Содержание
- 2. Overview Classification scheme Individual diseases within the alphabet soup Tables Quiz
- 3. Reminder Pathologic changes in interstitial lung disease involve cellular infiltration, scarring, and/or architectural disruption of the
- 4. Classification of ILDs (In total, there are over 200!) Unknown cause (idiopathic) Systemic causes Sarcoidosis Rheumatologic/autoimmune
- 5. Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias IPF NSIP COP (BOOP) DIP/RB-ILD AIP LIP Eosinophilic pneumonia Pulmonary histiocytosis X LAM
- 6. Granulomatous lung disease T lymphocytes, macrophages, and epithelioid cells make up the granuloma Can progress to
- 7. Inflammation and fibrosis Injury to the epithelial surface causes an inflammatory response in the air spaces
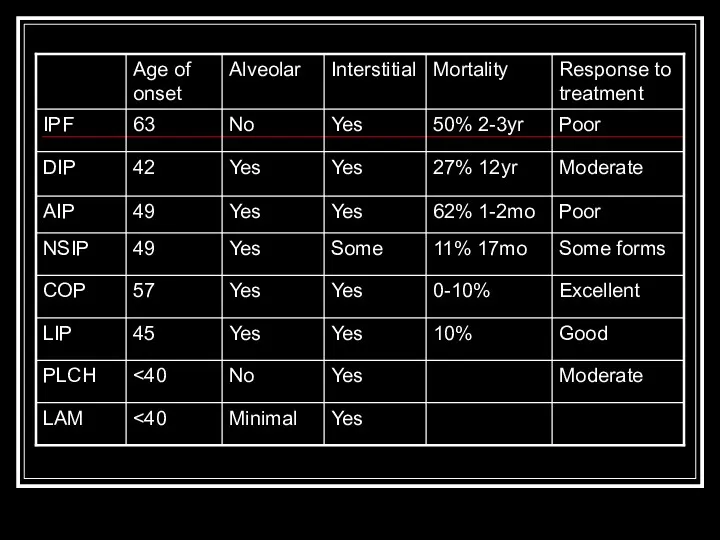
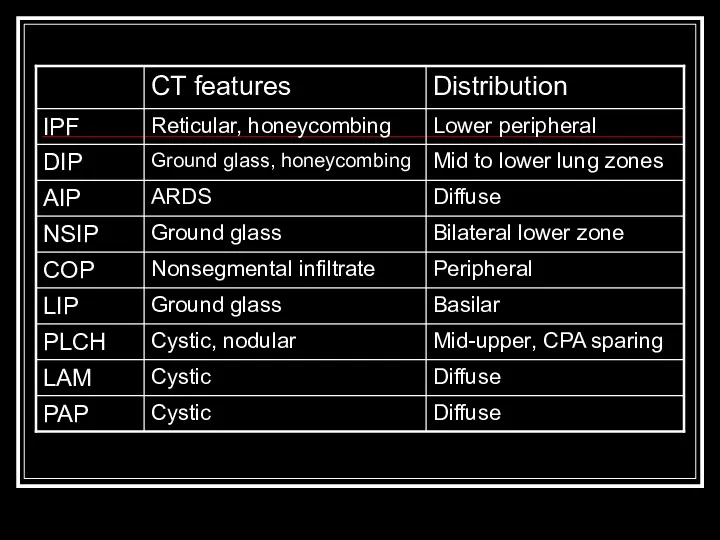
- 8. IPF Most common idiopathic interstitial pneumonia with distinctly poor prognosis Older age group (>50y.o.) Patchy, basilar
- 9. DIP Only in cigarette smokers Occurs in 30’s-40’s Diffuse hazy opacities Intra-alveolar macrophage infiltrate with minimal
- 10. AIP (Hamman-Rich Syndrome) Often in previously healthy patients with 7-14 day prodrome Most patients >40y.o. Diffuse,
