Содержание
- 2. Topic: Acute Alcohol Poisoning Alcohol poisoning (AP) is a serious – sometime deadly – result of
- 3. Signs and symptoms of AP may include: CONFUSION, STUPOR VOMITING SEIZURES SLOW OR IRREGULAR BREATING PILE
- 4. CAUSES: AP may result from accidental and intentional ingection: ETHANOL is found in alcoholic beverages as
- 5. Test and diagnosis: Visible signs and symptoms of AP Order blood tests to check blood alcohol
- 6. Ethylene glycol toxicity Occurs in 3 stages: First stage, called the neurologic phase, can occur in
- 7. Causes Ethanol may be ingested accidantally, as ofthen occurs in children. Methanol ingestion may result in
- 8. Physical Signs Ethanol: flushed face; diaphoresis. Ataxia, slurred speech; drowsiness; stupor or coma Methanol: Retinal edema,
- 9. Lab. Studies Ethanol: increase serum blood alcohol level, anemia. Elevation of hepatic transaminase levels. Prolongation of
- 10. AP treatment usually involves supportive care CAREFUL MONITORING Airway protection to prevent breathing or shoking problems
- 11. Emergency Department Care Methanol Forced diuresis; using sodium bicarbonate, administer folic acid (leucovorin), antidotal treatment: involves
- 12. Complications Ethanol ingestion complications. Hypoglycemia is common. “Holiday heart” in which dysrhythmias. Atrial fibrillation. Cyrrosis, esophageal
- 13. Toxicity, Carbon Monoxide Carbone Monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas produced by incomplete combustion carbonaceous
- 14. Symptoms of acute poisoning CO Dyspnea on exertion Malaise, flulike symptoms, fatique Lethargy, confusion, depression Impulsiveness,
- 15. Physical examination: Tachycardia, hypertension. Hyperthermia, marked tachypnea Classic cherry skin is rare, pallor is present more
- 16. Lab. Studies HbCO analysis (elevated level) Arterial blood gas Metabolic acidosis Troponin, creatinninekinase-MB, myoglobin Myocardial ischemia
- 17. Imaging Studies Chest Radiography CT – scanning Electrocardiogram (sinus tachycardia, arrhythmias) Neuropsychologic testing
- 18. Emergency Department Care Oxygen therapy Intubation for the comatose patients Cardiac monitoring, pulse oximetry Hyperbaric oxygen
- 20. Скачать презентацию

















 Епідеміологічний метод дослідження, його структура і зміст. Система епідеміологічного нагляду. Епідеміологія туберкульозу
Епідеміологічний метод дослідження, його структура і зміст. Система епідеміологічного нагляду. Епідеміологія туберкульозу Синдром гострого запалення слизових оболонок дихальних шляхів. Грип
Синдром гострого запалення слизових оболонок дихальних шляхів. Грип Ас қорыту физиологиясы
Ас қорыту физиологиясы Физиология и методы исследования системы гемостаза
Физиология и методы исследования системы гемостаза Родовые повреждения новорожденных
Родовые повреждения новорожденных Ведение нормальных родов. Управление родовым актом
Ведение нормальных родов. Управление родовым актом Трансформация патологии населения. Основные социально-гигиенические проблемы современного общества
Трансформация патологии населения. Основные социально-гигиенические проблемы современного общества Профилактика ВИЧ - инфекций
Профилактика ВИЧ - инфекций Рефракция и аккомодация глаза
Рефракция и аккомодация глаза Негізгі психопатологиялық синдромдар
Негізгі психопатологиялық синдромдар Риски расстройств пищевого поведения у спортсменов
Риски расстройств пищевого поведения у спортсменов Дошкольный и преддошкольный возраст
Дошкольный и преддошкольный возраст Беременность при туберкулезе
Беременность при туберкулезе Введение в иммунологию. Иммунная система
Введение в иммунологию. Иммунная система Гіполіпідемічні лікарські засоби
Гіполіпідемічні лікарські засоби Анатомо-физиологические особенности спинального и эпидурального пространств у детей раннего возраста
Анатомо-физиологические особенности спинального и эпидурального пространств у детей раннего возраста История медицинского халата
История медицинского халата Кровь. Функции и состав крови. Группы крови
Кровь. Функции и состав крови. Группы крови Бронхообструктивный синдром
Бронхообструктивный синдром ВПР мочевыводящей системы
ВПР мочевыводящей системы Пороки развития ЦНС
Пороки развития ЦНС Equipment and instruments of dental clinic
Equipment and instruments of dental clinic Классификация острого панкреатита
Классификация острого панкреатита Виявлення хворих на туберкульоз. (Лекція 2)
Виявлення хворих на туберкульоз. (Лекція 2) Ведение пациентов с болью в спине в практике терапевта и семейного врача
Ведение пациентов с болью в спине в практике терапевта и семейного врача Перикардиты у детей
Перикардиты у детей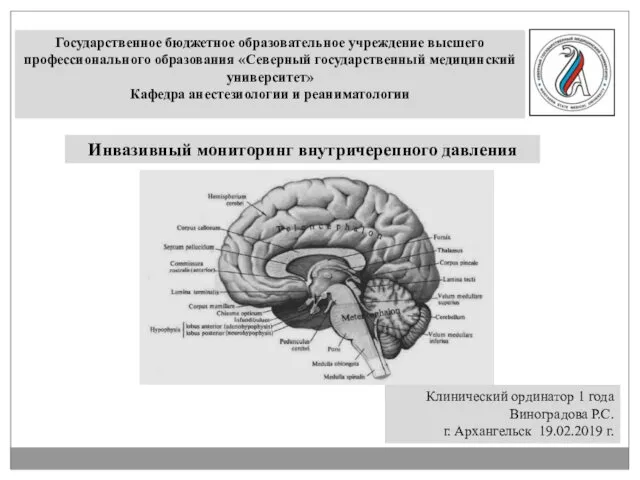 Инвазивный мониторинг внутричерепного давления
Инвазивный мониторинг внутричерепного давления Несеп жыныс жүйесі
Несеп жыныс жүйесі