Содержание
- 2. Glomerulonephritis (GN), also known as glomerular nephritis, is a term used to refer to several kidney
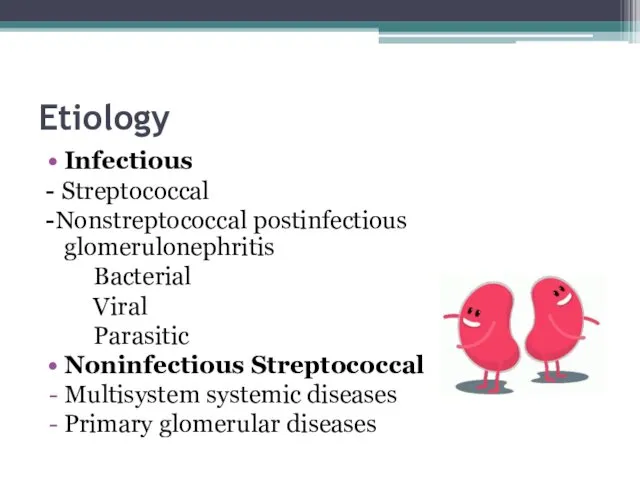
- 3. Etiology Infectious - Streptococcal -Nonstreptococcal postinfectious glomerulonephritis Bacterial Viral Parasitic Noninfectious Streptococcal Multisystem systemic diseases Primary
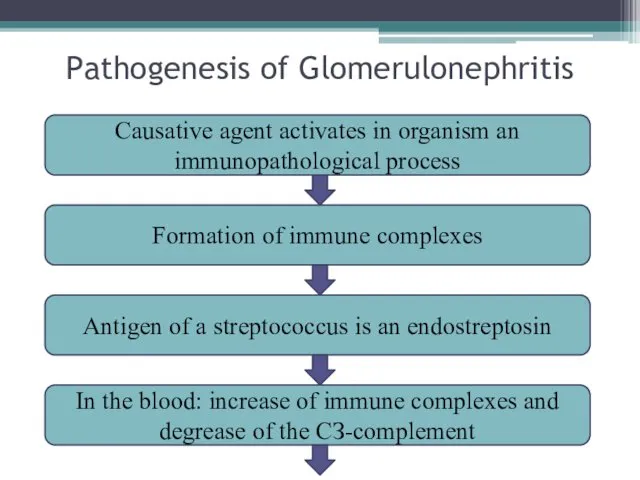
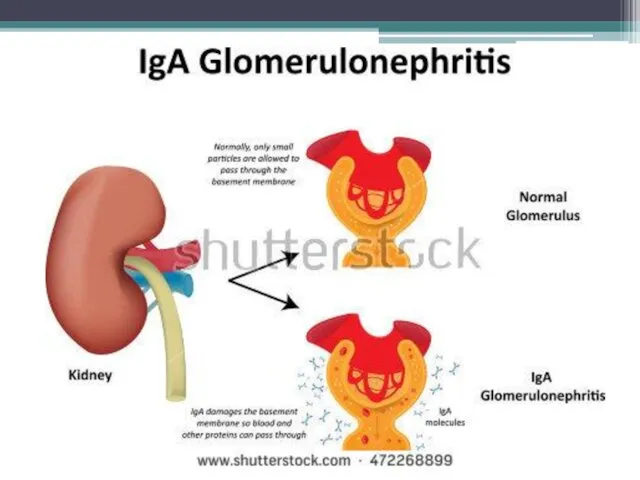
- 4. Pathogenesis of Glomerulonephritis Causative agent activates in organism an immunopathological process Formation of immune complexes In
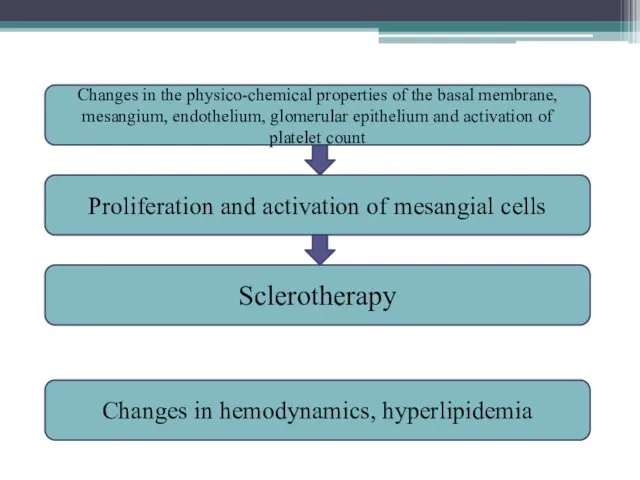
- 5. Sclerotherapy Proliferation and activation of mesangial cells Changes in the physico-chemical properties of the basal membrane,