- 11. NSIP Younger set of patients than IPF present with fevers and without clubbing Bilateral, subpleural ground-glass
- 12. COP/BOOP Presents in 40’s-50’s Bilateral patchy or diffuse alveolar and small nodular opacities with normal lung
- 13. LIP Rarest form, F > M Ground glass, reticular pattern with perivascular cysts BAL shows lymphocytosis
- 14. PLCH smoking-related Men 20-40y.o. PTX in ~25%, rarely hemoptysis and DI Ill-defined or stellate nodules, reticular
- 15. LAM Premenopausal women with emphysema, PTX, hemoptysis, chylous pleural effusion, mostly caucasians Proliferation of atypical pulmonary
- 16. PAP Not actually and ILD, actually autoimmune with and IgG against GM-CSF Defect in macrophage processing
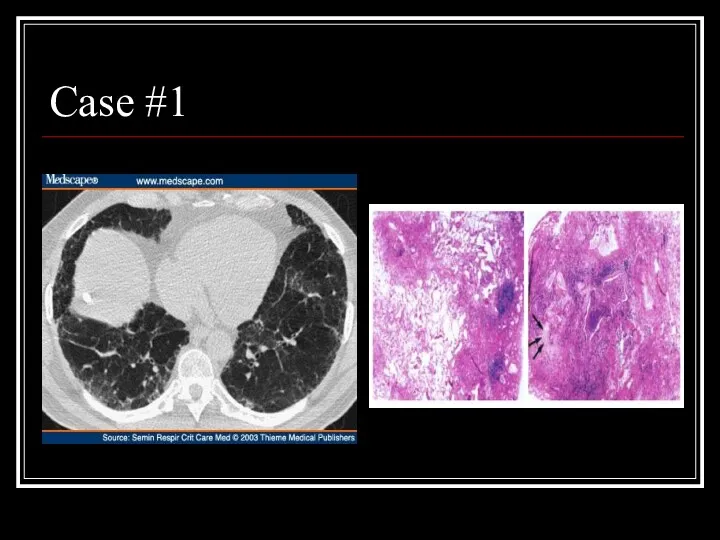
- 19. Case #1
- 20. Answer: IPF CT scan: heterogeneous pattern with subpleural disease concentrated posteriorly, traction bronchiectasis/honeycombing, no nodules, little
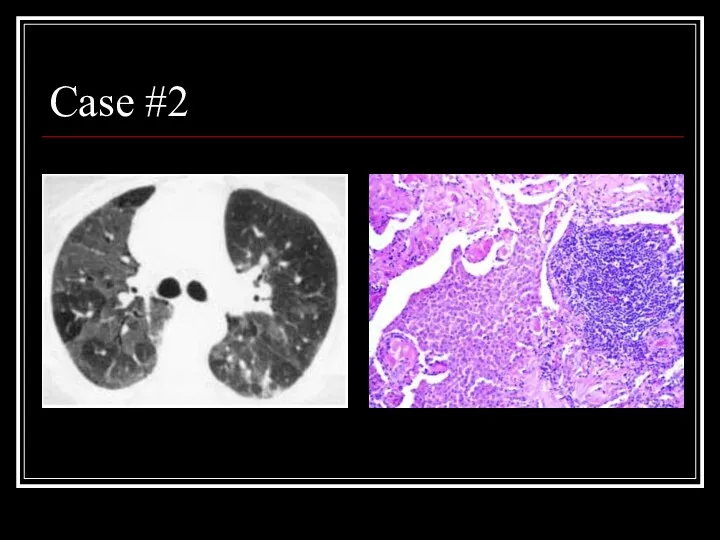
- 21. Case #2
- 22. Answer: DIP CT: Mosaic ground-glass opacity with vascular definition in the areas of ground-glass opacity and
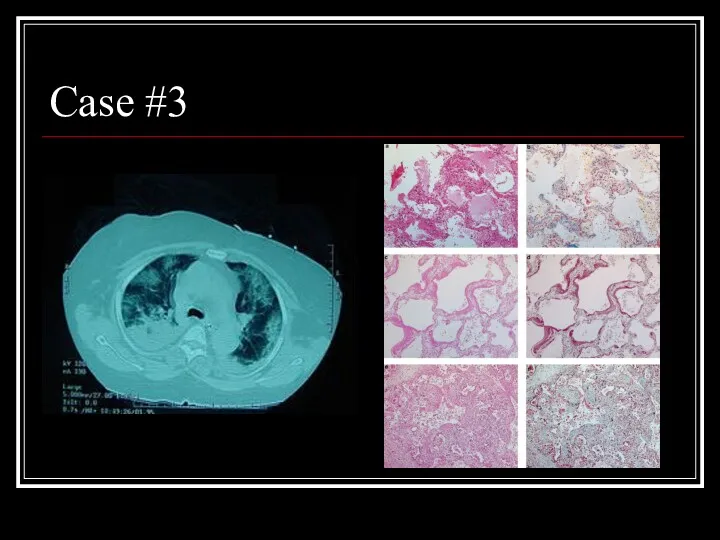
- 23. Case #3
