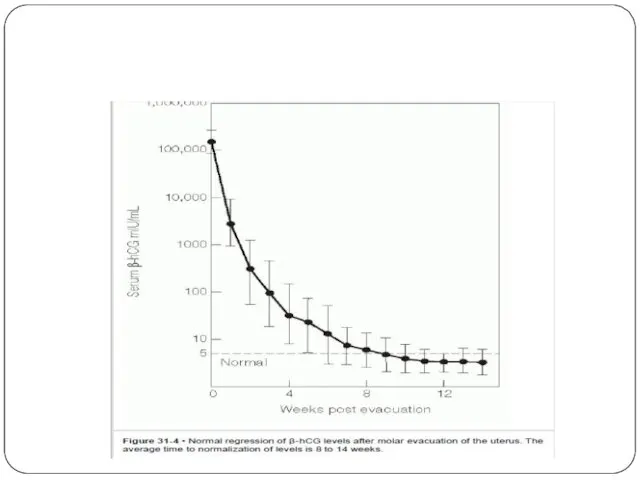
- 18. Follow up HCG weekly until normal for two values then monthly for one year. Repeat x-
- 20. Скачать презентацию












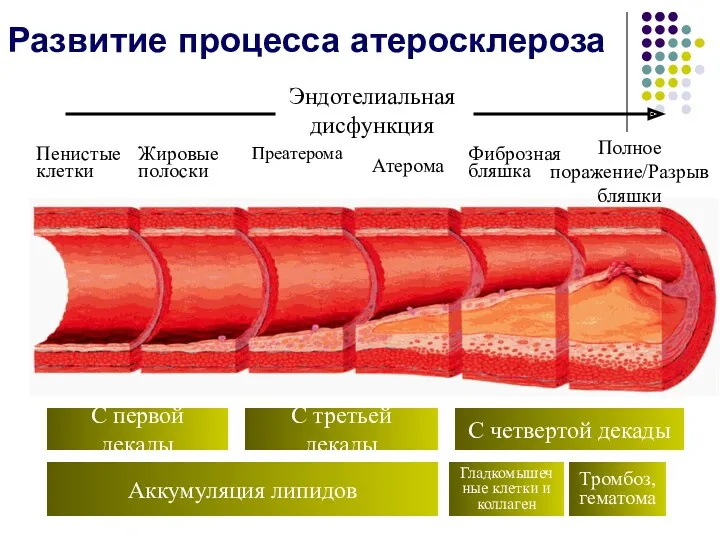 Развитие процесса атеросклероза
Развитие процесса атеросклероза Аналық бездің рагы және жүктілік
Аналық бездің рагы және жүктілік Водолікування. Вологе укутування
Водолікування. Вологе укутування Патофизиология периферического кровообращения
Патофизиология периферического кровообращения Координаторная система. Мозжечок, синдромы поражения. Экстрапирамидная система, синдромы поражения
Координаторная система. Мозжечок, синдромы поражения. Экстрапирамидная система, синдромы поражения Омыртқа жарақаттары. Жамбас жарақаттары. Бас сүйегі мен мидың жарақаттары. Көз жарақаттары
Омыртқа жарақаттары. Жамбас жарақаттары. Бас сүйегі мен мидың жарақаттары. Көз жарақаттары Первая помощь при переломах, вывихах, ушибах
Первая помощь при переломах, вывихах, ушибах Тератома
Тератома Введение в неврологию
Введение в неврологию Дисфагия, асқазан және ішек диспепсия синдромы кезінде пайдаланылатын дәрі-дәрімектер
Дисфагия, асқазан және ішек диспепсия синдромы кезінде пайдаланылатын дәрі-дәрімектер Нейроборрелиоз
Нейроборрелиоз Эффективная коммуникация с пациентом
Эффективная коммуникация с пациентом Остеоартроз
Остеоартроз Желудочно-кишечные кровотечения
Желудочно-кишечные кровотечения Современные экстракорпоральные технологии очищения крови в интенсивной терапии
Современные экстракорпоральные технологии очищения крови в интенсивной терапии Кардиомиопатия такоцубо
Кардиомиопатия такоцубо Первая помощь при кровотечении
Первая помощь при кровотечении Жарақаттар (буынның шығуы, сынық)
Жарақаттар (буынның шығуы, сынық) Туберкулёз и алкоголизм. Туберкулёз и наркомания
Туберкулёз и алкоголизм. Туберкулёз и наркомания Инфекционные болезни и их классификация
Инфекционные болезни и их классификация Автодорожное происшествие. Оказание первой помощи
Автодорожное происшествие. Оказание первой помощи Этическое отношение к искусственному размножению
Этическое отношение к искусственному размножению Атеросклероз
Атеросклероз Зрительный нерв. Заболевания зрительного нерва
Зрительный нерв. Заболевания зрительного нерва Социально ориентированная ПМСП как современная стратегия здравоохранения
Социально ориентированная ПМСП как современная стратегия здравоохранения Антисептика
Антисептика Blood vessels pathology. (Subject 14)
Blood vessels pathology. (Subject 14) Эндовидеолапароскопические вмешательства при опухолях женской мочеполовой системы
Эндовидеолапароскопические вмешательства при опухолях женской мочеполовой системы