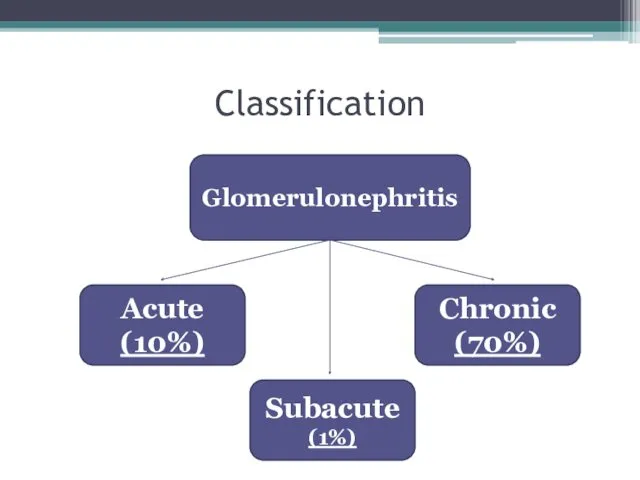
- 6. Classification Glomerulonephritis Acute (10%) Chronic (70%) Subacute (1%)
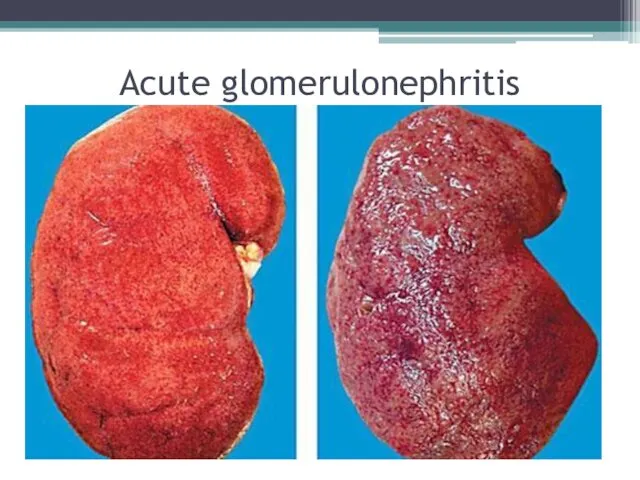
- 7. Acute glomerulonephritis It is an acute immunoinflammatory disease of the kidneys with the initial lesion of
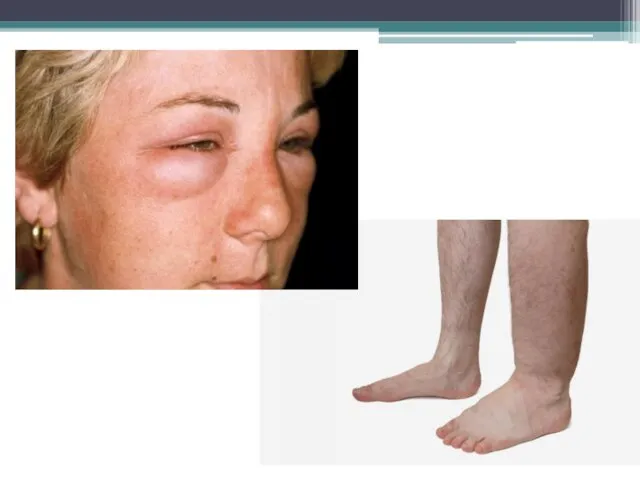
- 9. Syndroms Nephrotic syndrome Hypertonic syndrome Mixed syndrome
- 12. Acute glomerulonephritis
- 13. Diagnostics of AG Full blood count Clinical urine analysis Determination of creatinine, urea, uric acid Calculation
- 14. Treatment of AG Diet №7 Antibiotics: - Benzylpenicillin 1 000 000-2 000 000 UA/day, 7-10 days.
- 15. Antiaggregants - dipyridamole tablets of 25 mg, film-coated, 75 mg/day, tab; pentoxifylline 100 mg/day amp.