- 24. Answer: AIP CT: Bilateral alveolar and interstital infiltrates Path: Early exudative phase showing vascular congestion, with
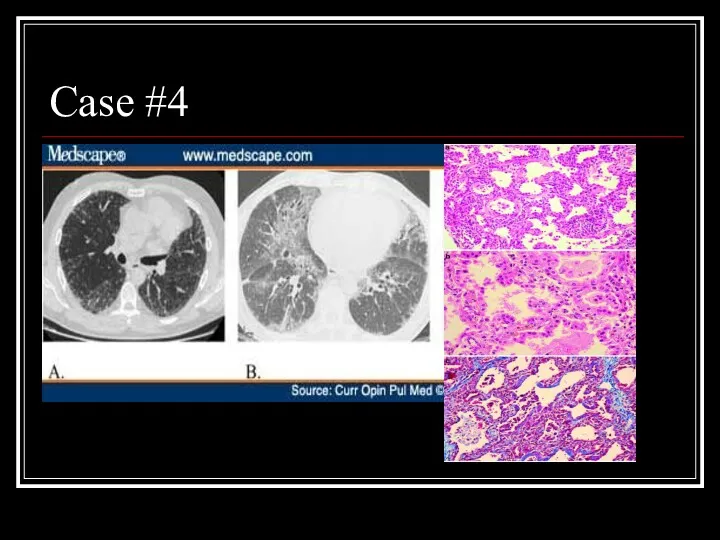
- 25. Case #4
- 26. Answer: NSIP A: Fibrotic variant with reticular subpleural lines with uniform distribution, bronchiolectasis, and areas of
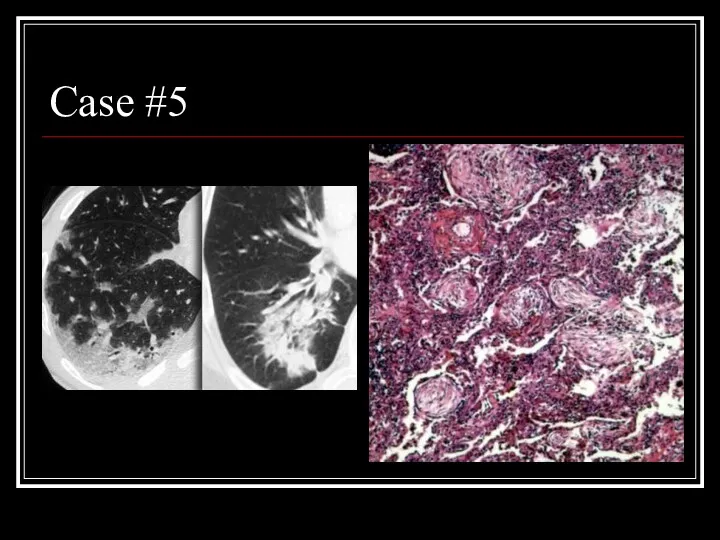
- 27. Case #5
- 28. Answer: COP CT: patchy non-segmental consolidations in a subpleural and peripheral distribution Path: diffuse fibrous organization
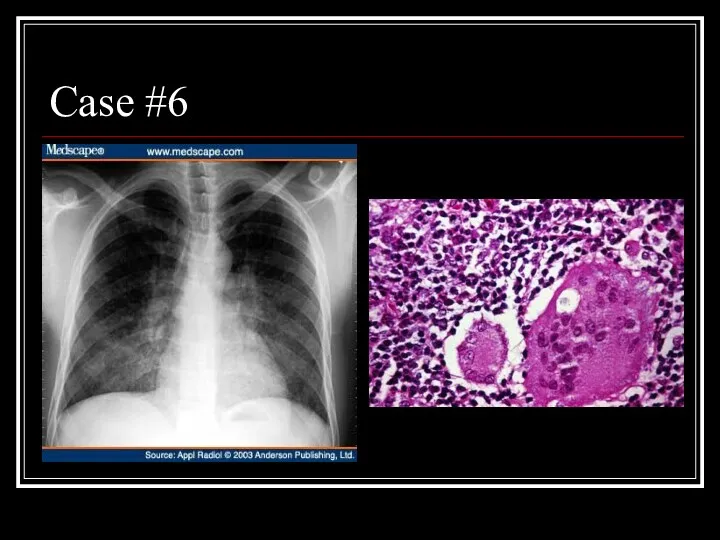
- 29. Case #6
- 30. Answer: LIP CXR: diffuse, fine nodular changes particularly in the lower lobes Path: Lymphocytes and plasma
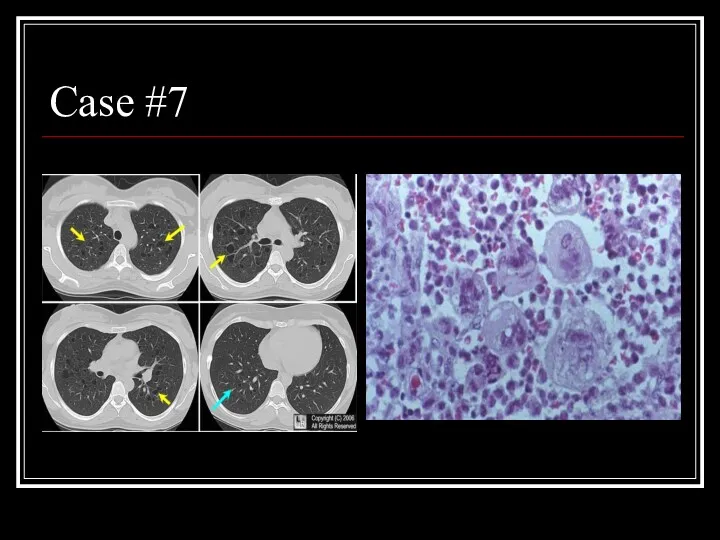
- 31. Case #7
- 32. Answer: PLCH CT: multiple small, irregularly-shaped, cysts of varying sizes with thin walls scattered throughout the
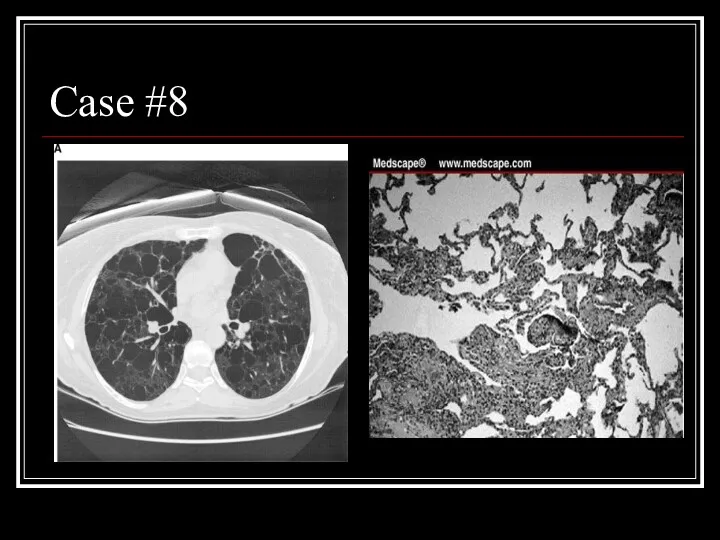
- 33. Case #8
- 34. Answer: LAM CT: Diffuse parenchymal cysts Path: nodular proliferation of smooth muscle (LAM) cells replacing the
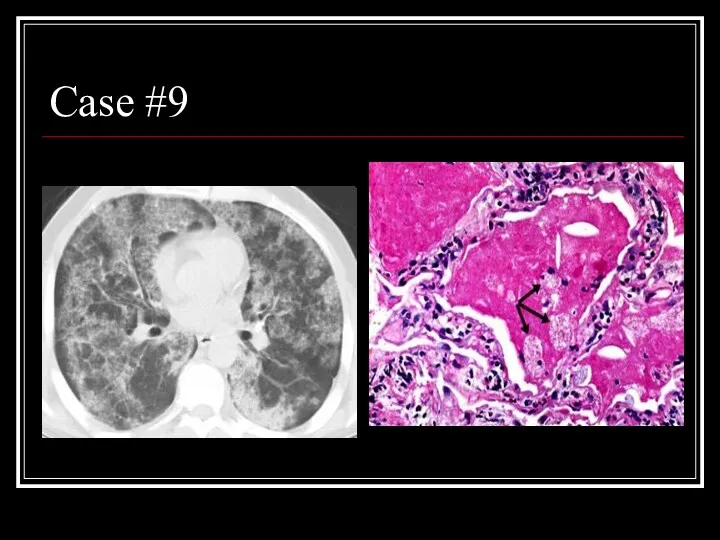
- 35. Case #9
- 36. Answer: PAP CT: patchy ground glass opacities and septal thickening in a geographic distribution Path: intra-alveolar
- 38. Скачать презентацию






















 Клиническая картина трансверсальной патологии прикуса
Клиническая картина трансверсальной патологии прикуса Тұрғындардың табиғи қозғалысының анализі. Адам өлімінің медициналық критерийлері: моральді мәселелері мен перспективалары
Тұрғындардың табиғи қозғалысының анализі. Адам өлімінің медициналық критерийлері: моральді мәселелері мен перспективалары Гигиенические требования к условиям обучения в общеобразовательных учреждениях
Гигиенические требования к условиям обучения в общеобразовательных учреждениях Вся правда о туберкулёзе
Вся правда о туберкулёзе Патология климактерия
Патология климактерия Этика и деонтология в педиатрии. Периоды детского возраста. Особенности ухода за детьми различного возраста
Этика и деонтология в педиатрии. Периоды детского возраста. Особенности ухода за детьми различного возраста Гиперпластические процессы эндометрия
Гиперпластические процессы эндометрия Ревматоидный артрит
Ревматоидный артрит Рассеянный склероз
Рассеянный склероз Скрининг беременных женщин
Скрининг беременных женщин Фармакология. Фармакокинетика лекарственных средств
Фармакология. Фармакокинетика лекарственных средств Шкода алкоголю, куріння та наркотиків
Шкода алкоголю, куріння та наркотиків Медицинская реабилитация при сколиозе