- 16. With antihypertensive and nephroprotective purpose, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: - fozinopril 20 mg/day, - enalapril 20 mg/day,
- 17. Chronic glomerulonephritis It is the same as an acute form. It can be difficult to detect
- 18. Diagnostics of CG 1. General blood test: HB, Erythrocytes, Leukocytes, Platelets, ESR before and after kidney
- 19. Treatment of CG Glucocorticoids: - Prednisolone 1 mg/kg 2 months endovenous Cytostatics: - Cyclophosphamide 2-3 mg/kg/day
- 20. Antiaggregants and anticoagulants: - Dipyridamole 400-600 mg/day - Clopidogrel 0,2-0,3 g/day
- 21. Antihypertensive therapy: ACE inhibitor - Captopril 50-100 mg/day - Enalapril 10-20 mg/day Сalcium channel blockers -
- 23. Скачать презентацию













 Митохондриальные болезни или опять во всем виноваты женщины
Митохондриальные болезни или опять во всем виноваты женщины Валеология. Цели, задачи и решения
Валеология. Цели, задачи и решения Гемодинамическая поддержка
Гемодинамическая поддержка Зачем мы делаем прививки
Зачем мы делаем прививки Нижний этаж брюшной полости
Нижний этаж брюшной полости Средства, влияющие на Н-холинорецепторы. Н-холиномиметики. Ганглиоблокаторы. Миорелаксанты периферического действия (Лекция 5)
Средства, влияющие на Н-холинорецепторы. Н-холиномиметики. Ганглиоблокаторы. Миорелаксанты периферического действия (Лекция 5) Возрастная анатомия черепа. Височно-нижнечелюстной сустав
Возрастная анатомия черепа. Височно-нижнечелюстной сустав Пищевое поведение
Пищевое поведение Топографическая анатомия и оперативная хирургия тонкой и толстой кишки
Топографическая анатомия и оперативная хирургия тонкой и толстой кишки Узкий таз в современном акушерстве
Узкий таз в современном акушерстве Дифференциальная диагностика болевого синдрома в заболеваниях ЖКТ
Дифференциальная диагностика болевого синдрома в заболеваниях ЖКТ Лекарственные средства влияющие на функцию органов пищеварения
Лекарственные средства влияющие на функцию органов пищеварения Лажсыздан сойылған мал етiн малдәрiгерлiк-санитариялық сараптау
Лажсыздан сойылған мал етiн малдәрiгерлiк-санитариялық сараптау Фармацевтің фармацевтикалық қызметті тұтынушыға
Фармацевтің фармацевтикалық қызметті тұтынушыға Система выделения. Функции почек
Система выделения. Функции почек Физическое развитие детей. Анатомо-физиологические особенности нервной системы, кожи, подкожно-жировой клетчатки и лимфоузлов
Физическое развитие детей. Анатомо-физиологические особенности нервной системы, кожи, подкожно-жировой клетчатки и лимфоузлов Туберкулез внелегочных локализаций: симптомы, выявление, профилактика
Туберкулез внелегочных локализаций: симптомы, выявление, профилактика Жүйелі склеродермия
Жүйелі склеродермия Хирургические заболевания органов брюшной полости
Хирургические заболевания органов брюшной полости Синдром Лайелла и Стивенса- Джонсона
Синдром Лайелла и Стивенса- Джонсона Farmakologia_17_2023_LS_Zheludochnye_Lektsia
Farmakologia_17_2023_LS_Zheludochnye_Lektsia Использование эндоскопических методов в операциях. Последние инновации
Использование эндоскопических методов в операциях. Последние инновации Клиническая фармакология лекарственных средств, влияющих на гемостаз
Клиническая фармакология лекарственных средств, влияющих на гемостаз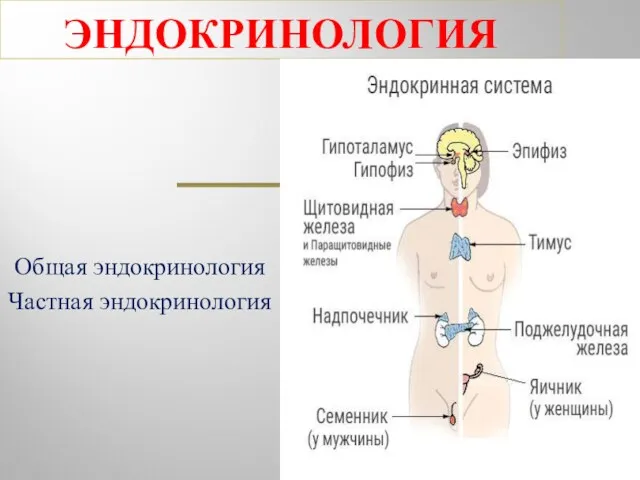 Эндокринология. Общая эндокринология. Частная эндокринология
Эндокринология. Общая эндокринология. Частная эндокринология Иммунопрофилатика. Нормативные документы в сфере иммунопрофилактики
Иммунопрофилатика. Нормативные документы в сфере иммунопрофилактики Сердечно–сосудистая система человека
Сердечно–сосудистая система человека Семиотика урологических заболеваний. Рентгенологические и аппаратные методы диагностики
Семиотика урологических заболеваний. Рентгенологические и аппаратные методы диагностики Лекарственные растения, обладающие противовоспалительными и противоязвенными свойствами
Лекарственные растения, обладающие противовоспалительными и противоязвенными свойствами