Медицинская реабилитация при сколиозе Екіншілік нейроинфекциялар
Екіншілік нейроинфекциялар Остеопороз
Остеопороз Патогенные и условно патогенные микроорганизмы
Патогенные и условно патогенные микроорганизмы Адам ағзасының антигендері.Ағзаның иммундық компоненті жасушаларымен антигендердің әсерленісуі
Адам ағзасының антигендері.Ағзаның иммундық компоненті жасушаларымен антигендердің әсерленісуі Сестринский процесс при новообразованиях
Сестринский процесс при новообразованиях Инвалидность и реабилитация как медико-социальная проблема
Инвалидность и реабилитация как медико-социальная проблема Аутист-жаңбыр балалары
Аутист-жаңбыр балалары Органы иммунной системы
Органы иммунной системы ВИЧ - инфекция
ВИЧ - инфекция Капсулы. История появления желатиновых капсул
Капсулы. История появления желатиновых капсул Туберкулез костей и суставов
Туберкулез костей и суставов Дефект межпредсердной перегородки
Дефект межпредсердной перегородки Интерферон короткого действия
Интерферон короткого действия Морально-этические аспекты врачебных ошибок
Морально-этические аспекты врачебных ошибок Этика и деонтология для работников регистратур медицинских организаций
Этика и деонтология для работников регистратур медицинских организаций